Securities Act File No. 333-23017
Investment Company Act File No. 811-08085
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM N-1A
Registration Statement Under The Securities Act of 1933
Post-Effective Amendment No. 13
and
Registration Statement Under The Investment Company Act of 1940
Amendment No. 16
AMERICAN SKANDIA ADVISOR FUNDS, INC.
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in Charter)
One Corporate Drive, Shelton, Connecticut 06484
-----------------------------------------------
(Address of Principal Executive Offices) (Zip Code)
(800) 628-6039
--------------
(Registrant's Telephone Number, Including Area Code)
EDWARD P. MACDONALD, ESQ., SECRETARY
AMERICAN SKANDIA ADVISOR FUNDS, INC.
One Corporate Drive, Shelton, Connecticut 06484
-----------------------------------------------
(Name and Address of Agent for Service)
Copies to:
ROBERT K. FULTON, ESQ.
STRADLEY RONON STEVENS & YOUNG, LLP
2600 ONE COMMERCE SQUARE, PHILADEPHIA, PA 19103-7098
It is proposed that this filing will become effective (check appropriate space)
_____ immediately upon filing pursuant to paragraph (b).
_____ on ________ pursuant to paragraph (b) of rule 485.
_____ 60 days after filing pursuant to paragraph (a)(1).
_____ on _______ pursuant to paragraph (a)(1).
X 75 days after filing pursuant to paragraph (a)(2).
_____ on _______ pursuant to paragraph (a)(2) of rule 485.
_____ this post-effective amendment designates a new effective
date for a previously filed post-effective amendment.
Shares of the Various Classes of American Skandia Advisor Funds, Inc.
(Title of Securities Being Registered)
This Registration Statement has also been executed by American Skandia Master Trust.
AMERICAN SKANDIA ADVISOR FUNDS, INC.
P R O S P E C T U S
Class A, Class B, Class C and Class X Shares
MARCH 1, 2001
---------------------------------
ASAF FOUNDERS INTERNATIONAL SMALL CAPITALIZATION FUND
ASAF AIM INTERNATIONAL EQUITY FUND
ASAF JANUS OVERSEAS GROWTH FUND*
ASAF AMERICAN CENTURY INTERNATIONAL GROWTH FUND
ASAF JANUS SMALL-CAP GROWTH FUND*
ASAF SCUDDER SMALL-CAP GROWTH FUND
ASAF GABELLI SMALL-CAP VALUE FUND
ASAF JANUS MID-CAP GROWTH FUND
ASAF NEUBERGER BERMAN MID-CAP GROWTH FUND
ASAF NEUBERGER BERMAN MID-CAP VALUE FUND
ASAF ALGER ALL-CAP GROWTH FUND
ASAF GABELLI ALL-CAP VALUE FUND
ASAF INVESCO TECHNOLOGY FUND
ASAF INVESCO HEALTH SCIENCES FUND
ASAF RYDEX MANAGED OTC FUND
ASAF ALLIANCE GROWTH FUND
ASAF MARSICO CAPITAL GROWTH FUND
ASAF JANUS CAPITAL GROWTH FUND
ASAF T. ROWE PRICE TAX MANAGED FUND
ASAF ALLIANCE/BERNSTEIN 50/50 GROWTH + VALUE FUND
ASAF SANFORD BERNSTEIN DEEP VALUE FUND
ASAF SANFORD BERNSTEIN MANAGED INDEX 500 FUND
ASAF ALLIANCE GROWTH AND INCOME FUND
ASAF MFS GROWTH WITH INCOME FUND
ASAF INVESCO EQUITY INCOME FUND
ASAF AMERICAN CENTURY STRATEGIC BALANCED FUND
ASAF FEDERATED HIGH YIELD BOND FUND
ASAF PIMCO TOTAL RETURN BOND FUND
ASAF JPM MONEY MARKET FUND
*Closed to new investors. See pages 34 and 38 for details.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
THESE SECURITIES HAVE NOT BEEN APPROVED OR DISAPPROVED BY THE SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION NOR HAS THE COMMISSION
PASSED UPON THE ACCURACY OR ADEQUACY OF THIS PROSPECTUS. ANY REPRESENTATION TO THE CONTRARY IS A CRIMINAL OFFENSE.
T A B L E O F C O N T E N T S
---------------------------------
RISK/RETURN SUMMARY.......................................................................................................3
PAST PERFORMANCE.........................................................................................................14
EXPENSE INFORMATION......................................................................................................24
Shareholder Transaction Expenses................................................................................24
Annual Fund Operating Expenses..................................................................................24
Expense Examples................................................................................................27
INVESTMENT PROGRAMS OF THE FUNDS.........................................................................................30
ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund...........................................................31
ASAF AIM International Equity Fund..............................................................................33
ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund.................................................................................34
ASAF American Century International Growth Fund.................................................................36
ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund................................................................................38
ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund..............................................................................40
ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund...............................................................................42
ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund..................................................................................44
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund.......................................................................46
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund........................................................................47
ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund..................................................................................49
ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund.................................................................................50
ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund....................................................................................51
ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund.................................................................................
ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund.....................................................................................52
ASAF Alliance Growth Fund.......................................................................................53
ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund................................................................................55
ASAF Janus Capital Growth Fund..................................................................................57
ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund...............................................................................
ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth + Value Fund.................................................................
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund............................................................................
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund...................................................................59
ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund............................................................................61
ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund................................................................................62
ASAF INVESCO Equity Income Fund.................................................................................63
ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund...................................................................64
ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund.............................................................................66
ASAF PIMCO Total Return Bond Fund...............................................................................68
ASAF JPM Money Market Fund......................................................................................71
PORTFOLIO TURNOVER.......................................................................................................73
HOW TO BUY SHARES........................................................................................................74
SPECIAL INVESTMENT PROGRAMS AND PRIVILEGES...............................................................................79
HOW TO REDEEM SHARES.....................................................................................................80
HOW TO EXCHANGE SHARES...................................................................................................82
DETERMINATION OF NET ASSET VALUE.........................................................................................83
SHAREHOLDER ACCOUNT RULES AND POLICIES...................................................................................83
SPECIAL INFORMATION ON THE "MASTER/FEEDER" FUND STRUCTURE................................................................84
MANAGEMENT OF THE FUNDS..................................................................................................85
The Investment Manager..........................................................................................85
The Sub-Advisors................................................................................................85
Fees and Expenses...............................................................................................89
DIVIDENDS, CAPITAL GAINS AND TAXES.......................................................................................91
FINANCIAL HIGHLIGHTS.....................................................................................................94
CERTAIN RISK FACTORS AND INVESTMENT METHODS.............................................................................104
RISK/RETURN SUMMARY
American Skandia Advisor Funds, Inc. (the "Company") is comprised of twenty-nine diversified investment
portfolios (the "Funds"). Five of the Funds -- ASAF American Century International Growth Fund, ASAF Janus Capital
Growth Fund, ASAF INVESCO Equity Income Fund, ASAF PIMCO Total Return Bond Fund and ASAF JPM Money Market Fund (the
"Feeder Funds") -- invest all of their investable assets in a corresponding portfolio (the "Portfolios") of American
Skandia Master Trust ("ASMT" or the "Trust"). Each Portfolio invests in securities in accordance with an investment
objective, investment policies and limitations identical to those of its corresponding Feeder Fund. This "master/feeder"
fund structure differs from that of the other Funds of the Company and many other investment companies that directly
invest and manage their own portfolio of securities. Those Funds of the Company that currently are not organized under a
"master/feeder" fund structure retain the right to become part of the master/feeder structure in the future. For
additional information regarding the "master/feeder" fund structure, see this Prospectus under "Special Information on
the 'Master/Feeder' Fund Structure."
The Company is designed to provide a wide range of investment options. Each Fund and Portfolio has its own
investment goal and style (and, as a result, its own level of risk). Some of the Funds and Portfolios offer potential
for high returns with correspondingly higher risk, while others offer stable returns with relatively less risk. It is
possible to lose money when investing even in the most conservative of the Funds or Portfolios. Investments in the Funds
and Portfolios are not bank deposits and are not insured or guaranteed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or
any other government agency.
It is not possible to provide an exact measure of the risk to which a Fund and Portfolio is subject, and a Fund
or Portfolio's risk will vary based on the securities that it holds at a given time. Nonetheless, based on each Fund and
Portfolio's investment style and the risks typically associated with that style, it is possible to assess in a general
manner the risks to which a fund will be subject. The following discussion highlights the investment strategies and
risks of the Funds and Portfolios. Additional information about each Fund and Portfolio's potential investments and its
risks is included in this Prospectus under "Investment Programs of the Funds."
International Funds and Portfolios:
Fund/Portfolio: Investment Goal: Primary Investments:
-------------- --------------- -------------------
Int'l Small Capitalization Capital growth The Fund invests primarily in equity securities of small
Fund capitalization foreign companies.
AIM International Equity Capital growth The Fund invests primarily in equity securities of foreign
Fund companies.
Overseas Growth Fund Capital growth The Fund invests primarily in common stocks of foreign
companies.
American Century Int'l Capital growth The Portfolio invests primarily in equity securities of
Growth Portfolio foreign companies.
Principal Investment Strategies:
-------------------------------
The ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund normally invests primarily in securities issued by foreign
companies that have market capitalizations of $1.5 billion or less. These securities may represent companies in both
established and emerging economies throughout the world. At least 65% of the Fund's total assets normally will be
invested in foreign securities representing a minimum of three countries. The Fund may invest in larger foreign
companies or in U.S.-based companies if, in the Sub-advisor's opinion, they represent better prospects for capital
growth.
The Sub-advisor to the Fund looks for companies whose fundamental strengths indicate potential for growth in earnings per
share. The Sub-advisor generally takes a "bottom up" approach to building the Fund, which means that the Sub-advisor
will search for individual companies that demonstrate the best potential for significant earnings growth, rather than
choose investments based on broader economic characteristics of countries or industries.
The ASAF AIM International Equity Fund seeks to meet its investment objective by investing, normally, at least 70% of its
assets in marketable equity securities of foreign companies that are listed on a recognized foreign securities exchange
or traded in a foreign over-the-counter market. The Fund will normally invest in a diversified portfolio that includes
companies located in at least four countries outside the United States, emphasizing investment in companies in the
developed countries of Western Europe and the Pacific Basin. The Sub-advisor does not intend to invest more than 20% of
the Fund's total assets in companies located in developing countries.
The Sub-advisor focuses on companies that have experienced above-average, long-term growth in earnings and have strong
prospects for future growth. In selecting countries in which the Fund will invest, the Sub-advisor also considers such
factors as the prospect for relative economic growth among countries or regions, economic or political conditions,
currency exchange fluctuations, tax considerations and the liquidity of a particular security. The Sub-advisor considers
whether to sell a particular security when any of those factors materially changes.
The ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund pursues its objective primarily through investments in common stocks of issuers
located outside the United States. The Fund has the flexibility to invest on a worldwide basis in companies and
organizations of any size, regardless of country of organization or place of principal business activity. The Fund
normally invests at least 65% of its total assets in securities of issuers from at least five different countries,
excluding the United States. Although the Fund intends to invest substantially all of its assets in issuers located
outside the United States, it may at times invest in U.S. issuers and it may at times invest all of its assets in fewer
than five countries or even a single country.
The Fund invests primarily in stocks selected for their growth potential. The Sub-advisor generally takes a "bottom up"
approach to choosing investments for the Fund. In other words, the Sub-advisor seeks to identify individual companies
with earnings growth potential that may not be recognized by the market at large, regardless of where the companies are
organized or where they primarily conduct business. Although themes may emerge in the Fund, securities are generally
selected without regard to any defined allocation among countries, geographic regions or industry sectors, or other
similar selection procedure.
The ASMT American Century International Growth Portfolio will seek to achieve its investment objective by investing
primarily in equity securities of international companies that the Sub-advisor believes will increase in value over
time. The Sub-advisor uses a growth investment strategy it developed that looks for companies with earnings and revenue
growth. Ideally, the Sub-advisor looks for companies whose earnings and revenues are not only growing, but are growing
at an accelerating pace. For purposes of the Portfolio, equity securities include common stocks, preferred stocks and
convertible securities.
The Sub-advisor tracks financial information for thousands of companies to research and selects the stocks it believes
will be able to sustain accelerating growth. This strategy is based on the premise that, over the long term, the stocks
of companies with accelerating earnings and revenues have a greater-than-average chance to increase in value.
The Sub-advisor recognizes that, in addition to locating strong companies with accelerating earnings, the allocation of
assets among different countries and regions also is an important factor in managing an international portfolio. For
this reason, the Sub-advisor will consider a number of other factors in making investment selections, including the
prospects for relative economic growth among countries or regions, economic and political conditions, expected inflation
rates, currency exchange fluctuations and tax considerations. Under normal conditions, the Portfolio will invest at
least 65% of its assets in equity securities of issuers from at least three countries outside of the United States.
While the Portfolio's focus will be on issuers in developed markets, the Sub-advisor expects to invest to some degree in
issuers in developing countries.
Principal Risks:
---------------
o All four of the international funds and portfolios are equity funds, and the primary risk of each is that the
value of the stocks they hold will decline. Stocks can decline for many reasons, including reasons related to the
particular company, the industry of which it is a part, or the securities markets generally.
o The level of risk of the international funds and portfolios will generally be higher than the level of risk
associated with domestic equity funds. Foreign investments involve risks such as fluctuations in currency exchange
rates, unstable political and economic structures, reduced availability of information, and lack of uniform financial
reporting and regulatory practices such as those that apply to U.S. issuers. While none of the international funds
invest primarily in companies located in developing countries, each may invest in those companies to some degree, and
investment in developing countries may accentuate the risks of foreign investing.
o As a fund that invests primarily in the securities of smaller foreign issuers, the ASAF Founders International
Small Capitalization Fund may be subject to a greater level of risk than the other international funds. Securities
of smaller companies tend to be subject to more abrupt and erratic price movements than securities of larger
companies, in part because they may have limited product lines, markets, or financial resources.
Capital Growth Funds and Portfolios:
Fund/Portfolio: Investment Goal: Primary Investments:
-------------- --------------- -------------------
Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund Capital growth The Fund invests primarily in common stocks of small
capitalization U.S. companies.
Scudder Small-Cap Growth Maximum capital growth The Fund invests primarily in equity securities of small
Fund capitalization companies.
Small-Cap Value Fund Long-term capital growth The Fund invests primarily in stocks and equity-related
securities of small capitalization U.S. companies that appear
to be undervalued.
Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund Long-term capital growth The Fund invests primarily in common stocks, with normally at
least 65% of the Fund's assets invested in medium-sized
companies.
Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Capital growth Invests primarily in common stocks of medium capitalization
Growth Fund companies.
Neuberger Berman Capital growth The Fund invests primarily in common stocks of medium
Mid-Cap Value Fund capitalization companies, using a value-oriented investment
approach.
All-Cap Growth Fund Long-term capital growth The Fund invests primarily in equity securities.
All-Cap Value Fund Capital growth The Fund invests primarily in readily marketable equity
securities.
Technology Fund Capital growth The Fund invests primarily in equity securities of companies
engaged in technology-related industries.
Health Sciences Fund Growth The Fund invests primarily in the equity securities of
companies that develop, produce or distribute products or
services related to health care.
Managed OTC Fund Provide investment results The Fund invests primarily in securities of companies
that correlate to the included in the NASDAQ 100 and leveraged instruments, such as
performance of the NASDAQ futures contracts and options, relating to the NASDAQ 100.
100 Index
Alliance Growth Fund Capital growth The Fund invests predominantly in the equity securities of a
limited number of large, high-quality U.S. companies.
Marsico Capital Growth Fund Capital growth The Fund invests primarily in common stocks, with the
majority of the Fund's assets in large-cap stocks.
Janus Capital Growth Capital growth The Portfolio invests primarily in common stocks.
Portfolio
Tax Managed Fund Long-term capital The Fund will invest primarily in large-capitalization stocks
appreciation on an selected mainly from the 1,000 largest U.S. companies
after-tax basis
50/50 Growth + Value Fund Capital Growth The Fund will invest approximately 50% of its assets in growth
stocks of large companies and 50% of its assets in value stocks
of large companies.
Deep Value Fund Long-term capital growth The Fund invests primarily in common stocks of large
capitalization companies that appear to be undervalued.
Managed Index 500 Fund To outperform the S&P 500 The Portfolio invests primarily in common stocks included in
Stock Index the S&P 500.
Principal Investment Strategies:
-------------------------------
The ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund pursues its objective by normally investing at least 65% of its total assets in the
common stocks of small-sized companies. For purposes of the Fund, small-sized companies are those that have market
capitalizations of less than $1.5 billion or annual gross revenues of less than $500 million. To a lesser extent, the
Fund may also invest in stocks of larger companies with potential for capital appreciation.
The Sub-advisor generally takes a "bottom up" approach to building the Fund. In other words, it seeks to identify
individual companies with earnings growth potential that may not be recognized by the market at large. Although themes
may emerge in the Fund, securities are generally selected without regard to any defined industry sector or other similar
selection procedure.
At least 65% of the ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund's total assets normally will be invested in the equity securities
of smaller companies, i.e., those having a market capitalization of $2 billion or less at the time of investment, many of
which would be in the early stages of their life cycle. Equity securities include common stocks and securities
convertible into or exchangeable for common stocks, including warrants and rights. The Portfolio intends to invest
primarily in stocks of companies whose earnings per share are expected by the Sub-advisor to grow faster than the market
average ("growth stocks").
In managing the Fund, the Sub-advisor emphasizes stock selection and fundamental research. The Sub-advisor considers a
number of factors in determining whether to invest in a growth stock, including return on equity and earnings growth
rate, low level of debt, strong balance sheet, good management and industry leadership. Other factors are patterns of
increasing sales growth, the development of new or improved products or services, favorable outlooks for growth in the
industry, the probability of increased operating efficiencies, emphasis on research and development, cyclical conditions,
or other signs that a company may grow rapidly. The Fund seeks attractive areas for investment that arise from factors
such as technological advances, new marketing methods, and changes in the economy and population.
The ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund (formerly, the ASAF T. Rowe Price Small Company Value Fund) will invest at least
65% of its total assets in stocks and equity-related securities of small companies ($1 billion or less in market
capitalization). Reflecting a value approach to investing, the Fund will seek the stocks of companies whose current stock
prices do not appear to reflect their underlying value as measured by assets, earnings, cash flow or business
franchises. The Sub-advisor's research team seeks to identify companies that appear to be undervalued by various
measures, and may be temporarily out of favor, but have good prospects for capital appreciation. In selecting
investments, the Sub-advisor generally looks to the following:
.........(1) Low price/earnings, price/book value or price/cash flow ratios relative to the S&P 500 Index, the company's
peers, or its own historic norm.
.........(2) Low stock price relative to a company's underlying asset values.
.........(3) A sound balance sheet and other positive financial characteristics.
The Sub-advisor then determines whether there is an emerging catalyst that will focus investor attention on the
underlying assets of the company, such as takeover efforts, a change in management, or a plan to improve the business
through restructuring or other means. The Fund may sell securities for a variety of reasons, such as to secure gains,
limit losses or re-deploy assets into more promising opportunities. The Fund will not sell a stock just because the
company has grown to a market capitalization of more than $1 billion, and it may on occasion purchase companies with a
market cap above $1 billion.
The ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund pursues its objective by investing primarily in common stocks selected for their
growth potential, and normally invests at least 65% of its total assets in medium-sized companies. For purposes of the
Fund, medium-sized companies are those whose market capitalizations (measured at the time of investment) fall within the
range of companies in the Standard & Poor's MidCap 400 Index (the "S&P 400"). The Sub-advisor generally takes a "bottom
up" approach to choosing investments for the Fund. In other words, the Sub-advisor seeks to identify individual
companies with earnings growth potential that may not be recognized by the market at large. The Sub-advisor makes this
assessment by looking at companies one at a time, regardless of size, country of organization, place of principal
business activity, or other similar selection criteria.
To pursue its objective, the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund primarily invests in the common stocks of mid-cap
companies. Companies with equity market capitalizations from $300 million to $10 billion at the time of investment are
considered mid-cap companies for purposes of the Fund. Some of the Fund's assets may be invested in the securities of
large-cap companies as well as in small-cap companies. The Fund seeks to reduce risk by diversifying among many
companies and industries.
The Fund is normally managed using a growth-oriented investment approach. The Sub-advisor looks for fast-growing
companies that are in new or rapidly evolving industries. Factors in identifying these companies may include
above-average growth of earnings or earnings that exceed analysts' expectations. The Sub-advisor may also look for other
characteristics in a company, such as financial strength, a strong position relative to competitors and a stock price
that is reasonable in light of its growth rate.
The Sub-advisor follows a disciplined selling strategy, and may sell a stock when it reaches a target price, fails to
perform as expected, or appears substantially less desirable than another stock.
To pursue its objective, the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund primarily invests in the common stocks of mid-cap
companies. Some of the Fund's assets may be invested in the securities of large-cap companies as well as in small-cap
companies. The Fund seeks to reduce risk by diversifying among many companies and industries.
Under the Fund's value-oriented investment approach, the Sub-advisor looks for well-managed companies whose stock prices
are undervalued and that may rise in price when other investors realize their worth. Factors that the Sub-advisor may
use to identify these companies include strong fundamentals, such as a low price-to-earnings ratio, consistent cash flow,
and a sound track record through all phases of the market cycle. The Sub-advisor may also look for other characteristics
in a company, such as a strong position relative to competitors, a high level of stock ownership among management, or a
recent sharp decline in stock price that appears to be the result of a short-term market overreaction to negative news.
The Sub-advisor generally considers selling a stock when it reaches a target price, when it fails to perform as expected,
or when other opportunities appear more attractive.
The ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund invests primarily in equity securities, such as common or preferred stocks, that are
listed on U.S. exchanges or in the over-the-counter market. The Fund may invest in the equity securities of companies of
all sizes, and may emphasize either larger or smaller companies at a given time based on the Sub-advisor's assessment of
particular companies and market conditions.
The Fund invests primarily in growth stocks. The Sub-advisor believes that these stocks are those of two types of
companies:
o High Unit Volume Growth Companies. These are vital creative companies that offer goods or services to a rapidly
expanding marketplace. They include both established and emerging firms, offering new or improved products, or firms
simply fulfilling an increased demand for an existing product line.
o Positive Life Cycle Change Companies. These are companies experiencing a major change that is expected to
produce advantageous results. These changes may be as varied as new management, products or technologies,
restructurings or reorganizations, or mergers and acquisitions.
The ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund will primarily invest in readily marketable equity securities including common
stocks, preferred stocks and securities that may be converted at a later time into common stock. The Fund may invest in
the securities of companies of all sizes, and may emphasize either larger or smaller companies at a given time based on
the Sub-advisor's assessment of particular companies and market conditions.
In making stock selections, the Fund strives to earn a 10% real rate of return. The Fund focuses on companies that
appear underpriced relative to the value that the Fund's Sub-advisor believes informed investors would be willing to pay
for the company. The Sub-advisor considers factors such as price, earnings expectations, earnings and price histories,
balance sheet characteristics and perceived management skills. The Sub-advisor also considers changes in economic and
political outlooks as well as individual corporate developments. The Sub-advisor will sell any Fund investments that
lose their perceived value relative to other investments.
The ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund normally invests at least 80% of its total assets in the equity securities of companies
engaged in the technology-related industries. These industries include, but are not limited to, applied technology,
biotechnology, communications, computers, video, electronics, Internet, IT services and consulting, oceanography, office
and factory automation, networking, robotics, and video. A portion of the Fund's assets may be invested outside of this
sector. The Sub-advisor uses a bottom-up approach to create the Fund's investment portfolio, focusing on company
fundamentals and growth prospects when selecting securities. In general, the Fund emphasizes strongly managed companies
that the Sub-advisor believes will generate above-average growth rates for the next three to five years. The Sub-advisor
prefers markets and industries where leadership is in a few hands, and tends to avoid slower-growing markets or
industries.
A core portion of the Fund's portfolio is invested in market-leading technology companies that the Sub-advisor believes
will maintain or improve their market share regardless of overall economic conditions. These companies are usually
large, established firms that are leaders in their field and have a strategic advantage over many of their competitors.
The remainder of the Fund's portfolio consists of faster-growing, more volatile technology companies that the Sub-advisor
believes to be emerging leaders in their fields.
The ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund invests primarily in the equity securities of companies that develop, produce or
distribute products or services related to health care. These companies include, but are not limited to, medical
equipment or supplies, pharmaceuticals, health care facilities, and applied research and development of new products or
services. A portion of the Fund's assets is not required to be invested in the sector. To determine whether a potential
investment is truly doing business in a particular sector, a company must meet at least one of the following tests:
o At least 50% of its gross income or its net sales must come from activities in the health sciences sector;
o At least 50% of its assets must be devoted to producing revenues from the health sciences sector; or
o Based on other available information, the Sub-advisor determines that its primary business is within the health
sciences sector.
The Fund is aggressively managed. It primarily invests in equity securities that the Sub-advisor believes will rise in
price faster than other securities, as well as options and other investments whose values are based upon the values of
equity securities. The Sub-advisor uses a "bottom up" investment approach to create the Fund's investment portfolio,
focusing on company fundamentals and growth prospects when selecting securities. In general, the Fund emphasizes
strongly managed companies that the Sub-advisor believes will generate above-average growth rates for the next three to
five years. The Sub-advisor prefers markets and industries where leadership is in a few hands, and tends to avoid
slower-growing markets or industries.
The ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund pursues its objective by investing primarily in securities of companies included in the
NASDAQ 100 Index (the "NASDAQ 100") and leveraged instruments, such as futures contracts and options, relating to the
NASDAQ 100. The NASDAQ 100 is a modified capitalization-weighted index composed of the equity securities of 100 of the
largest non-financial companies listed on the National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations System.
The Sub-advisor will attempt to consistently use leveraged instruments to increase the Fund's exposure to 125% of the
NASDAQ 100. If the Sub-advisor achieves this goal, the value of the Fund's shares will tend to increase on a daily basis
by 125% of the value of any increase in the NASDAQ 100. When the value of the NASDAQ 100 declines, the value of the
Fund's shares should also decrease on a daily basis by 125% of the value of any decrease in the Index (e.g., if the NASDAQ
100 goes down by 5%, the value of the Fund's shares should go down by 6.25% on that day).
The Sub-advisor uses quantitative analysis techniques to structure the Fund to obtain the highest correlation to the
NASDAQ 100, while remaining fully invested in all market environments. While it is not expected that the performance of
the Fund will deviate more than 10% from the Fund's goal of achieving results corresponding to 125% of the return of the
NASDAQ 100, certain factors may affect the Fund's ability to achieve this correlation. The Sub-advisor will monitor the
Fund on an ongoing basis, and make adjustments, as necessary, to minimize tracking error and to maximize liquidity.
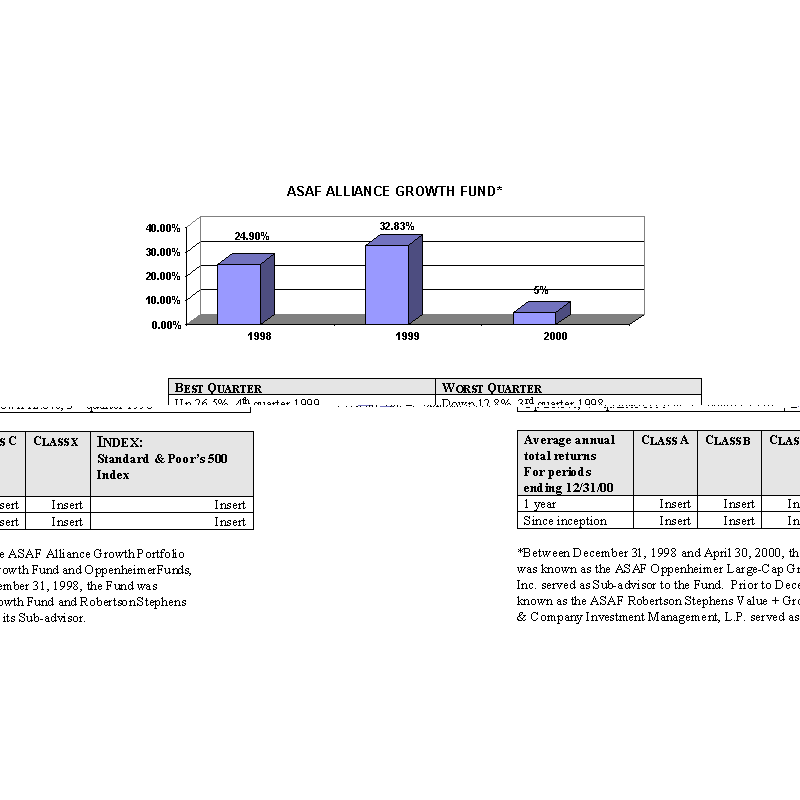
The ASAF Alliance Growth Fund (formerly, the ASAF Oppenheimer Large-Cap Growth Fund) normally invests at least 80% of its
total assets in the equity securities of U.S. companies. Normally, about 40-60 companies will be represented in the
Fund, with the 25 companies most highly regarded by the Sub-advisor usually constituting approximately 70% of the Fund 's
net assets. The Fund is thus atypical from many equity mutual funds in its focus on a relatively small number of
intensively researched companies.
The Sub-advisor relies heavily upon the fundamental analysis and research of its internal research staff, which generally
follows a primary research universe of more than 500 companies that have strong management, superior industry positions,
excellent balance sheets and superior earnings growth prospects. An emphasis is placed on identifying companies whose
substantially above average prospective earnings growth is not fully reflected in current market valuations.
During market declines, while adding to positions in favored stocks, the Fund becomes somewhat more aggressive, gradually
reducing the number of companies represented in its portfolio. Conversely, in rising markets, while reducing or
eliminating fully valued positions, the Fund becomes somewhat more conservative, gradually increasing the number of
companies represented in its portfolio. The Sub-advisor therefore seeks to gain positive returns in good markets while
providing some measure of protection in poor markets.
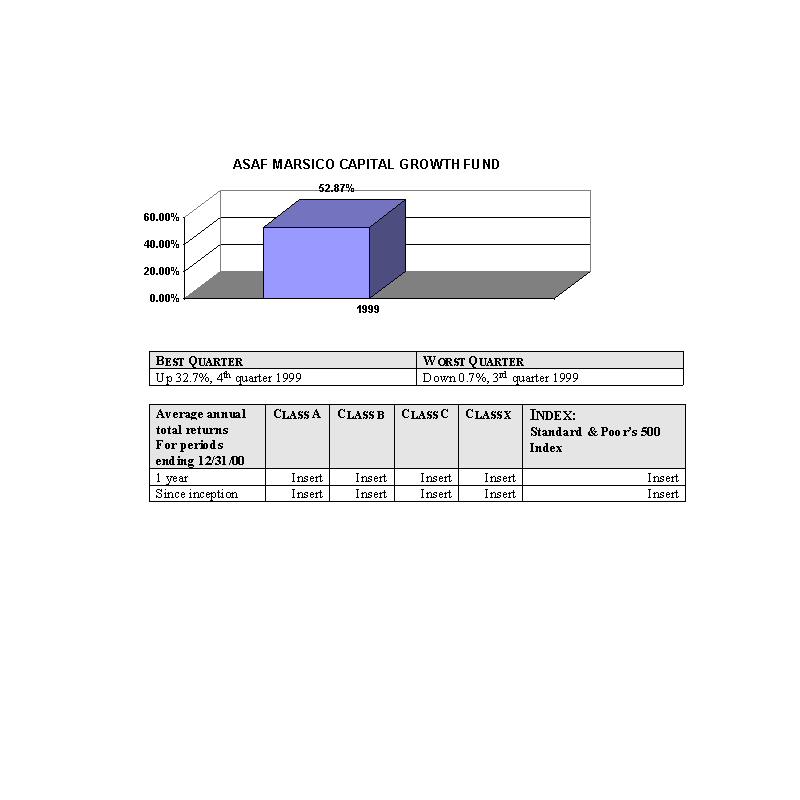
The ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund will pursue its objective by investing primarily in common stocks. The Sub-advisor
expects that the majority of the Fund's assets will be invested in the common stocks of larger, more established
companies.
In selecting investments for the Fund, the Sub-advisor uses an approach that combines "top down" economic analysis with
"bottom up" stock selection. The "top-down" approach takes into consideration such macro-economic factors as interest
rates, inflation, the regulatory environment, and the global competitive landscape. In addition, the Sub-advisor
examines such factors as the most attractive global investment opportunities, industry consolidation, and the
sustainability of economic trends. As a result of this "top down" analysis, the Sub-advisor identifies sectors,
industries and companies that should benefit from the trends the Sub-advisor has observed.
The Sub-advisor then looks for individual companies with earnings growth potential that may not be recognized by the
market at large. In determining whether a particular company is appropriate for investment by the Fund, the Sub-advisor
focuses on a number of different attributes, including the company's specific market expertise or dominance, its
franchise durability and pricing power, solid fundamentals (e.g., a strong balance sheet, improving returns on equity,
and the ability to generate free cash flow), strong management, and reasonable valuations in the context of projected
growth rates.
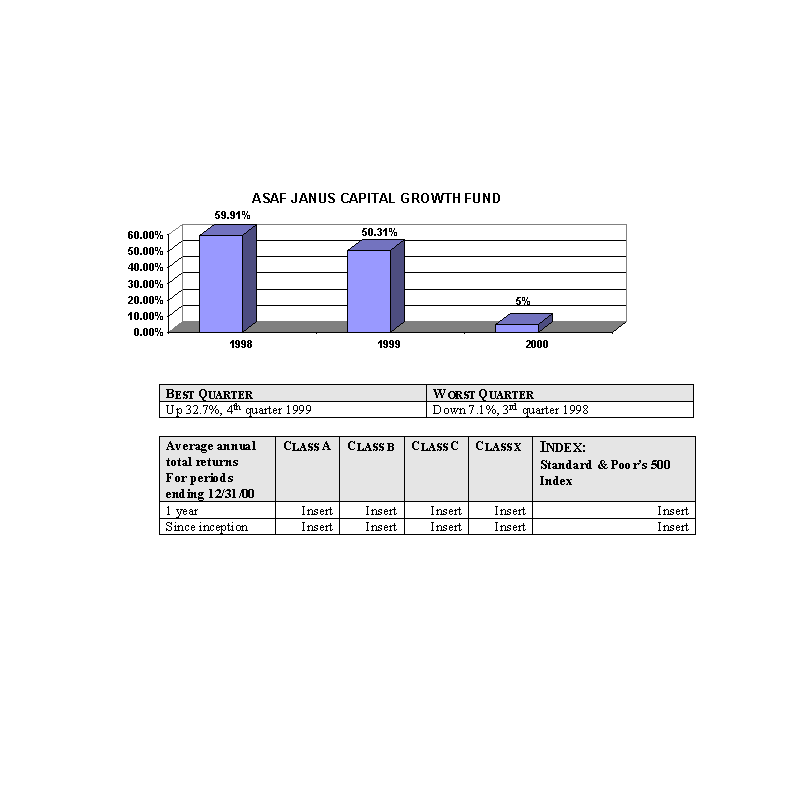
The ASMT Janus Capital Growth Portfolio will pursue its objective by investing primarily in common stocks. Common stock
investments will be in companies that the Sub-advisor believes are experiencing favorable demand for their products and
services, and which operate in a favorable competitive and regulatory environment. The Sub-advisor generally takes a
"bottom up" approach to choosing investments for the Fund. In other words, the Sub-advisor seeks to identify individual
companies with earnings growth potential that may not be recognized by the market at large.
The ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund will invest primarily in large-capitalization stocks selected mainly from the
1,000 largest U.S. companies. Stock selection is based on fundamental, bottom-up analysis that seeks to identify
companies with superior long-term appreciation prospects. Generally the Sub-advisor uses a growth approach to stock
selection, looking for companies with: a demonstrated ability to increase revenues, earnings, and cash flow consistently;
capable management; attractive business niches; and a sustainable competitive advantage. Valuation measures, such as a
company's price/earnings ratio relative to the market and its own growth rate, and its dividend yield relative to the
market, are also considered.
Generally, the Fund will limit exposure to high-yielding stocks. However, the payment of dividends - even
higher-than-average dividends - does not disqualify a stock from consideration for the Fund's portfolio. The Fund seeks
long-term appreciation while minimizing taxable distributions of capital gains and dividends. This approach should reduce
the negative effects of federal taxation and should increase after-tax returns compared with similar funds that do not
make tax efficiency a primary focus. To accomplish the Fund's goal of minimizing taxable distributions, the Sub-advisor
will strive to avoid realizing capital gains. However, gains may be realized when it is believed that the risk of holding
a security outweighs tax considerations. When gains are taken, the Sub-advisor will attempt to offset them with losses
from other securities. This may be accomplished by selling certain securities at a loss and investing the proceeds in
similar securities.
The ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth + Value Fund will invest primarily in common stocks of large U.S. companies
included in the Russell 1000 Index (the "Russell 1000"). The Russell 1000 is a market capitalization-weighted index that
measures the performance of the 1,000 largest U.S. companies. As of June 30, 2000, the average market capitalization of
the companies in the Russell 1000 index was approximately $14.1 billion.
Normally, about 60-85 companies will be represented in the Fund, with 25-35 companies primarily from the Russell 1000
Growth Index (the "Growth Index") constituting approximately 50% of the Fund's net assets, and 35-50 companies primarily
from the Russell 1000 Value Index (the "Value Index") constituting the remainder of the Fund's net assets. All daily cash
flows (that is, purchases and reinvested distributions) and outflows (that is, redemptions and expense items) will be
divided between the two portfolio segments for purposes of maintaining the targeted percentage allocation between growth
and value stocks. There will be a periodic rebalancing of each segment's assets to take account of market fluctuations
in order to maintain the approximately equal allocation. During periods between rebalancing, the allocation of assets
between portfolio segments may vary significantly from the target allocations. As a consequence, assets may be allocated
from the portfolio segment that has appreciated more or depreciated less to the other. In addition, rebalancing will
entail transaction costs which over time may be significant.
The ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund will pursue its objective by investing primarily in common stocks. The
Sub-advisor expects that the majority of the Fund's assets will be invested in the common stocks of large companies that
appear to be undervalued. Among other things, the Fund seeks to identify compelling buying opportunities created when
companies are undervalued on the basis of investor reactions to near-term problems or circumstances even though their
long-term prospects remain sound. The Sub-advisor's investment approach is value-based and price-driven, and it relies
on the intensive fundamental research of its internal research staff to identify these buying opportunities in the
marketplace.
Fund investments are selected by the Sub-advisor based upon a model portfolio of 125-175 stocks constructed by the
Sub-advisor. In selecting investments for the model portfolio, the Sub-advisor takes a "bottom-up" approach. In other
words, the Sub-advisor seeks to identify individual companies with earnings growth potential that may not be recognized
by the market at large. The Sub-advisor relates present value of each company's forecasted future cash flow to the
current price of its stock. The Sub-advisor ranks companies from the highest expected return to the lowest, with the
companies at the top of the ranking being the most undervalued.
The ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund (formerly, the ASAF Bankers Trust Managed Index 500 Fund) seeks to
outperform the Standard & Poor's 500 Composite Stock Price Index (the "S&P 500(R)") through stock selection resulting in
different weightings of common stocks relative to the index. The S&P 500 is an index of 500 common stocks, most of which
trade on the New York Stock Exchange Inc. (the "NYSE").
In seeking to outperform the S&P 500, the Sub-advisor starts with a portfolio of stocks representative of the holdings of
the index. It then uses a set of fundamental, quantitative criteria that are designed to indicate whether a particular
stock will predictably perform better or worse than the S&P 500. Based on these criteria, the Sub-advisor determines
whether the Fund should over-weight, under-weight or hold a neutral position in the stock relative to the proportion of
the S&P 500 that the stock represents. In addition, the Sub-advisor may determine based on the quantitative criteria
that (1) certain S&P 500 stocks should not be held by the Fund in any amount, and (2) certain equity securities that are
not included in the S&P 500 should be held by the Fund. The Fund may invest up to 15% of its total assets in equity
securities not included in the S&P 500.
While the Fund attempts to outperform the S&P 500, it is not expected that any outperformance will be substantial. The
Fund also may underperform the S&P 500 over short or extended periods.
Principal Risks:
---------------
All of the capital growth funds and portfolios are equity funds, and the primary risk of each is that the value of the
stocks they hold will decline. Stocks can decline for many reasons, including reasons related to the particular company,
the industry of which it is a part, or the securities markets generally. These declines can be substantial.
The risk to which the capital growth funds and portfolios are subject depends in part on the size of the companies in
which the particular fund or portfolio invests. Securities of smaller companies tend to be subject to more abrupt and
erratic price movements than securities of larger companies, in part because they may have limited product lines,
markets, or financial resources. Market capitalization, which is the total market value of a company's outstanding
stock, is often used to classify companies based on size. Therefore, the ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF
Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund and the ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund can be expected to be subject to the highest
degree of risk relative to the other capital growth funds. The ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF Neuberger Berman
Mid-Cap Growth Fund and the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund can be expected to be subject to somewhat less risk,
and the ASAF Alliance Growth Fund, the ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund, the ASMT Janus Capital Growth Portfolio, the
ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund, the ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth + Value Fund, the ASAF Sanford Bernstein
Deep Value Fund, the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund and the ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund to somewhat less
risk than the mid-cap funds. The ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund, however, will likely be subject to a greater level of risk
than the average large-cap fund because the Fund seeks to magnify the results of its benchmark index and because of the
relatively volatile nature of the securities in which it will invest. The ASAF Alger-All-Cap Growth Fund and the ASAF
Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund may invest in equity securities without regard to capitalization, and may include large and
small companies at the same time.
The ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund, the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund and the ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value
Fund and the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund take a value approach to investing, while the ASAF Janus Small-Cap
Growth Fund, the ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF Neuberger Berman
Mid-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF Alliance Growth Fund, the ASAF Marsico Capital Growth
Fund the ASMT Janus Capital Growth Portfolio, the ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund and the ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund
take a growth approach. Value stocks are believed to be selling at prices lower than what they are actually worth, while
growth stocks are those of companies that are expected to grow at above-average rates. A fund or portfolio investing
primarily in growth stocks will tend to be subject to more risk than a value fund, although this will not always be the
case. The ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund, like the S&P 500, and the ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth
+ Value Fund, will include both value and growth stocks.
The ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund and the ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund are subject to an additional risk factor because
they are less diversified than most equity funds and, therefore, a single security's increase or decrease in value may
have a greater impact on these Funds' share price and total return. Because of this, these Funds' share prices can be
expected to fluctuate more than comparable diversified funds.
The ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund and the ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund are subject to additional risk factors because
they concentrate their investments in specific market sectors. These investments could experience sharper price declines
than the market as a whole when conditions are unfavorable for the particular sector. Many of the products and services
offered by companies in the technology sector are subject to rapid obsolescence, which may reduce the value of the
securities of those companies. Many faster growing health care companies have limited operating histories and their
potential profitability may be dependent on regulatory approval of their products, which increases the volatility of
these companies' securities prices.
Growth and Income Funds and Portfolios:
Fund/Portfolio: Investment Goal: Primary Investments:
-------------- --------------- -------------------
Alliance Growth and Income Long term capital growth and The Fund invests primarily in common stocks that are believed to
Fund income be selling at reasonable valuations in relation to their
fundamental business prospects.
MFS Growth with Income Fund Reasonable current income The Fund invests primarily in common stocks and related
and long-term capital growth securities.
and income
Equity Income Portfolio Capital growth and current The Portfolio invests primarily in dividend-paying common and
income preferred stocks, and to a lesser extent in fixed income
securities.
Strategic Balanced Fund Capital growth and current The Fund normally invests approximately 60% of its assets in
income equity securities and the remainder in bonds and other fixed
income securities.
Principal Investment Strategies:
-------------------------------
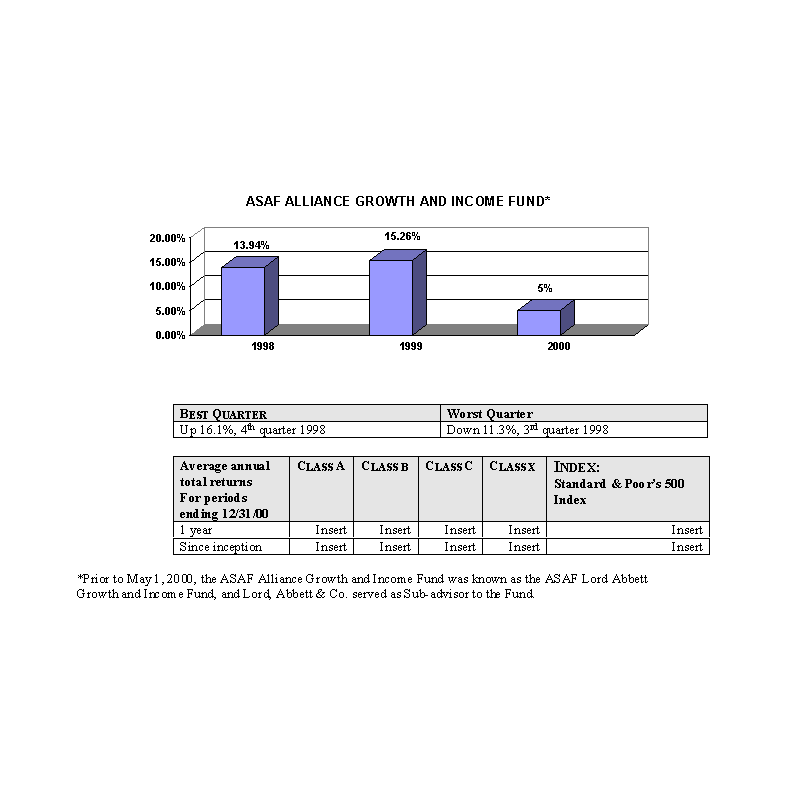
The ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund normally will invest in common stocks (and securities convertible into common
stocks). Typically, in choosing stocks, the Sub-advisor looks for companies using the following process:
Quantitative research is performed on a universe of large, seasoned, U.S. and multinational companies to identify which
stocks the Sub-advisor believes represent the best bargains; and
Fundamental research is conducted to assess a company's operating environment, resources and strategic plans and to
determine its prospects for exceeding the earnings expectations reflected in its stock price.
The Sub-advisor will take a value-oriented approach, in that it will try to keep the Fund's assets invested in securities
that are selling at reasonable prices in relation to their value. In doing so, the Fund may forgo some opportunities for
gains when, in the judgment of the Sub-advisor, they are too risky.
The ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund invests, under normal market conditions, at least 65% of its total assets in common
stocks and related securities, such as preferred stocks, convertible securities and depositary receipts. The stocks in
which the Fund invests generally will pay dividends. While the Fund may invest in companies of any size, the Fund
generally focuses on companies with larger market capitalizations that the Sub-advisor believes have sustainable growth
prospects and attractive valuations based on current and expected earnings or cash flow.
The Sub-advisor uses a "bottom up," as opposed to "top down," investment style in managing the Fund. This means that
securities are selected based upon fundamental analysis of individual companies by the Sub-advisor.
The ASMT INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio seeks to achieve its objective by investing in securities that are expected to
produce relatively high levels of income and consistent, stable returns. The Portfolio normally will invest at least 65%
of its assets in dividend-paying common and preferred stocks of domestic and foreign issuers. Up to 30% of the Fund's
assets may be invested in equity securities that do not pay regular dividends. In addition, the Portfolio normally will
have some portion of its assets invested in debt securities or convertible bonds.
The Sub-advisor to the ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund intends to maintain approximately 60% of the Fund's
assets in equity securities and the remainder in bonds and other fixed income securities. With the equity portion of the
Fund, the Sub-advisor utilizes quantitative management techniques in a two-step process that draws heavily on computer
technology. In the first step, the Sub-advisor ranks stocks, primarily the 1,500 largest publicly traded U.S. companies
as measured by market capitalization. These rankings are determined by using a computer model that combines measures of
a stock's value and measures of its growth potential. To measure value, the Sub-advisor uses ratios of stock price to
book value and stock price to cash flow, among others. To measure growth, the Sub-advisor uses, among others, the rate
of growth in a company's earnings and changes in its earnings estimates.
In the second step, the Sub-advisor uses a technique called portfolio optimization. In portfolio optimization, the
Sub-advisor uses a computer to build a portfolio of stocks from the ranking described earlier that it thinks will provide
the best balance between risk and expected return. The goal is to create an equity portfolio that provides better
returns than the S&P 500 Index without taking on significant additional risk.
The Sub-advisor intends to maintain approximately 80% of the Fund's fixed income assets in domestic fixed income
securities and up to 20% in foreign fixed income securities. This percentage will fluctuate and may be higher or lower
depending on the mix the Sub-advisor believes will be most appropriate for achieving the Fund's objectives. The fixed
income portion of the Fund is invested in a diversified portfolio of government securities, corporate fixed income
securities, mortgage-backed and asset-backed securities, and similar securities. The Sub-advisor's strategy is to
actively manage the Fund by investing the Fund's fixed income assets in sectors it believes are undervalued (relative to
the other sectors) and which represent better relative long-term investment opportunities.
The Sub-advisor will adjust weighted average portfolio maturity in response to expected changes in interest rates. Under
normal market conditions, the weighted average maturity of the fixed income portion of the Fund will range from 3 to 10
years.
Principal Risks:
---------------
Both equity securities (e.g., stocks) and fixed income securities (e.g., bonds) can decline in value, and the primary
risk of each of the growth and income funds and portfolios is that the value of the securities they hold will decline.
The degree of risk to which the growth and income funds are subject is likely to be somewhat less than a fund investing
exclusively for capital growth.
The values of equity securities tend to fluctuate more widely than the values of fixed income securities. Therefore,
because of their fixed income investments, the risk to which the ASMT INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio and the ASAF
American Century Strategic Balanced Fund are subject will likely be somewhat lower than a fund that invests exclusively
in equity securities, although both will generally invest the majority of their assets in equity securities. Fixed
income securities with longer maturities (or durations) are generally subject to greater risk than fixed income
securities with shorter maturities, in that their values will fluctuate more in response to changes in market interest
rates.
The ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund generally takes a growth approach to investing in equity securities,
while the other growth and income funds take a value approach. Growth stocks are those of companies that are expected to
grow at above-average rates, while value stocks are believed to be selling at prices lower than what they are actually
worth. A fund investing primarily in growth stocks will tend to be subject to more risk than a value fund, although this
will not always be the case.
Both the ASMT INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio and the ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund may invest a limited
portion of their assets in lower-quality fixed income securities, which are subject to greater risk that the issuer may
fail to make interest and principal payments on the securities when due.
Fixed Income Funds and Portfolios:
Fund/Portfolio: Investment Goal: Primary Investments:
-------------- --------------- -------------------
High Yield Bond Fund High current income The Fund invests primarily in lower-quality fixed income
securities.
Total Return Bond Portfolio Maximize total return, The Portfolio invests primarily in higher-quality fixed income
consistent with preservation securities of varying maturities, so that the Portfolio's
of capital expected average duration will be from three to six years.
Money Market Portfolio Maximize current income and The Portfolio invests in high-quality, short-term, U.S.
maintain high levels of dollar-denominated instruments.
liquidity
Principal Investment Strategies:
-------------------------------
The ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund will invest at least 65% of its assets in lower-rated corporate fixed income
securities ("junk bonds"). These fixed income securities may include preferred stocks, convertible securities, bonds,
debentures, notes, equipment lease certificates and equipment trust certificates. The securities in which the Fund
invests usually will be rated below the three highest rating categories of a nationally recognized rating organization
(AAA, AA, or A for Standard & Poor's Corporation ("Standard & Poor's") and Aaa, Aa or A for Moody's Investors Service,
Inc. ("Moody's")) or, if unrated, are of comparable quality. There is no lower limit on the rating of securities in
which the Fund may invest.
Methods by which the Sub-advisor attempts to reduce the risks involved in lower-rated securities include:
Credit Research. The Sub-advisor will perform its own credit analysis in addition to using rating organizations
and other sources, and may have discussions with the issuer's management or other investment analysts regarding issuers.
The Sub-advisor's credit analysis will consider the issuer's financial soundness, its responsiveness to changing business
and market conditions, and its anticipated cash flow and earnings. In evaluating an issuer, the Sub-advisor places
special emphasis on the estimated current value of the issuer's assets rather than their historical cost.
Diversification. The Sub-advisor invests in securities of many different issuers, industries, and economic
sectors.
Economic Analysis. The Sub-advisor will analyze current developments and trends in the economy and in the
financial markets.
The ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond Portfolio will invest at least 65% of its assets in the following types of fixed income
securities:
(1) securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or government-sponsored enterprises;
(2) corporate debt securities of U.S. and non-U.S. issuers, including convertible securities and corporate
commercial paper;
(3) mortgage and other asset-backed securities;
(4) inflation-indexed bonds issued by both governments and corporations;
(5) structured notes, including hybrid or "indexed" securities, event-linked bonds and loan participations;
(6) delayed funding loans and revolving credit securities;
(7) bank certificates of deposit, fixed time deposits and bankers' acceptances;
(8) repurchase agreements and reverse repurchase agreements;
(9) debt securities issued by state or local governments and their agencies and government-sponsored enterprises;
(10) obligations of foreign governments or their subdivisions, agencies and government-sponsored enterprises; and
(11) obligations of international agencies or supranational entities.
Portfolio holdings will be concentrated in areas of the bond market that the Sub-advisor believes to be relatively
undervalued. In selecting fixed income securities, the Sub-advisor uses economic forecasting, interest rate
anticipation, credit and call risk analysis, foreign currency exchange rate forecasting, and other securities selection
techniques. The proportion of the Portfolio's assets committed to investment in securities with particular
characteristics (such as maturity, type and coupon rate) will vary based on the Sub-advisor's outlook for the U.S. and
foreign economies, the financial markets, and other factors. The management of duration is one of the fundamental tools
used by the Sub-advisor.
The Portfolio will invest in fixed-income securities of varying maturities. The average portfolio duration of the
Portfolio generally will vary within a three- to six-year time frame based on the Sub-advisor's forecast for interest
rates. The Portfolio can and routinely does invest in certain complex fixed income securities (including mortgage-backed
and asset-backed securities) and engage in a number of investment practices (including futures, swaps and dollar rolls)
that many other fixed income funds do not utilize. The Portfolio may invest up to 10% of its assets in fixed income
securities that are rated below investment grade ("junk bonds") (or, if unrated, determined by the Sub-advisor to be of
comparable quality).
The ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio will invest in high-quality, short-term, U.S. dollar denominated corporate, bank and
government obligations. Under the regulatory requirements applicable to money market funds, the Portfolio must maintain
a weighted average portfolio maturity of not more than 90 days and invest in securities that have effective maturities of
not more than 397 days. In addition, the Portfolio will limit its investments to those securities that, in accordance
with guidelines adopted by the Directors of the Company, present minimal credit risks. The Portfolio will not purchase
any security (other than a United States Government security) unless:
(1) if rated by only one nationally recognized statistical rating organization (such as Moody's and Standard &
Poor's), such organization has rated it with the highest rating assigned to short-term debt securities;
(2) if rated by more than one nationally recognized statistical rating organization, at least two rating
organizations have rated it with the highest rating assigned to short-term debt securities; or
(3) it is not rated, but is determined to be of comparable quality in accordance with the guidelines noted above.
Principal Risks:
---------------
The risk of a fund or portfolio investing primarily in fixed income securities is determined largely by the quality and
maturity characteristics of its portfolio securities. Lower-quality fixed income securities are subject to greater risk
that the company may fail to make interest and principal payments on the securities when due. Fixed income securities
with longer maturities (or durations) are generally subject to greater risk than securities with shorter maturities, in
that their values will fluctuate more in response to changes in market interest rates.
As a fund that invests primarily in lower-quality fixed income securities, the ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund will
be subject to a level of risk that is high relative to other fixed income funds, and which may be comparable to or higher
than some equity funds. Like equity securities, lower-quality fixed income securities tend to reflect short-term market
developments to a greater extent than higher-quality fixed income securities. An economic downturn may adversely affect
the value of lower-quality securities, and the trading market for such securities is generally less liquid than the
market for higher-quality securities.
As a portfolio that invests primarily in high-quality fixed income securities of medium duration, the level of risk to
which the ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond Portfolio is subject can be expected to be less than most equity funds.
Nonetheless, the fixed income securities held by the Portfolio can decline in value because of changes in their quality,
in market interest rates, or for other reasons. In addition, while the complex fixed income securities invested in and
investment practices engaged in by the Portfolio are designed to increase its return or hedge its investment, these
securities and practices may increase the risk to which the Portfolio is subject.
The ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio seeks to preserve the value of your investment at $1.00 per share, but it is still
possible to lose money by investing in the Portfolio. An investment in the Portfolio is not insured or guaranteed by the
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or any other government agency. In addition, the income earned by the Portfolio
will fluctuate based on market conditions and other factors.
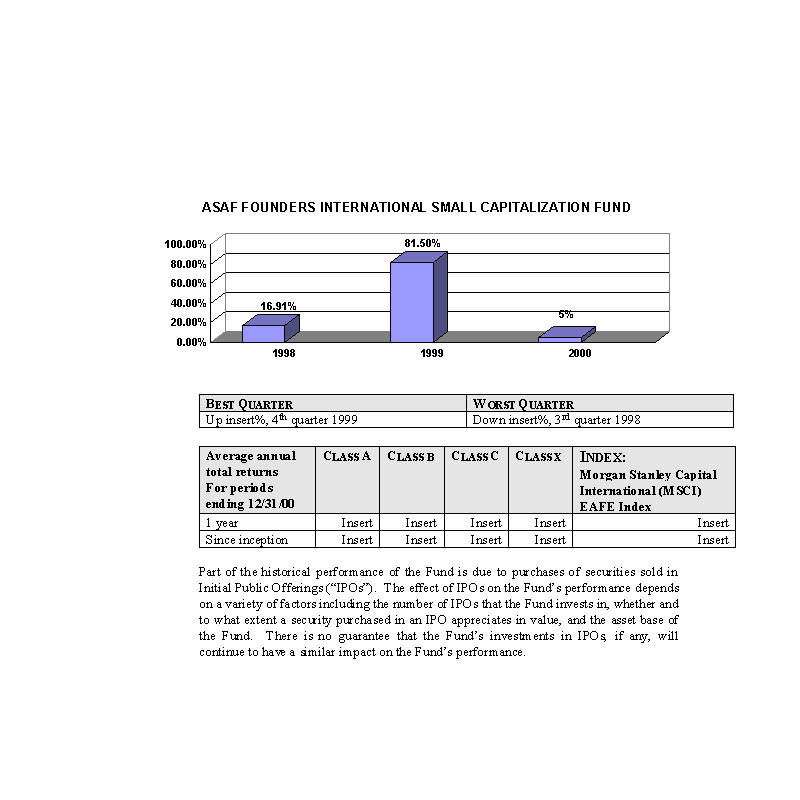
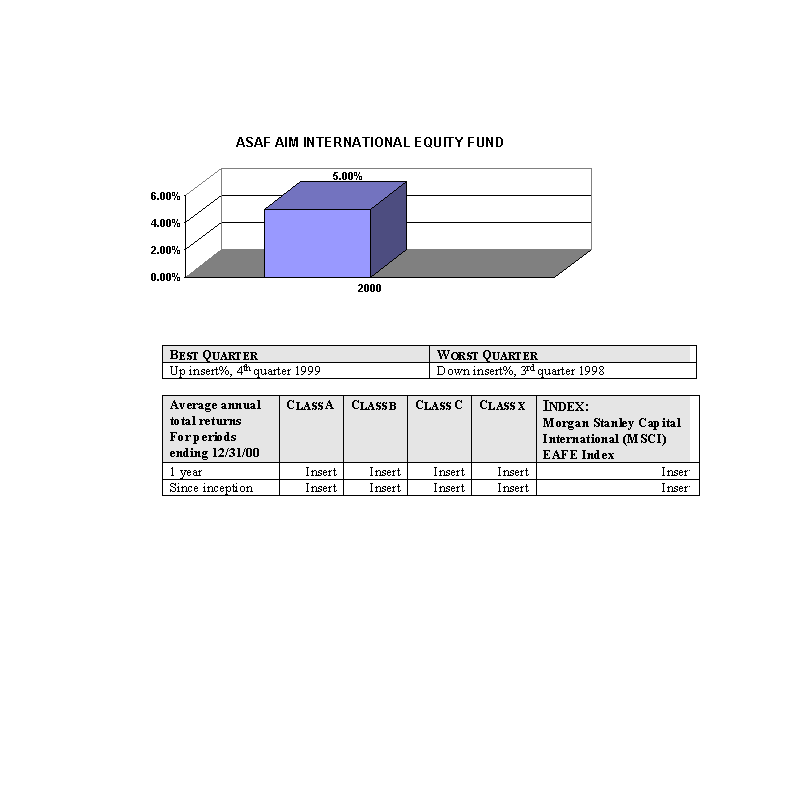
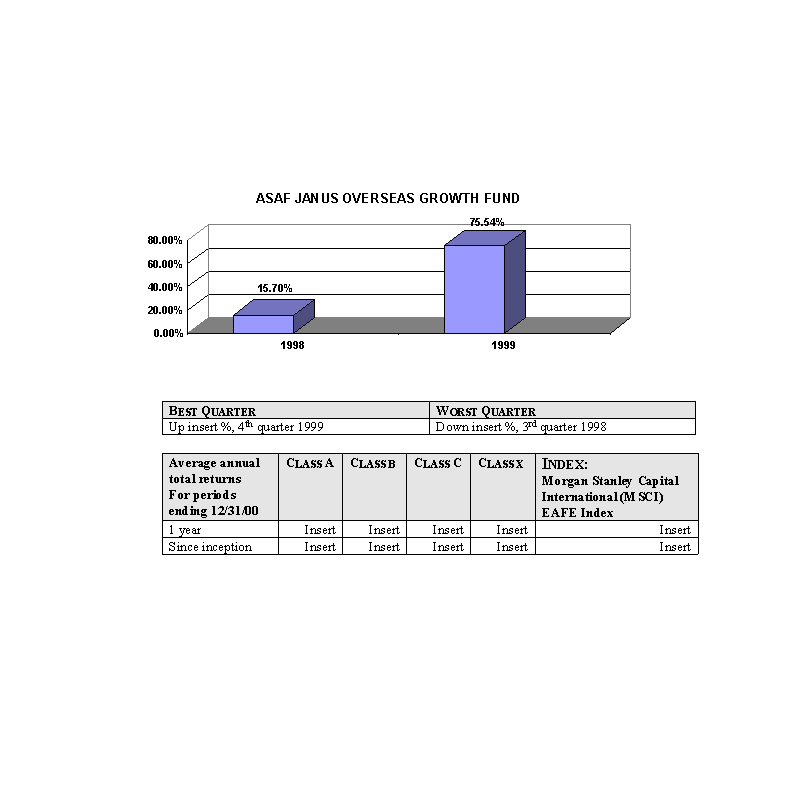
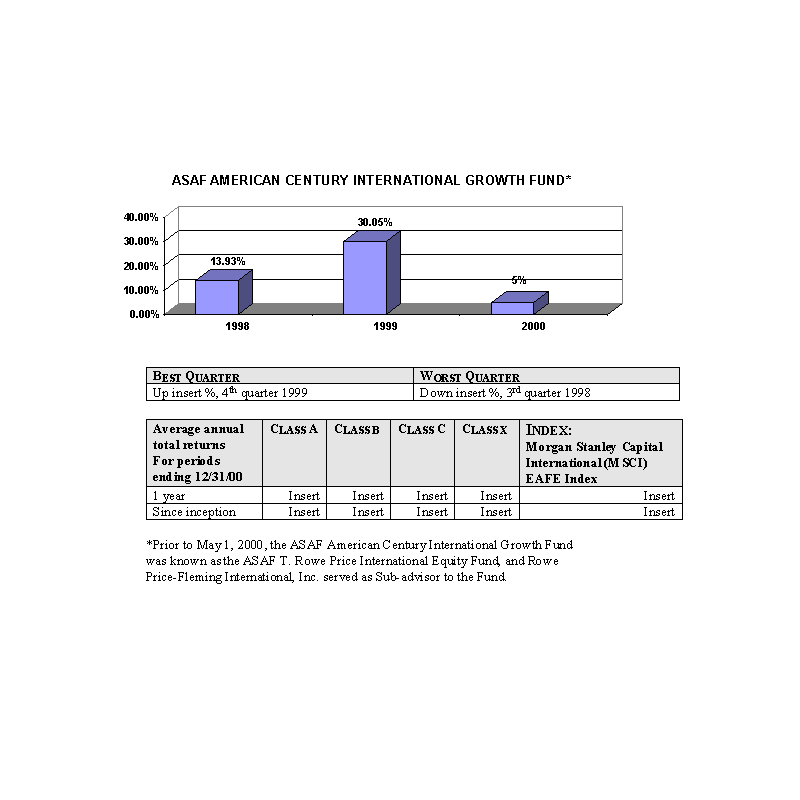
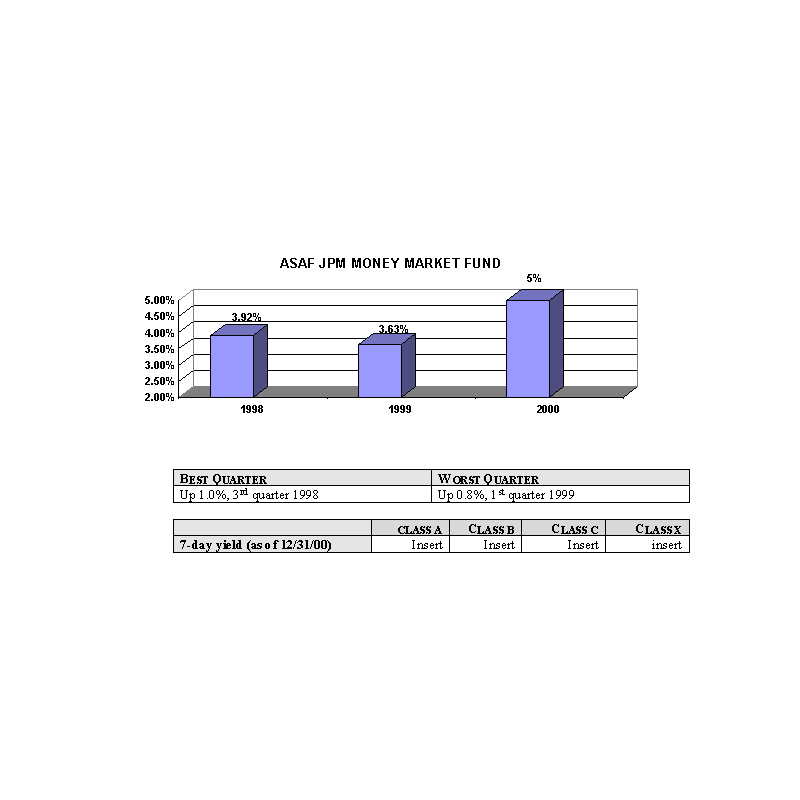
Past Performance
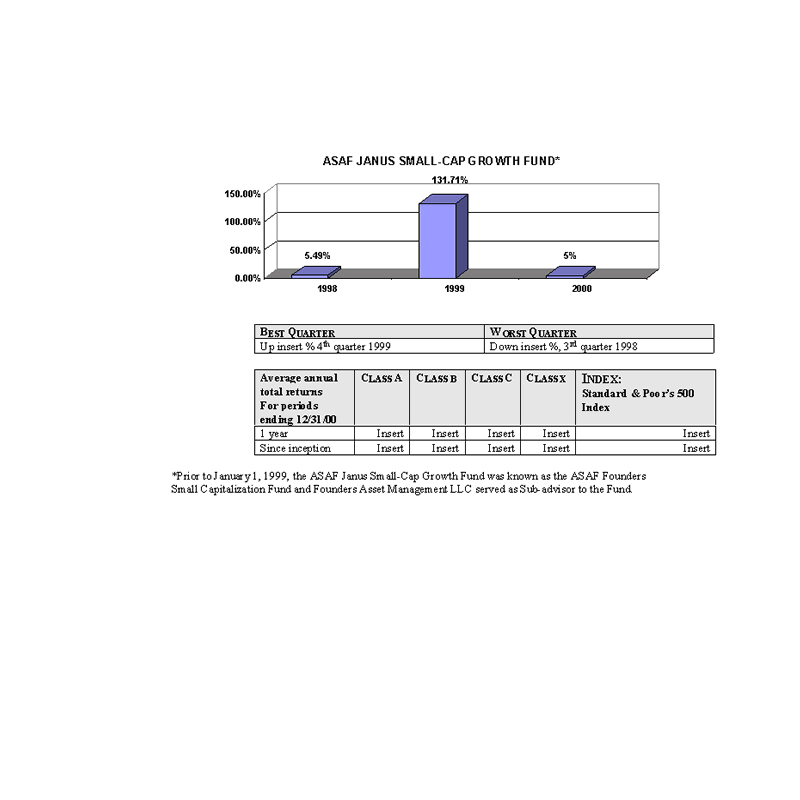
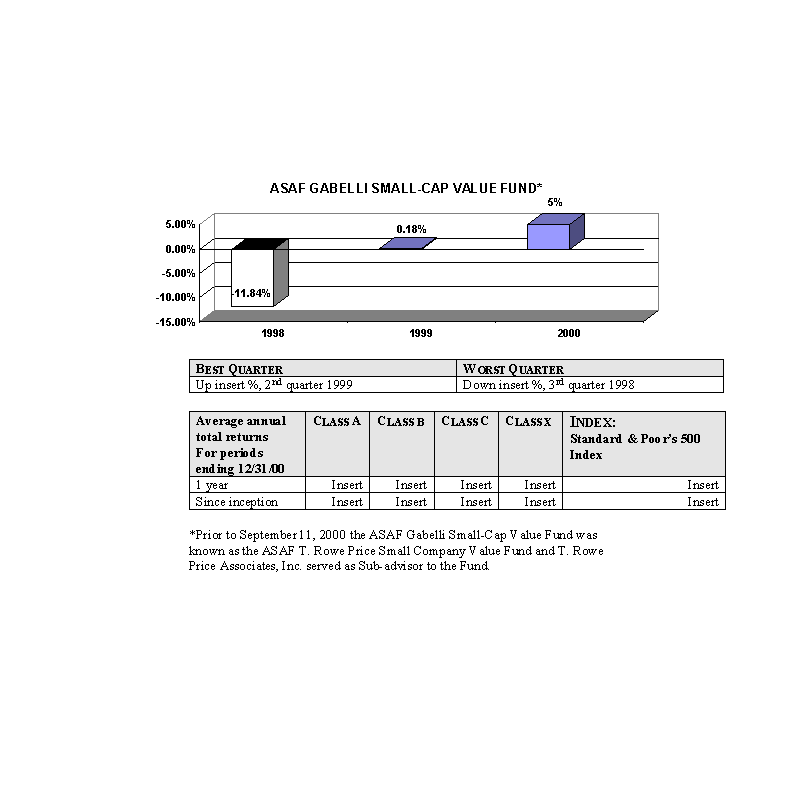
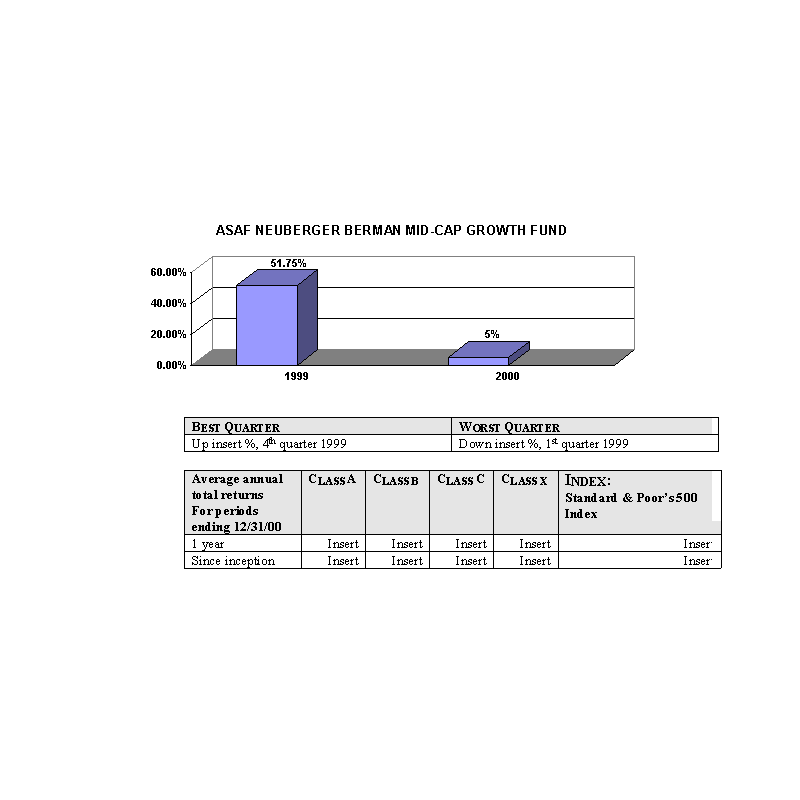
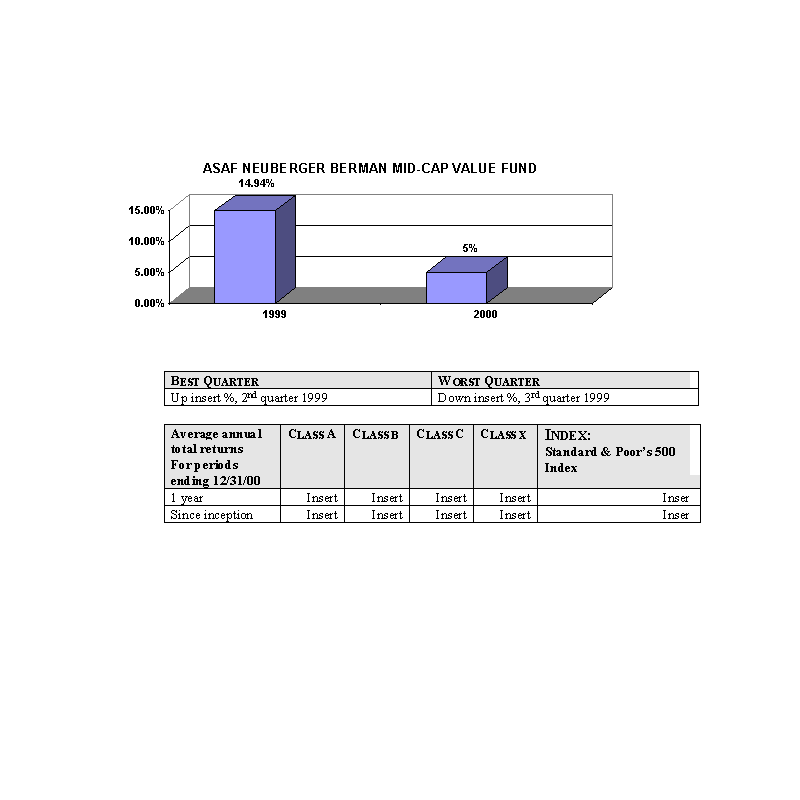
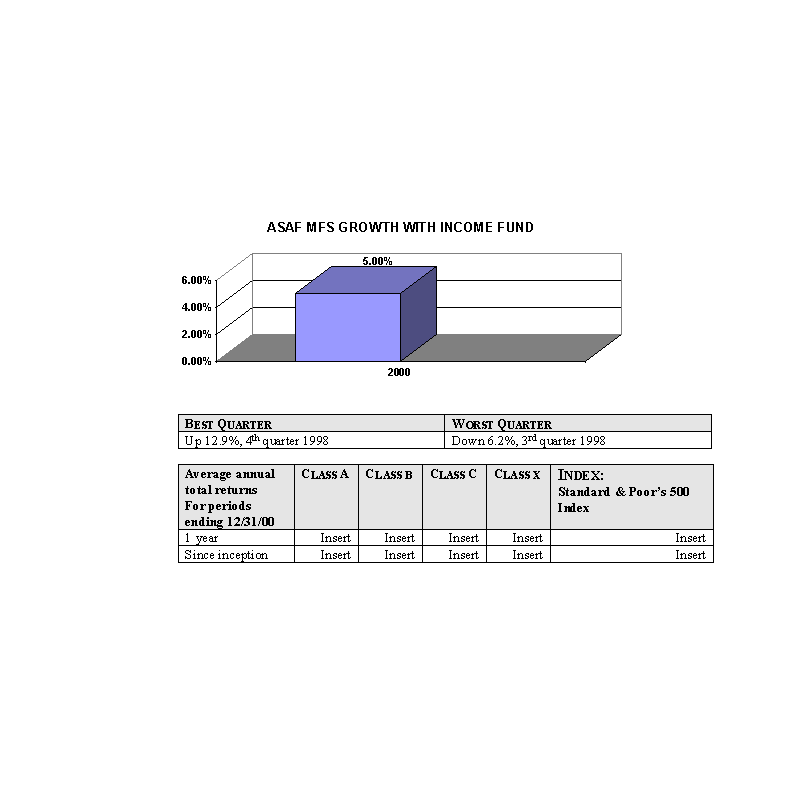
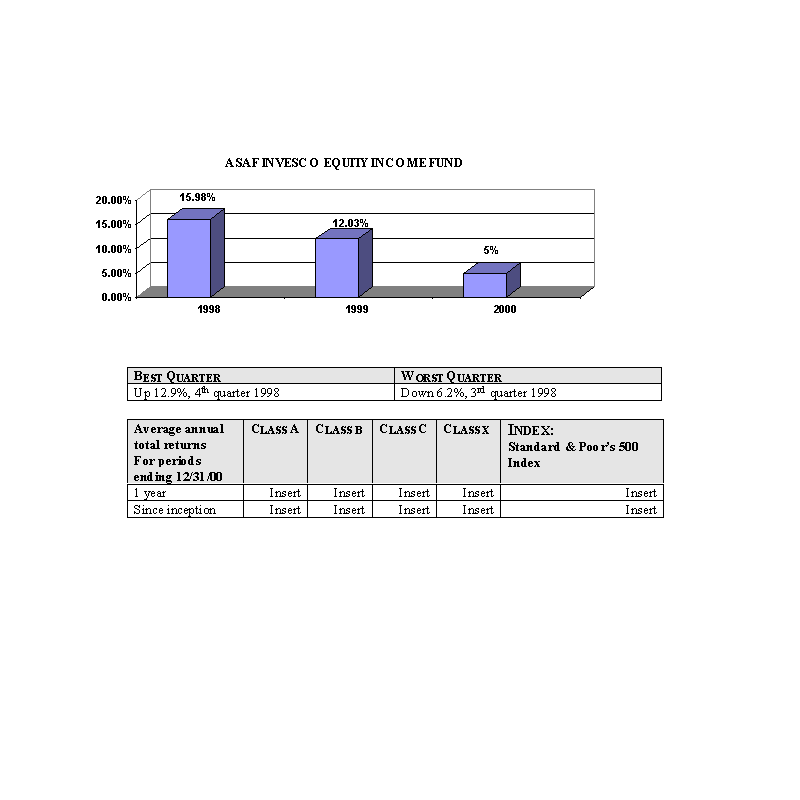
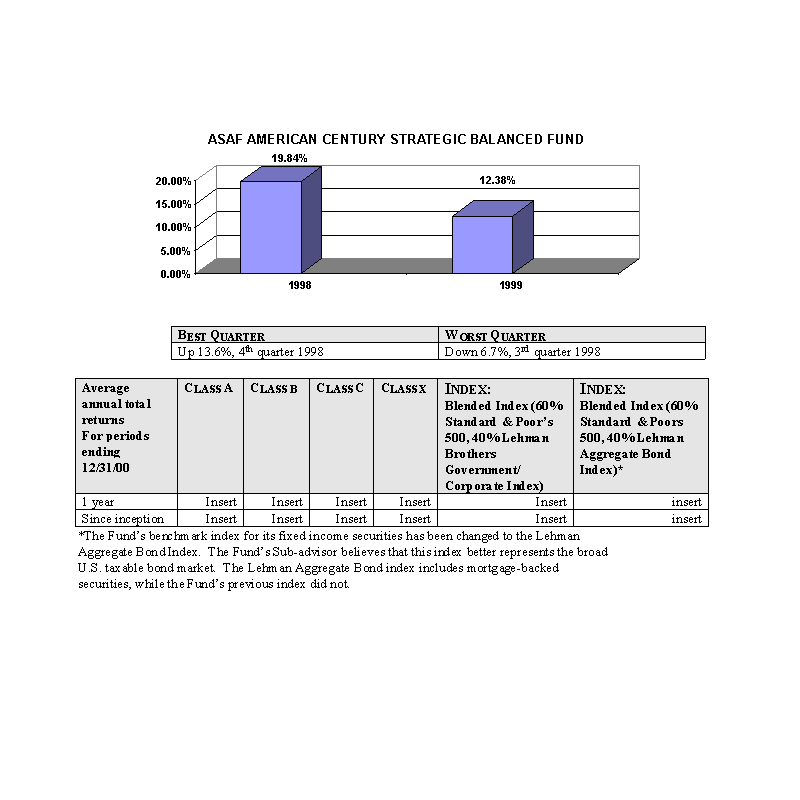
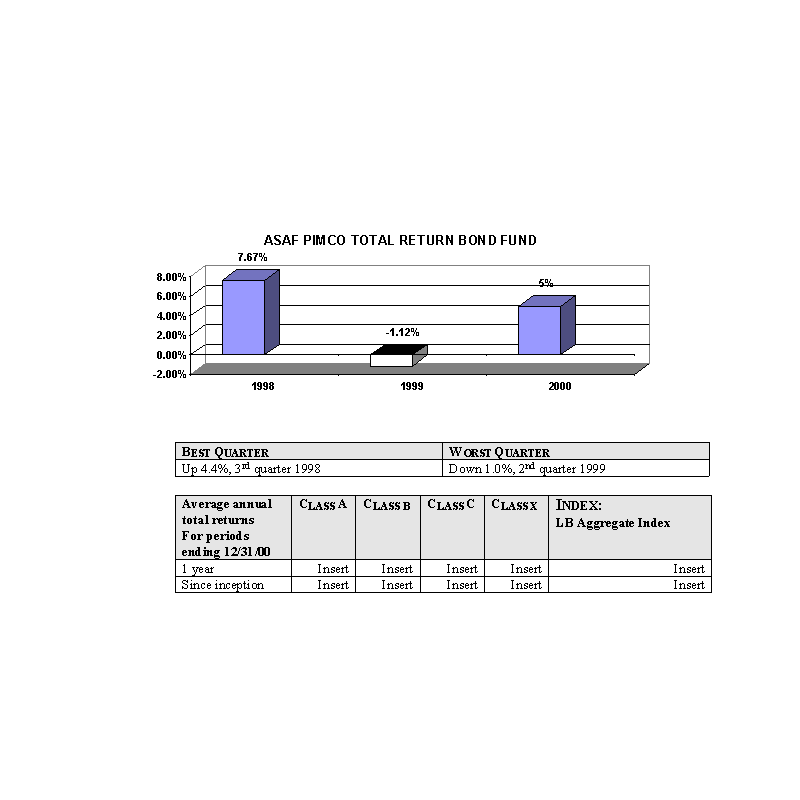
The bar charts show the performance of the Class A shares of each Fund for each full calendar year the Fund
has been in operation. The tables below the bar charts show each such Fund's best and worst quarters during the periods
included in the bar chart, as well as the average annual total returns for each Class of each Fund for 2000 and since
inception. This information may help provide an indication of each Fund's risks by showing changes in performance from
year to year and by comparing the Fund's performance with that of a broad-based securities index. The average annual
figures reflect sales charges; the other figures do not, and would be lower if they did. All figures assume reinvestment
of dividends. Past performance does not necessarily indicate how a Fund will perform in the future. The 1999
performance figures for some of the Funds reflect the substantial increases that occurred during 1999 in the markets for
the types of securities in which those Funds invest; it is unlikely that similarly large increases will continue in
future years. No performance information is included for those Portfolios that commenced operations after January, 2000
(the ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund, the ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund, the ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth
+ Value Fund and the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund).


EXPENSE INFORMATION
The maximum transaction costs and total annual operating expenses associated with investing in Class A, Class B,
Class C or Class X shares of each Fund are reflected in the following tables:
SHAREHOLDER TRANSACTION EXPENSES (fees paid directly from your investment):
.........
High Yield Bond & Total Return Bond All Other Funds:
Funds: (other than Class A shares of
Money Market Fund)(1)
Class A Class B & X Class C Class A Class B & X Class C
------- ----------- ------- ------- ----------- -------
Maximum Sales Charge (Load) on
Purchases 4.25% None 1.00% 5.75% None 1.00%
(as % of offering price)
Maximum Contingent Deferred Sales
Charge
(Load) (as % of lower of original None(2) 6.00%(3) 1.00%(3) None(2)
purchase price or redemption proceeds) 6.00%(3) 1.00%(3)
Redemption Fee None(4) None(4) None(4) None(4) None(4) None(4)
Exchange Fee None None None None None None
ANNUAL FUND OPERATING EXPENSES (expenses that are deducted from Fund assets, in %):
ASAF Fund: Management Estimated Other Total Annual Fee Waivers Net Annual Fund
Fees Distribution Expenses Fund Operating and Expense Operating
and Service Expenses Reimbursement(6) Expenses
(12b-1)
Fees(5)
----------------------------- --------------- -------------- ------------- ------------------ ---------------- -----------------
Int'l Small Capitalization
Class A 1.10 0.50 2.93 4.53 (2.33) 2.20
Class B 1.10 1.00 2.94 5.04 (2.34) 2.70
Class C 1.10 1.00 2.95 5.05 (2.35) 2.70
Class X 1.10 1.00 2.97 5.07 (2.37) 2.70
AIM International
Equity(7)
Class A 1.10 0.82 2.31 4.23 (1.81) 2.42
Class B 1.10 1.32 2.75 5.17 (2.25) 2.92
Class C 1.10 1.32 2.52 4.94 (2.02) 2.92
Class X 1.10 1.32 4.14 6.56 (3.64) 2.92
Overseas Growth
Class A 1.10 0.55 0.85 2.50 (0.35) 2.15
Class B 1.10 1.05 0.85 3.00 (0.35) 2.65
Class C 1.10 1.05 0.85 3.00 (0.35) 2.65
Class X 1.10 1.05 0.86 3.01 (0.36) 2.65
American Century
International Growth
Class A 1.00 0.54 1.84 3.38 (1.24) 2.14
Class B 1.00 1.04 1.84 3.88 (1.24) 2.64
Class C 1.00 1.04 1.88 3.92 (1.28) 2.64
Class X 1.00 1.04 1.92 3.96 (1.32) 2.64
Janus Small-Cap Growth
Class A 0.90 0.53 0.79 2.22 (0.39) 1.83
Class B 0.90 1.03 0.78 2.71 (0.38) 2.33
Class C 0.90 1.03 0.82 2.75 (0.42) 2.33
Class X 0.90 1.03 0.91 2.84 (0.51) 2.33
Scudder Small-Cap Growth(8)
Class A 0.95 0.54 0.68 2.17 (0.33) 1.84
Class B 0.95 1.04 0.68 2.67 (0.33) 2.34
Class C 0.95 1.04 0.68 2.67 (0.33) 2.34
Class X 0.95 1.04 0.68 2.67 (0.33) 2.34
Small-Cap Value
Class A 1.00 0.50 1.11 2.61 (0.71) 1.90
Class B 1.00 1.00 1.13 3.13 (0.73) 2.40
Class C 1.00 1.00 1.13 3.13 (0.73) 2.40
Class X 1.00 1.00 1.12 3.12 (0.72) 2.40
Janus Mid-Cap Growth(8)
Class A 1.00 0.54 0.71 2.25 (0.31) 1.94
Class B 1.00 1.04 0.71 2.75 (0.31) 2.44
Class C 1.00 1.04 0.71 2.75 (0.31) 2.44
Class X 1.00 1.04 0.71 2.75 (0.31) 2.44
Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap
Growth
Class A 0.90 0.56 1.23 2.69 (0.78) 1.91
Class B 0.90 1.06 1.22 3.18 (0.77) 2.41
Class C 0.90 1.06 1.25 3.21 (0.80) 2.41
Class X 0.90 1.06 1.27 3.23 (0.82) 2.41
Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap
Value
Class A 0.90 0.75 1.26 2.91 (0.81) 2.10
Class B 0.90 1.25 1.29 3.44 (0.84) 2.60
Class C 0.90 1.25 1.32 3.47 (0.87) 2.60
Class X 0.90 1.25 1.35 3.50 (0.90) 2.60
All-Cap Growth(8)
Class A 0.95 0.54 0.71 2.20 (0.31) 1.89
Class B 0.95 1.04 0.71 2.70 (0.31) 2.39
Class C 0.95 1.04 0.71 2.70 (0.31) 2.39
Class X 0.95 1.04 0.71 2.70 (0.31) 2.39
All-Cap Value(8)
Class A 0.95 0.54 0.71 2.20 (0.31) 1.89
Class B 0.95 1.04 0.71 2.70 (0.31) 2.39
Class C 0.95 1.04 0.71 2.70 (0.31) 2.39
Class X 0.95 1.04 0.71 2.70 (0.31) 2.39
Technology(8)
Class A 1.00 0.50 0.71 2.21 (0.31) 1.90
Class B 1.00 1.00 0.71 2.71 (0.31) 2.40
Class C 1.00 1.00 0.71 2.71 (0.31) 2.40
Class X 1.00 1.00 0.71 2.71 (0.31) 2.40
Health Sciences Fund
Class A Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Class B Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Class C Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Class X Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Managed OTC(8)
Class A 0.85 0.50 0.71 2.06 (0.31) 1.75
Class B 0.85 1.00 0.71 2.56 (0.31) 2.25
Class C 0.85 1.00 0.71 2.56 (0.31) 2.25
Class X 0.85 1.00 0.71 2.56 (0.31) 2.25
Alliance Growth
Class A 0.90 0.50 1.01 2.41 (0.61) 1.80
Class B 0.90 1.00 1.01 2.91 (0.61) 2.30
Class C 0.90 1.00 1.02 2.92 (0.62) 2.30
Class X 0.90 1.00 1.03 2.93 (0.63) 2.30
Marsico Capital Growth
Class A 1.00 0.52 0.52 2.04 (0.22) 1.82
Class B 1.00 1.02 0.52 2.54 (0.22) 2.32
Class C 1.00 1.02 0.52 2.54 (0.22) 2.32
Class X 1.00 1.02 0.52 2.54 (0.22) 2.32
Janus Capital Growth
Class A 1.00 0.53 0.49 2.02 (0.19) 1.83
Class B 1.00 1.03 0.50 2.53 (0.20) 2.33
Class C 1.00 1.03 0.49 2.52 (0.19) 2.33
Class X 1.00 1.03 0.47 2.50 (0.17) 2.33
Tax Managed Fund
Class A Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Class B Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Class C Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Class X Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
50/50 Growth + Value Fund
Class A Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Class B Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Class C Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Class X Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Deep Value Fund
Class A Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Class B Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Class C Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Class X Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Managed Index 500(7)
Class A 0.80 0.50 0.54 1.84 (0.34) 1.50
Class B 0.80 1.00 0.69 2.49 (0.49) 2.00
Class C 0.80 1.00 0.70 2.50 (0.50) 2.00
Class X 0.80 1.00 0.61 2.41 (0.41) 2.00
Alliance Growth and Income
Class A 1.00 0.59 0.68 2.27 (0.53) 1.74
Class B 1.00 1.09 0.68 2.77 (0.53) 2.24
Class C 1.00 1.09 0.69 2.78 (0.54) 2.24
Class X 1.00 1.09 0.69 2.78 (0.54) 2.24
MFS Growth with Income(7)
Class A 1.00 0.50 1.62 3.12 (1.32) 1.80
Class B 1.00 1.00 1.93 3.93 (1.63) 2.30
Class C 1.00 1.00 1.64 3.64 (1.34) 2.30
Class X 1.00 1.00 1.61 3.61 (1.31) 2.30
Equity Income
Class A 0.75 0.59 0.62 1.96 (0.17) 1.79
Class B 0.75 1.09 0.63 2.47 (0.18) 2.29
Class C 0.75 1.09 0.62 2.46 (0.17) 2.29
Class X 0.75 1.09 0.63 2.47 (0.18) 2.29
Strategic Balanced
Class A 0.90 0.50 0.75 2.15 (0.45) 1.70
Class B 0.90 1.00 0.77 2.67 (0.47) 2.20
Class C 0.90 1.00 0.77 2.67 (0.47) 2.20
Class X 0.90 1.00 0.77 2.67 (0.47) 2.20
High Yield Bond
Class A 0.70 0.50 0.61 1.81 (0.31) 1.50
Class B 0.70 1.00 0.61 2.31 (0.31) 2.00
Class C 0.70 1.00 0.62 2.32 (0.32) 2.00
Class X 0.70 1.00 0.62 2.32 (0.32) 2.00
Total Return Bond
Class A 0.65 0.50 0.58 1.73 (0.23) 1.50
Class B 0.65 1.00 0.58 2.23 (0.23) 2.00
Class C 0.65 1.00 0.59 2.24 (0.24) 2.00
Class X 0.65 1.00 0.60 2.25 (0.25) 2.00
Money Market
Class A 0.50 0.50 0.63 1.63 (0.13) 1.50
Class B 0.50 1.00 0.62 2.12 (0.12) 2.00
Class C 0.50 1.00 0.63 2.13 (0.13) 2.00
Class X 0.50 1.00 0.63 2.13 (0.13) 2.00
(1) Class A shares of the ASAF JPM Money Market Fund are sold without an initial sales charge (load).
(2) Under certain circumstances, purchases of Class A shares not subject to an initial sales charge (load) will be
subject to a contingent deferred sales charge (load) ("CDSC") if redeemed within 12 months of the calendar month of
purchase. For an additional discussion of the Class A CDSC, see this Prospectus under "How to Buy Shares."
(3) If you purchase Class B or X shares, you do not pay an initial sales charge but you may pay a CDSC if you redeem
some or all of your shares before the end of the seventh (in the case of Class B shares) or eighth (in the case of Class
X shares) year after which you purchased such shares. The CDSC is 6%, 5%, 4%, 3%, 2%, 2% and 1% for redemptions of Class
B shares occurring in years one through seven, respectively. The CDSC is 6%, 5%, 4%, 4%, 3%, 2%, 2% and 1% for
redemptions of Class X shares occurring in years one through eight, respectively. No CDSC is charged after these
periods. If you purchase Class C shares, you do not pay an initial sales charge but you may incur a CDSC if you redeem
some or all of your Class C shares within 12 months of the calendar month of purchase. For a discussion of the Class B,
X and C CDSC, see this Prospectus under "How to Buy Shares."
(4) A $10 fee may be imposed for wire transfers of redemption proceeds. For an additional discussion of wire
redemptions, see this Prospectus under "How to Redeem Shares."
(5) As discussed below under "How to Buy Shares - Distribution Plans," the Company and the Trust have adopted Plans
under Rule 12b-1 to permit an affiliate of Company's and Trust's Investment Manager to receive brokerage commissions in
connection with the purchase and sale of securities held by the Funds and Portfolios, and to use these commissions to
promote the sale of shares of the Funds. The staff of the Securities and Exchange Commission takes the position that
commission amounts received under these Supplemental Distribution Plans should be reflected in the expenses of the
Funds. In general, the estimated Distribution Fees are derived and annualized from data regarding commission amounts
directed to the affiliate under the Supplemental Distribution Plans for the fiscal year ended October 31, 2000.
(6) The Funds' investment manager has agreed to reimburse and/or waive fees for each Fund until at least July 1, 2001 so
that each Fund's operating expenses (and, in the case of the Feeder Funds, the Feeder Fund's pro rata share of operating
expenses of the Fund's corresponding Portfolio), exclusive of taxes, interest, brokerage commissions, distribution fees
and extraordinary expenses, do not exceed specified percentages of the Fund's average net assets as follows: ASAF
Founders International Small Capitalization Fund -- 1.70%; ASAF AIM International Equity Fund - 1.60%; ASAF Janus
Overseas Growth Fund - 1.60%; ASAF American Century International Growth Fund -- 1.60%; ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund
- 1.30%; ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund - 1.30%; ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund -- 1.40%; ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth
Fund - 1.40%; ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund - 1.35%; ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund - 1.35%; ASAF
Alger All-Cap Growth Fund - 1.35%; ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund - 1.35%; ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund - 1.40%; ASAF
INVESCO Health Sciences Fund - insert%; ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund - 1.25%; ASAF Alliance Growth Fund - 1.30%; ASAF
Marsico Capital Growth Fund - 1.30%; ASAF Janus Capital Growth Fund - 1.30%; ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund -
insert%; ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth + Value Fund - insert%; ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund - insert%;
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund - 1.00%; ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund - 1.15%; ASAF MFS Growth with
Income Fund - 1.30%; ASAF INVESCO Equity Income Fund -- 1.20%; ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund -- 1.20%;
ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund -- 1.00%; ASAF PIMCO Total Return Bond Fund -- 1.00%; and ASAF JPM Money Market Fund
-- 1.00%. Furthermore, the Investment Manager may reimburse and/or waive fees to a greater extent than indicated above
so that the percentages shown in the table under "Net Annual Fund Operating Expenses" may be lower than indicated.
(7) "Other Expenses" and "Estimated Distribution and Service Fees" shown are based on actual amounts for the semi-annual
period ended April 30, 2000.
(8) "Other Expenses" and "Estimated Distribution and Service Fees" shown are based on estimated amounts for the fiscal
year ending October 31, 2000.
Expenses shown for each of the Feeder Funds are based upon distribution and administration fees for the Fund and
management fees and other expenses for the Fund's corresponding Portfolio.
EXPENSE EXAMPLES:
This example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the Funds with the cost of investing in
other mutual funds.
Full Redemption. This Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in a Fund for the time periods indicated and then
redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return
each year, that the Funds' total operating expenses remain the same, and that the Funds' expense waivers and
reimbursements remain in effect until March 1, 2002. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower, based on these
assumptions your costs would be:
1 Year 3 Years
ASAF Fund: Class A Class B Class C Class X(*) Class A Class B Class C Class X(*)
--------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- -------
International Small $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert
Capitalization
AIM International Equity insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Overseas Growth insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
American Century insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
International Growth
Janus Small-Cap Growth insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Scudder Small-Cap Growth insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Small-Cap Value insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Janus Mid-Cap Growth insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Neuberger Berman insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Mid-Cap Growth
Neuberger Berman insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Mid-Cap Value
All-Cap Growth insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
All-Cap Value insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Technology insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Health Sciences Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Managed OTC insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Alliance Growth insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Marsico Capital Growth insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
1 Year 3 Years
ASAF Fund: Class A Class B Class C Class X(*) Class A Class B Class C Class X(*)
--------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- -------
Janus Capital Growth insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Tax Managed Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
50/50 Growth + Value Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Deep Value Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Managed Index 500 insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Alliance Growth and insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Income
MFS Growth with Income insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Equity Income insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Strategic Balanced insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
High Yield Bond insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Total Return Bond insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Money Market insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
5 Years 10 Years
ASAF Fund: Class A Class B Class C Class X(*) Class A Class B Class C Class X(*)
--------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- -------
International Small $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert
Capitalization
AIM International Equity insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Overseas Growth insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
American Century insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
International Growth
Janus Small-Cap Growth insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Scudder Small-Cap Growth n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Small Cap Value insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Janus Mid-Cap Growth n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Neuberger Berman insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Mid-Cap Growth
5 Years 10 Years
ASAF Fund: Class A Class B Class C Class X(*) Class A Class B Class C Class X(*)
--------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- -------
Neuberger Berman insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Mid-Cap Value
All-Cap Growth n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
All-Cap Value n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Technology n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Health Sciences n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Managed OTC n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Alliance Growth insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Marsico Capital Growth insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Janus Capital Growth insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Tax Managed n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
50/50 Growth + Value n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Fund
Deep Value n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Managed Index 500 insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Alliance insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Growth and Income
MFS insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Growth with Income
Equity Income insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Strategic Balanced insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
High Yield Bond insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Total Return Bond insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Money Market insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
No Redemption. You would pay the following expenses based on the above assumptions except that you do not redeem
your shares at the end of each period:
1 Year 3 Years
ASAF Fund: Class A Class B Class C Class X(*) Class A Class B Class C Class X(*)
--------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- -------
International Small $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert
Capitalization
1 Year 3 Years
ASAF Fund: Class A Class B Class C Class X(*) Class A Class B Class C Class X(*)
--------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- -------
AIM International insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Equity
Overseas Growth insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
American Century insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
International Growth
Janus Small-Cap Growth Insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Scudder Small-Cap Growth Insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Small-Cap Value Insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Janus Mid-Cap Growth Insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Neuberger Berman Insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Mid-Cap Growth
Neuberger Berman Insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Mid-Cap Value
All-Cap Growth Insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
All-Cap Value Insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Technology Insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Health Sciences Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Managed OTC Insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Alliance Growth Insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Marsico Capital Growth Insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Janus Capital Growth Insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Tax Managed Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
50/50 Growth + Value Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Deep Value Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Managed Index 500 Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Alliance Growth and Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Income
1 Year 3 Years
ASAF Fund: Class A Class B Class C Class X(*) Class A Class B Class C Class X(*)
--------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- -------
MFS Growth with Income Insert insert insert insert insert insert insert insert
Equity Income Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Strategic Balanced Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
High Yield Bond Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Total Return Bond Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Money Market Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
5 Years 10 Years
ASAF Fund: Class A Class B Class C Class X(*) Class A Class B Class C Class X(*)
--------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- -------
International Small $Insert $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert $insert
Capitalization
AIM International Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Equity
Overseas Growth Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
American Century Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
International Growth
Janus Small-Cap Growth Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Scudder Small-Cap n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Growth
Small-Cap Value Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Janus Mid-Cap Growth n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Neuberger Berman Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Mid-Cap Growth
Neuberger Berman Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Mid-Cap Value
All-Cap Growth n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
All-Cap Value n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Technology n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Health Sciences n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
5 Years 10 Years
ASAF Fund: Class A Class B Class C Class X(*) Class A Class B Class C Class X(*)
--------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- -------
Managed OTC n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Alliance Growth Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Marsico Capital Growth Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Janus Capital Growth Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Tax Managed n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
50/50 Growth + Value n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Deep Value n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Managed Index 500 Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Alliance Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Growth and Income
MFS Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Growth with Income
Equity Income Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Strategic Balanced Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
High Yield Bond Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Total Return Bond Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
Money Market Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert Insert
(*) Expense examples for purchases of Class X shares of the Funds reflect the shareholder's receipt of additional "bonus
shares." For a discussion of the issuance of "bonus shares," see this Prospectus under "How to Buy Shares: Purchase of
Class X Shares."
INVESTMENT PROGRAMS OF THE FUNDS
The investment objective, policies and limitations for each of the Funds are described below. Each Feeder Fund
seeks to meet its investment objective by investing all of its investable assets in a corresponding Portfolio of the
Trust, which in turn invests directly in a portfolio of securities. The investment objective, policies and limitations
of each Feeder Fund are identical to those of its corresponding Portfolio.
While certain policies apply to all Funds and Portfolios, generally each Fund and Portfolio has a different
investment objective and investment focus. As a result, the risks, opportunities and returns of investing in each Fund
or Portfolio will differ. Those investment policies specifically labeled as "fundamental" may not be changed without
shareholder approval. However, the investment objective of each Fund and Portfolio generally is not a fundamental policy
and may be changed by the Directors of the Company or Trustees of the Trust without shareholder approval. Similarly,
most of the Funds' and Portfolios' investment policies and limitations are not fundamental policies.
There can be no assurance that the investment objective of any Fund or Portfolio will be achieved. Risks
relating to certain types of securities and instruments in which the Funds and Portfolios may invest are described in
this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
If approved by the Directors of the Company, the Company may add more Funds and may cease to offer any existing
Funds in the future.
ASAF FOUNDERS INTERNATIONAL SMALL CAPITALIZATION FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
To achieve its objective, the Fund normally invests primarily in securities issued by foreign companies that have
market capitalizations of $1.5 billion (this maximum may be revised from time to time based on stock market valuations
and industry standards) or less. These securities may represent companies in both established and emerging economies
throughout the world.
At least 65% of the Fund's total assets normally will be invested in foreign securities representing a minimum of
three countries. The Fund may invest in larger foreign companies or in U.S.-based companies if, in the Sub-advisor's
opinion, they represent better prospects for capital growth. The Sub-advisor looks for companies whose fundamental
strengths indicate potential for growth in earnings per share. The Sub-advisor generally takes a "bottom up" approach to
building the Fund, which means that the Sub-advisor will search for individual companies that demonstrate the best
potential for significant earnings growth, rather than choose investments based on broader economic characteristics of
countries or industries.
As discussed below, foreign securities are generally considered to involve more risk than those of U.S.
companies, and securities of smaller companies are generally considered to be riskier than those of larger companies.
Therefore, because the Fund's investment focus is on securities of small and medium-sized foreign companies, the risk of
loss and share price fluctuation of this Fund likely will be high relative to most of the other Funds of the Company and
popular market averages.
Foreign Securities. For purposes of the Fund, the term "foreign securities" refers to securities of issuers,
that, in the judgment of the Sub-advisor, have their principal business activities outside of the United States, and may
include American Depositary Receipts. The determination of whether an issuer's principal activities are outside of the
United States will be based on the location of the issuer's assets, personnel, sales, and earnings (specifically on
whether more than 50% of the issuer's assets are located, or more than 50% of the issuer's gross income is earned,
outside of the United States) or on whether the issuer's sole or principal stock exchange listing is outside of the
United States. The foreign securities in which the Fund will invest typically will be traded on the applicable country's
principal stock exchange but may also be traded on regional exchanges or over-the-counter.
Investments in foreign securities involve different risks than U.S. investments, including fluctuations in
currency exchange rates, unstable political and economic structures, reduced availability of information, and lack of
uniform financial reporting and regulatory practices such as those that apply to U.S. issuers. Foreign investments of
the Fund may include securities issued by companies located in developing countries. Developing countries are subject to
more economic, political and business risk than major industrialized nations, and the securities they issue are expected
to be more volatile and more uncertain as to payment of interest and principal. The Fund is permitted to use forward
foreign currency contracts in connection with the purchase or sale of a specific security or for hedging purposes.
For an additional discussion of the risks involved in foreign securities, see this Prospectus under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods."
Small and Medium-Sized Companies. Investments in small and medium-sized companies involve greater risk than is
customarily associated with more established companies. Generally, small and medium-sized companies are still in the
developing stages of their life cycles and are attempting to achieve rapid growth in both sales and earnings. While
these companies often have growth rates that exceed those of large companies, smaller companies often have limited
operating histories, product lines, markets, or financial resources, and they may be dependent upon one-person
management. These companies may be subject to intense competition from larger entities, and the securities of such
companies may have a limited market and may be subject to more abrupt or erratic movements in price.
Other Investments:
In addition to investing in common stocks, the Fund may invest in other types of securities and may engage in
certain investment practices. The Fund may invest in convertible securities, preferred stocks, bonds, debentures, and
other corporate obligations when the Sub-advisor believes that these investments offer opportunities for capital
appreciation. Current income will not be a substantial factor in the selection of these securities.
The Fund will only invest in bonds, debentures, and corporate obligations (other than convertible securities and
preferred stock) rated investment grade at the time of purchase. Convertible securities and preferred stocks purchased
by the Fund may be rated in medium and lower categories by Moody's or S&P, but will not be rated lower than B. The Fund
may also invest in unrated convertible securities and preferred stocks if the Sub-advisor believes that the financial
condition of the issuer or the terms of the securities limits risk to a level similar to that of securities rated B or
above.
In addition, the Fund may enter into stock index, interest rate and foreign currency futures contracts (or
options thereon) for hedging purposes. The Fund may write covered call options on any or all of its portfolio securities
as the Sub-advisor considers appropriate. The Fund also may purchase options on securities and stock indices for hedging
purposes. The Fund may buy and sell options on foreign currencies for hedging purposes.
For more information on these securities and investment practices and their risks, see this Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Temporary Investments. Up to 100% of the assets of the Fund may be invested temporarily in cash or cash
equivalents if the Sub-advisor determines that it would be appropriate for purposes of increasing liquidity or preserving
capital in light of market or economic conditions. Temporary investments may include U.S. government obligations,
commercial paper, bank obligations, and repurchase agreements. While the Fund is in a defensive position, the
opportunity to achieve its investment objective of capital growth will be limited.
ASAF AIM INTERNATIONAL EQUITY FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek long-term capital growth by investing in a
diversified portfolio of international equity securities the issuers of which are considered to have strong earnings
momentum.
Principal Investment Objectives and Risks:
The Fund seeks to meet its investment objective by investing, normally, at least 70% of its total assets in
marketable equity securities of foreign companies that are listed on a recognized foreign securities exchange or traded
in a foreign over-the-counter market. The Fund will normally invest in a diversified portfolio that includes companies
located in at least four countries outside the United States, emphasizing investment in companies in the developed
countries of Western Europe and the Pacific Basin. The Sub-advisor does not intend to invest more than 20% of the Fund's
total assets in companies located in developing countries (i.e., those that are in the initial stages of their industrial
cycles).
The Sub-advisor focuses on companies that have experienced above-average, long-term growth in earnings and have
strong prospects for future growth. In selecting countries in which the Fund will invest, the Sub-advisor also considers
such factors as the prospect for relative economic growth among countries or regions, economic or political conditions,
currency exchange fluctuations, tax considerations and the liquidity of a particular security. The Sub-advisor considers
whether to sell a particular security when any of those factors materially changes.
As with any equity fund, the fundamental risk associated with the Fund is the risk that the value of the
securities it holds might decrease. The prices of equity securities change in response to many factors, including the
historical and prospective earnings of the issuer, the value of its assets, general economic conditions, interest rates,
investor perceptions and market liquidity.
As a fund that invests primarily in the securities of foreign issuers, the risk and degree of share price
fluctuation of the Fund may be greater than a fund investing primarily in domestic securities. The risks of investing in
foreign securities, which are described in more detail below under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods," include
political and economic conditions and instability in foreign countries, less available information about foreign
companies, lack of strict financial and accounting controls and standards, less liquid and more volatile securities
markets, and fluctuations in currency exchange rates. While the Fund has authority to engage in transactions intended to
hedge its exposure to fluctuations in foreign currencies, it does not currently intend to do so. To the extent the Fund
invests in securities of issuers in developing countries, the Fund may be subject to even greater levels of risk and
share price fluctuation. Transaction costs are often higher in developing countries and there may be delays in
settlement of transactions.
Other Investments:
The Fund may invest up to 20% of its total assets in debt or preferred equity securities exchangeable for or
convertible into marketable equity securities of foreign companies. In addition, the Fund may regularly invest up to 20%
of its total assets in high-grade short-term debt securities, including U.S. Government obligations, investment grade
corporate bonds or taxable municipal securities, whether denominated in U.S. dollars or foreign currencies.
The Fund may use futures contracts and related options, options on securities, securities indices and currencies
to attempt to hedge against the overall level of risk normally associated with the Fund's investments. The Fund also may
from time to time make short sales of securities "against the box."
Additional information about convertible securities, options, futures contracts, short sales and other
investments and investment practices of the Fund is included in this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and
Investment Methods."
Temporary Investments. In addition to regularly investing up to 20% of its total assets in short-term debt
securities as noted above, the Fund may hold all or a significant portion of its assets in cash, money market
instruments, bonds or other debt securities in anticipation of or in response to adverse market conditions or for cash
management purposes. While the Fund is in such a defensive position, the opportunity to achieve its investment objective
of capital growth may be limited.
ASAF JANUS OVERSEAS GROWTH FUND*:
* The Fund was closed to new investors effective March 1, 2000. Shareholders of the Fund as of the close of business on
February 29, 2000 may continue to make additional purchases and to reinvest dividends and capital gains in existing
accounts. Any participant in a participant-directed defined contribution plan that held Fund shares in a plan-level
omnibus account as of January 18, 2000 can continue to allocate amounts to the Fund, whether or not the participant had
amounts allocated to the Fund as of that date.
Investors may be required to demonstrate eligibility to purchase shares of the Fund before an investment is accepted.
The Company may resume sales of shares of the Fund to new investors at some future date, but it has no present intention
to do so.
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek long-term growth of capital.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund pursues its objective primarily through investments in common stocks of issuers located outside the
United States. The Fund has the flexibility to invest on a worldwide basis in companies and organizations of any size,
regardless of country of organization or place of principal business activity.
The Fund normally invests at least 65% of its total assets in securities of issuers from at least five different
countries, excluding the United States. Although the Fund intends to invest substantially all of its assets in issuers
located outside the United States, it may at times invest in U.S. issuers and it may at times invest all of its assets in
fewer than five countries or even a single country.
The Fund invests primarily in stocks selected for their growth potential. The Sub-advisor generally takes a
"bottom up" approach to choosing investments for the Fund. In other words, the Sub-advisor seeks to identify individual
companies with earnings growth potential that may not be recognized by the market at large, regardless of where the
companies are organized or where they primarily conduct business. Although themes may emerge in the Fund, securities are
generally selected without regard to any defined allocation among countries, geographic regions or industry sectors, or
other similar selection procedure. Current income is not a significant factor in choosing investments, and any income
realized by the Fund will be incidental to its objective.
As with any common stock fund, the fundamental risk associated with the Fund is the risk that the value of the
stocks it holds might decrease. Stock values may fluctuate in response to the activities of an individual company or in
response to general market and/or economic conditions. As a fund that invests primarily in the securities of foreign
issuers, the risk associated with the Fund may be greater than a fund investing primarily in domestic securities. For a
further discussion of the risks involved in investing in foreign securities, see this Prospectus under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods." In addition, the fund may invest to some degree in smaller or newer issuers, which are
more likely to realize substantial growth as well as suffer significant losses than larger or more established issuers.
The Fund generally intends to purchase securities for long-term investment rather than short-term gains.
However, short-term transactions may occur as the result of liquidity needs, securities having reached a desired price or
yield, anticipated changes in interest rates or the credit standing of an issuer, or by reason of economic or other
developments not foreseen at the time the investment was made. To a limited extent, the Fund may purchase securities in
anticipation of relatively short-term price gains. The Fund may also sell one security and simultaneously purchase the
same or a comparable security to take advantage of short-term differentials in bond yields or securities prices.
Special Situations. The Fund may invest in "special situations" from time to time. A special situation arises
when, in the opinion of the Sub-advisor, the securities of a particular issuer will be recognized and increase in value
due to a specific development with respect to that issuer. Developments creating a special situation might include a new
product or process, a technological breakthrough, a management change or other extraordinary corporate event, or
differences in market supply of and demand for the security. Investment in special situations may carry an additional
risk of loss in the event that the anticipated development does not occur or does not attract the expected attention.
Other Investments:
The Fund may invest to a lesser degree in types of securities other than common stocks, including preferred
stocks, warrants, convertible securities and debt securities. The Fund is subject to the following percentage limitations
on investing in certain types of debt securities:
-- 35% of its assets in bonds rated below investment grade by the primary rating agencies ("junk" bonds).
-- 25% of its assets in mortgage- and asset-backed securities.
-- 10% of its assets in zero coupon, pay-in-kind and step coupon securities (securities that do not, or may not
under certain circumstances, make regular interest payments).
The Fund may make short sales "against the box." In addition, the Fund may invest in the following types of securities
and engage in the following investment techniques:
Futures, Options and Other Derivative Instruments. The Fund may enter into futures contracts on securities,
financial indices and foreign currencies and options on such contracts and may invest in options on securities, financial
indices and foreign currencies and interest rate swaps and swap-related products (collectively "derivative
instruments"). The Fund intends to use most derivative instruments primarily to hedge the value of its portfolio against
potential adverse movements in securities prices, foreign currency markets or interest rates. To a limited extent, the
Fund may also use derivative instruments for non-hedging purposes such as seeking to increase income. The Fund may also
use currency hedging techniques, including forward currency exchange contracts, to manage exchange rate risk with respect
to investments exposed to foreign currency fluctuations.
Index/structured Securities. The Fund may invest in indexed/structured securities, which typically are short- to
intermediate-term debt securities whose value at maturity or interest rate is linked to currencies, interest rates,
equity securities, indices, commodity prices or other financial indicators. Such securities may offer growth potential
because of anticipated changes in interest rates, credit standing, currency relationships or other factors
For more information on the types of securities and instruments other than common stocks in which the Portfolio
may invest and their risks, see this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods" and the Company's SAI
under "Investment Programs of the Funds."
Temporary Investments. When the Sub-advisor believes that market conditions are not favorable for profitable
investing or when the Sub-advisor is otherwise unable to locate favorable investment opportunities, the Fund's
investments may be hedged to a greater degree and/or its cash or similar investments may increase. In other words, the
Fund does not always stay fully invested in stocks and bonds. The Fund's cash and similar investments may include
high-grade commercial paper, certificates of deposit, repurchase agreements and money market funds managed by the
Sub-advisor. While the Fund is in a defensive position, the opportunity to achieve its investment objective of long-term
growth of capital will be limited.
ASAF AMERICAN CENTURY INTERNATIONAL GROWTH FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund (formerly, the ASAF T. Rowe Price International Equity Fund)
is to seek capital growth.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund will seek to achieve its investment objective by investing in its corresponding Portfolio, which in turn
will invest primarily in equity securities of international companies that the Sub-advisor believes will increase in
value over time. The Sub-advisor uses a growth investment strategy it developed that looks for companies with earnings
and revenue growth. Ideally, the Sub-advisor looks for companies whose earnings and revenues are not only growing, but
are growing at an accelerating pace. Accelerating growth is shown, for example, by growth that is faster this quarter
than last or faster this year than the year before. For purposes of the Portfolio, equity securities include common
stocks, preferred stocks and convertible securities.
The Sub-advisor tracks financial information for thousands of companies to research and selects the stocks it
believes will be able to sustain accelerating growth. This strategy is based on the premise that, over the long term,
the stocks of companies with accelerating earnings and revenues have a greater-than-average chance to increase in value.
The Sub-advisor recognizes that, in addition to locating strong companies with accelerating earnings, the
allocation of assets among different countries and regions also is an important factor in managing an international
portfolio. For this reason, the Sub-advisor will consider a number of other factors in making investment selections,
including the prospects for relative economic growth among countries or regions, economic and political conditions,
expected inflation rates, currency exchange fluctuations and tax considerations. Under normal conditions, the Portfolio
will invest at least 65% of its assets in equity securities of issuers from at least three countries outside of the
United States. In order to maintain investment flexibility, the Portfolio has not otherwise established geographic
requirements for asset distribution.
While the Portfolio's focus will be on issuers in developed markets, the Sub-advisor expects to invest to some
degree in issuers in developing countries. The Portfolio may make foreign investments either directly in foreign
securities, or indirectly by purchasing depositary receipts. Securities purchased in foreign markets may either be
traded on foreign securities exchanges or in the over-the-counter markets.
As with all stocks, the value of the stocks held by the Portfolio can decrease as well as increase. As a fund
investing primarily in equity securities of foreign issuers, the Portfolio (and, therefore, the Fund) may be subject to a
level of risk and share price fluctuation higher than most funds that invest primarily in domestic equities. Foreign
companies may be subject to greater economic risks than domestic companies, and foreign securities are subject to certain
risks relating to political, regulatory and market structures and events that domestic securities are not subject to. To
the extent the Portfolio invests in securities of issuers in developing countries, the Portfolio may be subject to even
greater levels of risk and share price fluctuation.
Other Investments:
Securities of U.S. issuers may be included in the Portfolio from time to time. The Portfolio also may invest in
bonds, notes and debt securities of companies and obligations of domestic or foreign governments and their agencies. The
Portfolio will limit its purchases of debt securities to investment grade obligations. The Portfolio may enter into
non-leveraged stock index futures contracts and may make short sales "against the box."
Derivative Securities. The Portfolio may invest in derivative securities. Certain of these derivative
securities may be described as "index/structured" securities, which are securities whose value or performance is linked
to other equity securities (as in the case of depositary receipts), currencies, interest rates, securities indices or
other financial indicators ("reference indices"). The Portfolio may not invest in a derivative security unless the
reference index or the instrument to which it relates is an eligible investment for the Portfolio. For example, a
security whose underlying value is linked to the price of oil would not be a permissible investment because the Portfolio
may not invest in oil and gas leases or futures. The Portfolio may make short sales "against the box."
Forward Currency Exchange Contracts. As a fund investing primarily in foreign securities, the value of the
Portfolio will be affected by changes in the exchange rates between foreign currencies and the U.S. dollar. To protect
against adverse movements in exchange rates, the Portfolio may, for hedging purposes only, enter into forward foreign
currency exchange contracts. The Portfolio may enter into a forward contract to "lock-in" an exchange rate for a
specific purchase or sale of a security. Less frequently, the Portfolio may enter into a forward contract to seek to
protect its holdings in a particular currency from a decline in that currency. Predicting the relative future values of
currencies is very difficult, and there is no assurance that any attempt to reduce the risk of adverse currency movements
through the use of forward contracts will be successful.
Indirect Foreign Investments. The Portfolio may invest up to 10% of its assets in certain foreign countries
indirectly through investment funds and registered investment companies that invest in those countries. If the Portfolio
invests in investment companies, it will bear its proportionate share of the costs incurred by such companies, including
any investment advisory fees.
Additional information about the securities that the Portfolio may invest in and their risks is included below
under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Temporary Investments. Under exceptional market or economic conditions, the Portfolio may temporarily invest all
or a substantial portion of its assets in cash or investment-grade short-term securities. While the Portfolio is in a
defensive position, the ability to achieve its investment objective of capital growth may be limited.
ASAF JANUS SMALL-CAP GROWTH FUND*:
* The Fund was closed to new investors effective January 19, 2000. Shareholders of the Fund as of the close of business
on January 18, 2000 may continue to make additional purchases and to reinvest dividends and capital gains in existing
accounts. Any participant in a participant-directed defined contribution plan that held Fund shares in a plan-level
omnibus account as of January 18, 2000 can continue to allocate amounts to the Fund, whether or not the participant had
amounts allocated to the Fund as of that date.
Investors may be required to demonstrate eligibility to purchase shares of the Fund before an investment is accepted.
The Company may resume sales of shares of the Fund to new investors at some future date, but it has no present intention
to do so.
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund pursues its objective by normally investing at least 65% of its total assets in the common stocks of
small-sized companies. For purposes of the Fund, small-sized companies are those that have market capitalizations of
less than $1.5 billion or annual gross revenues of less than $500 million. To a lesser extent, the Fund may also invest
in stocks of larger companies with potential for capital appreciation.
The Sub-advisor generally takes a "bottom up" approach to building the Fund. In other words, it seeks to
identify individual companies with earnings growth potential that may not be recognized by the market at large. Although
themes may emerge in the Fund, securities are generally selected without regard to any defined industry sector or other
similar selection procedure. Current income is not a significant factor in choosing investments.
Because the Fund invests primarily in common stocks, the fundamental risk of investing in the Fund is that the
value of the stocks it holds might decrease. Stock values may fluctuate in response to the activities of an individual
company or in response to general market or economic conditions. As a Fund that invests primarily in smaller or newer
issuers, the Fund may be subject to greater risk of loss and share price fluctuation than funds investing primarily in
larger or more established issuers. Smaller companies are more likely to realize substantial growth as well as suffer
significant losses than larger issuers. Smaller companies may lack depth of management, they may be unable to generate
funds necessary for growth or potential development internally or to generate such funds through external financing on
favorable terms, or they may be developing or marketing products or services for which there are not yet, and may never
be, established markets. In addition, such companies may be subject to intense competition from larger competitors, and
may have more limited trading markets than the markets for securities of larger issuers.
While the Sub-advisor tries to reduce the risk of the Fund by diversifying its assets among issuers (so that the
effect of any single holding is reduced), and by not concentrating its assets in any particular industry, there is no
assurance that these effort will be successful in reducing the risks to which the Fund is subject.
The Fund generally intends to purchase securities for long-term investment rather than short-term gains.
However, short-term transactions may occur as the result of liquidity needs, securities having reached a desired price or
yield, anticipated changes in interest rates or the credit standing of an issuer, or by reason of economic or other
developments not foreseen at the time the investment was made. To a limited extent, the Fund may purchase securities in
anticipation of relatively short-term price gains. The Fund may also sell one security and simultaneously purchase the
same or a comparable security to take advantage of short-term differentials in bond yields or securities prices.
Special Situations. The Fund may invest in "special situations" from time to time. A special situation arises
when, in the opinion of the Sub-advisor, the securities of a particular issuer will be recognized and increase in value
due to a specific development with respect to that issuer. Developments creating a special situation might include a new
product or process, a technological breakthrough, a management change or other extraordinary corporate event, or
differences in market supply of and demand for the security. Investment in special situations may carry an additional
risk of loss in the event that the anticipated development does not occur or does not attract the expected attention.
Other Investments:
The Fund may invest to a lesser degree in types of securities other than common stocks, including preferred
stocks, warrants, convertible securities and debt securities. The Fund is subject to the following percentage
limitations on investing in certain types of debt securities:
-- 35% of its assets in bonds rated below investment grade by the primary rating agencies ("junk" bonds).
-- 25% of its assets in mortgage- and asset-backed securities.
-- 10% of its assets in zero coupon, pay-in-kind and step coupon securities (securities that do not, or may not
under certain circumstances, make regular interest payments).
The Fund may make short sales "against the box." In addition, the Fund may invest in the following types of securities
and engage in the following investment techniques:
Index/structured Securities. The Fund may invest in indexed/structured securities, which typically are short- to
intermediate-term debt securities whose value at maturity or interest rate is linked to currencies, interest rates,
equity securities, indices, commodity prices or other financial indicators. Such securities may offer growth potential
because of anticipated changes in interest rates, credit standing, currency relationships or other factors.
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest without limit in foreign equity and debt securities. The Fund may
invest directly in foreign securities denominated in foreign currencies, or may invest through depositary receipts or
passive foreign investment companies. Generally, the same criteria are used to select foreign securities as domestic
securities. The Sub-advisor seeks companies that meet these criteria regardless of country of organization or principal
business activity. However, certain factors such as expected inflation and currency exchange rates, government policies
affecting businesses, and a country's prospects for economic growth may warrant consideration in selecting foreign
securities.
Futures, Options and Other Derivative Instruments. The Fund may enter into futures contracts on securities,
financial indices and foreign currencies and options on such contracts, and may invest in options on securities,
financial indices and foreign currencies, forward contracts and interest rate swaps and swap-related products
(collectively "derivative instruments"). The Fund intends to use most derivative instruments primarily to hedge the
value of its portfolio against potential adverse movements in securities prices, currency exchange rates or interest
rates. To a limited extent, the Fund may also use derivative instruments for non-hedging purposes such as seeking to
increase income.
For more information on the types of securities other than common stocks in which the Fund may invest, see this
Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods" and the Company's SAI under "Investment Programs for the
Funds."
Temporary Investments. When the Sub-advisor believes that market conditions are not favorable for profitable
investing or when the Sub-advisor is otherwise unable to locate favorable investment opportunities, the Fund's
investments may be hedged to a greater degree and/or its cash or similar investments may increase. In other words, the
Fund does not always stay fully invested in stocks and bonds. The Fund's cash and similar investments may include
high-grade commercial paper, certificates of deposit, repurchase agreements and money market funds managed by the
Sub-advisor. While the Fund is in a defensive position, the opportunity to achieve its investment objective of capital
growth will be limited.
ASAF SCUDDER SMALL-CAP GROWTH FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek maximum growth of investors' capital from a
portfolio primarily of growth stocks of smaller companies.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
At least 65% of the Fund's total assets normally will be invested in the equity securities of smaller companies,
i.e., those having a market capitalization of $2 billion or less at the time of investment, many of which would be in the
early stages of their life cycle. Equity securities include common stocks and securities convertible into or
exchangeable for common stocks, including warrants and rights.
The Fund intends to invest primarily in stocks of companies whose earnings per share are expected by the
Sub-advisor to grow faster than the market average ("growth stocks"). Growth stocks tend to trade at higher price to
earnings (P/E) ratios than the general market, but the Sub-advisor believes that the potential for above average earnings
of the stocks in which the Fund invests more than justifies their price.
In managing the Fund, the Sub-advisor emphasizes stock selection and fundamental research. The Sub-advisor
considers a number of factors in determining whether to invest in a growth stock, including return on equity and earnings
growth rate, low level of debt, strong balance sheet, good management and industry leadership. Other factors are
patterns of increasing sales growth, the development of new or improved products or services, favorable outlooks for
growth in the industry, the probability of increased operating efficiencies, emphasis on research and development,
cyclical conditions, or other signs that a company may grow rapidly.
The Fund seeks attractive areas for investment that arise from factors such as technological advances, new
marketing methods, and changes in the economy and population. Currently, the Sub-advisor believes that such investment
opportunities may be found among:
o companies engaged in high technology fields such as electronics, medical technology and computer software and
specialty retailing;
o companies whose earnings outlooks have improved as the result of changes in the economy, acquisitions, mergers,
new management, changes in corporate strategy or product innovation;
o companies supplying new or rapidly growing services to consumers and businesses in such fields as automation,
data processing, communications, and marketing and finance; and
o companies that have innovative concepts or ideas.
In the selection of investments, long-term capital appreciation will take precedence over short range market
fluctuations. However, the Fund may occasionally make investments for short-term capital appreciation. Current income
will not be a significant factor in selecting investments.
Like all common stocks, the market values of the common stocks held by the Fund can fluctuate significantly,
reflecting the business performance of the issuing company, investor perception or general economic or financial market
movements. Because of the Fund's focus on the stocks of smaller growth companies, investment in the Fund may involve
substantially greater than average share price fluctuation and investment risk. A fund focusing on growth stocks will
generally involve greater risk and share price fluctuation than a fund investing primarily in value stocks.
In addition, investments in securities of smaller companies are generally considered to offer greater opportunity
for appreciation and to involve greater risk of depreciation than securities of larger companies. Smaller companies
often have limited product lines, markets or financial resources, and they may be dependent upon one or a few key people
for management. Because the securities of small-cap companies are not as broadly traded as those of larger companies,
they are often subject to wider and more abrupt fluctuations in market price. Additional reasons for the greater price
fluctuations of these securities include the less certain growth prospects of smaller firms and the greater sensitivity
of small companies to changing economic conditions.
Other Investments:
In addition to investing in common stocks, the Fund may also invest to a limited degree in preferred stocks and
debt securities when they are believed by the Sub-advisor to offer opportunities for capital growth. Other types of
securities in which the Fund may invest include:
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest in securities of foreign issuers in the form of depositary receipts or
that are denominated in U.S. dollars. Foreign securities in which the Fund may invest include any type of security
consistent with its investment objective and policies. The prices of foreign securities may be more volatile than those
of domestic securities.
Options, Financial Futures and Other Derivatives. The Fund may deal in options on securities and securities
indices, which options may be listed for trading on a national securities exchange or traded over-the-counter. Options
transactions may be used to pursue the Fund's investment objective and also to hedge against currency and market risks,
but are not intended for speculation. The Fund may engage in financial futures transactions on commodities exchanges or
boards of trade in an attempt to hedge against market risks.
In addition to options and financial futures, the Fund may invest in a broad array of other "derivative"
instruments in an effort to manage investment risk, to increase or decrease exposure to an asset class or benchmark (as a
hedge or to enhance return), or to create an investment position indirectly. The types of derivatives and techniques
used by the Fund may change over time as new derivatives and strategies are developed or as regulatory changes occur.
Additional information about the other investments that the Fund may make and their risks is included below under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Temporary Investments. When a defensive position is deemed advisable because of prevailing market conditions,
the Fund may invest without limit in high grade debt securities, commercial paper, U.S. Government securities or cash or
cash equivalents, including repurchase agreements. While the Fund is in a defensive position, the opportunity to achieve
its investment objective of maximum capital growth will be limited.
ASAF GABELLI SMALL-CAP VALUE FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund (formerly, the ASAF T. Rowe Price Small Company Value Fund)
is to provide long-term capital growth by investing primarily in small-capitalization stocks that appear to be undervalued.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund will invest at least 65% of its total assets in stocks and equity-related securities of small companies
($1 billion or less in market capitalization). Reflecting a value approach to investing, the Fund will seek the stocks
of companies whose current stock prices do not appear to adequately reflect their underlying value as measured by assets,
earnings, cash flow or business franchises. The Sub-advisor's research team seeks to identify companies that appear to
be undervalued by various measures, and may be temporarily out of favor, but have good prospects for capital
appreciation. In selecting investments, the Sub-advisor generally looks to the following:
(1) Low price/earnings, price/book value or price/cash flow ratios relative to the company's peers.
(2) Low stock price relative to a company's underlying asset values.
(3) A sound balance sheet and other positive financial characteristics.
The Sub-advisor then determines whether there is an emerging catalyst that will focus investor attention on the
underlying assets of the company, such as takeover efforts, a change in management, or a plan to improve the business
through restructuring or other means.
The Fund may sell securities for a variety of reasons, such as to secure gains, limit losses or re-deploy assets
into more promising opportunities. The Fund will not sell a stock just because the company has grown to a market
capitalization of more than $1 billion, and it may on occasion purchase companies with a market cap above $1 billion.
As with all stock funds, the Fund's share price can fall because of weakness in the securities market as a whole,
in particular industries or in specific holdings. Investing in small companies involves greater risk of loss than is
customarily associated with more established companies. Stocks of small companies may be subject to more abrupt or
erratic price movements than larger company stocks. Small companies often have limited product lines, markets, or
financial resources, and their management may lack depth and experience. While a value approach to investing is
generally considered to involve less risk than a growth approach, investing in value stocks carries the risks that the
market will not recognize the stock's intrinsic value for a long time or that a stock judged to be undervalued may
actually be appropriately priced.
Other Investments:
Although the Fund will invest primarily in U.S. common stocks, it may also purchase other types of securities,
for example, preferred stocks, convertible securities, warrants and bonds when considered consistent with the Fund's
investment objective and policies. The Fund may purchase preferred stock for capital appreciation where the issuer has
omitted, or is in danger of omitting, payment of the dividend on the stock. Debt securities would be purchased in
companies that meet the investment criteria for the Fund.
The Fund may invest up to 20% of its total assets in foreign securities, including American Depositary Receipts
and securities of companies in developing countries, and may enter into forward foreign currency exchange contracts.
(The Fund may invest in foreign cash items as described below in excess of this 20% limit.) The Fund may enter into
stock index or currency futures contracts (or options thereon) for hedging purposes or to provide an efficient means of
managing the Fund's exposure to the equity markets. The Fund may also write (sell) call and put options and purchase put
and call options on securities, financial indices, and currencies. The Fund may invest up to 10% of its total assets in
hybrid instruments, which combine the characteristics of futures, options and securities. For additional information
about these investments and their risks, see this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods" and the
Company's SAI under "Investment Programs of the Funds."
Temporary Investments. The Fund may establish and maintain cash reserves without limitation for temporary
defensive purposes. The Fund's reserves may be invested in high-quality domestic and foreign money market instruments,
including repurchase agreements and money market mutual funds managed by the Sub-advisor. Cash reserves also provide
flexibility in meeting redemptions and paying expenses. While the Fund is in a defensive position, the opportunity to
achieve its investment objective of long-term capital growth will be limited.
ASAF JANUS MID-CAP GROWTH FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek long-term growth of capital.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund pursues its objective by investing primarily in common stocks selected for their growth potential, and
normally invests at least 65% of its total assets in medium-sized companies. For purposes of the Fund, medium-sized
companies are those whose market capitalizations (measured at the time of investment) fall within the range of companies
in the Standard & Poor's MidCap 400 Index (the "S&P 400"). The market capitalizations within the S&P 400 will vary, but
as of December 31, 1999, they ranged from approximately $170 million to $37 billion. The Sub-advisor generally takes a
"bottom up" approach to choosing investments for the Fund. In other words, the Sub-advisor seeks to identify individual
companies with earnings growth potential that may not be recognized by the market at large. The Sub-advisor makes this
assessment by looking at companies one at a time, regardless of size, country of organization, place of principal
business activity, or other similar selection criteria.
Because the Fund may invest substantially all of its assets in common stocks, the main risk of investing in the
Fund is that the value of the stocks it holds might decrease. Stock values may fluctuate in response to the activities
of an individual company or in response to general market or economic conditions. As a fund that invests primarily in
mid-cap companies, the Fund's risk and share price fluctuation can be expected to be more than that of many funds
investing primarily in large-cap companies, but less than that of many funds investing primarily in small-cap companies.
In general, the smaller the company, the more likely it is to suffer significant losses as well as to realize substantial
growth. Smaller companies may lack depth of management, they may be unable to generate funds necessary for growth or
potential development, or they may be developing or marketing products or services for which there are not yet, and may
never be, established markets. In addition, such companies may be subject to intense competition from larger companies,
and may have more limited trading markets than the markets for securities of larger issuers.
The Fund generally intends to purchase securities for long-term investment rather than short-term gains.
However, short-term transactions may occur as the result of liquidity needs, securities having reached a desired price or
yield, anticipated changes in interest rates or the credit standing of an issuer, or by reason of economic or other
developments not foreseen at the time the investment was made. To a limited extent, the Fund may purchase securities in
anticipation of relatively short-term price gains. The Fund may also sell one security and simultaneously purchase the
same or a comparable security to take advantage of short-term differentials in bond yields or securities prices.
Non-Diversified Status. The Fund is classified as a "non-diversified" investment company under the Investment
Company Act of 1940 (the "1940 Act"). In other words, it may hold larger positions in a smaller number of securities
than a diversified fund. As a result, a single security's increase or decrease in value may have a greater impact on the
Fund's share price and total return. Because of this, the Fund's share price can be expected to fluctuate more than a
comparable diversified fund.
Special Situations. The Fund may invest in "special situations". A "special situation" arises when, in the
opinion of the Sub-advisor, the securities of a particular company will be recognized and appreciate in value due to a
specific development, such as a technological breakthrough, management change or new product at that company. Investment
in "special situations" carries an additional risk of loss in the event that the anticipated development does not occur
or does not attract the expected attention.
Other Investments:
Although the Sub-advisor expects to invest primarily in domestic and foreign equity securities, which may include
preferred stocks, common stocks, warrants and securities convertible into common or preferred stocks, the Fund may also
invest to a lesser degree in other types of securities, such as debt securities. The Fund is subject to the following
percentage limitations on investing in certain types of debt securities:
-- 35% of its assets in bonds rated below investment grade ("junk" bonds).
-- 10% of its assets in zero coupon, pay-in-kind and step coupon securities (securities that do not, or may not under
certain circumstances, make regular interest payments).
The Fund may make short sales "against the box." In addition, the Fund may invest in the following types of
securities and engage in the following investment techniques:
Index/structured Securities. The Fund may invest in indexed/structured securities, which typically are short- to
intermediate-term debt securities whose value at maturity or interest rate is linked to currencies, interest rates,
equity securities, indices, commodity prices or other financial indicators. Such securities may be positively or
negatively indexed (i.e., their value increase or decrease if the reference index or instrument appreciates).
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest up to 25% of its net assets in foreign securities denominated in foreign
currencies and not publicly traded in the United States. The Fund may also invest in foreign companies through
depository receipts or passive foreign investment companies. Generally, the same criteria are used to select foreign
securities as are used to select domestic securities. Foreign securities are generally selected on a stock-by-stock
basis without regard to any defined allocation among countries or geographic regions. However, certain factors such as
expected levels of inflation, government policies influencing business conditions, the outlook for currency
relationships, and prospects for economic growth among countries, regions or geographic areas may warrant greater
consideration in selecting foreign securities.
For more information on foreign securities and their risks, see this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and
Investment Methods."
Futures, Options and Other Derivative Instruments. The Fund may enter into futures contracts on securities,
financial indices and foreign currencies and options on such contracts and may invest in options on securities, financial
indices and foreign currencies, forward contracts and interest rate swaps and swap-related products (collectively
"derivative instruments"). The Fund may use derivative instruments to hedge or protect its portfolio from adverse
movements in securities prices, currency exchange rates, and interest rates. To a limited extent, the Fund may also use
derivative instruments for non-hedging purposes such as seeking to enhance return.
For more information on the types of securities other than common stocks in which the Fund may invest, see this
Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Temporary Investments. When the Sub-advisor believes that market conditions are unfavorable for profitable
investing, or when the Sub-advisor is otherwise unable to locate attractive investment opportunities, the Fund's cash or
similar investments may increase. In other words, the Fund does not always stay fully invested in stocks. Even when the
Fund is essentially fully invested, some residual amount of Fund assets will remain in cash and similar investments.
These investments may include commercial paper, certificates of deposit, repurchase agreements, short-term debt
obligations, and money market funds (including funds managed by the Sub-advisor). When the Fund's investments in cash or
similar investments increase, the opportunity to achieve its investment objective of long-term growth of capital may be
limited.
ASAF NEUBERGER BERMAN MID-CAP GROWTH FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
To pursue its objective, the Fund primarily invests in the common stocks of mid-cap companies. Companies with
equity market capitalizations from $300 million to $10 billion at the time of investment are considered mid-cap companies
for purposes of the Fund. The Company may revise this definition based on market conditions. Some of the Fund's assets
may be invested in the securities of large-cap companies as well as in small-cap companies. The Fund seeks to reduce
risk by diversifying among many companies and industries. The Fund does not seek to invest in securities that pay
dividends or interest, and any such income is incidental.
The Fund is normally managed using a growth-oriented investment approach. For growth investors, the aim is to
invest in companies that are already successful but could be even more so. The Sub-advisor looks for fast-growing
companies that are in new or rapidly evolving industries. Factors in identifying these companies may include
above-average growth of earnings or earnings that exceed analysts' expectations. The Sub-advisor may also look for other
characteristics in a company, such as financial strength, a strong position relative to competitors and a stock price
that is reasonable in light of its growth rate.
The Sub-advisor follows a disciplined selling strategy, and may sell a stock when it reaches a target price,
fails to perform as expected, or appears substantially less desirable than another stock.
As a Fund that invests primarily in the stocks of mid-cap companies, the Fund's risk and share price fluctuation
can be expected to be more than that of many funds investing primarily in large-cap companies, but less than that of many
funds investing primarily in small-cap companies. Mid-cap stocks may fluctuate more widely in price than the market as a
whole, may underperform other types of stocks when the market or the economy is not robust, or fall in price or be
difficult to sell during market downturns. In addition, the Fund's growth investment program will generally involve
greater risk and price fluctuation than funds that invest in more undervalued securities. Because the prices of growth
stocks tend to be based largely on future expectations, these stocks tend to be more sensitive than value stocks to bad
economic news and negative earnings surprises.
Other Investments:
Although equity securities are normally the Fund's primary investments, it may invest in preferred stocks and
convertible securities, as well as the types of securities described below. Additional information about these
investments and the special risk factors that apply to them is included in this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors
and Investment Methods."
Fixed Income Securities. The Fund may invest up to 35% of its total assets, measured at the time of investment,
in investment grade fixed income or debt securities. If the quality of any fixed income securities held by the Fund
deteriorates so that they are no longer investment grade, the Fund will sell such securities in an orderly manner so that
the Fund's holdings of such securities do not exceed 5% of its total assets.
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest up to 10% of the value of its total assets, measured at the time of
investment, in equity and debt securities that are denominated in foreign currencies. There is no limitation on the
percentage of the Fund's assets that may be invested in securities of foreign companies that are denominated in U.S.
dollars. In addition, the Fund may enter into foreign currency transactions, including forward foreign currency
contracts and options on foreign currencies, to manage currency risks, to facilitate transactions in foreign securities,
and to repatriate dividend or interest income received in foreign currencies.
Covered Call Options. The Fund may try to reduce the risk of securities price or exchange rate changes (hedge)
or generate income by writing (selling) covered call options against securities held in its portfolio, and may purchase
call options in related closing transactions.
Temporary Investments. When the Fund anticipates unusual market or other conditions, it may temporarily depart
from its objective of capital growth and invest substantially in high-quality short-term investments. This could help
the Fund avoid losses but may mean lost opportunities.
ASAF NEUBERGER BERMAN MID-CAP VALUE FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
To pursue its objective, the Fund primarily invests in the common stocks of mid-cap companies. Some of the
Fund's assets may be invested in the securities of large-cap companies as well as in small-cap companies. The Fund seeks
to reduce risk by diversifying among many companies and industries.
Under the Fund's value-oriented investment approach, the Sub-advisor looks for well-managed companies whose stock
prices are undervalued and that may rise in price when other investors realize their worth. Fund managers may identify
value stocks in several ways, including based on earnings, book value or other financial measures. Factors that the
Sub-advisor may use to identify these companies include strong fundamentals, such as a low price-to-earnings ratio,
consistent cash flow, and a sound track record through all phases of the market cycle.
The Sub-advisor may also look for other characteristics in a company, such as a strong position relative to
competitors, a high level of stock ownership among management, or a recent sharp decline in stock price that appears to
be the result of a short-term market overreaction to negative news.
The Sub-advisor generally considers selling a stock when it reaches a target price, when it fails to perform as
expected, or when other opportunities appear more attractive.
As a Fund that invests primarily in the stocks of mid-cap companies, the Fund's risk and share price fluctuation
can be expected to be more than that of many funds investing primarily in large-cap companies, but less than that of many
funds investing primarily in small-cap companies. Mid-cap stocks may fluctuate more widely in price than the market as a
whole, may underperform other types of stocks when the market or the economy is not robust, or fall in price or be
difficult to sell during market downturns. While value investing historically has involved less risk than investing in
growth companies, the stocks purchased by the Fund may remain undervalued during a short or extended period of time.
This may happen because value stocks as a category lose favor with investors compared to growth stocks, or because the
Sub-advisor failed to anticipate which stocks or industries would benefit from changing market or economic conditions.
Other Investments:
Although equity securities are normally the Fund's primary investments, it may invest in preferred stocks and
convertible securities, as well as the types of securities described below. Additional information about these
investments and the special risk factors that apply to them is included in this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors
and Investment Methods."
Fixed Income Securities. The Fund may invest up to 35% of its total assets, measured at the time of investment,
in fixed income or debt securities. The Fund may invest up to 15% of its total assets, measured at the time of
investment, in debt securities that are rated below investment grade or comparable unrated securities. There is no
minimum rating on the fixed income securities in which the Fund may invest.
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest up to 10% of the value of its total assets, measured at the time of
investment, in equity and debt securities that are denominated in foreign currencies. There is no limitation on the
percentage of the Fund's assets that may be invested in securities of foreign companies that are denominated in U.S.
dollars. In addition, the Fund may enter into foreign currency transactions, including forward foreign currency
contracts and options on foreign currencies, to manage currency risks, to facilitate transactions in foreign securities,
and to repatriate dividend or interest income received in foreign currencies.
Covered Call Options. The Fund may try to reduce the risk of securities price changes (hedge) or generate income
by writing (selling) covered call options against securities held in its portfolio, and may purchase call options in
related closing transactions. The value of securities against which options will be written will not exceed 10% of the
Fund's net assets.
Temporary Investments. When the Fund anticipates unusual market or other conditions, it may temporarily depart
from its objective of capital growth and invest substantially in high-quality short-term investments. This could help
the Fund avoid losses but may mean lost opportunities.
ASAF ALGER ALL-CAP GROWTH FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek long-term capital growth.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund invests primarily in equity securities, such as common or preferred stocks, that are listed on U.S.
exchanges or in the over-the-counter market. The Fund may invest in the equity securities of companies of all sizes, and
may emphasize either larger or smaller companies at a given time based on the Sub-advisor's assessment of particular
companies and market conditions.
The Fund invests primarily in growth stocks. The Sub-advisor believes that these stocks are those of two types
of companies:
High Unit Volume Growth Companies. These are vital, creative companies that offer goods or services to a rapidly
expanding marketplace. They include both established and emerging firms offering new or improved products, or firms
simply fulfilling an increased demand for an existing product line.
Positive Life Cycle Change Companies. These are companies experiencing a major change that is expected to
produce advantageous results. These changes may be as varied as new management, products or technologies, restructurings
or reorganizations, or mergers and acquisitions.
As with any fund investing primarily in equity securities, the value of the securities held by the Fund may
decline. These declines can be substantial. In addition, the growth stocks in which the Fund invests primarily tend to
fluctuate in price more than other types of stocks. Prices of growth stocks tend to be higher in relation to their
companies' earnings, and may be more sensitive to market, political and economic developments than other stocks. The
Fund's level of risk will vary based upon the size of the companies it invests in at a given time. To the extent that the
Fund emphasizes small-cap stocks, it will be subject to a level of risk higher than a fund investing primarily in more
conservative large-cap stocks.
Other Investments:
In addition to investing in common and preferred stocks, the Fund may invest in securities convertible into or
exchangeable for equity securities, including warrants and rights. The Fund may invest up to 20% of its total assets in
foreign securities. (American Depositary Receipts or other U.S. dollar denominated securities of foreign issuers are not
subject to the 20% limitation.)
The Fund may purchase put and call options and write (sell) put and covered call options on securities and
securities indices to increase gain or to hedge against the risk of unfavorable price movements. However, the
Sub-advisor does not currently intend to rely on these option strategies extensively, if at all. The Fund may purchase
and sell stock index futures contracts and options on stock index futures contracts. The Fund may sell securities "short
against the box."
An additional discussion of these types of investments and their risks is included in this Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Temporary Investments. The Fund may invest up to 100% of its assets in cash, commercial paper, high-grade bonds
or cash equivalents for temporary defensive reasons if the Sub-advisor believes that adverse market or other conditions
warrant. This is to attempt to protect the Fund from a temporary unacceptable risk of loss. However, while the Fund is
in a defensive position, the opportunity to achieve its investment objective of long-term capital growth will be limited.
ASAF GABELLI ALL-CAP VALUE FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth.
Principal Investment Strategies and Risks:
The Fund will primarily invest in readily marketable equity securities including common stocks, preferred stocks
and securities that may be converted at a later time into common stock. The Fund may invest in the securities of
companies of all sizes, and may emphasize either larger or smaller companies at a given time based on the Sub-advisor's
assessment of particular companies and market conditions.
In making stock selections, the Fund strives to earn a 10% real rate of return. The Fund focuses on companies that
appear underpriced relative to their private market value ("PMV"). PMV is the value that the Fund's Sub-advisor believes
informed investors would be willing to pay for a company. The Sub-advisor considers factors such as price, earnings
expectations, earnings and price histories, balance sheet characteristics and perceived management skills. The
Sub-advisor also considers changes in economic and political outlooks as well as individual corporate developments. The
Sub-advisor will sell any Fund investments that lose their perceived value relative to other investments.
Investments will be made based on the Sub-advisor's perception of their potential for capital growth. Current income may
also be considered. However, many of the common stocks the Fund will buy will not pay dividends.
As a fund that invests primarily in equity securities, the principal risk to which the Fund is subject is that
the value of the securities held by the Fund will decline. The value of equity securities will fluctuate due to many
factors, including the past and predicted earnings of the issuer, the quality of the issuer's management, general market
conditions, the forecasts for the issuer's industry and the value of the issuer's assets. While value investing
historically has involved less risk that investing in growth companies, the Fund is subject to the risks that the PMVs of
the stocks purchased by the Fund may never be realized by the market, or that the Sub-advisor may be incorrect in its
assessment of the PMVs.
In addition, the Fund's level of risk will vary based upon the size of the companies it invests in at a given
time. To the extent the Fund emphasizes small-cap stocks, it will be subject to a level of risk higher than a fund
investing primarily in more conservative "large-cap" stocks. The Fund may be subject to additional risks as a result of
its investments in foreign securities, including unfavorable foreign government actions, political instability, the
absence of accurate information about foreign issuers, and exposure to foreign currencies that may decline in value
relative to the U.S. dollar.
Other Investments:
The Fund may invest up to 25% of its total assets in securities of non-U.S. issuers. While the Fund does not intend to
do so to a significant degree, the Fund may enter into futures contracts and related options, and may purchase and sell
call and put options on securities and securities indices. The Fund also may invest in warrants to purchase securities,
and may engage in short sales "against the box".
Temporary Investments. When adverse market or economic conditions occur, the Fund may temporarily invest all or a
portion of its assets in defensive investments. Such investments include high grade debt securities, obligations of the
U.S. Government and its agencies and instrumentalities or short-term money market instruments. While the Fund is in a
defensive position, the opportunity to achieve its investment objective will be limited.
ASAF INVESCO TECHNOLOGY FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth by investing primarily in the
equity securities of companies engaged in technology-related industries.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund normally invests at least 80% of its total assets in the equity securities of companies engaged in the
technology-related industries. These industries include, but are not limited to, applied technology, biotechnology,
communications, computers, video, electronics, Internet, IT services and consulting, oceanography, office and factory
automation, networking, robotics, and video. A portion of the Fund's assets may be invested outside of this sector. To
determine whether a potential investment is doing business in the technology sector, a company must meet at least one of
the following tests:
o At least 50% of its gross income or its net sales must come from activities in the technology sector;
o At least 50% of its assets must be devoted to producing revenues from the technology sector; or
o Based on other available information, the Sub-advisor determines that its primary business is within the
technology sector
The Sub-advisor uses a bottom-up approach to create the Fund's investment portfolio, focusing on company
fundamentals and growth prospects when selecting securities. In general, the Fund emphasizes strongly managed companies
that the Sub-advisor believes will generate above-average growth rates for the next three to five years. The Sub-advisor
prefers markets and industries where leadership is in a few hands, and tends to avoid slower-growing markets or
industries.
A core portion of the Fund's portfolio is invested in market-leading technology companies that the Sub-advisor
believes will maintain or improve their market share regardless of overall economic conditions. These companies are
usually large, established firms that are leaders in their field and have a strategic advantage over many of their
competitors. The remainder of the Fund's portfolio consists of faster-growing, more volatile technology companies that
the Sub-advisor believes to be emerging leaders in their fields.
As with any fund investing primarily in equity securities, the Fund is subject to the risk that the equity
securities in which it invests will decline in value. Although the Fund's investments are diversified across the
technology sector, they are limited to a comparatively narrow segment of the economy. Therefore, the Fund is not as
diversified as most other mutual funds, and far less diversified than the broad securities market. This means that the
Fund's share price may fluctuate more rapidly and to a greater degree than other funds. In addition, many of the
products and services offered by the technology companies in which the Fund invests are subject to rapid obsolescence,
which may reduce the value of the securities of those companies. To the extent the Fund invests in smaller,
faster-growing technology companies, the Fund's level of risk and share price fluctuation may increase.
Other Investments:
In addition to investing in equity securities, the Fund may also invest in debt securities. The Fund may invest
up to 25% of its assets in securities of non-U.S. issuers. Securities of Canadian issuers and American Depositary
Receipts are not subject to this 25% limitation. Although the Fund may invest in futures contracts, options on specific
securities, stock indices and stock index futures, forward foreign currency exchange contracts, and other types of
derivative instruments (including swaps, caps, floors and collars), the Fund currently does not expect to do so to a
significant degree.
Temporary Investments. When securities markets or economic conditions are unfavorable or unsettled, the
Sub-advisor might try to protect the assets of the Fund by investing in high quality money market instruments, such as
short-term U.S. government obligations, commercial paper or repurchase agreements. The Fund has the right to invest up
to 100% of its assets in these securities, although it is unlikely to do so. While the fund is in a defensive position,
the opportunity to achieve its investment objective will be limited.
ASAF INVESCO HEALTH SCIENCES FUND
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek growth.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund invests primarily in the equity securities of companies that develop, produce or distribute products or
services related to health care. These companies include, but are not limited to, medical equipment or supplies,
pharmaceuticals, health care facilities, and applied research and development of new products or services. A portion of
the Fund's assets is not required to be invested in the sector. To determine whether a potential investment is truly
doing business in a particular sector, a company must meet at least one of the following tests:
o At least 50% of its gross income or its net sales must come from activities in the health sciences sector;
o At least 50% of its assets must be devoted to producing revenues from the health sciences sector; or
o Based on other available information, the Sub-advisor determines that its primary business is within the health
sciences sector.
The Fund is aggressively managed. It primarily invests in equity securities that the Sub-advisor believes will
rise in price faster than other securities, as well as options and other investments whose values are based upon the
values of equity securities.
The Sub-advisor uses a "bottom up" investment approach to create the Fund's investment portfolio, focusing on
company fundamentals and growth prospects when selecting securities. In general, the Fund emphasizes strongly managed
companies that the Sub-advisor believes will generate above-average growth rates for the next three to five years. The
Sub-advisor prefers markets and industries where leadership is in a few hands, and tends to avoid slower-growing markets
or industries.
The Fund targets strongly managed, innovative companies with new products. The Sub-advisor attempts to blend
well-established health care firms with faster-growing, more dynamic entities. Well-established health care companies
typically provide liquidity and earnings visibility for the investment portfolio and represent core holdings in the
Fund. The remainder of the portfolio consists of faster-growing, more dynamic health care companies, which have new
products or are increasing their market share of existing products. Many faster-growing health care companies have
limited operating histories and their potential profitability may be dependent on regulatory approval of their products,
which increases the volatility of these companies' securities prices.
Many of these activities are funded or subsidized by governments; withdrawal or curtailment of this support could
lower the profitability and market prices of such companies. Changes in government regulation could also have an adverse
impact. Continuing technological advances may mean rapid obsolescence of products and services.
The Fund's investments are diversified across the health sciences sector. However, because those investments are
limited to a comparatively narrow segment of the economy, the Fund's investments are not as diversified as investments of
most mutual funds, and far less diversified than the broad securities markets. This means that the Fund tends to be more
volatile than other mutual funds, and the values of its portfolio investments tend to go up and down more rapidly. As a
result, the value of a Fund share may rise or fall rapidly.
The Fund is subject to other principal risks such as potential conflicts, market, foreign securities, liquidity,
counterparty and lack of timely information risks.
Other Investments:
The Fund may also invest in American Depositary Receipts (ADRs) and repurchase agreements. The Fund may use
futures contracts and related options, options on securities, securities indices and currencies to attempt to hedge
against the overall level of risk normally associated with the Fund's investments. The Fund may invest up to 25% of
their respective assets in securities of non-U.S. issuers. Securities of Canadian issuers and ADRs are not subject to
this 25% limitation. For additional information about these investments and risks, see this Prospectus under "Certain
Risk Factors and Investment Methods" and the Company's SAI under "Investment Programs of the Funds."
Temporary Investments. When securities markets or economic conditions are unfavorable or unsettled, the
Sub-advisor might try to protect the assets of the Fund by investing in securities that are highly liquid such as high
quality money market instruments, like short-term U.S. government obligations, commercial paper or repurchase agreements,
even though that is not the normal investment strategy of the Fund. The Sub-advisor has the right to invest up to 100%
of the Fund's assets in these securities, although the Sub-advisor is unlikely to do so. Even though the securities
purchased for defensive purposes often are considered the equivalent of cash, they have their own risks. Investments
that are highly liquid or comparatively safe tend to offer lower returns. Therefore, the Fund's performance could be
comparatively lower if it concentrates in defensive holdings. While the fund is in a defensive position, the opportunity
to achieve its investment objective will be limited.
ASAF RYDEX MANAGED OTC FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to provide investment results that correlate to the
performance of a benchmark for securities that are traded in the over-the-counter market. The Fund's current benchmark
is the NASDAQ 100 Index.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund will pursue its objective by investing primarily in securities of companies included in the NASDAQ 100
Index (the "NASDAQ 100") and leveraged instruments, such as futures contracts and options, relating to the NASDAQ 100.
The NASDAQ 100 is a modified capitalization-weighted index composed of the equity securities of 100 of the largest
non-financial companies listed on the National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations System. The
Sub-advisor will attempt to consistently use leveraged instruments to increase the Fund's exposure to 125% of the NASDAQ
100. If the Sub-advisor achieves this goal, the value of the Fund's shares will tend to increase on a daily basis by
125% of the value of any increase in the NASDAQ 100. When the value of the NASDAQ 100 declines, the value of the Fund's
shares should also decrease on a daily basis by 125% of the value of any decrease in the Index (e.g., if the NASDAQ 100
goes down by 5%, the value of the Fund's shares should go down by 6.25% on that day).
The Sub-advisor uses quantitative analysis techniques to structure the Fund to obtain the highest correlation to
the NASDAQ 100, while remaining fully invested in all market environments. The Sub-advisor will monitor the Fund on an
ongoing basis, and make adjustments as necessary to minimize tracking error and to maximize liquidity.
As a fund that invests a substantial portion of its assets in stocks, the Fund is subject to the risks associated
with stock investments, and the Fund's share price therefore may fluctuate substantially. Because the Fund seeks to
provide investment results that magnify fluctuations in the NASDAQ 100, and will use leveraged instruments to help
achieve this correlation, the Fund will be subject to greater risk and share price fluctuation than a Fund that attempts
to match the performance of the Index. In addition, while it is anticipated that the Fund will invest mainly in the
securities of large companies, the Fund may be subject to a greater level of risk than the average large-cap fund based
upon the relatively volatile nature of the securities in which the Fund will invest. While it is not expected that the
performance of the Fund will deviate more than 10% from the Fund's goal of achieving results corresponding to 125% of the
return of the NASDAQ 100, factors such as Fund expenses, imperfect correlation between the Fund's investments and those
of the NASDAQ 100, rounding of share prices, changes to the benchmark, regulatory policies, and leverage, may affect the
Fund's ability to achieve this correlation. The magnitude of any tracking error may be affected by a higher portfolio
turnover rate.
Non-Diversified Status. The Fund is classified as a "non-diversified" investment company under the 1940 Act.
This means it may invest in the securities of a relatively small number of issuers. If the assets of the Fund are
invested in a limited number of issuers, a single security's increase or decrease in value may have a greater impact on
the Fund's share price and total return, and the Fund may be more susceptible to a single adverse economic or regulatory
occurrence. Because of this, the Fund's share price can be expected to fluctuate more than a comparable diversified fund.
Other Investments:
As noted above, the Fund may enter into futures and options transactions. Specifically, the Fund may purchase
call options and write (sell) put options on securities and securities indices, and may enter into stock index futures
contracts and related options. The Fund may use futures contracts and related options for bona fide hedging purposes to
offset changes in the value of securities held or expected to be acquired. They may also be used to gain or increase
exposure to a particular market or instrument, to create a synthetic money market position, and for certain other
tax-related purposes. The Fund will only enter into futures contracts traded on a national futures exchange or board of
trade. The Fund may also purchase U.S. Government securities.
For further information on these securities and investment practices and their risks, see this Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods" and the Company's SAI under "Investment Programs of the Funds."
ASAF ALLIANCE GROWTH FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund (formerly, the ASAF Oppenheimer Large-Cap Growth Fund) is to
seek long-term growth of capital by investing predominantly in the equity securities of a limited number of large,
carefully selected, high-quality U.S. companies that are judged likely to achieve superior earnings growth.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund normally invests at least 80% of its total assets in the equity securities of U.S. companies. A U.S.
company is a company that is organized under United States law, has its principal office in the United States and issues
equity securities that are traded principally in the United States. For purposes of the Fund, a non-U.S. company is a
company that (i) is organized outside the United States, (ii) has its principal place of business outside the United
States, and (iii) issues securities that are traded principally in foreign countries. Companies that do not fall within
this definition shall be deemed to be U.S. companies. Normally, about 40-60 companies will be represented in the Fund,
with the 25 companies most highly regarded by the Sub-advisor usually constituting approximately 70% of the Fund's net
assets. The Fund is thus atypical from many equity mutual funds in its focus on a relatively small number of intensively
researched companies.
The Sub-advisor's investment strategy for the Fund emphasizes stock selection. The Sub-advisor relies heavily
upon the fundamental analysis and research of its internal research staff, which generally follows a primary research
universe of more than 500 companies that have strong management, superior industry positions, excellent balance sheets
and superior earnings growth prospects. An emphasis is placed on identifying companies whose substantially above average
prospective earnings growth is not fully reflected in current market valuations.
In managing the Fund, the Sub-advisor seeks to utilize market volatility judiciously (assuming no change in
company fundamentals), striving to capitalize on apparently unwarranted price fluctuations, both by purchasing or
increasing positions on weakness and selling or reducing overpriced holdings. The Fund normally remains nearly fully
invested and does not take significant cash positions for market timing purposes. During market declines, while adding
to positions in favored stocks, the Fund becomes somewhat more aggressive, gradually reducing the number of companies
represented in its portfolio.
Conversely, in rising markets, while reducing or eliminating fully valued positions, the Fund becomes somewhat
more conservative, gradually increasing the number of companies represented in its portfolio. The Sub-advisor therefore
seeks to gain positive returns in good markets while providing some measure of protection in poor markets.
The Sub-advisor expects the average market capitalization of companies represented in the Fund normally to be in
the range, or in excess, of the average market capitalization of companies included in the S&P 500 Index.
Because the Fund invests primarily in stocks, the Fund is subject to the risks associated with stock investments,
and the Fund's share price therefore may fluctuate substantially. The Fund's share price will be affected by changes in
the stock markets generally, and factors specific to a company or an industry will affect the prices of particular stocks
held by the Fund (for example, poor earnings, loss of major customers, availability of basic resources or supplies, major
litigation against a company, or changes in governmental regulation affecting an industry). The Fund's focus on large,
more-established companies may mean that its level of risk is lower than a fund investing primarily in smaller
companies. Because the Fund invests in a smaller number of securities than many other funds, changes in the value of a
single security may have a more significant effect, either negative or positive, on the Fund's share price.
Other Investments:
In addition to investing in equity securities, the Fund also may:
-- invest up to 20% of its net assets in convertible securities;
-- invest up to 5% of its net assets in rights or warrants;
-- invest up to 15% of its total assets in foreign securities;
-- purchase and sell exchange-traded index options and stock index futures contracts; and
-- write covered exchange-traded call options on its securities up to 15% of its total assets, and purchase
exchange-traded call and put options on common stocks up to, for all options, 10% of its total assets.
For additional information on the types of investments other than common stocks in which the Fund may invest, see
this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Temporary Investments. Although it does not expect to do so ordinarily, when business or financial conditions
warrant the Fund may assume a temporary defensive position and invest in high-grade, short-term, fixed-income securities
(which may include U.S. Government securities) or hold its assets in cash. While the Fund is in a defensive position,
the opportunity to achieve its investment objective will be limited.
ASAF MARSICO CAPITAL GROWTH FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth. This is a fundamental objective
of the Fund. Income is not an investment objective and any income realized on the Fund's investments, therefore, will be
incidental to the Fund's objective.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund will pursue its objective by investing primarily in common stocks. The Sub-advisor expects that the
majority of the Fund's assets will be invested in the common stocks of larger, more established companies.
In selecting investments for the Fund, the Sub-advisor uses an approach that combines "top down" economic
analysis with "bottom up" stock selection. The "top down" approach takes into consideration such macro-economic factors
as interest rates, inflation, the regulatory environment, and the global competitive landscape. In addition, the
Sub-advisor examines such factors as the most attractive global investment opportunities, industry consolidation, and the
sustainability of economic trends. As a result of this "top down" analysis, the Sub-advisor identifies sectors,
industries and companies that should benefit from the trends the Sub-advisor has observed.
The Sub-advisor then looks for individual companies with earnings growth potential that may not be recognized by
the market at large. In determining whether a particular company is appropriate for investment by the Fund, the
Sub-advisor focuses on a number of different attributes, including the company's specific market expertise or dominance,
its franchise durability and pricing power, solid fundamentals (e.g., a strong balance sheet, improving returns on
equity, and the ability to generate free cash flow), strong management, and reasonable valuations in the context of
projected growth rates. This is called "bottom up" stock selection.
The primary risk associated with investment in the Fund will be the risk that the equity securities held by the
Fund will decline in value. The risk of the Fund is expected to be commensurate with that of other funds using a growth
strategy to invest in the stocks of large and medium-sized companies.
Although it is the general policy of the Fund to purchase and hold securities for capital growth, changes in the
Fund will be made as the Sub-advisor deems advisable. For example, portfolio changes may result from liquidity needs,
securities having reached a desired price, or by reason of developments not foreseen at the time of the investment was
made.
Special Situations. The Fund may invest in "special situations" from time to time. A "special situation" arises
when, in the opinion of the Sub-advisor, the securities of a particular company will be recognized and increase in value
due to a specific development, such as a technological breakthrough, management change or new product at that company.
Investment in "special situations" carries an additional risk of loss in the event that the anticipated development does
not occur or does not attract the expected attention.
Other Investments:
The Fund may also invest to a lesser degree in preferred stocks, convertible securities, warrants, and debt
securities when the Fund perceives an opportunity for capital growth from such securities. The Fund may invest up to 10%
of its total assets in debt securities, which may include corporate bonds and debentures and government securities.
The Fund may also purchase securities of foreign issuers, including foreign equity and debt securities and
depositary receipts. Foreign securities are selected primarily on a stock-by-stock basis without regard to any defined
allocation among countries or geographic regions. The Fund may also use a variety of currency hedging techniques,
including forward currency contracts, to manage exchange rate risk with respect to investments exposed to foreign
currency fluctuations.
Index/structured Securities. The Fund may invest without limit in index/structured securities, which are debt
securities whose value at maturity or interest rate is linked to currencies, interest rates, equity securities, indices,
commodity prices or other financial indicators. Such securities may be positively or negatively indexed (i.e., their
value may increase or decrease if the reference index or instrument appreciates). Index/structured securities may have
return characteristics similar to direct investments in the underlying instruments, but may be more volatile than the
underlying instruments. The Fund bears the market risk of an investment in the underlying instruments, as well as the
credit risk of the issuer of the index/structured security.
Futures, Options and Other Derivative Instruments. The Fund may purchase and write (sell) options on securities,
financial indices, and foreign currencies, and may invest in futures contracts on securities, financial indices, and
foreign currencies, options on futures contracts, forward contracts and swaps and swap-related products. These
instruments will be used primarily to hedge the Fund's positions against potential adverse movements in securities
prices, foreign currency markets or interest rates. To a limited extent, the Fund may also use derivative instruments
for non-hedging purposes such as increasing the Fund's income or otherwise enhancing return.
For an additional discussion of many of these types of securities and their risks, see this Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Temporary Investments. Although the Sub-advisor expects to invest primarily in equity securities, the
Sub-advisor may increase the Fund's cash position without limitation when the Sub-advisor believes that appropriate
investment opportunities for capital growth with desirable risk/reward characteristics are unavailable. Cash and similar
investments (whether made for defensive purposes or to receive a return on idle cash) will include high-grade commercial
paper, certificates of deposit and repurchase agreements. While the Fund is in a defensive position, the opportunity to
achieve its investment objective of capital growth will be limited.
ASAF JANUS CAPITAL GROWTH FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek growth of capital.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund will pursue its objective by investing in its corresponding Portfolio, which in turn will invest
primarily in common stocks. Common stock investments will be in companies that the Sub-advisor believes are experiencing
favorable demand for their products and services, and which operate in a favorable competitive and regulatory
environment. The Sub-advisor generally takes a "bottom up" approach to choosing investments for the Portfolio. In other
words, the Sub-advisor seeks to identify individual companies with earnings growth potential that may not be recognized
by the market at large. Current income is not a significant factor in choosing investments.
Because the Portfolio invests a substantial portion (or all) of its assets in stocks, the Portfolio is subject to
the risks associated with stock investments, and the Portfolio's (and Fund's) share price therefore may fluctuate
substantially. This is true despite the Portfolio's focus on the stocks of larger more-established companies. The
Portfolio's share price will be affected by changes in the stock markets generally, and factors specific to a company or
an industry will affect the prices of particular stocks held by the Portfolio (for example, poor earnings, loss of major
customers, major litigation against an issuer, or changes in government regulations affecting an industry). Because of
the types of securities in which the Portfolio invests, the Fund is designed for those who are investing for the long
term.
The Portfolio generally intends to purchase securities for long-term investment rather than short-term gains.
However, short-term transactions may occur as the result of liquidity needs, securities having reached a desired price or
yield, anticipated changes in interest rates or the credit standing of an issuer, or by reason of economic or other
developments not foreseen at the time the investment was made.
Special Situations. The Portfolio may invest in "special situations" from time to time. A "special situation"
arises when, in the opinion of the Sub-advisor, the securities of a particular company will be recognized and appreciate
in value due to a specific development, such as a technological breakthrough, management change or new product at that
company. Investment in "special situations" carries an additional risk of loss in the event that the anticipated
development does not occur or does not attract the expected attention.
Other Investments:
Although the Sub-advisor expects to invest primarily in equity securities, the Portfolio may also invest to a
lesser degree in preferred stocks, convertible securities, warrants, and debt securities when the Portfolio perceives an
opportunity for capital growth from such securities. The Portfolio is subject to the following percentage limitations on
investing in certain types of debt securities:
-- 35% of its assets in bonds rated below investment grade by the primary rating agencies ("junk" bonds).
-- 25% of its assets in mortgage- and asset-backed securities.
-- 10% of its assets in zero coupon, pay-in-kind and step coupon securities (securities that do not, or may not
under certain circumstances, make regular interest payments).
The Fund may make short sales "against the box." In addition, the Portfolio may invest in the following types of
securities and engage in the following investment techniques:
Foreign Securities. The Portfolio may also purchase securities of foreign issuers, including foreign equity and
debt securities and depositary receipts. Foreign securities are selected primarily on a stock-by-stock basis without
regard to any defined allocation among countries or geographic regions. No more than 25% of the Portfolio's assets may
be invested in foreign securities denominated in foreign currencies and not publicly traded in the United States.
Futures, Options and Other Derivative Instruments. The Portfolio may enter into futures contracts on securities,
financial indices and foreign currencies and options on such contracts and may invest in options on securities, financial
indices and foreign currencies, forward contracts and interest rate swaps and swap-related products (collectively
"derivative instruments"). The Portfolio intends to use most derivative instruments primarily to hedge the value of its
portfolio against potential adverse movements in securities prices, foreign currency markets or interest rates. To a
limited extent, the Portfolio may also use derivative instruments for non-hedging purposes such as seeking to increase
income. The Portfolio may also use a variety of currency hedging techniques, including forward foreign currency exchange
contracts, to manage exchange rate risk with respect to investments exposed to foreign currency fluctuations.
For more information on the types of securities other than common stocks in which the Portfolio may invest, see
this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Temporary Investments. The Sub-advisor may increase the Portfolio's cash position without limitation when the
Sub-advisor is of the opinion that appropriate investment opportunities for capital growth with desirable risk/reward
characteristics are unavailable. Cash and similar investments (whether made for defensive purposes or to receive a
return on idle cash) will include high-grade commercial paper, certificates of deposit, repurchase agreements and money
market funds managed by the Sub-advisor. While the Portfolio is in a defensive position, the opportunity for the
Portfolio and the Fund to achieve their investment objectives of capital growth will be limited.
ASAF T. ROWE PRICE TAX MANAGED FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek attractive long-term capital appreciation on an
after-tax basis.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund will invest primarily in large-capitalization stocks selected mainly from the 1,000 largest U.S.
companies. Stock selection is based on fundamental, bottom-up analysis that seeks to identify companies with superior
long-term appreciation prospects. Generally the Sub-advisor uses a growth approach to stock selection, looking for
companies with: a demonstrated ability to increase revenues, earnings, and cash flow consistently; capable management;
attractive business niches; and a sustainable competitive advantage. Valuation measures, such as a company's
price/earnings ratio relative to the market and its own growth rate, and its dividend yield relative to the market, are
also considered.
Generally, the Fund will limit exposure to high-yielding stocks. However, the payment of dividends - even
higher-than-average dividends - does not disqualify a stock from consideration for the Fund's portfolio.
The Fund seeks long-term appreciation while minimizing taxable distributions of capital gains and dividends. This
approach should reduce the negative effects of federal taxation and should increase after-tax returns compared with
similar funds that do not make tax efficiency a primary focus. To accomplish the Fund's goal of minimizing taxable
distributions, the Sub-advisor will strive to avoid realizing capital gains. However, gains may be realized when it is
believed that the risk of holding a security outweighs tax considerations. When gains are taken, the Sub-advisor will
attempt to offset them with losses from other securities. This may be accomplished by selling certain securities at a
loss and investing the proceeds in similar securities.
When shares that have appreciated are sold, the Sub-advisor will attempt to limit realized capital gains by
selling the highest-cost securities in a position first (that is, the shares on which the Fund has the smallest gain).
The Sub-advisor will strive to keep income from taxable dividends low. There is no guarantee the Sub-advisor's attempts
to manage the Fund in a tax-efficient manner will be successful, or that the Fund will achieve its objectives.
Growth stocks can be volatile for several reasons. Since companies usually reinvest a high proportion of their
earnings in their own businesses, they may lack the dividends often associated with value stocks that could cushion their
decline in a falling market. Also, since investors buy growth stocks because of their expected superior earnings growth,
earnings disappointments often result in sharp price declines. Investors should be aware that, during periods of adverse
economic and market conditions, stock prices may fall despite favorable earnings trends.
Other Investments:
While most assets will be invested in U.S. common stocks, other securities may also be purchased, including
convertible securities, warrants, foreign stocks, futures, and options in keeping with Fund objectives.
The Fund may invest up to 25% of its total assets in foreign securities, including nondollar-denominated
securities traded outside of the U.S. and dollar-denominated securities of foreign issuers traded in the U.S. (such as
ADRs). The Fund may also enter into foreign exchange contracts. The Fund may enter into futures and options contracts
for a number of reasons, including: to manage Fund exposure to changes in securities prices and foreign currencies; as an
efficient means of adjusting Fund overall exposure to certain markets; to hedge against a potentially unfavorable change
in interest rates; in an effort to enhance income; as a cash management tool; and to protect the value of portfolio
securities. Call and put options may be purchased or sold on securities, financial indices, and foreign currencies. The
Fund may invest up to 10% of its total assets in hybrid instruments, which combine the characteristics of futures,
options and securities.
For additional information about these investments and risks, see this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and
Investment Methods" and the Company's SAI under "Investment Programs of the Funds."
Temporary Investments. The Fund may establish and maintain cash reserves without limitation for temporary
defensive purposes. The Fund's reserves may be invested in short-term, tax-exempt money market securities (including
money market mutual funds managed by the Sub-advisor or affiliates), as well as short-term, investment-grade securities,
including tax-exempt commercial paper, municipal notes, and short-term maturity bonds. Some of these securities may have
adjustable, variable, or floating rates. The effect of taking such a position is that the Fund may not achieve its
investment objective.
ASAF ALLIANCE/BERNSTEIN 50/50 GROWTH + VALUE FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth by investing approximately 50% of
its assets in growth stocks of large companies and approximately 50% of its assets in value stocks of large companies.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund will invest primarily in common stocks of large U.S. companies included in the Russell 1000 Index (the
"Russell 1000"). The Russell 1000 is a market capitalization-weighted index that measures the performance of the 1,000
largest U.S. companies. As of June 30, 2000, the average market capitalization of the companies in the Russell 1000
index was approximately $14.1 billion.
Normally, about 60-85 companies will be represented in the Fund, with 25-35 companies primarily from the Russell
1000 Growth Index (the "Growth Index") constituting approximately 50% of the Fund's net assets, and 35-50 companies
primarily from the Russell 1000 Value Index (the "Value Index") constituting the remainder of the Fund's net assets. All
daily cash flows (that is, purchases and reinvested distributions) and outflows (that is, redemptions and expense items)
will be divided between the two portfolio segments for purposes of maintaining the targeted percentage allocation between
growth and value stocks. There will be a periodic rebalancing of each segment's assets to take account of market
fluctuations in order to maintain the approximately equal allocation. During periods between rebalancing, the allocation
of assets between portfolio segments may vary significantly from the target allocations. As a consequence, assets may be
allocated from the portfolio segment that has appreciated more or depreciated less to the other. In addition,
rebalancing will entail transaction costs which over time may be significant.
The Growth Index measures the performance of the Russell 1000 companies with higher price-to-book ratios and
higher forecasted growth values. The Value Index measures the performance of the Russell 1000 companies with lower
price-to-book ratios and lower forecasted growth values. This combination of growth stocks and value stocks is intended
to enhance performance of the Fund over time, and reduce the Fund's overall risk in comparison to funds which invest
exclusively in growth or value stocks. During particular periods, the Fund may outperform or underperform funds which
invest exclusively in growth or in value stocks.
The investment strategy of the Sub-advisor responsible for the portion of the Fund's assets invested in growth
stocks emphasizes stock selection. The Sub-advisor relies heavily upon the fundamental analysis and rigorous research of
its internal research staff. The Sub-advisor selects investments based on strong management, superior industry
positions, excellent balance sheets and superior earnings growth; where all of these strengths have not been reflected in
the company's stock price. In managing the Fund, the Sub-advisor seeks to take advantage of market volatility. During
market declines, the Sub-advisor will add to positions, causing the Fund to become somewhat more aggressive. Conversely,
in rising markets, the Sub-advisor will trim or eliminate positions and as a result the Fund will become more
conservative.
The method of selecting the investments used by the Sub-advisor responsible for the portion of the Fund's assets
invested in value stocks is to measure each stock's long-term expected return by comparing the price of the security to
the company's long-term cash flows. The Sub-advisor will only purchase those stocks that it has above-average confidence
in the reliability of its analysts' forecasts. The Sub-advisor may delay its purchase of securities if recent weakness
in the stock or negative earnings revisions by analysts indicate that the stock price is likely to decline in the near
future, and it may delay its sale of securities if recent strength in the stock or upward earnings revisions indicate the
stock is likely to rise soon. The Sub-advisor will control risk within the value portion of the Fund by reviewing
whether there is undue portfolio exposure to industry sector and other risk factors. The Sub-advisor will take more risk
when unusually large value distortions within the value realm create unusually large opportunities to add returns, and it
will take less risk when the opportunities are limited.
Because the Fund invests primarily in stocks, the Fund is subject to the risks associated with stock investments,
and the Fund's share price therefore may fluctuate substantially. The Fund's share price will be affected by changes in
the stock markets generally, and factors specific to a company or an industry will affect the prices of particular stocks
held by the Fund (for example, poor earnings, loss of major customers, availability of basic resources or supplies, major
litigation against a company, or changes in governmental regulation affecting an industry). The Fund's focus on large,
more-established companies may mean that its level of risk is lower than a fund investing primarily in smaller
companies. Because the Fund invests in a smaller number of securities than many other funds, changes in the value of a
single security may have a more significant effect, either negative or positive, on the Fund's share price.
Other Investments:
In addition to investing in equity securities, the Fund also may:
o invest up to 20% of the growth portion of its net assets in convertible securities;
o invest up to 5% of the growth portion of its net assets in rights or warrants;
o invest up to 15% of its total assets in foreign securities
o purchase and sell exchange-traded index options and stock index futures contracts and;
o write covered exchange-traded call options on its securities up to 15% of the growth portion of its total assets,
and purchase exchange-traded call and put options on common stocks up to, for all options, 10% of the growth
portion of its total assets.
For purposes of the Fund a foreign security is a security issued by a non-U.S. company, which is defined as a
company that: (1) is organized outside the United States; (ii) has its principal place of business outside the United
States; and (iii) issues securities traded principally in a foreign country. Companies that do not fall within the
definition of a non-U.S. company would be considered a U.S. company and therefore not subject to the above limitation on
foreign securities.
American Depository Receipts (ADRs) are not considered foreign securities for purposes of the 15% limitation set
forth above and may be purchased by the Fund.
For additional information about these investments and risks, see this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and
Investment Methods" and the Company's SAI under "Investment Programs of the Funds."
Temporary Investments. Although it does not expect to do so ordinarily, when business or financial conditions
warrant, the Fund may assume a temporary defensive position and invest in high-grade, short-term, fixed-income securities
(which may include U.S. Government securities) or hold its assets in cash. While the Fund is in a defensive position,
the opportunity to achieve its investment objective will be limited.
ASAF SANFORD BERNSTEIN DEEP VALUE FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek long-term capital growth.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund will pursue its objective by investing primarily in common stocks. The Sub-advisor expects that the
majority of the Fund's assets will be invested in the common stocks of large companies that appear to be undervalued.
Among other things, the Fund seeks to identify compelling buying opportunities created when companies are undervalued on
the basis of investor reactions to near-term problems or circumstances even though their long-term prospects remain
sound. The Sub-advisor's investment approach is value-based and price-driven, and it relies on the intensive fundamental
research of its internal research staff to identify these buying opportunities in the marketplace.
Fund investments are selected by the Sub-advisor based upon a model portfolio of 125-175 stocks constructed by
the Sub-advisor. In selecting investments for the model portfolio, the Sub-advisor takes a "bottom-up" approach. In
other words, the Sub-advisor seeks to identify individual companies with earnings growth potential that may not be
recognized by the market at large. The Sub-advisor relates present value of each company's forecasted future cash flow
to the current price of its stock. The Sub-advisor ranks companies from the highest expected return to the lowest, with
the companies at the top of the ranking being the most undervalued.
Once the expected return for each stock is calculated, the Sub-advisor adjusts for timing and concentration
risks. Securities are ranked by risk-adjusted expected returns. Securities ranked in the top third of its valuation
universe, if selected, are over-weighted because they represent the most undervalued stocks in its universe. The
Sub-advisor market weights securities ranked in the middle third of its universe, if selected, to add diversification to
the Fund. To control variability in premium, the Sub-advisor also holds the largest capitalization securities (at
under-weighted positions) even when they rank in bottom third of the universe. If a security falls in the ranking from
the top third of the Sub-advisor's valuation universe to the middle third, the Sub-advisor may reduce the position to
market weight. If the security's ranking continues to fall into the bottom third of its universe, the Sub-advisor may
either sell it or, if it is a very large capitalization stock, will underweight it. The Sub-advisor may from time to
time deviate from the foregoing process with respect to the weighting of individual securities when determined
appropriate by the Sub-advisor.
The Sub-advisor may delay the Fund's purchase of securities if recent weakness in the stock or negative earnings
revisions by analysts indicate that the stock price is likely to decline in the near future, and it may delay the Fund's
sale of securities if recent strength in the stock or upward earnings revisions indicate the stock is likely to rise
soon. The Sub-advisor will control risk by reviewing whether there is undue portfolio exposure to industry sector and
other risk factors. The Sub-advisor will take more risk when unusually large value distortions within the value realm
create unusually large opportunities to add returns, and it will take less risk when the opportunities are limited.
The Sub-advisor also seeks to control risks by correlating the size of initial purchases by the Fund to the
security's benchmark weighting, within plus or minus 0.5%. If market appreciation of a security brings the security's
weighting to 1.0% above or below its benchmark weighting (at the time), the size of the holding is generally increased or
reduced accordingly. Because the Fund invests primarily in stocks, the Fund is subject to the risks associated with
stock investments, and the Fund's share price therefore may fluctuate substantially. The Fund's share price will be
affected by changes in the stock markets generally, and factors specific to a company or an industry will affect the
prices of particular stocks held by the Fund (for example, poor earnings, loss of major customers, availability of basic
resources or supplies, major litigation against a company, or changes in governmental regulation affecting an industry).
The Fund's focus on large, more-established companies may mean that its level of risk is lower than a fund investing
primarily in smaller companies. While the Fund's value investing historically has involved less risk than investing in
growth companies, investing in value stocks carries the risks that the market will not recognize the stock's intrinsic
value for a long time or that a stock judged to be undervalued may actually be appropriately priced.
Other Investments:
Derivatives. The Fund may invest in various instruments that are or may be considered derivatives, including
securities index futures contracts and related options These instruments may be used for several reasons: to simulate
full investment in equities while retaining cash for fund management purposes, to facilitate trading, or to reduce
transaction costs. The Fund will not use derivatives for speculative purposes or to leverage its assets. The Fund will
limit its use of securities index futures contracts and related options so that, at all times, margin deposits for
futures contracts and premiums on related options do not exceed 5% of the Fund's assets and the percentage of the Fund's
assets being used to cover its obligations under futures and options does not exceed 50%.
Additional information about these derivative instruments and their risks is included in this Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Temporary Investments. The Fund may maintain up to 25% of its assets in short-term debt securities and money
market instruments to meet redemption requests. These securities include obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S.
Government or its agencies or instrumentalities or by any of the states, repurchase agreements, commercial paper, and
certain bank obligations. The Fund will not invest in these securities as part of a temporary defensive strategy to
protect against potential market declines.
ASAF SANFORD BERNSTEIN MANAGED INDEX 500 FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund (formerly, the ASAF Bankers Trust Managed Index 500 Fund) is
to outperform the Standard & Poor's 500 Composite Stock Price Index (the "S&P 500(R)") through stock selection resulting in
different weightings of common stocks relative to the index.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund will invest primarily in the common stocks of companies included in the S&P 500. The S&P 500 is an
index of 500 common stocks, most of which trade on the New York Stock Exchange Inc. (the "NYSE"). The Sub-advisor
believes that the S&P 500 is representative of the performance of publicly traded common stocks in the U.S. in general.
In seeking to outperform the S&P 500, the Sub-advisor starts with a portfolio of stocks representative of the
holdings of the index. It then uses a set of fundamental quantitative criteria that are designed to indicate whether a
particular stock will predictably perform better or worse than the S&P 500. Based on these criteria, the Sub-advisor
determines whether the Fund should over-weight, under-weight or hold a neutral position in the stock relative to the
proportion of the S&P 500 that the stock represents. In addition, the Sub-advisor may determine based on the
quantitative criteria that (1) certain S&P 500 stocks should not be held by the Fund in any amount, and (2) certain
equity securities that are not included in the S&P 500 should be held by the Fund. The Fund will not invest more than
15% of its total assets in equity securities of companies not included in the S&P 500.
As a mutual fund investing primarily in common stocks, the Fund is subject to the risk that common stock prices
will decline over short or even extended periods. The U.S. stock market tends to be cyclical, with periods when stock
prices generally rise and periods when prices generally decline. The Sub-advisor believes that the various quantitative
criteria used to determine which stocks to over- or under-weight will balance each other so that the overall risk of the
Fund is not likely to differ materially from the risk of the S&P 500 itself. While the Fund attempts to outperform the
S&P 500, it is not expected that any outperformance will be substantial. The Fund also may underperform the S&P 500 over
short or extended periods.
About the S&P 500. The S&P 500 is a well-known stock market index that includes common stocks of 500 companies
from several industrial sectors representing a significant portion of the market value of all common stocks publicly
traded in the United States. Stocks in the S&P 500 are weighted according to their market capitalization (the number of
shares outstanding multiplied by the stock's current price). The composition of the S&P 500 is determined by S&P based
on such factors as market capitalization, trading activity, and whether the stock is representative of stocks in a
particular industry group. The composition of the S&P 500 may be changed from time to time. "Standard & Poor's(R)", "S&P
500(R)", "Standard & Poor's 500", and "500" are trademarks of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. and have been licensed for
use by the Investment Manager. The Fund is not sponsored, endorsed, sold or promoted by Standard & Poor's and Standard &
Poor's makes no representation regarding the advisability of investing in the Fund.
Other Investments:
Derivatives. The Fund may invest in various instruments that are or may be considered derivatives, including
securities index futures contracts and related options, warrants and convertible securities. These instruments may be
used for several reasons: to simulate full investment in the S&P 500 while retaining cash for fund management purposes,
to facilitate trading, to reduce transaction costs or to seek higher investment returns when the futures contract,
option, warrant or convertible security is priced more attractively than the underlying equity security or the S&P 500.
The Fund will not use derivatives for speculative purposes or to leverage its assets. The Fund will limit its use of
securities index futures contracts and related options so that, at all times, margin deposits for futures contracts and
premiums on related options do not exceed 5% of the Fund's assets and the percentage of the Fund's assets being used to
cover its obligations under futures and options does not exceed 50%.
Additional information about these derivative instruments and their risks is included in this Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Temporary Investments. The Fund may maintain up to 25% of its assets in short-term debt securities and money
market instruments to meet redemption requests or to facilitate investment in the securities of the S&P 500. These
securities include obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies or instrumentalities or by any
of the states, repurchase agreements, commercial paper, and certain bank obligations. The Fund will not invest in these
securities as part of a temporary defensive strategy to protect against potential market declines.
ASAF ALLIANCE GROWTH AND INCOME FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund (formerly, the ASAF Lord Abbett Growth and Income Fund) is
long-term growth of capital and income while attempting to avoid excessive fluctuations in market value.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund normally will invest in common stocks (and securities convertible into common stocks). The Sub-advisor
will take a value-oriented approach, in that it will try to keep the Fund's assets invested in securities that are
selling at reasonable valuations in relation to their fundamental business prospects. In doing so, the Fund may forgo
some opportunities for gains when, in the judgement of the Sub-advisor, they are too risky.
In seeking to achieve its objective, the Fund invests primarily in the equity securities of U.S. companies that
the Sub-advisor believes are undervalued. The Sub-advisor believes that, over time, stock prices (of companies in which
the Fund invests) will come to reflect the companies' intrinsic economic values. The Sub-advisor uses a disciplined
investment process to evaluate the companies in its extensive research universe. Through this process, the Sub-advisor
seeks to identify the stocks of companies that offer the best combination of value and potential for price appreciation.
The Sub-advisor's analysts prepare their own earnings estimates and financial models for each company followed.
The Sub-advisor employs these models to identify equity securities whose current market prices do not reflect what it
considers to be their intrinsic economic value. In determining a company's intrinsic economic value, the Sub-advisor
takes into account may factors it believes bear on the ability of the company to perform in the future, including
earnings growth, prospective cash flows, dividend growth and growth in book value. The Sub-advisor then ranks, at least
weekly, each of the companies in its research universe in the relative order of disparity between their stock prices and
their intrinsic economic values, with companies with the greatest disparities receiving the highest ranking (i.e. being
considered the most undervalued).
The prices of the common stocks that the Fund invests in will fluctuate. Therefore, the Fund's share price will
also fluctuate, and may decline substantially. While there is the risk that an investment will never reach what the
Sub-advisor believes is its full value, or go down in value, the Fund's risk and share price fluctuation (and potential
for gain) may be less than many other stock funds because of the Fund's emphasis on large, seasoned company value stocks.
Other Investments:
The Fund, in addition to investing in common stocks and convertible securities, may write covered call options
listed on domestic securities exchanges with respect to securities in the Fund. It is not intended for the Fund to write
covered call options with respect to securities with an aggregate market value of more than 10% of the Fund's net assets
at the time an option is written. The Fund also may purchase and sell forward and futures contracts and related options
for hedging purposes. The Fund may also invest up to 10% of the Fund's net assets (at the time of investment) in foreign
securities, and invest in straight bonds and other debt securities.
Temporary Investments. The Fund may invest in short-term debt and other high quality fixed-income securities to
create reserve purchasing power and also for temporary defensive purposes. While the Fund is in a defensive position,
the opportunity to achieve its investment objective will be limited.
ASAF MFS GROWTH WITH INCOME FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek to provide reasonable current income and long-term
capital growth and income.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund invests, under normal market conditions, at least 65% of its total assets in common stocks and related
securities, such as preferred stocks, convertible securities and depositary receipts. The stocks in which the Fund
invests generally will pay dividends. While the Fund may invest in companies of any size, the Fund generally focuses on
companies with larger market capitalizations that the Sub-advisor believes have sustainable growth prospects and
attractive valuations based on current and expected earnings or cash flow.
The Sub-advisor uses a "bottom up," as opposed to "top down," investment style in managing the Fund. This means
that securities are selected based upon fundamental analysis of individual companies (such as analysis of the companies'
earnings, cash flows, competitive position and management abilities) by the Sub-advisor.
The Fund may invest up to 20% of its total assets in foreign equity securities.
As with any fund investing primarily in common stocks, the value of the securities held by the Fund may decline
in value, either because of changing economic, political or market conditions or because of the economic condition of the
company that issued the security. These declines may be substantial. In light of the Fund's focus on income-producing
large-cap stocks, the risk and share price fluctuations of the Fund (and its potential for gain) may be less than many
other stock funds. The Fund may invest in foreign companies, including companies located in developing countries, and it
therefore will be subject to risks relating to political, social and economic conditions abroad, risks resulting from
differing regulatory standards in non-U.S. markets, and fluctuations in currency exchange rates.
Other Investments:
Although the Fund will invest primarily in common stocks and related securities, the Fund may also invest in debt
securities, including variable and floating rate securities and zero coupon, deferred interest and pay-in-kind bonds. The
Fund may also purchase warrants and make short sales "against the box."
Futures and Forward Contracts. The Fund may purchase and sell futures contracts on securities indices, foreign
currencies and interest rates for hedging and non-hedging purposes. The Fund may also enter into forward contracts for
the purchase or sale of foreign currencies for hedging and non-hedging purposes.
For more information on the types of securities other than common stocks in which the Fund may invest, see this
Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods" and the Company's SAI under "Investment Programs for the
Funds."
Temporary Investments. The Fund may depart from its principal investment strategy by temporarily investing for
defensive purposes when adverse market, economic or political conditions exist. When investing for defensive purposes,
the Fund may hold cash or invest in cash equivalents such as short-term U.S. government securities, commercial paper and
bank instruments. While the Fund is in a defensive position, the opportunity to achieve its investment objective will be
limited.
ASAF INVESCO EQUITY INCOME FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth and current income while following
sound investment practices.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund seeks to achieve its objective by investing in its corresponding Portfolio, which in turn will seek to
invest in securities that are expected to produce relatively high levels of income and consistent, stable returns. The
Portfolio normally will invest at least 65% of its assets in dividend-paying common and preferred stocks of domestic and
foreign issuers. Up to 30% of the Portfolio's assets may be invested in equity securities that do not pay regular
dividends. In addition, the Portfolio normally will have some portion of its assets invested in debt securities or
convertible bonds. The Portfolio may invest up to 25% of its total assets in foreign securities, including securities of
issuers in countries considered to be developing. These foreign investments may serve to increase the overall risks of
the Portfolio.
The Portfolio's investments in common stocks may, of course, decline in value, which will result in declines in
the Portfolio's (and Fund's) share price. Such declines could be substantial. To minimize the risk this presents, the
Sub-advisor will not invest, with respect to 75% of the value of its total assets, more than 5% of the Portfolio's assets
in the securities of any one company or more than 25% of the Portfolio's assets in any one industry. In light of the
Portfolio's focus on income producing stocks, its risk and share price fluctuation (and potential for gain) may be less
than many other stock funds.
Debt Securities. The Portfolio's investments in debt securities will generally be subject to both credit risk
and market risk. Credit risk relates to the ability of the issuer to meet interest or principal payments, or both, as
they come due. Market risk relates to the fact that the market values of debt securities in which the Portfolio invests
generally will be affected by changes in the level of interest rates. An increase in interest rates will tend to reduce
the market values of debt securities, whereas a decline in interest rates will tend to increase their values. Although
the Sub-advisor will limit the Portfolio's debt security investments to securities it believes are not highly
speculative, both kinds of risk are increased by investing in debt securities rated below the top four grades by Standard
& Poor's Corporation or Moody's Investors Services, Inc., or equivalent unrated debt securities ("junk bonds").
In order to minimize its risk in investing in debt securities, the Portfolio will invest no more than 15% of its
assets in junk bonds, and in no event will the Portfolio ever invest in a debt security rated below Caa by Moody's or CCC
by Standard & Poor's. While the Sub-advisor will monitor all of the debt securities in the Portfolio for the issuers'
ability to make required principal and interest payments and other quality factors, the Sub-advisor may retain in the
Portfolio a debt security whose rating is changed to one below the minimum rating required for purchase of such a
security. For a discussion of the special risks involved in lower-rated bonds, see this Prospectus under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods."
Temporary Investments:
In periods of uncertain market and economic conditions, the Portfolio may assume a defensive position with up to
100% of its assets temporarily invested in high quality corporate bonds or notes or government securities, or held in
cash. While the Portfolio is in a defensive position, the opportunity for the Portfolio and Fund to achieve their
investment objectives may be limited.
ASAF AMERICAN CENTURY STRATEGIC BALANCED FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth and current income.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Sub-advisor intends to maintain approximately 60% of the Fund's assets in equity securities and the remainder
in bonds and other fixed income securities. Both the Fund's equity and fixed income investments will fluctuate in
value. The equity securities will fluctuate depending on the performance of the companies that issued them, general
market and economic conditions, and investor confidence. The fixed income investments will be affected primarily by
rising or falling interest rates and the credit quality of the issuers. As a Fund that invests both in equity and fixed
income securities, the Fund's risk of loss and share price fluctuation will tend to be less than funds investing
primarily in equity securities and more than funds investing primarily in fixed income securities.
Equity Investments. With the equity portion of the Fund, the Sub-advisor utilizes quantitative management
techniques in a two-step process that draws heavily on computer technology. In the first step, the Sub-advisor ranks
stocks, primarily the 1,500 largest publicly traded U.S. companies as measured by market capitalization. These rankings
are determined by using a computer model that combines measures of a stock's value and measures of its growth potential.
To measure value, the Sub-advisor uses ratios of stock price to book value and stock price to cash flow, among others.
To measure growth, the Sub-advisor uses, among others, the rate of growth in a company's earnings and changes in its
earnings estimates.
In the second step, the Sub-advisor uses a technique called portfolio optimization. In portfolio optimization,
the Sub-advisor uses a computer to build a portfolio of stocks from the ranking described earlier that it thinks will
provide the best balance between risk and expected return. The goal is to create an equity portfolio that provides
better returns than the S&P 500 Index without taking on significant additional risk.
Fixed Income Investments. The Sub-advisor intends to maintain approximately 40% of the Fund's assets in fixed
income securities. Up to 20% of the Portfolio's fixed income securities may be invested in foreign fixed income
securities. These percentages will fluctuate and may be higher or lower depending on the mix the Sub-advisor believes
will be most appropriate for achieving the Fund's objectives.
The fixed income portion of the Fund is invested in a diversified portfolio of government securities, corporate
fixed income securities, mortgage-backed and asset-backed securities, and similar securities. The Sub-advisor's strategy
is to actively manage the Fund by investing the Fund's fixed income assets in sectors it believes are undervalued
(relative to the other sectors) and which represent better relative long-term investment opportunities.
The Sub-advisor will adjust the weighted average portfolio maturity in response to expected changes in interest
rates. Under normal market conditions, the weighted average maturity of the fixed income portion of the Fund will range
from 3 to 10 years. During periods of rising interest rates, the weighted average maturity may be reduced in order to
reduce the effect of bond price declines on the Fund's net asset value. When interest rates are falling and bond prices
are rising, the Fund may be moved toward the longer end of its maturity range.
Debt securities that comprise the Fund's fixed income portfolio will primarily be investment grade obligations.
However, the Fund may invest up to 10% of its fixed income assets in high-yield securities or "junk bonds." Regardless
of rating levels, all debt securities considered for purchase by the Fund are analyzed by the Sub-advisor to determine,
to the extent reasonably possible, that the planned investment is sound, given the investment objective of the Fund. For
an additional discussion of lower-rated securities and their risks, see this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and
Investment Methods."
In determining the allocation of assets among U.S. and foreign capital markets, the Sub-advisor considers the
condition and growth potential of the various economies; the relative valuations of the markets; and social, political,
and economic factors that may affect the markets. The Sub-advisor also considers the impact of foreign exchange rates in
selecting securities denominated in foreign currencies.
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest up to 25% of its total assets in equity and debt securities of foreign
issuers, including foreign governments and their agencies, when these securities meet its standards of selection. (As
noted above, up to 20% of the fixed income portion of the Fund normally may be invested in foreign securities.) These
investments will be made primarily in issuers in developed markets. The Fund may make such investments either directly
in foreign securities, or by purchasing depositary receipts for foreign securities. To protect against adverse movements
in exchange rates between currencies, the Fund may, for hedging purposes only, enter into forward currency exchange
contracts and buy put and call options relating to currency futures contracts.
Other Investments:
The Fund may make short sales "against the box." The Fund may also invest in derivative securities. Certain of
these derivative securities may be described as "index/structured" securities, which are securities whose value or
performance is linked to other equity securities (as in the case of depositary receipts), currencies, interest rates,
securities indices or other financial indicators ("reference indices"). The Fund may not invest in a derivative security
unless the reference index or the instrument to which it relates is an eligible investment for the Fund. For example, a
security whose underlying value is linked to the price of oil would not be a permissible investment because the Fund may
not invest in oil and gas leases or futures.
For further information on these securities and investment practices, see this Prospectus under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods."
ASAF FEDERATED HIGH YIELD BOND FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek high current income by investing primarily in
fixed income securities. The fixed income securities in which the Fund intends to invest are lower-rated corporate debt
obligations.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund will invest at least 65% of its assets in lower-rated corporate fixed income securities ("junk bonds").
These fixed income securities may include preferred stocks, convertible securities, bonds, debentures, notes, equipment
lease certificates and equipment trust certificates. The securities in which the Fund invests usually will be rated
below the three highest rating categories of a nationally recognized rating organization (AAA, AA, or A for Standard &
Poor's Corporation ("Standard & Poor's") and Aaa, Aa or A for Moody's Investors Service, Inc. ("Moody's")) or, if
unrated, are of comparable quality. There is no lower limit on the rating of securities in which the Fund may invest.
The Fund may purchase or hold securities rated in the lowest rating category or securities in default.
A fund that invests primarily in lower-rated fixed income securities will be subject to greater risk and share
price fluctuation than a typical fixed income fund, and may be subject to an amount of risk that is comparable to or
greater than many equity funds. Lower-rated securities will usually offer higher yields than higher-rated securities,
but with more risk of loss of principal and interest. This is because of the reduced creditworthiness of the securities
and the increased risk of default. Like equity securities, lower-rated fixed income securities tend to reflect
short-term corporate and market developments to a greater extent than higher-rated fixed income securities, which tend to
react primarily to fluctuations in market interest rates.
An economic downturn may adversely affect the value of some lower-rated bonds. Such a downturn may especially
affect highly leveraged companies or companies in industries sensitive to market cycles, where deterioration in a
company's cash flow may impair its ability to meet its obligations under the bonds. From time to time, issuers of
lower-rated bonds may seek or may be required to restructure the terms and conditions of the securities they have
issued. As a result of these restructurings, the value of the securities may fall, and the Fund may bear legal or
administrative expenses in order to maximize recovery from an issuer.
The secondary trading market for lower-rated bonds is generally less liquid than the secondary trading market for
higher-rated bonds. Adverse publicity and the perception of investors relating to these securities and their issuers,
whether or not warranted, may also affect the price or liquidity of lower-rated bonds. For an additional discussion of
the risks involved in lower-rated securities, see this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Methods by which the Sub-advisor attempts to reduce the risks involved in lower-rated securities include:
Credit Research. The Sub-advisor will perform its own credit analysis in addition to using rating
organizations and other sources, and may have discussions with the issuer's management or other investment analysts
regarding issuers. The Sub-advisor's credit analysis will consider the issuer's financial soundness, its responsiveness
to changing business and market conditions, and its anticipated cash flow and earnings. In evaluating an issuer, the
Sub-advisor places special emphasis on the estimated current value of the issuer's assets rather than their historical
cost.
Diversification. The Sub-advisor invests in securities of many different issuers, industries, and
economic sectors to reduce portfolio risk.
Economic Analysis. The Sub-advisor will analyze current developments and trends in the economy and in
the financial markets.
Other Investments:
Under normal circumstances, the Fund will not invest more than 10% of its total assets in equity securities. The
Fund may invest up to 10% of its total assets in foreign securities that are not publicly traded in the United States.
The Fund may own zero coupon bonds or pay-in-kind securities, which are fixed income securities that do not make
regular cash interest payments. The prices of these securities are generally more sensitive to changes in market
interest rates than are conventional bonds. Additionally, interest on zero coupon bonds and pay-in-kind securities must
be reported as taxable income to the Fund even though it receives no cash interest until the maturity of such securities.
The Portfolio may invest in securities issued by real estate investment trusts, which are companies that hold
real estate or mortgage investments. Usually, real estate investment trusts are not diversified, and, therefore, are
subject to the risks of a single project or a small number of projects. They also may be heavily dependent on cash flows
from the property they own, may bear the risk of defaults on mortgages, and may be affected by changes in the value of
the underlying property.
Temporary Investments. The Fund may also invest all or a part of its assets temporarily in cash or cash items
for defensive purposes during times of unusual market conditions or to maintain liquidity. Cash items may include
certificates of deposit and other bank obligations; commercial paper (generally lower-rated); short-term notes;
obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. government or its agencies or instrumentalities; and repurchase agreements.
While the Fund is in a defensive position, the opportunity to achieve its investment objective of high current income may
be limited.
ASAF PIMCO TOTAL RETURN BOND FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek to maximize total return, consistent with
preservation of capital and prudent investment management.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
The Fund will invest in its corresponding Portfolio, at least 65% of the assets of which will be invested in the
following types of fixed income securities;
o securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or government-sponsored enterprises;
o corporate debt securities of U.S. and non-U.S. issuers, including convertible securities and corporate commercial
paper;
o mortgage and other asset-backed securities;
o inflation-indexed bonds issued by both governments and corporations;
o structured notes, including hybrid or "indexed" securities, event-linked bonds and loan participations;
o delayed funding loans and revolving credit securities;
o bank certificates of deposit, fixed time deposits and bankers' acceptances;
o repurchase agreements and reverse repurchase agreements;
o debt securities issued by state or local governments and their agencies and government-sponsored enterprises;
o obligations of foreign governments or their subdivisions, agencies and government-sponsored enterprises; and
o obligations of international agencies or supranational entities.
Portfolio holdings will be concentrated in areas of the bond market (based on quality, sector, interest rate or
maturity) that the Sub-advisor believes to be relatively undervalued. In selecting fixed income securities, the
Sub-advisor uses economic forecasting, interest rate anticipation, credit and call risk analysis, foreign currency
exchange rate forecasting, and other securities selection techniques. The proportion of the Portfolio's assets committed
to investment in securities with particular characteristics (such as maturity, type and coupon rate) will vary based on
the Sub-advisor's outlook for the U.S. and foreign economies, the financial markets, and other factors. The management
of duration (a measure of a fixed income security's expected life that incorporates its yield, coupon interest payments,
final maturity and call features into one measure) is one of the fundamental tools used by the Sub-advisor.
The Portfolio will invest in fixed-income securities of varying maturities. The average portfolio duration of
the Portfolio generally will vary within a three- to six-year time frame based on the Sub-advisor's forecast for interest
rates. The Portfolio may invest up to 10% of its assets in fixed income securities that are rated below investment grade
("junk bonds") but are rated B or higher by Moody's Investors Services, Inc. ("Moody's") or Standard & Poor's Corporation
("S&P") (or, if unrated, determined by the Sub-advisor to be of comparable quality).
Generally, over the long term, the return obtained by a portfolio investing primarily in fixed income securities
such as the Portfolio is not expected to be as great as that obtained by a portfolio investing in equity securities. At
the same time, the risk and price fluctuation of a fixed income portfolio is expected to be less than that of an equity
portfolio, so that a fixed income portfolio is generally considered to be a more conservative investment. However, the
Portfolio can and routinely does invest in certain complex fixed income securities (including various types of
mortgage-backed and asset-backed securities) and engage in a number of investment practices (including futures, options,
swaps and dollar rolls) as described below, that many other fixed income funds do not utilize. These investments and
practices are designed to increase the Portfolio's return or hedge its investments, but may increase the risk to which
the Portfolio is subject.
Like other fixed income funds, the Portfolio is subject to market risk. Bond values fluctuate based on changes
in interest rates, market conditions, investor confidence and announcements of economic, political or financial
information. Generally, the value of fixed income securities will change inversely with changes in market interest
rates. As interest rates rise, market value tends to decrease. This risk will be greater for long-term securities than
for short-term securities. Certain mortgage-backed and asset-backed securities and derivative instruments in which the
Portfolio may invest may be particularly sensitive to changes in interest rates. The Portfolio is also subject to credit
risk, which is the possibility that an issuer of a security (or a counterparty to a derivative contract) will default or
become unable to meet its obligation. Generally, the lower the rating of a security, the higher its degree of credit
risk.
The following paragraphs describe some specific types of fixed-income investments that the Portfolio may invest
in, and some of the investment practices that the Portfolio will engage in. More information about some of these
investments, including futures, options and mortgage-backed and asset-backed securities, is included below under "Certain
Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
U.S. Government Securities. The Portfolio may invest in various types of U.S. Government securities, including
those that are supported by the full faith and credit of the United States; those that are supported by the right of the
issuing agency to borrow from the U.S. Treasury; those that are supported by the discretionary authority of the U.S.
Government to purchase the agency's obligations; and still others that are supported only by the credit of the
instrumentality.
Corporate Debt Securities. Corporate debt securities include corporate bonds, debentures, notes and other
similar instruments, including convertible securities and preferred stock. Debt securities may be acquired with warrants
attached. The rate of return or return of principal on some debt obligations may be linked or indexed to exchange rates
between the U.S. dollar and a foreign currency or currencies.
While the Sub-advisor may regard some countries or companies as favorable investments, pure fixed income
opportunities may be unattractive or limited due to insufficient supply or legal or technical restrictions. In such
cases, the Portfolio may consider equity securities or convertible bonds to gain exposure to such investments.
Variable and Floating Rate Securities. Variable and floating rate securities provide for a periodic adjustment
in the interest rate paid on the obligations. The interest rates on these securities are tied to other interest rates,
such as money-market indices or Treasury bill rates, and reset periodically. While these securities provide the
Portfolio with a certain degree of protection against losses caused by rising interest rates, they will cause the
Portfolio's interest income to decline if market interest rates decline.
Inflation-Indexed Bonds. Inflation-indexed bonds are fixed income securities whose principal value is
periodically adjusted according to the rate of inflation. The interest rate on these bonds is fixed at issuance, and is
generally lower than the interest rate on typical bonds. Over the life of the bond, however, this interest will be paid
based on a principal value that has been adjusted for inflation. Repayment of the adjusted principal upon maturity may
be guaranteed, but the market value of the bonds is not guaranteed, and will fluctuate. The Portfolio may invest in
inflation-indexed bonds that do not provide a repayment guarantee. While these securities are expected to be protected
from long-term inflationary trends, short-term increases in inflation may lead to losses.
Event-Linked Bonds. Event-linked bonds are fixed income securities for which the return of principal and payment
of interest is contingent upon the non-occurrence of a specific "trigger" event, such as a hurricane, earthquake or other
physical or weather-related phenomenon. Some event-linked bonds are commonly referred to as "catastrophe bonds." If the
trigger event occurs, the Portfolio may lose all or a portion of the amount it invested in the bond. Event-linked bonds
often provide for an extension of maturity to process and audit loss claims where a trigger event has, or possibly has,
occurred. An extension of maturity may increase volatility. Event-linked bonds may also expose the Fund to certain
unanticipated risks including credit risk, adverse regulatory or jurisdictional interpretations, and adverse tax
consequences. Event-linked bonds may also be subject to liquidity risk.
Mortgage-Backed and Other Asset-Backed Securities. The Portfolio may invest all of its assets in mortgage-backed
and other asset-backed securities, including collateralized mortgage obligations. The value of some mortgage-backed and
asset-backed securities in which the Portfolio invests may be particularly sensitive to changes in market interest rates.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements and Dollar Rolls. In addition to entering into reverse repurchase agreements (as
described below under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods"), the Portfolio may also enter into dollar rolls. In
a dollar roll, the Portfolio sells mortgage-backed or other securities for delivery in the current month and
simultaneously contracts to purchase substantially similar securities on a specified future date. The Portfolio forgoes
principal and interest paid on the securities sold in a dollar roll, but the Portfolio is compensated by the difference
between the sales price and the lower price for the future purchase, as well as by any interest earned on the proceeds of
the securities sold. The Portfolio also could be compensated through the receipt of fee income. Reverse repurchase
agreements and dollar rolls can be viewed as collateralized borrowings and, like any borrowings, will tend to exaggerate
fluctuations in Portfolio's (and Fund's) share price and may cause the Portfolio to need to sell portfolio securities at
times when it would otherwise not wish to do so.
Foreign Securities. The Portfolio may invest up to 20% of its assets in securities denominated in foreign
currencies and may invest beyond this limit in U.S. dollar-denominated securities of foreign issuers. The Portfolio may
invest up to 10% of its assets in securities of issuers based in developing countries (as determined by the
Sub-advisor). The Portfolio may buy and sell foreign currency futures contracts and options on foreign currencies and
foreign currency futures contracts, and enter into forward foreign currency exchange contracts for the purpose of hedging
currency exchange risks arising from the Portfolio's investment or anticipated investment in securities denominated in
foreign currencies.
Short Sales "Against the Box." The Portfolio may sell securities short "against the box." For a discussion of
this practice, see this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Derivative Instruments. The Portfolio may purchase and write call and put options on securities, securities
indices and on foreign currencies. The Portfolio may invest in interest rate futures contracts, stock index futures
contracts and foreign currency futures contracts and options thereon that are traded on U.S. or foreign exchanges or
boards of trade. The Portfolio may also enter into swap agreements with respect to foreign currencies, interest rates
and securities indices. The Portfolio may use these techniques to hedge against changes in interest rates, currency
exchange rates or securities prices or as part of its overall investment strategy.
For a discussion of futures and options and their risks, see this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and
Investment Methods." The Portfolio's investments in swap agreements are described directly below.
Swap Agreements. The Portfolio may enter into interest rate, index and currency exchange rate swap agreements
for the purposes of attempting to obtain a desired return at a lower cost than if the Portfolio had invested directly in
an instrument that yielded the desired return. Swap agreements are two-party contracts entered into primarily by
institutional investors for periods ranging from a few weeks to more than one year. In a standard "swap" transaction,
the two parties agree to exchange the returns (or differentials in rates of return) earned or realized on particular
investments or instruments. The returns to be exchanged between the parties are calculated with respect to a "notional
amount," i.e., a specified dollar amount that is hypothetically invested at a particular interest rate, in a particular
foreign currency, or in a "basket" of securities representing a particular index. Commonly used swap agreements include
interest rate caps, under which, in return for a premium, one party agrees to make payments to the other to the extent
that interest rates exceed a specified rate or "cap"; interest floors, under which, in return for a premium, one party
agrees to make payments to the other to the extent that interest rates fall below a specified level or "floor"; and
interest rate collars, under which a party sells a cap and purchases a floor or vice versa in an attempt to protect
itself against interest rate movements exceeding given minimum or maximum levels.
Under most swap agreements entered into by the Portfolio, the parties' obligations are determined on a "net
basis." Consequently, the Portfolio's obligations (or rights) under a swap agreement will generally be equal only to a
net amount based on the relative values of the positions held by each party.
Whether the Portfolio's use of swap agreements will be successful will depend on the sub-advisor's ability to
predict that certain types of investments are likely to produce greater returns than other investments. Moreover, the
Portfolio may not receive the expected amount under a swap agreement if the other party to the agreement defaults or
becomes bankrupt. The swaps market is relatively new and is largely unregulated.
ASAF JPM MONEY MARKET FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek high current income and maintain high levels of
liquidity.
Principal Investment Policies and Risks:
As a money market fund, the Fund seeks to maintain a stable net asset value of $1.00 per share. In other words,
the Fund attempts to operate so that shareholders do not lose any of the principal amount they invest in the Fund. Of
course, there can be no assurance that the Fund will achieve its goal of a stable net asset value, and shares of the Fund
are neither insured nor guaranteed by the U.S. government or any other entity. For instance, the issuer or guarantor of
a portfolio security or the other party to a contract could default on its obligation, and this could cause the Fund's
net asset value to fall below $1. In addition, the income earned by the Fund will fluctuate based on market conditions
and other factors.
The Fund invests in its corresponding Portfolio. Under the regulatory requirements applicable to money market
funds, the Portfolio must maintain a weighted average portfolio maturity of not more than 90 days and invest in high
quality U.S. dollar-denominated securities that have effective maturities of not more than 397 days. In addition, the
Portfolio will limit its investments to those securities that, in accordance with guidelines adopted by the Directors of
the Company, present minimal credit risks. The Portfolio will not purchase any security (other than a United States
Government security) unless:
o if rated by only one nationally recognized statistical rating organization (such as Moody's and Standard &
Poor's), such organization has rated it with the highest rating assigned to short-term debt securities;
o if rated by more than one nationally recognized statistical rating organization, at least two rating
organizations have rated it with the highest rating assigned to short-term debt securities; or
o it is not rated, but is determined to be of comparable quality in accordance with procedures noted above.
These standards must be satisfied at the time an investment is made. If the quality of the investment later
declines, the Portfolio may continue to hold the investment, subject in certain circumstances to a finding by the
Trustees that disposing of the investment would not be in the Portfolio's best interest.
Subject to the above requirements, the Portfolio will invest in one or more of the types of investments described
below.
United States Government Obligations. The Portfolio may invest in obligations of the U.S. Government and its
agencies and instrumentalities either directly or through repurchase agreements. U.S. Government obligations include:
(i) direct obligations issued by the United States Treasury such as Treasury bills, notes and bonds; and (ii) instruments
issued or guaranteed by government-sponsored agencies acting under authority of Congress. Some U.S. Government
Obligations are supported by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Treasury; others are supported by the right of the
issuer to borrow from the Treasury; others are supported by the discretionary authority of the U.S. Government to
purchase the agency's obligations; still others are supported only by the credit of the agency. There is no assurance
that the U.S. Government will provide financial support to one of its agencies if it is not obligated to do so by law.
Bank Obligations. The Portfolio may invest in high quality United States dollar-denominated negotiable
certificates of deposit, time deposits and bankers' acceptances of U.S. and foreign banks, savings and loan associations
and savings banks meeting certain total asset minimums. The Portfolio may also invest in obligations of international
banking institutions designated or supported by national governments to promote economic reconstruction, development or
trade between nations (e.g., the European Investment Bank, the Inter-American Development Bank, or the World Bank).
These obligations may be supported by commitments of their member countries, and there is no assurance these commitments
will be undertaken or met.
Commercial Paper; Bonds. The Portfolio may invest in high quality commercial paper and corporate bonds issued by
United States corporations. The Portfolio may also invest in bonds and commercial paper of foreign issuers if the
obligation is United States dollar-denominated and is not subject to foreign withholding tax.
Asset-Backed Securities. As may be permitted by current laws and regulations, the Portfolio may invest in
asset-backed securities up to 10% of its net assets.
Synthetic Instruments. As may be permitted by current laws and regulations and if expressly permitted by the
Trustees of the Trust, the Portfolio may invest in certain synthetic instruments. Such instruments generally involve the
deposit of asset-backed securities in a trust arrangement and the issuance of certificates evidencing interests in the
trust. The Sub-advisor will review the structure of synthetic instruments to identify credit and liquidity risks and
will monitor such risks.
Foreign Securities. Foreign investments must be denominated in U.S. dollars and may be made directly in
securities of foreign issuers or in the form of American Depositary Receipts and European Depositary Receipts.
For more information on certain of these investments, see this Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and
Investment Methods."
PORTFOLIO TURNOVER
Each Non-Feeder Fund and Portfolio may sell its portfolio securities, regardless of the length of time that they
have been held, if the Sub-advisor and/or the Investment Manager determines that it would be in the Fund's or Portfolio's
best interest to do so. It may be appropriate to buy or sell portfolio securities due to economic, market, or other
factors that are not within the Sub-advisor's or Investment Manager's control. Such transactions will increase a Fund's
"portfolio turnover." A 100% portfolio turnover rate would occur if all of the securities in a portfolio of investments
were replaced during a given period.
Although turnover rates may vary substantially from year to year, it is anticipated that the following Portfolios
and Non-Feeder Funds may regularly have annual rates of turnover exceeding 100%.
ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund
ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund
ASMT American Century International Growth Portfolio
ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund
ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund
ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund
ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund
ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund
ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund
ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund
ASMT Janus Capital Growth Portfolio
ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth + Value Fund*
ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond Portfolio
A high rate of portfolio turnover (100% or more) involves correspondingly higher brokerage commission expenses
and other transaction costs, which are borne by a Fund and will reduce its performance. High portfolio turnover rates
may also generate larger taxable income and taxable capital gains, which may increase your tax liability.
*Portfolio turnover for the growth portion of the Fund may exceed 100%.
HOW TO BUY SHARES
MINIMUM INVESTMENTS:
You can open a Fund account with a minimum initial investment of $1,000 in a particular Fund and make additional
investments to the account at any time with as little as $50. The initial investment minimum is reduced to $50 per Fund
through "Automatic Investment Plans," which are discussed in this Prospectus under "Special Investment Programs and
Privileges." Lower minimum initial and additional investments may also be applicable in certain other circumstances,
including purchases by certain tax deferred retirement programs. There is no minimum investment requirement when you are
buying shares by reinvesting dividends and distributions from a Fund.
METHODS OF BUYING SHARES:
Each Fund offers four different classes of shares -- Class A shares, Class B shares, Class C shares and Class X
shares. The different classes of shares represent investments in the same portfolio of securities but are subject to
different sales charges, expenses and, likely, different share prices. When you purchase shares of the Funds, be sure to
specify the class of shares of the Fund(s) you wish to purchase. If you do not choose, your investment will be made in
Class A shares. See below for a detailed description of each class.
You can purchase shares of the Funds through any selling dealer, broker, bank or other financial institution
("dealers"), or directly through the Company. Methods of purchasing shares include:
Buying Shares Through Your Dealer. Your dealer will place your order with the Company on your behalf.
Buying Shares Through the Company. Make your check payable to "American Skandia Advisor Funds, Inc." and mail
your investment, along with your completed account application, to the address indicated on the application. Please
include an investment dealer on the application. If an application is submitted without a dealer listed, American
Skandia Marketing, Incorporated (the "Distributor") will act as your agent in buying the Shares.
Buying Shares Through Wire Transfer. You should instruct your bank to transfer funds by wire to:
ABA # 011000028
State Street Bank & Trust Company
Boston, Massachusetts
DDA # 99052995
FBO: American Skandia Advisor Funds, Inc.
Fund Name and Class of Shares
Shareholder Name and Account Number
Buying Shares Through Bank-Linked Accounts. If you have selected this option on your account application,
you may link your Fund account to your designated bank account electronically. Purchase minimums and sales charges will
apply.
PURCHASE ORDERS:
Purchase orders for the Funds are accepted only on days on which the New York Stock Exchange ("NYSE") is open for
business (a "business day"). Orders received by Boston Financial Data Services, Inc. (the "Transfer Agent") on any
business day prior to the close of trading on the NYSE (normally 4:00 p.m. Eastern Time) will receive the offering price
calculated at the close of trading that day. The offering price is the net asset value ("NAV") plus any initial sales
charge that applies. Orders received by the Transfer Agent after the close of trading on a business day, but prior to
the close of trading on the next business day, will receive the offering price calculated at the close of trading on that
next business day. For a discussion of how NAV is determined, see this Prospectus under "Determination of Net Asset
Value." If you purchase shares through a dealer, your dealer is responsible for forwarding payment promptly to the
Transfer Agent.
The Company, the Distributor or the Transfer Agent reserves the right to reject any order for the purchase of a
Fund's shares. The Company may cancel any purchase order for which payment has not been received by the fifth business
day after placement of the order. Additionally, if the purchase payment does not clear, your purchase will be canceled
and you could be liable for any losses or fees the Fund or the Transfer Agent has incurred. If the Transfer Agent deems
it appropriate, additional documentation for any order may be required, and the order will not be considered to be
received until such additional documentation is received.
PURCHASE OF CLASS A SHARES:
Class A shares (other than Class A shares of the ASAF JPM Money Market Fund) are sold at an offering price that
normally equals NAV plus an initial sales charge that varies depending on the amount of your investment. In certain
instances described below, however, purchases are either not subject to an initial sales charge (and the offering price
will be at NAV) or will be eligible for reduced sales charges. The Fund receives an amount equal to the NAV to invest
for your account. A portion of the sales charge is retained by the Distributor and a portion is allocated to your
dealer. The Distributor may allocate the entire amount of the initial sales charge to dealers for all sales occurring
during a particular period. The current sales charge rates are as follows:
High Yield Bond & Total Return Bond Funds: All Other Funds (other than Money Market
Fund):
Front-end Sales Front-end Sales Front-end Sales Front-end Sales
Charge (as % of Charge (as % of amt. Charge (as % of Charge (as % of amt.
-------- ------------- -------- ------------
offering price) invested) offering price) invested)
--------------- --------- --------------- ---------
Amount of Purchase:
------------------
Less than $50,000 4.25% 4.44% 5.75% 6.10%
$50,000 up to $100,000 3.75% 3.90% 5.00% 5.26%
$100,000 up to $250,000 3.25% 3.36% 4.00% 4.17%
$250,000 up to $500,000 2.25% 2.30% 3.00% 3.09%
$500,000 up to $1 million 1.50% 1.52% 2.25% 2.30%
Class A shares of the ASAF JPM Money Market Fund are sold at their net asset value without an initial sales
charge. However, holders of Class A shares of this Fund may be charged a sales charge when they exchange those shares
for Class A shares of the other Funds. See "How to Exchange Shares" below.
Purchases Subject to a Contingent Deferred Sales Charge ("CDSC"). There is no initial sales charge on purchases
of Class A shares of any one or more of the Funds in the following cases:
o Purchases aggregating $1 million or more;
o Purchases by an employer-sponsored retirement plan under section 403(b) of the Code that features an employer
contribution or "match"; or
o Purchases by an employer-sponsored retirement plan under section 401(a) of the Code (including a 401(k) plan)
with at least 25 eligible employees or that uses the services of a third party administrator that has
established an electronic link with the Company.
However, if such Class A shares are redeemed within 12 months of the first business day of the calendar month of
their purchase, a CDSC ("Class A CDSC") will be deducted from the redemption proceeds. The Class A CDSC will not apply
to redemptions of shares acquired by the reinvestment of dividends or capital gains distributions or redemptions for the
purpose of making distributions or loans to section 401(a) or 403(b)(7) plan participants, and will be waived under
certain circumstances described in the Company's SAI. The Class A CDSC will be equal to 1.0% of the lesser of the
shares' NAV at the time of redemption or the time of purchase. Therefore, any increase in the share price is not subject
to the CDSC. The Class A CDSC is paid to the Distributor to reimburse expenses incurred in providing
distribution-related services to the Fund. To determine whether the Class A CDSC applies to a redemption, the Fund will
first redeem shares acquired by reinvestment of dividends and capital gains distributions, and then will redeem shares in
the order in which they were purchased (such that shares held the longest are redeemed first).
Reduction of Initial Sales Charges for Class A Shares. You may be eligible to buy Class A shares at reduced
initial sales charge rates in one or more of the following ways:
Combined Purchases. Initial sales charge reductions are available by combining into a single
transaction the purchase of Class A shares with the purchase of any other class of shares. Qualifying purchases include
those by you, your spouse and your children under the age of 21 (if all parties are purchasing shares for their own
account), those by certain tax qualified plans such as IRAs, SIMPLE IRAs, individual type 403(b)(7) plans, and single
participant Keogh type plans for the benefit of such individuals, and those by a company controlled by such individuals
Rights of Accumulation. The initial sales charge for your investment in Fund shares may also be reduced
by aggregating the amount of such investment with the current value of all Fund shares currently owned by you at the time
of your current purchase. The rules described above under "Combined Purchases" may apply.
Letter of Intent ("LOI"). You may reduce the initial sales charge rate that applies to your purchases
of Class A shares by meeting the terms of an LOI -- a non-binding commitment to invest a certain amount within a
thirteen-month period from your initial purchase. The total amount of your intended purchases of all Classes of shares
will determine the sales charge rate for Class A shares purchased during that period. This can include purchases made up
to 90 days before the date of the LOI. Part of the LOI amount will be held in escrow to cover additional sales charges
that may be due if your total investments over the LOI period are not sufficient to qualify for the intended sales charge
reduction. The rules described above under "Combined Purchases" may apply.
Waiver of All Class A Sales Charges. No sales charge is imposed on purchases of Class A shares in connection
with various types of transactions and for various types of investors. These sales charge waivers include: (1) shares
purchased by the reinvestment of loan repayments by a participant in a retirement plan; (2) shares purchased by the
reinvestment of distributions received from a Fund; (3) shares purchased and paid for with the proceeds of shares
redeemed in the prior 180 days from a mutual fund on which an initial sales charge or CDSC was paid; (4) purchases by
former participants in a qualified retirement plan, where a portion of the plan was invested in the Company; (5)
purchases by non-qualified deferred compensation plans; (6) purchases under arrangements between the Company and
organizations which make recommendations to or permit group solicitations of its employees, members or participants; (7)
purchases by employees and registered representatives (and their parents, spouses and dependent children) of dealers if
the purchase is for the purchaser's own account (or for the benefit of an employee's parents, spouse, parents of spouse,
or minor children); and (8) purchases by clients of a dealer or other investment professional that has entered into an
agreement with the Distributor providing for the use of Fund shares in investment products or services made available to
its clients (those clients may be charged separate fees by their dealer for the products or services).
In order to receive the above sales charge reductions or waivers, you must notify the Transfer Agent of the
reduction or waiver request when you place your purchase order. The Transfer Agent may require evidence of your
qualification for such reductions or waivers. Additional information about the above sales charge reductions or waivers
can be obtained from the Transfer Agent by calling 1-800-SKANDIA.
PURCHASE OF CLASS B SHARES:
Because in most cases it is more advantageous for an investor to purchase Class A shares for amounts in
excess of $500,000, a request to purchase Class B shares for $500,000 or more will normally be considered as a purchase
request for Class A shares or declined.
Class B shares are sold at NAV per share without an initial sales charge. However, if Class B shares are
redeemed within 7 years of their purchase, a CDSC ("Class B CDSC") will be deducted from the redemption proceeds. The
Class B CDSC will not apply to redemptions of shares purchased by the reinvestment of dividends or capital gains
distributions and may be waived under certain circumstances described below. The charge will be assessed on the lesser
of the shares' NAV at the time of redemption or the time of purchase. Therefore, any increase in the share price is not
subject to the CDSC. The Class B CDSC is paid to the Distributor to reimburse expenses incurred in providing
distribution-related services to the Fund in connection with the sale of Class B shares. The Distributor has assigned
its right to receive any Class B CDSC, as well as any distribution and service fees discussed below under "Distribution
Plans," to a third party that provides funding for the up-front sales concession payments.
To determine whether the Class B CDSC applies to a redemption, the Fund will first redeem shares acquired by
reinvestment of dividends and capital gains distributions, and then will redeem shares in the order in which they were
purchased (such that shares held the longest are redeemed first). The amount of the Class B CDSC will depend on the
number of years since your investment and the amount being redeemed, according to the following schedule:
Redemption During: Class B CDSC (as % of amount subject to charge):
----------------- -----------------------------------------------
1st year after purchase 6.0%
2nd year after purchase 5.0%
3rd year after purchase 4.0%
4th year after purchase 3.0%
5th year after purchase 2.0%
6th year after purchase 2.0%
7th year after purchase 1.0%
8th year after purchase None
For purposes of determining the CDSC, all purchases are considered to have been made on the first business day of
the month in which the purchase was actually made.
Waiver of Class B CDSC. The Class B CDSC will be waived in the following cases if shares are redeemed and the
Transfer Agent is notified: (1) redemptions under a Systematic Withdrawal Plan as described in this Prospectus under
"Special Investment Programs and Privileges"; (2) redemptions to pay premiums for optional insurance coverage described
in this Prospectus under "Special Investment Programs and Privileges"; (3) redemptions following death or post-purchase
disability (as defined by Section 72(m)(7) of the Code); (4) the portion of a mandated minimum distribution from an IRA,
SIMPLE IRA or an individual type 403(b)(7) plan equal to the percentage of your plan assets held in Class B shares of the
Company; (5) the portion of any substantially equal periodic payments (as described in Section 72(t) of the Code) equal
to the percentage of your plan assets held in Class B shares of the Company; and (6) the return of excess contributions
from an IRA or SIMPLE IRA.
Automatic Conversion of Class B Shares. Eight years after you purchase Class B shares of a Fund, those shares
will automatically convert to Class A shares of that Fund. This conversion feature relieves Class B shareholders of the
higher asset-based distribution charge that applies to Class B shares under the Class B Distribution and Service Plan
described below under "Distribution Plans." The conversion is based on the relative NAV of the two classes, and no sales
charge is imposed. At the time of conversion, a portion of the Class B shares purchased through the reinvestment of
dividends or capital gains ("Dividend Shares") will also convert to Class A shares. The portion of Dividend Shares that
will convert is determined by the ratio of your converting Class B non-Dividend Shares to your total Class B non-Dividend
Shares.
PURCHASE OF CLASS X SHARES:
Class X shares are currently only offered to certain "Qualified" purchasers (including, but not limited to, IRAs,
Roth IRAs, Education IRAs, SEP IRAs, SIMPLE IRAs and 403(b)(7) plans). Any request for "Non-Qualified" purchases of
Class X shares up to $500,000 will normally be considered as a purchase request for Class B shares or declined. Any
request for "Non-Qualified" purchases of Class X shares above $500,000 will be considered as a purchase request for Class
A shares or declined. Because it is more advantageous for an investor to purchase Class A shares for amounts in excess
of $1,000,000, a request to purchase Class X shares for $1,000,000 or more will normally be considered as a purchase
request for Class A shares or declined.
Class X shares are sold at NAV per share without an initial sales charge. In addition, investors purchasing
Class X shares will receive, as a bonus, additional shares having a value equal to 2.50% of the amount invested ("Bonus
Shares"). The Distributor pays for the Bonus Shares as part of its services to the Funds. The Distributor expects to
recover the costs of purchasing Bonus Shares through fees received under the Class X Distribution and Service Plan
discussed below. Shares purchased by the reinvestment of dividends or capital gains distributions are not eligible for
Bonus Shares.
Although Class X shares are sold without an initial sales charge, if Class X shares are redeemed within 8 years
of their purchase (7 years in the case of Class X shares purchased prior to August 19, 1998), a CDSC ("Class X CDSC")
will be deducted from the redemption proceeds. The Class X CDSC will not apply to redemptions of Bonus Shares or shares
purchased by the reinvestment of dividends or capital gains distributions and may be waived under certain circumstances
described below. The Class X CDSC will be assessed on the lesser of the NAV of the shares at the time of redemption or
the time of purchase. Therefore, any increase in the share price is not subject to the CDSC. The Class X CDSC is paid
to the Distributor to reimburse expenses incurred in providing distribution-related services to the Fund in connection
with the sale of Class X shares. The Distributor has assigned its right to receive any Class X CDSC, as well as any
distribution and service fees discussed below under "Distribution Plans," to a third party that provides funding for the
up-front sales concession payments.
To determine whether the Class X CDSC applies to a redemption, the Fund first redeems shares not subject to a
CDSC (shares acquired by reinvestment of dividends and capital gains distributions, Bonus Shares, and shares held for
over 8 years) and then redeems other shares in the order they were purchased (such that shares held the longest are
redeemed first). The amount of the Class X CDSC will depend on the number of years since your investment and the amount
being redeemed, according to the following schedule:
Redemption During: Class X CDSC (as % of amount subject to charge):
----------------- -----------------------------------------------
1st year after purchase 6.0%
2nd year after purchase 5.0%
3rd year after purchase 4.0%
4th year after purchase 4.0%
5th year after purchase 3.0%
6th year after purchase 2.0%
7th year after purchase 2.0%
8th year after purchase 1.0%
9th or 10th year after purchase None
For purposes of determining the CDSC, all purchases are considered to have been made on the first business day of
the month in which the purchase was actually made. In the case of Class X shares purchased prior to August 19, 1998, the
CDSC imposed will be 6% during the first year after purchase, 5% during the second year, 4% during the third year, 3%
during the fourth year, 2% during the fifth and sixth years, 1% during the seventh year, and none thereafter.
Waiver of Class X CDSC. The Class X CDSC will be waived in the following cases if shares are redeemed and the
Transfer Agent is notified: (1) redemptions to pay premiums for optional insurance coverage described in this Prospectus
under "Special Investment Programs and Privileges"; (2) redemptions following death or post-purchase disability (as
defined by Section 72(m)(7) of the Code); (3) the portion of a mandated minimum distribution from an IRA, SIMPLE IRA or
an individual type 403(b)(7) plan equal to the percentage of your plan assets held in Class X shares of the Company; (4)
the portion of any substantially equal periodic payments (as described in Section 72(t) of the Code) equal to the
percentage of your plan assets held in Class X shares of the Company; and (5) the return of excess contributions from an
IRA or SIMPLE IRA.
Automatic Conversion of Class X Shares. Ten years after you purchase Class X shares of a Fund (eight years in
the case of Class X shares purchased prior to August 19, 1998), those shares will automatically convert to Class A shares
of that Fund. This conversion feature relieves Class X shareholders of the higher asset-based distribution charge that
applies to Class X shares under the Class X Distribution and Service Plan described below under "Distribution Plans."
The conversion is based on the relative NAV of the two classes, and no sales charge is imposed. At the time of
conversion, a portion of the Class X shares purchased through the reinvestment of dividends or capital gains ("Dividend
Shares") will also convert to Class A shares. The portion of Dividend Shares that will convert is determined by the
ratio of your converting Class X non-Dividend Shares to your total Class X non-Dividend Shares.
PURCHASE OF CLASS C SHARES:
Because it is more advantageous for an investor to purchase Class A shares for amounts in excess of $1,000,000, a
request to purchase Class C shares for $1,000,000 or more will normally be considered as a purchase request for Class A
shares or declined.
Class C shares are sold at an offering price equal to their NAV per share plus an initial sales charge of 1% of
the offering price (1.01% of the amount invested). The Fund receives an amount equal to the NAV to invest for your
account.
If Class C shares are redeemed within 12 months of the first business day of the calendar month of their
purchase, a CDSC ("Class C CDSC") of 1.0% will be deducted from the redemption proceeds. The Class C CDSC will not apply
to redemptions of shares purchased by the reinvestment of dividends or capital gains distributions and will be waived
under certain circumstances described below. The charge will be assessed on the lesser of the NAV of the shares at the
time of redemption or the time of purchase. Therefore, any increase in the share price is not subject to the CDSC. The
Class C CDSC is paid to the Distributor to reimburse its expenses of providing distribution-related services to the Fund
in connection with the sale of Class C shares.
To determine whether the Class C CDSC applies to a redemption, the Fund will first redeem shares acquired by
reinvestment of dividends and capital gains distributions, and then will redeem shares in the order in which they were
purchased (such that shares held the longest are redeemed first).
Waiver of Class C Initial Sales Charge. No initial sales charge is imposed on purchases of Class C shares in
connection with the following types of transactions: (1) purchases by participants in an asset allocation program
sponsored by ASISI or its affiliates; (2) purchases by SIMPLE IRAs; and (3) purchases by employer-sponsored retirement
plans that are not eligible to purchase Class A shares of the Funds without an initial sale charge.
Waiver of Class C CDSC. The Class C CDSC will be waived in the following cases if shares are redeemed and the
Transfer Agent is notified: (1) redemptions under a Systematic Withdrawal Plan as described in this Prospectus under
"Special Investment Programs and Privileges"; (2) redemptions to pay premiums for optional insurance coverage described
in this Prospectus under "Special Investment Programs and Privileges"; (3) redemptions of shares purchased under an asset
allocation program sponsored by ASISI or its affiliates; (4) redemptions following death or post-purchase disability (as
defined by Section 72(m)(7) of the Code); (5) distributions or loans to participants of qualified retirement plans and
other employee benefit plans; (6) the portion of a mandated minimum distribution from an IRA, SIMPLE IRA or an individual
type 403(b)(7) plan equal to the percentage of your plan assets held in Class C shares of the Company; (7) the portion of
any substantially equal periodic payments (as described in Section 72(t) of the Code) equal to the percentage of your
plan assets held in Class C shares of the Company; and (8) the return of excess contributions from an IRA, SIMPLE IRA or
401(k) plan
DISTRIBUTION PLANS:
The Company has adopted a Distribution and Service Plan (commonly known as a "12b-1 Plan") for each Class of
shares to compensate the Distributor for its services and costs in distributing shares and servicing shareholder
accounts. Under the Distribution and Service Plan for Class A shares, the Fund pays the Distributor 0.50% of the Fund's
average daily net assets attributable to Class A shares. Under the Plans for Class B, X and C shares, the Fund pays the
Distributor 1.00% of the Fund's average daily net assets attributable to the relevant Class of shares. Because these
fees are paid out of a Fund's assets on an ongoing basis, these fees may, over time, increase the cost of an investment
in the Fund and may be more costly than other types of sales charges.
The Distributor uses distribution and service fees received under each Plan to compensate qualified dealers for
services provided in connection with the sale of shares and the maintenance of shareholder accounts. In addition, the
Distributor uses distribution and service fees received under the Class X Plans as reimbursement for its purchases of
Bonus Shares.
In addition, the Company has adopted a Supplemental Distribution Plan under Rule 12b-1 and the Trust has adopted
a Distribution Plan under Rule 12b-1 (together, the "Supplemental Plans"). The Supplemental Plans permit the Distributor
to receive brokerage commissions in connection with purchases and sales of securities held by the Funds and Portfolios,
and to use these commissions to promote the sale of shares of the Company. Under the Supplemental Plans, transactions
for the purchase and sale of securities for a Fund or Portfolio may be directed to certain brokers for execution
("clearing brokers") who have agreed to pay part of the brokerage commissions received on these transactions to the
Distributor for "introducing" transactions to the clearing broker. In turn, the Distributor will use the brokerage
commissions received as an introducing broker to pay various distribution-related expenses, such as advertising, printing
of sales materials, and payments to selling dealers. No Fund or Portfolio will pay any new fees or charges resulting
from the Supplemental Plans, nor is it expected that the brokerage commissions paid by a Fund or Portfolio will increase
as the result of implementation of the Supplemental Plans.
SPECIAL INVESTMENT PROGRAMS AND PRIVILEGES
Automatic Investment Plans ("AIP"). You may make regular monthly investments through an automatic withdrawal
from your bank account ($50 minimum per Fund). Sales charges will apply.
Automatic Dividend Reinvestment. Dividend and capital gains distributions can automatically be reinvested in
additional shares at no sales charge.
Automatic Dividend Diversification ("ADD"). You may automatically reinvest dividends and capital gains
distributions paid by one Fund into shares of the same class of another Fund, provided that you have already met that
Fund's minimum initial purchase requirement. No initial sales charge or CDSC will apply to the purchased shares.
Dollar Cost Averaging ("DCA"). You can set up monthly or quarterly exchanges in amounts of $50 or more from one
Fund to the same class of shares of another Fund. You may set up more than one of these programs simultaneously.
Systematic Withdrawal Plan ("SWP"). You may set up monthly, quarterly, semi-annual or annual redemptions from
any account with a value of $5,000 or more. You may direct a Fund to make regular payments in fixed dollar amounts of
$50 or more, in an amount equal to the value of a fixed number of shares (5 shares or more) at the time of withdrawal, or
in an amount equal to a fixed percentage of your account value at the time of withdrawal. Any applicable CDSC will be
waived for shares redeemed under a SWP (other than Class X shares held by shareholders who first purchased Class X shares
after August 18, 1998) where: (i) in the case of SWPs based on a fixed dollar amount or number of shares, SWP redemptions
are limited to no more than 10% annually of your account value or number of shares, respectively, as of the date the
Transfer Agent receives your SWP request; or (ii) in the case of SWPs based on a fixed percentage, each SWP redemption is
limited to an amount that would not exceed 10% on an annualized basis of your account value at the time of withdrawal.
Exchange Privilege. You may exchange your shares of a Fund for shares of the same class of any other Fund. For
complete policies governing exchanges, see this Prospectus under "How to Exchange Shares."
Reinvestment Privilege. If you redeem Class A, B or X shares on which you paid an initial sales charge or a
CDSC, you have up to 180 days to reinvest all or part of the redemption proceeds in Class A shares of the Funds without
paying another sales charge. If you redeem Class C shares on which you paid an initial sales charge you have up to 180
days to reinvest all or part of the redemption proceeds in Class C shares of the Funds without paying another initial
sales charge. You must ask the Transfer Agent for this privilege when you send your payment.
Retirement Plans. Certain classes of Fund shares are available as an investment option for your retirement
plans. A number of different retirement plans can be used by individuals and employers including IRAs, Roth IRAs,
Education IRAs, SEP IRAs, SIMPLE IRAs, 401 plans and 403(b)(7) plans. Please call 1-800-SKANDIA for the applicable plan
documents, which contain important information and applications.
The above programs and privileges may be selected at the time of your initial investment or at a later date.
Optional Benefits. American Skandia Life Assurance Corporation ("ASLAC") -- an "affiliated person" of the
Company under the 1940 Act -- intends to make certain life insurance coverage available to certain persons on whose
behalf shares are purchased. The benefits of this coverage, which are payable at death, will be related to the amounts
paid to purchase shares and to the value of the shares held. Therefore, coverage will terminate if all shares are
redeemed.
Purchasers of the life insurance coverage are required to authorize periodic redemptions of Fund shares to pay
the premiums for such coverage. These redemptions will not be subject to contingent deferred sales charges, but will
have the same tax consequences as any other Fund redemptions.
The life insurance coverage will be available to eligible persons who enroll for the coverage within a limited
time period after shares of the Company are first held for the person's benefit. In addition, coverage cannot be made
available unless ASLAC knows for whose benefit shares are purchased. For instance, coverage cannot be made available for
shares registered in the name of your broker unless the broker provides ASLAC with information regarding the beneficial
owners of such shares. Other restrictions on the coverage will apply, such as the age of the persons upon whose life the
coverage is issued. This insurance coverage may not be available in all states and may be subject to additional
restrictions or limitations on coverage. Purchasers of shares should also make themselves familiar with the impact on
the life coverage of purchasing additional shares, reinvestment of dividends and capital gains distributions and
redemptions.
Please call 1-800-SKANDIA for more information and application forms for any of the above programs and privileges.
HOW TO REDEEM SHARES
You can arrange to take money out of your Fund account on any business day by redeeming some or all of your
shares. Your shares will be sold at the next NAV calculated after your order is received in good order. The Company
offers you a number of ways to sell your shares, including in writing, by telephone, by Automated Clearing House ("ACH")
bank transfer or by wire transfer. You can also set up a Systematic Withdrawal Plan to redeem shares on a regular basis
(as described in this Prospectus under "Special Investment Programs and Privileges").
If you hold Fund shares through a retirement account, call the Transfer Agent in advance for additional
information and any necessary forms. There are special income tax withholding requirements for distributions from
retirement plans and you must submit a withholding form with your request. If your retirement plan account is held for
you by your employer, you must arrange for the distribution request to be sent by the plan administrator or trustee.
Redeeming Shares by Mail:
If you want to redeem your shares by mail, write a "letter of instruction" that includes the following
information:
o Your name
o Fund's name
o Your Fund account number (from your account statement)
o Dollar amount or number of shares to be redeemed
o Any special payment instructions
o Signatures of all registered owners exactly as the account is registered
o Any special requirements or documents requested by the Transfer Agent to assure proper authorization of the
person requesting the redemption
Send Requests by Regular Mail to: Send Requests by Courier or Express Mail to:
American Skandia Advisor Funds, Inc. American Skandia Advisor Funds, Inc.
P.O. Box 8012 66 Brooks Drive
Boston, Massachusetts 02266-8012 Braintree, Massachusetts 02184
Redeeming Shares by Telephone:
You may also redeem shares by telephone by calling 1-800-SKANDIA. To receive the redemption price calculated on
the business day that you call, your call must be received by the Transfer Agent before the close of the NYSE that day,
which is normally 4:00 P.M. Eastern Time. Shares held in tax-qualified retirement plans may not be redeemed by
telephone. You may have a check sent to the address on the account statement, or, if you have linked your Fund account
to your bank account, you may have the proceeds transferred to that bank account.
Telephone Redemptions Paid By Check. You may make one redemption request by telephone in any 7-day period for
any amount up to $50,000. The check must be payable to all owners of record of the shares and must be sent to the
address on the account. This service is not available within 30 days after changing the address on an account.
Telephone Redemptions Through Bank-Linked Accounts. If you have selected this option on your account
application, you may link your Fund account to your designated bank account electronically. You can redeem Fund shares
in amounts as little as $50 or as much as $50,000 using the ACH network to have funds transferred to your bank account.
Normally, the transfer to your bank is initiated on the business day after the redemption.
Redeeming Shares Through Your Broker:
The Distributor has made arrangements to redeem Fund shares upon orders from brokers on behalf of their customers
at the offering price next determined after receipt of the order. Brokers may charge for this service.
CHECKWRITING:
After completing the appropriate authorization form, holders of Class A and Class C shares of the ASAF JPM Money
Market Fund may redeem those shares by check. You must own shares of the Fund with a total value of at least $5,000 in
order to establish this checkwriting option for your account, and checks must be written for at least $500. Shareholders
with joint accounts may authorize each owner to write checks. The person to whom a check is made payable may cash or
deposit it in the same way as an ordinary bank check.
Of course, checks cannot be paid if they are written for more than the account value of your ASAF JPM Money
Market Fund shares. To avoid dishonor of checks due to fluctuations in account value, shareholders are advised against
redeeming all or most of their account by check. You may not write a check that would require the Fund to redeem shares
that were purchased by check within the prior 15 days. There is presently no charge for checkwriting privileges, but the
Fund or the Transfer Agent may impose such charges in the future or may modify or terminate the privilege. Any
applicable CDSC will be deducted when a check is paid.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION:
To protect you and the Funds from fraud, redemption requests must be in writing and must include a signature
guarantee in the following situations (the Company or the Transfer Agent may require a signature guarantee in other
situations at their discretion):
o You wish to redeem more than $50,000 worth of shares and receive a check
o A redemption check is not payable to all shareholders listed on the account statement
o A redemption check is not sent to the address of record on your statement
o Shares are being transferred to a Fund account with a different owner or name
o Shares are redeemed by someone other than the owners (such as an Executor)
The Transfer Agent may delay forwarding a check or processing a payment via bank-linked account for the sale of
recently purchased shares, but only until the purchase payment has cleared. Such delay may be as long as 15 calendar
days from the date the shares were purchased, and may be avoided if you purchase shares by certified check. You may be
charged a fee of up to $10 for wire transfers of redemption proceeds, which will be deducted from such proceeds. There
is no fee for ACH wire transfers.
If you have any questions about any of the above procedures, and especially if you are redeeming shares in a
special situation, such as due to the death of the owner or from a retirement plan, please call 1-800-SKANDIA for
assistance.
HOW TO EXCHANGE SHARES
Except as described below, shares of a Fund may be exchanged for shares of the same class of other Funds at NAV
per share at the time of exchange. Exchanges of shares involve a redemption of the shares of the Fund you own and a
purchase of shares of another Fund. Shares are normally redeemed and purchased in the exchange transaction on the
business day on which the Transfer Agent receives an exchange request that is in proper form, if the request is received
by the close of the NYSE that day. You should consider the differences in investment objectives and expenses between the
Funds before making an exchange. Exchanges may be taxable transactions and may be subject to special tax rules about
which you should consult your tax adviser.
You may exchange your Fund shares (other than Class A shares of the ASAF JPM Money Market Fund) for shares of any
other Fund without a sales charge. If you exchange such shares for shares of another Fund, any applicable CDSC and the
date for automatic conversion of Class B and Class X shares to Class A shares will be calculated based on the date on
which you acquired the original shares. Investors will not receive Bonus Shares on Class X shares obtained through an
exchange.
Exchanges of Class A shares of the ASAF JPM Money Market Fund on which an initial sales charge has not been paid
for Class A shares of any other Fund are subject to the initial sales charge applicable to the other Fund. Class A
shares of the Money Market Fund acquired by exchange of Class A shares of another Fund are exchanged at NAV.
Exchanges may be requested in writing, by telephone or by other means acceptable to the Company. For written
exchange requests you should submit a letter of instruction, signed by all owners of the account, to the Transfer Agent
at P.O. Box 8012, Boston, Massachusetts 02266-8012. To initiate a telephone exchange, you should call 1-800-SKANDIA.
All exchanges are subject to the following restrictions:
o You may exchange only between Funds that are registered in the same name, address and taxpayer identification
number.
o You may only exchange for shares of the same class of another Fund.
o You must meet the minimum purchase requirements for the Fund you purchase by exchange.
The Company may refuse or delay exchanges by any person or group if, in the Investment Manager's judgment, a Fund
would be unable to invest the money effectively in accordance with its investment objective and policies, or a Fund would
otherwise potentially be adversely affected. Your exchanges may also be restricted or refused if a Fund receives or
anticipates simultaneous orders affecting significant portions of the Fund's assets. In particular, the amount, frequency
and pattern of exchanges that a shareholder engages in may be determined to be excessive trading or "market timing" that
is detrimental to the Company and other shareholders. If this occurs, the Company may terminate the availability of
exchanges to that shareholder and may bar that shareholder from purchasing other Funds. Although the Company will
attempt to give you prior notice whenever it is reasonably able to do so, it may impose these restrictions at any time.
Each Fund reserves the right to terminate or modify the exchange privilege in the future.
DETERMINATION OF NET ASSET VALUE
The net asset value ("NAV") per share is determined for each class of shares for each Fund as of the close of the
NYSE (normally 4:00 p.m. Eastern Time) on each business day (as previously defined under "How to Buy Shares: Purchase
Orders") by dividing the value of the Fund's total assets attributable to a class, less any liabilities, by the number of
total shares of that class outstanding. In general, the assets of each Non-Feeder Fund and Portfolio (except the ASMT
JPM Money Market Portfolio) are valued on the basis of market quotations. However, in certain circumstances where market
quotations are not readily available or where market quotations for a particular security or asset are believed to be
incorrect, securities and other assets are valued by methods that are believed to accurately reflect their fair value.
The assets of the ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio are valued by the amortized cost method, which is intended to
approximate market value. Because NAV is calculated and purchases may be made only on business days, and because
securities traded on foreign exchanges may trade on other days, the value of a Fund or Portfolio's investments may change
on days when you will not be able to purchase or redeem shares.
SHAREHOLDER ACCOUNT RULES AND POLICIES
o The offering of any class of Fund shares may be suspended when the determination of NAV is suspended, and
may be suspended or terminated by the Directors of the Company at any time they believe it is in a Fund's best interest
to do so.
o Telephone transaction privileges or privileges using electronic means for purchases, redemptions or
exchanges may be modified, suspended or terminated by a Fund at any time. If an account has more than one owner, the
Fund and the Transfer Agent may rely on the instructions of any one of the owners or the dealer representative of record
for the account unless an owner instructs the Transfer Agent otherwise. The Transfer Agent will record any telephone
calls to verify data concerning transactions and has adopted other procedures to confirm that telephone or electronic
instructions are genuine. If the Company does not use reasonable procedures, the Company or its agents may be liable for
losses due to unauthorized transactions, but otherwise the Company or its agents will not be liable for losses or
expenses arising out of telephone instructions or instructions received by electronic means that they reasonably believe
to be genuine. If you are unable to reach the Transfer Agent during periods of unusual market activity, you may not be
able to complete a telephone transaction and should consider placing your order by mail.
o Purchase, redemption or exchange requests will not be honored until the Transfer Agent receives all required
documents in proper form.
o In certain instances, purchase, redemption and exchange requests received by the Transfer Agent from a
dealer or other intermediary after the close of trading on a business day or on the next business day will be effected at
the offering price calculated as of the close of trading on the first business day if the dealer or intermediary received
the order prior to the close of trading on the first business day and has been authorized by the Company to transmit such
requests at the later time.
o There are no share certificates for the Company's shares.
o Dealers that can perform account transactions for their clients through the National Securities Clearing
Corporation are responsible for obtaining their clients' permission to do so and are responsible to their clients if they
perform any transaction erroneously or improperly.
o All purchases must be made in U.S. dollars and checks must be drawn on U.S. banks. You may not purchase
shares with a third-party check.
o Payment for redeemed shares is ordinarily forwarded within 7 calendar days after the business day on which
the Transfer Agent receives the redemption request in proper form. Payment will be forwarded within 3 business days for
accounts registered in the name of a dealer. Redemptions may be suspended or payment dates postponed when the NYSE is
closed (other than weekends or holidays), when trading is restricted or as permitted by the Securities and Exchange
Commission.
o A Fund may redeem small accounts without a shareholder request if the account value has fallen below $500
(for reasons other than a drop in market value of shares) and at least 30 days notice has been given to the shareholder.
No CDSC will be charged on such redemptions.
o Under unusual circumstances shares of a Fund may be redeemed "in kind," which means that the redemption
proceeds will be paid with securities from the Fund's portfolio of securities.
o "Backup withholding" of Federal income tax may be applied at the rate of 31% from dividends, distributions
and redemption proceeds (including exchanges) if you fail to furnish the Fund a Social Security or Employer
Identification Number when you sign your application, or if you violate Internal Revenue Service regulations on the
reporting of income.
SPECIAL INFORMATION ON THE
"MASTER/FEEDER" FUND STRUCTURE
An investor in the Feeder Funds should be aware that these Funds, unlike mutual funds that directly acquire and
manage their own portfolios of securities, seek to achieve their investment objectives by investing all of their
investable assets in a corresponding Portfolio of the Trust (although each Feeder Fund may temporarily hold small amounts
of cash). The Portfolios of the Trust, which have the same investment objective, policies and limitations as their
corresponding Feeder Funds, in turn invest their assets directly in a portfolio of securities. Therefore, each of the
Feeder Funds acquires an indirect interest in the securities owned by its corresponding Portfolio.
Members of the general public may not purchase a direct interest in a Portfolio of the Trust. However, in
addition to selling an interest to its corresponding Feeder Fund, each Portfolio may sell interests to other affiliated
and non-affiliated investment companies and/or institutional investors. Such investors will invest in a Portfolio on the
same terms and conditions as the corresponding Feeder Fund and will pay a proportionate share of the Portfolio's
expenses. Other investors in a Portfolio, however, are not required to sell their shares to the public at the same price
as the corresponding Feeder Fund, and may have different sales commissions and operating expenses. These differences may
result in differences in returns among the investment companies that invest exclusively in the Portfolios. Currently, of
the investment companies that invest in the Portfolios, only shares of the Feeder Funds may be purchased by the general
public in the United States.
The Directors of the Company believe that the "master/feeder" fund structure offers opportunities for substantial
growth in the assets of the Portfolios that may enable the Portfolios to reduce their operating expenses, thereby
producing higher returns and benefiting the shareholders of the Feeder Funds. A Feeder Fund's investment in its
corresponding Portfolio may, however, be adversely affected by the actions of other investors in the Portfolio. For
example, if a large investor withdraws from a Portfolio, the remaining investors may bear higher pro rata operating
expenses. However, this possibility also exists for traditionally structured funds with large investors.
Each of the Feeder Funds may withdraw (completely redeem) all of its assets from its corresponding Portfolio at
any time if the Directors of the Company determine that it is in the best interest of the Fund to do so. A Feeder Fund
might withdraw, for example, if other investors in the Fund's corresponding Portfolio voted to, by a vote of all
investors in the Portfolio (including the Fund), change the investment objective, policies or limitations of the
Portfolio in a manner not acceptable to the Directors of the Company. The withdrawal of all a Feeder Fund's assets from
a corresponding Portfolio may affect the investment performance of the Feeder Fund. If the Directors of the Company
determine that a Feeder Fund should withdraw all of its assets from its corresponding Portfolio, the Directors would
consider what action should be taken, including investing all of the Fund's assets in another pooled investment entity or
retaining an investment adviser to manage the Fund's assets directly.
Investor Meetings and Voting. Each Portfolio normally will not hold meetings of investors except as required by
the 1940 Act. Each investor in a Portfolio (including a Feeder Fund) will be entitled to vote in proportion to its
interest in the Portfolio. When a Feeder Fund is requested to vote on matters pertaining to a Portfolio, the Fund will
hold a meeting of its shareholders and will vote its interest in the Portfolio for or against such matters
proportionately to the instructions to vote for or against such matters received from Fund shareholders.
MANAGEMENT OF THE FUNDS
THE INVESTMENT MANAGER:
American Skandia Investment Services, Incorporated ("ASISI," as previously defined), One Corporate Drive,
Shelton, Connecticut 06484, acts as investment manager to each of the Non-Feeder Funds and Portfolios pursuant to
separate investment management agreements with the Company and the Trust, respectively (the "Management Agreements").
Because each of the Feeder Funds invests all of its investable assets in a corresponding Portfolio of the Trust, the
Feeder Funds do not require an investment manager. In addition to serving as investment manager to the Company and the
Trust, ASISI has served since 1992 as the investment manager to American Skandia Trust, an investment company whose
shares are made available to life insurance companies writing variable annuity contracts and variable life insurance
policies.
The Management Agreements provide that ASISI will furnish each Non-Feeder Fund and Portfolio with investment
advice and investment management and administrative services subject to the supervision of the Directors of the Company
or the Trustees of the Trust, and in conformity with the stated investment objectives, policies and limitations of the
applicable Fund or Portfolio. The Investment Manager is responsible for monitoring the activities of the Sub-advisors it
engages to manage the Non-Feeder Funds and Portfolios and reporting on such activities to the Directors of the Company or
the Trustees of the Trust. The Investment Manager must also provide, or obtain and supervise, the executive,
administrative, accounting, custody, transfer agent and shareholder servicing services that are deemed advisable by the
Directors or the Trustees.
The Company, the Trust, and American Skandia Investment Services, Incorporated ("ASISI") have obtained an exemption from
the Securities and Exchange Commission that permits ASISI to change sub-advisors for a Fund or Portfolio and to enter
into new sub-advisory agreements, without obtaining shareholder approval of the changes. Any such Sub-advisor change
would continue to be subject to approval by the Board of Directors of the Company or the Board of Trustees of the Trust,
as appropriate. This exemption (which is similar to exemptions granted to other investment companies that are operated
in a similar manner as the Company and the Trust) is intended to facilitate the efficient supervision and management of
the Sub-advisors by ASISI and the Directors of the Company and the Trustees of the Trust.
THE SUB-ADVISORS:
ASISI currently engages the following Sub-advisors to manage the investments of each Non-Feeder Fund and
Portfolio in accordance with the Fund or Portfolio's investment objective, policies and limitations and any investment
guidelines established by the Investment Manager. Each Sub-advisor is responsible, subject to the supervision and
control of the Investment Manager, for the purchase, retention and sale of securities in the Fund or Portfolio's
investment portfolio under its management.
Unless otherwise noted, each portfolio manager listed below has managed his or her respective Fund or Portfolio's
investment portfolio since its inception.
Founders Asset Management LLC ("Founders") serves as Sub-advisor for the ASAF Founders International Small
Capitalization Fund. Founders, located at Founders Financial Center, 2930 East Third Avenue, Denver, Colorado 80206, and
its predecessor companies have acted as investment advisors since 1938 and serves as investment advisor to a number of
other investment companies and private accounts. Founders managed assets aggregating approximately $[insert] billion as
of December 31, 2000.
Tracy P. Stouffer, a Vice President of Investments of Founders and Chartered Financial Analyst, has been
responsible for the day-to-day management of the ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund since July 1999.
Before joining Founders, Ms. Stouffer was a vice president and portfolio manager with Federated Global Incorporated from
1995 until July 1999.
A I M Capital Management, Inc. ("AIM"), 11 Greenway Plaza, Suite 100, Houston, Texas 77046-1173, serves as
Sub-advisor for the ASAF AIM International Equity Fund. AIM has acted as an investment advisor since 1986 and, together
with its parent, A I M Advisors, Inc., advises or manages over 125 investment portfolios encompassing a broad range of
investment objectives. As of December 31, 2000, AIM managed approximately $[insert] billion in assets.
AIM uses a team approach to investment management. The members of the team responsible for the management of the
ASAF AIM International Equity Fund are A. Dale Griffin, III, Clas G. Olsson, Barrett K. Sides and Jason Holzer. Except
for Mr. Holzer, all members of the team are officers of AIM. Mr. Griffin, Senior Portfolio Manager, has been associated
with AIM and/or its affiliates since 1989. Mr. Olsson, Portfolio Manager, has been associated with AIM and/or its
affiliates since 1994. Mr. Sides, Senior Portfolio Manager, has been associated with AIM and/or its affiliates since
1990. Mr. Holzer, Senior Portfolio Manager, has been associated with AIM and/or its affiliates since 1996. From 1994 to
1996, he was an associate with JMB Realty.
Janus Capital Corporation ("Janus") serves as Sub-advisor for the ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund, the ASAF Janus
Small-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund and the ASMT Janus Capital Growth Portfolio. Janus, located at
100 Fillmore Street, Denver, Colorado 80206-4923, serves as the investment advisor to the Janus Funds, as well as advisor
or sub-advisor to several other mutual funds and individual, corporate, charitable and retirement accounts. As of
December 31, 2000, Janus managed assets worth approximately $[insert] billion.
The portfolio managers responsible for management of the ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund are Helen Young Hayes,
CFA and Laurance Chang, CFA. Ms. Hayes has been managing the Fund since its inception, while Mr. Chang has been managing
the Fund since January 2000. Ms. Hayes is a Vice President of Janus and joined Janus in 1987. Mr. Chang is a Vice
President of Janus and joined Janus in 1993.
The ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund is managed by William H. Bales. Mr. Bales has managed the Fund since Janus
became the Fund's Sub-advisor in January, 1999. Mr. Bales has been a Portfolio Manager with Janus since 1997 and a
research analyst since 1993. He joined Janus in 1991.
The portfolio manager responsible for management of the ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund is Matthew A. Ankrum,
CFA. Mr. Ankrum, who has managed the Fund since its inception, joined Janus as an intern in June 1996 and became an
equity research analyst in August 1997.
The portfolio manager responsible for management of the ASMT Janus Capital Growth Portfolio is Scott W.
Schoelzel. Mr. Schoelzel, a Senior Portfolio Manager at Janus who has managed the Portfolio since August, 1997, joined
Janus in January, 1994 as Vice President of Investments.
American Century Investment Management, Inc. ("American Century") serves as Sub-advisor for the ASMT American
Century International Growth Portfolio and the ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund. American Century, located
at American Century Towers, 4500 Main Street, Kansas City, Missouri 64111, has been providing investment advisory
services to investment companies and institutional clients since 1958. As of December 31, 2000, American Century and its
affiliates managed assets totaling approximately $[insert] billion.
American Century utilizes a team of portfolio managers, assistant portfolio managers and analysts acting together to
manage the assets of the ASMT American Century International Growth Portfolio and the ASAF American Century Strategic
Balanced Fund.
The portfolio manager members of the portfolio team responsible for management of the ASMT American Century
International Growth Portfolio are Henrik Strabo and Mark S. Kopinski. Henrik Strabo joined American Century in 1993 as
an investment analyst, has been a portfolio manager member of the international team since 1994 and has managed the Fund
since American Century became the Fund's Sub-advisor in May 2000. Mark S. Kopinski, Vice President and Portfolio Manager
for American Century, rejoined American Century in April 1997 and has co-managed the Fund since American Century became
the Fund's Sub-advisor. From June 1995 to March 1997, Mr. Kopinski served as Vice President and Portfolio Manager for
Federated Investors, Inc. Prior to June 1995, Mr. Kopinski was a Vice President and Portfolio Manager for American
Century.
The portfolio manager members of the portfolio team responsible for the day-to-day management of the equity
portion of the ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund are John Schniedwind, Kurt Borgwardt, Jeffrey R. Tyler and
William Martin. Mr. Schniedwind is Senior Vice President and Group Leader -- Quantitative Equity for American Century,
and has been with American Century since 1982. Mr. Borgwardt is Vice President, Portfolio Manager and Director of
Quantitative Equity Research for American Century, and has been with American Century since 1990. Mr. Tyler, Senior Vice
President and Portfolio Manager, joined American Century in 1988. William Martin, Vice President and Senior Portfolio
Manager, joined American Century in 1989. The fixed income portion of the Fund is managed by a team of portfolio
managers with expertise in different areas of fixed income investing. The portfolio manager leader of the team
responsible for the day-to-day management of the fixed income portion of the Fund is Brian Howell. Mr. Howell joined
American Century in 1987 as a research analyst and was promoted to his current position as portfolio manager in January
1994.
Zurich Scudder Investments, Inc. ("Zurich Scudder"), 345 Park Avenue, New York, New York, serves as Sub-advisor
of the ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund. Zurich Scudder is one of the largest investment managers in the country with
approximately $[insert] billion under management as of December 31, 2000 and has been engaged in the management of
investment funds for more than seventy years.
Peter Chin, CFA is the lead portfolio manager for the Fund, and Roy C. McKay, CFA is the other portfolio
manager. Both have managed the Fund since its inception. Mr. Chin is a Managing Director of Zurich Scudder and has been
with the firm since 1973. Mr. McKay is a Manager Director of Zurich Scudder and has been with the firm since 1988.
GAMCO Investors, Inc. ("GAMCO"), with principal offices located at One Corporate Center, Rye, New York
10580-1434, serves as Sub-advisor to the ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund and the ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund.
GAMCO managed approximately $[insert] billion in assets as of December 31, 2000 and is a wholly-owned subsidiary of
Gabelli Asset Management Inc.
Mario J. Gabelli, CFA, is primarily responsible for the day-to-day management of the ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value
Fund and the ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund. Mr. Gabelli has been Chief Executive Officer and Chief Investment Officer
of GAMCO and its predecessor since the predecessor's inception in 1978.
Neuberger Berman Management Inc. ("NB Management") serves as sub-advisor for the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap
Growth Fund and the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund. NB Management and its predecessor firms have specialized
in the management of mutual funds since 1950. Neuberger Berman, LLC ("Neuberger Berman"), an affiliate of NB Management,
acts as a principal broker in the purchase and sale of portfolio securities for the Funds for which it serves as
Sub-advisor, and provides NB Management with certain assistance in the management of the Funds without added cost to the
Funds or ASISI. Neuberger Berman and its affiliates manage securities accounts, including mutual funds, that had
approximately $[insert] billion of assets as of December 31, 2000.
Jennifer K. Silver and Brooke A. Cobb are primarily responsible for the day-to-day management of the ASAF
Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund. Ms. Silver is Director of the Neuberger Berman Growth Equity Group, and both she
and Mr. Cobb are Vice Presidents of NB Management. Ms. Silver is a principal of Neuberger Berman. Previously, Ms.
Silver was a portfolio manager for several large mutual funds managed by a prominent investment adviser. Mr. Cobb was
the chief investment officer for an investment advisory firm managing individual accounts from 1995 to 1997.
Robert I. Gendelman and S. Basu Mullick are primarily responsible for the day-to-day management of the ASAF
Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund. Mr. Gendelman has been managing the Fund since its inception, while Mr. Mullick has
been managing the Fund since October 1998. Mr. Gendelman has been with NB Management since 1994, where he is currently a
Vice President. Mr. Mullick has been a Vice President of NB Management since October 1998. From 1993 to 1998, Mr.
Mullick was a portfolio manager for a prominent investment adviser.
Fred Alger Management, Inc. ("Alger"), One World Trade Center, Suite 9333, New York, New York 10048, serves as
Sub-advisor for the ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund. Alger has been an investment advisor since 1964, and as of December
31, 2000 managed mutual fund and other assets totaling approximately $[insert] billion.
The portfolio managers responsible for the management of this Fund are David Alger and Seilai Khoo. Mr. Alger
has managed the Portfolio since its inception, while Ms. Khoo has been managing the Fund since June 2000. Mr. Alger has
been employed by Alger since 1971 and served as Executive Vice President and Director of Research prior to being named
President in 1995. Ms. Khoo has been employed by Alger since 1989, and has been a Senior Vice President and Portfolio
Manager since 1995.
INVESCO Funds Group, Inc. ("INVESCO") serves as Sub-advisor for the ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund, ASAF Health
Sciences Fund and the ASMT INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio. INVESCO, located at 7800 East Union Avenue, P.O. Box 173706,
Denver, Colorado 80217-3706, was established in 1932. AMVESCAP PLC, the parent of INVESCO, is one of the largest
independent investment management businesses in the world and managed over $[insert] billion of assets as of December 31,
2000.
The portfolio manager responsible for the day-to-day management of the ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund is William R.
Keithler, CFA. Mr. Keithler joined INVESCO in January 1999 and is a Senior Vice President of INVESCO. From 1993 until
1998, Mr. Keithler was a portfolio manager with Berger Associates, Inc.
The portfolio managers responsible for the day-to-day management of the ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund are
John R. Schroer and Thomas R. Wald. Mr. Schroer, Director of Research and a Senior Vice President of INVESCO, joined
INVESCO in 1992. Mr. Wald joined INVESCO in January 1997 and is a Vice President of INVESCO. From 1995 until 1996, Mr.
Wald was an analyst with Munder Capital Management.
The portfolio managers responsible for the day-to-day management of the ASMT INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio are
Charles P. Mayer, Portfolio Co-Manager, and Donovan J. (Jerry) Paul, Portfolio Co-Manager. Mr. Mayer began his
investment career in 1969 and is now a director and a senior vice president of INVESCO. Mr. Paul entered the investment
management industry in 1976 and has been a senior vice president of INVESCO since 1994.
Rydex Global Advisors ("Rydex"), 6116 Executive Boulevard, Suite 400, Rockville, Maryland 20852, serves as
Sub-advisor for the ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund. As of December 31, 2000, Rydex managed approximately $[insert] billion
in net assets.
The portfolio manager responsible for management of the ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund is Michael P. Byrum. Mr.
Byrum is a Vice President and a senior portfolio manager who joined Rydex in 1993.
Alliance Capital Management, L.P. ("Alliance"), 1345 Avenue of the Americas, New York, NY 10105, serves as
Sub-advisor for the ASAF Alliance Growth Fund and ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund and for the portion of the ASAF
Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth + Value Fund invested in growth stocks. Alliance is a leading international investment
adviser supervising client accounts with assets as of December 31, 2000 totaling more than $[insert] billion (of which
more than $185 billion represented assets of investment companies).
Alfred Harrison and James G. Reilly have been the individuals primarily responsible for the management of the
ASAF Alliance Growth Fund since Alliance became the Portfolio's Sub-advisor in May 2000. Mr. Harrison is Vice Chairman
of Alliance Capital Management Corporation ("ACMC"), the sole general partner of Alliance, and has been associated with
Alliance since 1978. Mr. Reilly is Executive Vice President of ACMC and has been associated with Alliance since 1984.
Paul Rissman and Frank Caruso have been primarily responsible for the management of the ASAF Alliance Growth and
Income Fund since Alliance became the Portfolio's Sub-advisor in May 2000. Mr. Rissman has been Senior Vice President of
ACMC since 1994 and has been associated with Alliance since 1989. Mr. Caruso is a Senior Vice President of ACMC and has
been associated with Alliance since 1994.
Day to day investment decisions for the growth portion of the ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth +Value Fund
will be made by Alfred Harrison and Stephanie Simon. Mr. Harrison is Vice Chairman of ACMC, the sole general partner of
Alliance, and has been associated with Alliance since 1978. Ms. Simon is Vice President and Large Cap Portfolio Manager
and joined ACMC in 1998 after serving as Chief Investment Officer for Sargent Management Company from 1996 to 1998.
T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc. ("T. Rowe Price") serves as Sub-advisor for the ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed
Fund. T. Rowe Price, located at 100 East Pratt Street, Baltimore, Maryland 21202, was founded in 1937 by the late Thomas
Rowe Price, Jr. As of June 30, 2000, T. Rowe Price and its affiliates managed approximately $179 billion for
approximately eight million individual and institutional accounts.
The ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax-Efficient Growth Fund is managed by an Investment Advisory Committee. Douglas J.
Peters, Committee Chairman, has day-to-day responsibility for managing the Fund and works with the Committee in
developing and executing the Fund's investment program. Mr. Peters joined T. Rowe Price in 1993 and has been managing
investments since 1993.
Marsico Capital Management, LLC ("Marsico Capital"), 1200 17th Street, Suite 1300, Denver, CO 80202, serves as
Sub-advisor for the ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund. Thomas F. Marsico has primary responsibility for management of the
Fund. Mr. Marsico is Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, and has sole voting control, of Marsico Capital. Prior to
forming Marsico Capital in September, 1997, Mr. Marsico served as Executive Vice President and Portfolio Manager at Janus
Capital Corporation ("Janus"). Mr. Marsico joined Janus in March, 1986. As of December 31, 2000, Marsico Capital
managed more than $[insert] billion in assets.
Sanford C. Bernstein & Co., LLC ("Bernstein"), 767 Fifth Avenue, New York, New York 10153, serves as Sub-advisor
for the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund, ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund and for the portion of the
ASAF Alliance/Bernstein Growth & Value Fund invested in value stocks. Bernstein is an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary
of Alliance Capital Management, L.P. ("Alliance") and management of the Funds are conducted by Bernstein with the
investment management assistance of the Bernstein Investment Research and Management unit (the "Bernstein Unit") of
Alliance. The Bernstein Unit services the former investment research and management business of Sanford C. Bernstein &
Co., Inc., a registered investment advisor and broker/dealer acquired by Alliance in October 2000 that managed
value-oriented investment portfolios since 1967.
Day-to-day investment management decisions for the value portion of the ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth +
Value Fund and the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund will be made by Lewis A. Sanders and Marilyn Goldstein Fedak.
Mr. Sanders is the Chairman and a Director of Bernstein since September 2000 and is a Vice Chairman, Chief Investment
Officer and a Director of Alliance Capital Management Corporation since October 2000. Mr. Sanders previously served as
Chairman of the Board of Directors and Chief Executive Officer of Sanford C. Bernstein & Co., Inc. since 1993. Ms.
Fedak, Executive Vice President and Chief Investment Officer- U.S. Value Equities of Alliance since October 2000 and
prior to that Chief Investment Officer and Chairman of the U.S. Equity Investment Policy Group at Sanford C. Bernstein &
Co, Inc. since 1993.
Day-to-day investment management decisions for the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund will be made by
Bernstein's Investment Policy Group for Structured Equities, which is chaired by Steven Pisarkiewicz. Mr. Pisarkiewicz
joined Bernstein in 1989 and assumed his current position as Chief Investment Officer for Structured Equity Services in
1998. Mr. Pisarkiewicz and the Investment Policy Group for Structured Equities have managed the Fund since Bernstein
became the Fund's Sub-advisor in May, 2000.
Massachusetts Financial Services Company ("MFS") serves as Sub-advisor for the ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund.
MFS, which is located at 500 Boylston Street, Boston, Massachusetts 02116, and its predecessor organizations have a
history of money management dating from 1924. As of December 31, 2000, the net assets under the management of the MFS
organization were approximately $[insert] billion.
The ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund is managed by John D. Laupheimer and Mitchell D. Dynan. Mr. Laupheimer is a
Senior Vice President of MFS, and has been employed by MFS in the investment management area since 1981. Mr. Dynan is
also a Senior Vice President of MFS, and has been employed by MFS in the investment management area since 1986.
Federated Investment Counseling ("Federated Investment") serves as Sub-advisor for the ASAF Federated High Yield
Bond Fund. Federated Investment, located at Federated Investors Tower, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15222-3779, was
organized as a Delaware business trust in 1989. Federated Investment and its affiliates serve as investment advisors to
a number of investment companies and private accounts. As of December 31, 2000, total assets under management or
administration by Federated and its affiliates was over $[insert] billion.
The portfolio manager responsible for the day-to-day management of the ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund is
Mark E. Durbiano. Mr. Durbiano joined Federated Investment's parent company in 1982 and has been a Senior Vice President
of an affiliate of Federated Investment since January 1996.
Pacific Investment Management Company LLC ("PIMCO") serves as Sub-advisor for the ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond
Portfolio. PIMCO, located at 840 Newport Center Drive, Suite 300, Newport Beach, California 92660, is an investment
counseling firm founded in 1971. As of December 31, 2000, PIMCO had approximately $[insert] billion of assets under
management.
The portfolio manager responsible for the day-to-day management of the ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond Portfolio is
William H. Gross. Mr. Gross is Managing Director of PIMCO and has been associated with the firm since 1971.
J.P. Morgan Investment Management Inc. ("J.P. Morgan") serves as Sub-advisor for the ASMT JPM Money Market
Portfolio. J.P. Morgan has principal offices at 522 Fifth Avenue, New York, New York 10036. J.P. Morgan and its
affiliates offer a wide range of services to governmental, institutional, corporate and individual customers, and act as
investment advisor to individual and institutional clients with combined assets under management of approximately
$[insert] billion as of December 31, 2000. J.P. Morgan has managed investments for clients since 1913, and has managed
short-term fixed income assets for clients since 1969.
FEES AND EXPENSES:
Investment Management Fees. ASISI receives a monthly fee from each Non-Feeder Fund and Portfolio for the
performance of its services. ASISI pays each Sub-advisor a portion of such fee for the performance of the sub-advisory
services at no additional cost to any Fund or Portfolio. The investment management fee for each Non-Feeder Fund and
Portfolio will differ, reflecting, among other things, the investment objective, policies and limitations of each Fund
and Portfolio. Each investment management fee is accrued daily for the purposes of determining the sale and redemption
price of the Fund's shares. The fees paid to ASISI for the fiscal year ended October 31, 2000 (or, for those Funds that
have not been in operation for a full fiscal year, the fee rates payable to ASISI), stated as a percentage of the
Non-Feeder Fund or Portfolio's average daily net assets, are as follows:
Fund/Portfolio: Annual Rate:
-------------- -----------
ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund: 1.10%
ASAF AIM International Equity Fund: 1.10%
ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund: 1.00%
ASMT American Century International Growth Portfolio: 1.00%
ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund: 0.90%
ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund 0.95%
ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund: 1.00%
ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund: 1.00%
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund: 0.90%
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund: 0.90%
ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund: 0.95%
ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund: 0.95%
ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund: 1.00%
ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund: insert%
ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund: 0.85%
ASAF Alliance Growth Fund: 0.92%
ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund: 1.00%
ASMT Janus Capital Growth Portfolio: 1.00%
ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund: Insert%
ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth + Value Fund: Insert%
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund: Insert%
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund: 0.80%
ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund: 0.80%
ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund: 1.00%
ASMT INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio: 0.75%
ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund: 0.90%
ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund: 0.70%
ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond Portfolio: 0.65%
ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio: 0.50%
For more information about investment management fees, including voluntary fee waivers and the fee rates
applicable at various asset levels, and the fees payable by ASISI to each of the Sub-advisors, please see the Company's
SAI under "Investment Advisory & Administration Services."
Other Expenses. In addition to Investment Management fees, each Fund and Portfolio pays other expenses,
including costs incurred in connection with the maintenance of its securities law registration, printing and mailing
prospectuses and SAIs to shareholders, certain financial accounting services, taxes or governmental fees, brokerage
commissions, custodial, transfer and shareholder servicing agent costs, expenses of outside counsel and independent
accountants, preparation of shareholder reports and expenses of director and shareholder meetings. Expenses not directly
attributable to any specific Fund(s) or Portfolio(s) are allocated on the basis of the relative net assets of the Funds
or Portfolios. For additional information regarding Fund and Portfolio expenses, as well as voluntary agreements by the
Investment Manager to limit such expenses, see this Prospectus under "Expense Information" and the Company's SAI under
"Fund Expenses."
DIVIDENDS, CAPITAL GAINS AND TAXES
DIVIDENDS:
Each Fund intends to distribute substantially all of its net income and capital gains to shareholders at least
once a year. Normally, dividends from net investment income of each Fund will be declared and paid on the following
basis:
Fund Declared Paid
---- -------- ----
ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization annually annually
ASAF AIM International Equity annually annually
ASAF Janus Overseas Growth annually annually
ASAF American Century International Growth annually annually
ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth annually annually
ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Portfolio annually annually
ASAF T. Rowe Price Small Company Value annually annually
ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth annually annually
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth annually annually
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value annually annually
ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth annually annually
ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value annually annually
ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund annually annually
ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund annually annually
ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund annually annually
ASAF Alliance Growth annually annually
ASAF Marsico Capital Growth annually annually
ASAF Janus Capital Growth annually annually
ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund annually annually
ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth + Value Fund annually annually
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund annually annually
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 annually annually
ASAF Alliance Growth and Income annually annually
ASAF MFS Growth with Income annually annually
ASAF INVESCO Equity Income semi-annually semi-annually
ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced semi-annually semi-annually
ASAF Federated High Yield Bond daily monthly
ASAF PIMCO Total Return Bond daily quarterly
ASAF JPM Money Market daily monthly
DISTRIBUTION OPTIONS:
When you open your account, specify on your application how you want to receive your distributions. Unless you
specify otherwise, all dividends and distributions will be automatically reinvested in additional full or fractional
shares of each Fund. You have the following five distribution options:
Reinvest All Distributions in the Fund. You can elect to reinvest all dividends and long term capital gains
distributions in additional shares of the applicable Fund.
Reinvest Income Dividends Only. You can elect to reinvest investment income dividends in a Fund while receiving
capital gains distributions.
Reinvest Long-Term Capital Gains Only. You can elect to reinvest long-term capital gains in the Fund while
receiving dividends.
Receive All Distributions in Cash. You can elect to receive a check for all dividends and long-term capital
gains distributions.
Reinvest Distributions in Another Fund of the Company. You can reinvest all distributions in another Fund of the
Company. For additional information, see this Prospectus under "Special Investment Programs and Privileges."
TAXES:
Each of the Funds intends to make distributions that may be taxed as ordinary income and capital gains. The tax
consequences of distributions from a Fund will vary depending upon the type of account that you maintain.
If you establish an IRA or other tax-deferred retirement account, dividends and capital gains distributions from
the Funds generally will not be subject to current taxation. If you establish an account outside a tax-deferred
retirement account, the following tax consequences generally will apply. For regular investment accounts established by
individuals, dividends paid by a Fund from net investment income and net short-term capital gains, whether you choose to
receive them in cash or reinvest them in additional shares, will be taxable as ordinary income. If you receive your
distributions in cash, the value of your Fund account effectively will be reduced by the amount of the distribution.
Capital gains distributions are made by a Fund when it realizes net gains on sales of portfolio securities. A
Fund's capital gains may vary substantially from year to year and, therefore, its capital gains distributions also may
vary substantially. A Fund will not make capital gains distributions in years in which the Fund has a net capital loss.
Distributions paid by a Fund from net long term capital gains will be taxable as long-term capital gains, regardless of
how long you have owned the Fund's shares.
Because of their varying investment strategies, distributions from some of the Funds are likely to consist
primarily of capital gains distributions, while distributions from others are likely to consist primarily of ordinary
income. Distributions from the ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund, the ASAF PIMCO Total Return Bond Fund, and the ASAF
JPM Money Market Fund are likely to consist primarily of ordinary income. Because the Funds are new, as of the date of
this Prospectus no Fund has yet distributed any long-term capital gains. Over time, however, it is expected that
distributions from a number of the Funds, particularly those with capital growth as their investment objective, will
consist primarily of capital gains.
Certain distributions by a Fund may be classified under federal tax laws as constituting returns of your
capital. These are not taxable to you when received. Federal income tax laws provide, however, that a distribution of
this type will reduce the acquisition price of your shares in the Fund used to determine your tax liability when you
redeem or exchange the shares. Therefore, the return of capital may result in a larger gain or smaller loss upon
redemption or exchange.
If you purchase shares of a Fund shortly before the date used to determine eligibility for a dividend or capital
gains distribution, you will receive a portion of your investment back as a taxable distribution. This is sometimes
referred to as "buying a dividend."
In order to satisfy distribution requirements of the Code, the Funds may declare year-end dividend and capital
gains distributions. If received by shareholders by January 31, these special distributions are treated as having been
paid by the Funds and received by shareholders on December 31 of the prior year.
The investment income of certain Funds may be subject to foreign income taxes. The Company may elect to pass
these taxes through to the shareholders of the Funds. If you are a shareholder, you will be required to report a share
of these taxes as income in determining your federal income tax liability. You will be able to deduct these taxes or,
under certain circumstances, you may be able to claim them as a credit against your federal income tax.
The Company will provide you with an annual statement as to the federal income tax status of all distributions
for the preceding year, including any amount of foreign taxes passed through to you.
Taxes on Redemptions and Exchanges. A redemption of shares in a Fund or an exchange of a Fund's shares for
shares in another Fund will be treated as a sale under the Code, which may result in a capital gain or loss and current
tax liability. However, you will not have a federal tax gain or loss when Class B or Class X shares of a Fund
automatically convert to Class A shares. The Class A shares you receive after conversion will be considered to have the
same acquisition price as the converted Class B or X shares for purposes of determining your gain or loss upon subsequent
redemptions or exchanges.
Dividends, capital gains distributions and capital gains or losses from redemptions and exchanges may be subject
to state and local taxes in addition to Federal income taxes.
The above tax discussion is for general information only. A more detailed discussion of federal income tax
considerations for the Funds is included in the Company's SAI under "Additional Tax Considerations." You should consult
with your own tax adviser concerning possible tax consequences of investing in a Fund. If you are considering an IRA or
other tax deferred account, you should consult with your tax adviser regarding the requirements under Federal tax law
governing your specific type of account.
Regulated Investment Company Status. As each Fund intends to qualify as a "regulated investment company" under
the Code, each Fund generally is entitled to deduct all dividends paid to shareholders in determining its taxable
income. However, the deductibility of dividends paid by regulated investment companies that issue more than one class of
shares, such as the Company, is subject to certain requirements under the Code. In this regard, the Company may deduct
dividends only when shares in each class receive proportionate distributions and where no class is preferred over any
other class in a manner not permitted by the formal dividend rights of the preferred class.
The Company has received separate opinions of counsel from the law firms of Caplin & Drysdale and Rogers & Wells
which, when taken together, conclude that the Funds' particular multiple class structure will not prevent the
deductibility of dividends paid by the Funds. However, the Company has not obtained a ruling on the matter from the
IRS. The Company does not believe that the IRS has considered a multiple class structure with all of the features of the
Funds' structure, including the Bonus Share feature applicable to Class X shares, and the IRS could disagree with the
conclusions expressed in the opinions. Changes in federal income tax law also could affect the continued validity of the
conclusions stated in the opinions.
If dividends on any class of a Fund's shares are treated as preferential to another class, dividends in that year
on all classes of that Fund's shares would become non-deductible by the Fund. The effect of such a development is that
income and gains realized by a Fund could be subject to double taxation -- that is, both the Fund and shareholders could
be subject to taxation. In addition to the tax liability, the Fund could be liable for interest and penalties. All
these liabilities could substantially reduce the value of your investment in the Fund. There could also be personal
income tax consequences to shareholders of the Fund, such as reclassification of capital gains distributions as ordinary
income, which may be taxable at higher rates.
FINANCIAL HIGHLIGHTS
The financial highlights table is intended to help you understand the Funds' financial performance since their
inception. Certain information reflects financial results for a single Fund share. The total returns in the table
represent the rate that an investor would have earned or lost on an investment in a Fund (assuming reinvestment of all
dividends and distributions). The information has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, the Company's independent
accountants. The report of the independent accountants, along with the Funds' financial statements, are included in the
Company's annual report, which is available upon request. No financial information is included for the ASAF INVESCO
Health Sciences Fund, ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund, ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth + Value Fund or the ASAF
Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund, which had not commenced operations prior to March 1, 2001.
To be provided by future amendment.
CERTAIN RISK FACTORS AND INVESTMENT METHODS
The following is a description of certain securities and investment methods that the Funds and Portfolios may
invest in or use, and certain of the risks associated with such securities and investment methods. The primary
investment focus of each Fund and Portfolio is described above under "Investment Programs of the Funds," and an investor
should refer to that section to obtain information about each Fund and Portfolio. In general, whether a particular Fund
or Portfolio may invest in a specific type of security or use an investment method is described above or in the Company's
SAI under "Investment Programs of the Funds." As noted below, however, certain risk factors and investment methods apply
to all or most of the Funds or Portfolios. Any reference to the "Funds" in the discussion below generally includes the
Non-Feeder Funds and Portfolios.
DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS:
To the extent permitted by the investment objectives and policies of a Fund, a Fund may invest in securities and
other instruments that are commonly referred to as "derivatives." For instance, a Fund may purchase and write (sell)
call and put options on securities, securities indices and foreign currencies, enter into futures contracts and use
options on futures contracts, and enter into swap agreements with respect to foreign currencies, interest rates, and
securities indices. In general, derivative instruments are securities or other instruments whose value is derived from
or related to the value of some other instrument or asset.
There are many types of derivatives and many different ways to use them. Some derivatives and derivative
strategies involve very little risk, while others can be extremely risky and can lead to losses in excess of the amount
invested in the derivative. A Fund may use derivatives to hedge against changes in interest rates, foreign currency
exchange rates or securities prices, to generate income, as a low cost method of gaining exposure to a particular
securities market without investing directly in those securities, or for other reasons.
The use of these strategies involves certain special risks, including the risk that the price movements of
derivative instruments will not correspond exactly with those of the investments from which they are derived. Strategies
involving derivative instruments that are intended to reduce the risk of loss can also reduce the opportunity for gain.
Furthermore, regulatory requirements for a Fund to set aside assets to meet its obligations with respect to derivatives
may result in a Fund being unable to purchase or sell securities when it would otherwise be favorable to do so, or in a
Fund needing to sell securities at a disadvantageous time. A Fund may also be unable to close out its derivatives
positions when desired. There is no assurance that a Fund will engage in derivative transactions. Certain derivative
instruments and some of their risks are described in more detail below.
Options. Most of the Funds (except for the ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund, the ASMT INVESCO Equity Income
Portfolio, the ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund, and the ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio) may engage in at least some
types of options transactions. The purchaser of an option on a security or currency obtains the right to purchase (in
the case of a call option) or sell (in the case of a put option) the security or currency at a specified price within a
limited period of time. Upon exercise by the purchaser, the writer (seller) of the option has the obligation to buy or
sell the underlying security at the exercise price. An option on a securities index is similar to an option on an
individual security, except that the value of the option depends on the value of the securities comprising the index, and
all settlements are made in cash.
A Fund will pay a premium to the party writing the option when it purchases an option. In order for a call
option purchased by a Fund to be profitable, the market price of the underlying security must rise sufficiently above the
exercise price to cover the premium and other transaction costs. Similarly, in order for a put option to be profitable,
the market price of the underlying security must decline sufficiently below the exercise price to cover the premium and
other transaction costs.
Generally, the Funds will write call options only if they are covered (i.e., the Fund owns the security subject
to the option or has the right to acquire it without additional cost). By writing a call option, a Fund assumes the risk
that it may be required to deliver a security for a price lower than its market value at the time the option is
exercised. Effectively, a Fund that writes a covered call option gives up the opportunity for gain above the exercise
price should the market price of the underlying security increase, but retains the risk of loss should the price of the
underlying security decline. A Fund will write call options in order to obtain a return from the premiums received and
will retain the premiums whether or not the options are exercised, which will help offset a decline in the market value
of the underlying securities. A Fund that writes a put option likewise receives a premium, but assumes the risk that it
may be required to purchase the underlying security at a price in excess of its current market value.
A Fund may sell an option that it has previously purchased prior to the purchase or sale of the underlying
security. Any such sale would result in a gain or loss depending on whether the amount received on the sale is more or
less than the premium and other transaction costs paid on the option. A Fund may terminate an option it has written by
entering into a closing purchase transaction in which it purchases an option of the same series as the option written.
Futures Contracts and Related Options. Each Fund (except the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF
Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund, the ASMT INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio, the ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund,
and the ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio) may enter into financial futures contracts and related options. The seller of a
futures contract agrees to sell the securities or currency called for in the contract and the buyer agrees to buy the
securities or currency at a specified price at a specified future time. Financial futures contracts may relate to
securities indices, interest rates or foreign currencies. Futures contracts are usually settled through net cash
payments rather than through actual delivery of the securities underlying the contract. For instance, in a stock index
futures contract, the two parties agree to take or make delivery of an amount of cash equal to a specified dollar amount
times the difference between the stock index value when the contract expires and the price specified in the contract. A
Fund may use futures contracts to hedge against movements in securities prices, interest rates or currency exchange
rates, or as an efficient way to gain exposure to these markets.
An option on a futures contract gives the purchaser the right, in return for the premium paid, to assume a
position in the contract at the exercise price at any time during the life of the option. The writer of the option is
required upon exercise to assume the opposite position.
Pursuant to regulations of the Commodity Futures Trading Commission ("CFTC"), no Fund will:
(i) purchase or sell futures or options on futures contracts or stock indices for purposes other than bona
fide hedging transactions (as defined by the CFTC) if as a result the sum of the initial margin deposits and premiums
required to establish positions in futures contracts and related options that do not fall within the definition of bona
fide hedging transactions would exceed 5% of the fair market value of each Fund's net assets; and
(ii) enter into any futures contracts if the aggregate amount of that Fund's commitments under outstanding
futures contracts positions would exceed the market value of its total assets.
Risks of Options and Futures Contracts. Options and futures contracts can be highly volatile and their use can
reduce a Fund's performance. Successful use of these strategies requires the ability to predict future movements in
securities prices, interest rates, currency exchange rates, and other economic factors. If a Sub-advisor seeks to
protect a Fund against potential adverse movements in the relevant financial markets using these instruments, and such
markets do not move in the predicted direction, the Fund could be left in a less favorable position than if such
strategies had not been used. A Fund's potential losses from the use of futures extends beyond its initial investment in
such contracts.
Among the other risks inherent in the use of options and futures are (a) the risk of imperfect correlation
between the price of options and futures and the prices of the securities or currencies to which they relate, (b) the
fact that skills needed to use these strategies are different from those needed to select portfolio securities and (c)
the possible need to defer closing out certain positions to avoid adverse tax consequences. With respect to options on
stock indices and stock index futures, the risk of imperfect correlation increases the more the holdings of the Fund
differ from the composition of the relevant index. These instruments may not have a liquid secondary market. Option
positions established in the over-the-counter market may be particularly illiquid and may also involve the risk that the
other party to the transaction fails to meet its obligations.
FOREIGN SECURITIES:
Investments in securities of foreign issuers may involve risks that are not present with domestic investments.
While investments in foreign securities can reduce risk by providing further diversification, such investments involve
"sovereign risks" in addition to the credit and market risks to which securities generally are subject. Sovereign risks
includes local political or economic developments, potential nationalization, withholding taxes on dividend or interest
payments, and currency blockage (which would prevent cash from being brought back to the United States). Compared to
United States issuers, there is generally less publicly available information about foreign issuers and there may be less
governmental regulation and supervision of foreign stock exchanges, brokers and listed companies. Foreign issuers are not
generally subject to uniform accounting, auditing and financial reporting standards, practices and requirements
comparable to those applicable to domestic issuers. In some countries, there may also be the possibility of
expropriation or confiscatory taxation, difficulty in enforcing contractual and other obligations, political or social
instability or revolution, or diplomatic developments that could affect investments in those countries.
Securities of some foreign issuers are less liquid and their prices are more volatile than securities of
comparable domestic issuers. Further, it may be more difficult for the Company's agents to keep currently informed about
corporate actions and decisions that may affect the price of portfolio securities. Brokerage commissions on foreign
securities exchanges, which may be fixed, may be higher than in the United States. Settlement of transactions in some
foreign markets may be less frequent or less reliable than in the United States, which could affect the liquidity of
investments.
American Depositary Receipts ("ADRs"), European Depositary Receipts ("EDRs"), Global Depositary Receipts
("GDRs"), and International Depositary Receipts ("IDRs"). ADRs are U.S. dollar-denominated receipts generally issued by
a domestic bank evidencing its ownership of a security of a foreign issuer. ADRs generally are publicly traded in the
United States. ADRs are subject to many of the same risks as direct investments in foreign securities, although
ownership of ADRs may reduce or eliminate certain risks associated with holding assets in foreign countries, such as the
risk of expropriation. EDRs, GDRs and IDRs are receipts similar to ADRs that typically trade in countries other than the
United States.
Depositary receipts may be issued as sponsored or unsponsored programs. In sponsored programs, the issuer makes
arrangements to have its securities traded as depositary receipts. In unsponsored programs, the issuer may not be
directly involved in the program. Although regulatory requirements with respect to sponsored and unsponsored programs
are generally similar, the issuers of unsponsored depositary receipts are not obligated to disclose material information
in the United States and, therefore, the import of such information may not be reflected in the market value of such
securities.
Developing Countries. Although none of the Funds invest primarily in securities of issuers in developing
countries, many of the Funds may invest in these securities to some degree. Many of the risks described above with
respect to investing in foreign issuers are accentuated when the issuers are located in developing countries. Developing
countries may be politically and/or economically unstable, and the securities markets in those countries may be less
liquid or subject to inadequate government regulation and supervision. Securities of issuers in developing countries may
be more volatile and, in the case of debt securities, more uncertain as to payment of interest and principal.
Investments in developing countries may include securities created through the Brady Plan, under which certain
heavily-indebted countries have restructured their bank debt into bonds.
Currency Fluctuations. Investments in foreign securities may be denominated in foreign currencies. The value of
a Fund's investments denominated in foreign currencies may be affected, favorably or unfavorably, by exchange rates and
exchange control regulations. A Fund's share price and the amounts it distributes to shareholders in dividends may,
therefore, also be affected by changes in currency exchange rates. Foreign currency exchange rates generally are
determined by the forces of supply and demand in foreign exchange markets, including perceptions of the relative merits
of investment in different countries, actual or perceived changes in interest rates or other complex factors. Currency
exchange rates also can be affected unpredictably by the intervention or the failure to intervene by U.S. or foreign
governments or central banks, or by currency controls or political developments in the U.S. or abroad. In addition, a
Fund may incur costs in connection with conversions between various currencies.
Foreign Currency Transactions. A Fund that invests in securities denominated in foreign currencies will need to
engage in foreign currency exchange transactions. Such transactions may occur on a "spot" basis at the exchange rate
prevailing at the time of the transaction. Alternatively, a fund may enter into forward foreign currency exchange
contracts. A forward contract involves an obligation to purchase or sell a specified currency at a specified future date
at a price set at the time of the contract. A Fund may enter into a forward contract when it wishes to "lock in" the
U.S. dollar price of a security it expects to or is obligated to purchase or sell in the future. This practice may be
referred to as "transaction hedging." In addition, when a Fund's Sub-advisor believes that the currency of a particular
country may suffer or enjoy a significant movement compared to another currency, the Fund may enter into a forward
contract to sell or buy the first foreign currency (or a currency that acts as a proxy for such currency). This practice
may be referred to as "portfolio hedging." In any event, the precise matching of the forward contract amounts and the
value of the securities involved generally will not be possible. No Fund will enter into a forward contract if it would
be obligated to sell an amount of foreign currency in excess of the value of the Fund's securities or other assets
denominated in that currency, or will sell an amount of proxy currency in excess of the value of securities denominated
in the related currency. The effect of entering into a forward contract on a Fund share price will be similar to selling
securities denominated in one currency and purchasing securities denominated in another. Although a forward contract may
reduce a Fund's losses on securities denominated in foreign currency, it may also reduce the potential for gain on the
securities if the currency's value moves in a direction not anticipated by the Sub-advisor. In addition, foreign
currency hedging may entail significant transaction costs.
COMMON AND PREFERRED STOCKS:
Stocks represent shares of ownership in a company. Generally, preferred stock has a specified dividend and
ranks after bonds and before common stocks in its claim on the company's income for purposes of receiving dividend
payments and on the company's assets in the event of liquidation. (Some of the Sub-advisors consider preferred stocks to
be equity securities for purposes of the various Funds' investment policies and restrictions, while others consider them
fixed income securities.) After other claims are satisfied, common stockholders participate in company profits on a pro
rata basis; profits may be paid out in dividends or reinvested in the company to help it grow. Increases and decreases
in earnings are usually reflected in a company's stock price, so common stocks generally have the greatest appreciation
and depreciation potential of all corporate securities.
FIXED INCOME SECURITIES:
Most of the Funds, including the Funds that invest primarily in equity securities, may invest to some degree in
bonds, notes, debentures and other obligations of corporations and governments. Fixed-income securities are generally
subject to two kinds of risk: credit risk and market risk. Credit risk relates to the ability of the issuer to meet
interest and principal payments as they come due. The ratings given a security by Moody's Investors Service, Inc.
("Moody's") and Standard & Poor's Corporation ("S&P"), which are described in detail in the Appendix to the Company's
SAI, provide a generally useful guide as to such credit risk. The lower the rating, the greater the credit risk the
rating service perceives to exist with respect to the security. Increasing the amount of Fund assets invested in
lower-rated securities generally will increase the Fund's income, but also will increase the credit risk to which the
Fund is subject. Market risk relates to the fact that the prices of fixed income securities generally will be affected
by changes in the level of interest rates in the markets generally. An increase in interest rates will tend to reduce
the prices of such securities, while a decline in interest rates will tend to increase their prices. In general, the
longer the maturity or duration of a fixed income security, the more its value will fluctuate with changes in interest
rates.
Lower-Rated Fixed Income Securities. Lower-rated high-yield bonds (commonly known as "junk bonds") are those
that are rated lower than the four highest categories by a nationally recognized statistical rating organization (for
example, lower than Baa by Moody's or BBB by S&P), or, if not rated, are of equivalent investment quality as determined
by the Sub-advisor. Lower-rated bonds are generally considered to be high risk investments as they are subject to
greater credit risk than higher-rated bonds. In addition, the market for lower-rated bonds may be thinner and less
active than the market for higher-rated bonds, and the prices of lower-rated high-yield bonds may fluctuate more than the
prices of higher-rated bonds, particularly in times of market stress. Because the risk of default is higher in
lower-rated bonds, a Sub-advisor's research and analysis tend to be very important ingredients in the selection of these
bonds. In addition, the exercise by an issuer of redemption or call provisions that are common in lower-rated bonds may
result in their replacement by lower yielding bonds.
Bonds rated in the four highest ratings categories are frequently referred to as "investment grade." However,
bonds rated in the fourth category (Baa or BBB) are considered medium grade and may have speculative characteristics.
MORTGAGE-BACKED SECURITIES:
Mortgage-backed securities are securities representing interests in "pools" of mortgage loans on residential or
commercial real property and that generally provide for monthly payments of both interest and principal, in effect
"passing through" monthly payments made by the individual borrowers on the mortgage loans (net of fees paid to the issuer
or guarantor of the securities). Mortgage-backed securities are frequently issued by U.S. Government agencies or
Government-sponsored enterprises, and payments of interest and principal on these securities (but not their market
prices) may be guaranteed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Government or by the agency only, or may be supported
by the issuer's ability to borrow from the U.S. Treasury. Mortgage-backed securities created by non-governmental issuers
may be supported by various forms of insurance or guarantees.
Like other fixed-income securities, the value of a mortgage-backed security will generally decline when interest
rates rise. However, when interest rates are declining, their value may not increase as much as other fixed-income
securities, because early repayments of principal on the underlying mortgages (arising, for example, from sale of the
underlying property, refinancing, or foreclosure) may serve to reduce the remaining life of the security. If a security
has been purchased at a premium, the value of the premium would be lost in the event of prepayment. Prepayments on some
mortgage-backed securities may necessitate that a Fund find other investments, which, because of intervening market
changes, will often offer a lower rate of return. In addition, the mortgage securities market may be particularly
affected by changes in governmental regulation or tax policies.
Collateralized Mortgage Obligations (CMOs). CMOs are a type of mortgage-backed security that are typically
issued in multiple series with each series having a different maturity. Principal and interest payments from the
underlying collateral are first used to pay the principal on the series with the shortest maturity; in turn, the
remaining series are paid in order of their maturities. Therefore, depending on the type of CMOs in which a Fund
invests, the investment may be subject to greater or lesser risk than other types of mortgage-backed securities.
Stripped Mortgage-Backed Securities. Stripped mortgage-backed securities are mortgage-backed securities that
have been divided into interest and principal components. "IOs" (interest only securities) receive the interest payments
on the underlying mortgages while "POs" (principal only securities) receive the principal payments. The cash flows and
yields on IO and PO classes are extremely sensitive to the rate of principal payments (including prepayments) on the
underlying mortgage loans. If the underlying mortgages experience higher than anticipated prepayments, an investor in an
IO class of a stripped mortgage-backed security may fail to recoup fully its initial investment, even if the IO class is
highly rated or is derived from a security guaranteed by the U.S. Government. Conversely, if the underlying mortgage
assets experience slower than anticipated prepayments, the price on a PO class will be affected more severely than would
be the case with a traditional mortgage-backed security. Unlike other fixed-income and other mortgage-backed securities,
the value of IOs tends to move in the same direction as interest rates.
ASSET-BACKED SECURITIES:
Asset-backed securities conceptually are similar to mortgage-backed securities, but they are secured by and
payable from payments on assets such as credit card, automobile or trade loans, rather than mortgages. The credit
quality of these securities depends primarily upon the quality of the underlying assets and the level of credit support
or enhancement provided. In addition, asset-backed securities involve prepayment risks that are similar in nature to
those of mortgage-backed securities.
CONVERTIBLE SECURITIES AND WARRANTS:
Certain of the Funds may invest in convertible securities. Convertible securities are bonds, notes, debentures
and preferred stocks that may be converted into or exchanged for shares of common stock. Many convertible securities are
rated below investment grade because they fall below ordinary debt securities in order of preference or priority on the
issuer's balance sheet. Convertible securities generally participate in the appreciation or depreciation of the
underlying stock into which they are convertible, but to a lesser degree. Frequently, convertible securities are
callable by the issuer, meaning that the issuer may force conversion before the holder would otherwise choose.
Warrants are options to buy a stated number of shares of common stock at a specified price any time during the
life of the warrants. The value of warrants may fluctuate more than the value of the securities underlying the
warrants. A warrant will expire without value if the rights under such warrant are not exercised prior to its expiration
date.
WHEN-ISSUED, DELAYED-DELIVERY AND FORWARD COMMITMENT TRANSACTIONS:
The Funds (other than the ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund, ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap
Growth Fund, ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund, ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund, ASAF Alliance Growth Fund, ASAF
Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Value + Growth Fund, ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund, ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed
Index 500 Fund and ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund) may purchase securities on a when-issued, delayed-delivery or
forward commitment basis. These transactions generally involve the purchase of a security with payment and delivery due
at some time in the future. A Fund does not earn interest on such securities until settlement and bears the risk of
market value fluctuations in between the purchase and settlement dates. If the seller fails to complete the sale, the
Fund may lose the opportunity to obtain a favorable price and yield. While the Funds will generally engage in such
when-issued, delayed-delivery or forward commitment transactions with the intent of actually acquiring the securities, a
Fund may sometimes sell such a security prior to the settlement date. The ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio will not enter
into these commitments if they would exceed 15% of the value of the Fund's total assets less its liabilities other than
liabilities created by these commitments.
Certain Funds may also sell securities on a delayed-delivery or forward commitment basis. If the Fund does so,
it will not participate in future gains or losses on the security. If the other party to such a transaction fails to pay
for the securities, the Fund could suffer a loss.
ILLIQUID AND RESTRICTED SECURITIES:
Subject to guidelines adopted by the Directors of the Company or Trustees of the Trust, each Fund may invest up
to 15% of its net assets in illiquid securities (except for the ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio, which is limited to 10%
of its net assets, and the ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Value + Growth Fund, ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund and
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund, which is limited to 5% of its net assets). Illiquid securities are those
that, because of the absence of a readily available market or due to legal or contractual restrictions on resale, cannot
be sold within seven days in the ordinary course of business at approximately the amount at which the Fund has valued the
investment. Therefore, a Fund may find it difficult to sell illiquid securities at the time considered most advantageous
by its Sub-advisor and may incur expenses that would not be incurred in the sale of securities that were freely
marketable.
Certain securities that would otherwise be considered illiquid because of legal restrictions on resale to the
general public may be traded among qualified institutional buyers under Rule 144A of the Securities Act of 1933. These
Rule 144A securities, and well as commercial paper that is sold in private placements under Section 4(2) of the
Securities Act, may be deemed liquid by the Fund's Sub-advisor under the guidelines adopted by the Directors of the
Company. However, the liquidity of a Fund's investments in Rule 144A securities could be impaired if trading does not
develop or declines.
REPURCHASE AGREEMENTS:
Each Fund may enter into repurchase agreements. Repurchase agreements are agreements by which a Fund purchases a
security and obtains a simultaneous commitment from the seller to repurchase the security at an agreed upon price and
date. The resale price is in excess of the purchase price and reflects an agreed upon market rate unrelated to the
coupon rate on the purchased security. Repurchase agreements must be fully collateralized and can be entered into only
with well-established banks and broker-dealers that have been deemed creditworthy by the Sub-advisor. Repurchase
transactions are intended to be short-term transactions, usually with the seller repurchasing the securities within seven
days. Repurchase agreements that mature in more than seven days are subject to a Fund's limit on illiquid securities.
A Fund that enters into a repurchase agreement may lose money in the event that the other party defaults on its
obligation and the Fund is delayed or prevented from disposing of the collateral. A Fund also might incur a loss if the
value of the collateral declines, and it might incur costs in selling the collateral or asserting its legal rights under
the agreement. If a defaulting seller filed for bankruptcy or became insolvent, disposition of collateral might be
delayed pending court action.
The ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund will not invest more than 25% of its net assets in repurchase
agreements.
REVERSE REPURCHASE AGREEMENTS:
Certain Funds (specifically, the ASAF AIM International Equity Fund, the ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund, the
ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund, the
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund, the ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund, the ASMT Janus Capital Growth Portfolio,
ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund, the ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond Portfolio, and the ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio)
may enter into reverse repurchase agreements. In a reverse repurchase agreement, a Fund sells a portfolio instrument and
agrees to repurchase it at an agreed upon date and price, which reflects an effective interest rate. It may also be
viewed as a borrowing of money by the Fund and, like borrowing money, may increase fluctuations in a Fund's share price.
When entering into a reverse repurchase agreement, a Fund must set aside on its books cash or other liquid assets in an
amount sufficient to meet its repurchase obligation.
BORROWING:
Each Fund may borrow money from banks. Each Fund's borrowings are limited so that immediately after such
borrowing the value of the Fund's assets (including borrowings) less its liabilities (not including borrowings) is at
least three times the amount of the borrowings. Should a Fund, for any reason, have borrowings that do not meet the
above test, such Fund must reduce such borrowings so as to meet the necessary test within three business days. Certain
Funds (the ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund, the ASAF AIM International Equity Fund, the ASAF
Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund, the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value
Fund, the ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund, the ASAF T. Price Tax Managed Fund and the ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio)
will not purchase securities when outstanding borrowings are greater than 5% of the Fund's total assets. If a Fund
borrows money, its share price may fluctuate more widely until the borrowing is repaid.
LENDING PORTFOLIO SECURITIES:
Each Fund may lend securities with a value of up to 33 1/3% of its total assets to broker-dealers, institutional
investors, or others for the purpose of realizing additional income. Voting rights on loaned securities typically pass
to the borrower, although a Fund has the right to terminate a securities loan, usually within three business days, in
order to vote on significant matters or for other reasons. All securities loans will be collateralized by cash or
securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies at least equal in value to the market value of the
loaned securities. Nonetheless, lending securities involves certain risks, including the risk that the Fund will be
delayed or prevented from recovering the collateral if the borrower fails to return a loaned security.
OTHER INVESTMENT COMPANIES:
The Company has made arrangements with certain money market mutual funds so that the Sub-advisors for the various
Funds can "sweep" excess cash balances of the Fund to those funds for temporary investment purposes. In addition,
certain Sub-advisors may invest Fund assets in money market funds that they advise or in other investment companies.
Mutual funds pay their own operating expenses, and the Funds, as shareholders in the funds, will indirectly pay their
proportionate share of such funds' expenses.
SHORT SALES "AGAINST THE BOX":
While none of the Funds will make short sales generally, the ASAF AIM International Equity Fund, the ASAF Janus
Overseas Growth Fund, the ASMT American Century International Growth Portfolio, the ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund, the
ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund, the ASMT Janus
Capital Growth Portfolio, the ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund, the ASMT INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio, the ASAF
American Century Strategic Balanced Fund and the ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond Portfolio may make short sales "against the
box." A short sale against the box involves selling a security that the Fund owns, or has the right to obtain without
additional cost, for delivery at a specified date in the future. A Fund may make a short sale against the box to hedge
against anticipated declines in the market price of a portfolio security. If the value of the security sold short
increases instead, the Fund loses the opportunity to participate in the gain.
Mailing Address
P.O. Box 8012
Boston, MA 02266-8012
Investment Manager
American Skandia Investment Services, Incorporated
One Corporate Drive
Shelton, CT 06484
Sub-Advisors
A I M Capital Management, Inc.
Alliance Capital Management L.P.
American Century Investment Management, Inc.
Federated Investment Counseling
Founders Asset Management LLC
Fred Alger Management, Inc.
GAMCO Investors, Inc.
INVESCO Funds Group, Inc.
Janus Capital Corporation
J.P. Morgan Investment Management Inc.
Massachusetts Financial Services Company
Marsico Capital Management, LLC
Neuberger Berman Management Inc.
Pacific Investment Management Company LLC
Rydex Global Advisors
Sanford C. Bernstein & Co., LLC
T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc.
Zurich Scudder Investments, Inc.
Distributor
American Skandia Marketing, Incorporated
One Corporate Drive
Shelton, CT 06484
Transfer and Dividend Paying Agent
Boston Financial Data Services, Inc.
66 Brooks Drive
Braintree, Massachusetts 02184
Custodians
PFPC Trust Company The Chase Manhattan Bank
Airport Business Center, International Court 2 One Pierrepont Plaza
200 Stevens Drive Brooklyn, NY 11201
Philadelphia, PA 19113
Administrator
PFPC Inc.
103 Bellevue Parkway
Wilmington, DE 19809
Independent Accountants
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
1700 Two Commerce Square
Philadelphia, PA 19103
Legal Counsel
Stradley Ronon Stevens & Young, LLP
2600 One Commerce Square
Philadelphia, PA 19103
INVESTOR INFORMATION SERVICES:
The Company provides 24-hour information services via a toll-free number on Fund yields and prices, dividends,
account balances, and your latest transaction as well as the ability to request prospectuses, account and tax forms, and
duplicate statements. In addition, telephone representatives are available during normal business hours to provide the
information and services you need. Shareholder inquiries should be made by calling 1-800-SKANDIA or by writing to
"American Skandia Advisor Funds, Inc." at P.O. Box 8012, Boston, Massachusetts 02266-8012. There may be a small charge
for historical account information for prior years.
Additional information about the Funds is included in a Statement of Additional Information, which is
incorporated by reference into this Prospectus. Additional information about the Funds' investments is available in the
Funds' annual and semi-annual reports to shareholders. In the Funds' annual report, you will find a discussion of the
market conditions and investment strategies that significantly affected each Fund's performance during its last fiscal
year. The Statement of Additional Information and additional copies of annual and semi-annual reports are available
without charge by calling the above number.
Delivery of Prospectus and other Documents to Households. To lower costs and eliminate duplicate documents sent
to your address, the Company, in accordance with applicable laws and regulations, may begin mailing only one copy of the
Company's prospectus, prospectus supplements, annual and semi-annual reports, proxy statements and information
statements, or any other required documents to your address even if more than one shareholder lives there. If you have
previously consented to have any of these documents delivered to multiple investors at a shared address, as required by
law, and wish to revoke this consent of otherwise would prefer to continue to receive your own copy, you should call
1-800-SKANDIA or write to "American Skandia Advisor Funds, Inc." at P.O. Box 8012, Boston, Massachusetts 02266-8012. The
Company will begin sending individual copies to you within thirty days of receipt of revocation.
The information in Company filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (including the Statement of
Additional Information) is available from the Commission. Copies of this information may be obtained, upon payment of
duplicating fees, by electronic request to [email protected] or by writing the Public Reference Section of the
------------------
Commission, Washington, D.C. 20549-0102. The information can also be reviewed and copied at the Commission's Public
Reference Room in Washington, D.C. Information on the operation of the Public Reference Room may be obtained by calling
the Commission at 1-800-942-8090. Finally, information about the Company is available on the EDGAR Database on the
Commission's Internet site at HTTP://WWW.SEC.GOV.
------------------
Investment Company Act File No. 811-08085
STATEMENT OF ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
March 1, 2001
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
AMERICAN SKANDIA ADVISOR FUNDS, INC.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Table of Contents Page
----------------- ----
General Information.......................................................................................................2
Investment Programs of the Funds..........................................................................................2
ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund............................................................3
ASAF AIM International Equity Fund..............................................................................10
ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund.................................................................................17
ASAF American Century International Growth Fund.................................................................20
ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund................................................................................24
ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund..............................................................................28
ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund...............................................................................31
ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund..................................................................................40
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund.......................................................................44
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund........................................................................50
ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund..................................................................................57
ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund.................................................................................60
ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund....................................................................................65
ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund.................................................................................
ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund.....................................................................................74
ASAF Alliance Growth Fund.......................................................................................77
ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund................................................................................82
ASAF Janus Capital Growth Fund..................................................................................84
ASAF Alliance Bernstein 50/50 Growth + Value Fund.................................................................
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund............................................................................
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund...................................................................87
ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund............................................................................90
ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund................................................................................92
ASAF INVESCO Equity Income Fund................................................................................102
ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund..................................................................103
ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund............................................................................108
ASAF PIMCO Total Return Bond Fund..............................................................................111
ASAF JPM Money Market Fund.....................................................................................124
Fundamental Investment Restrictions.....................................................................................125
Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods.............................................................................127
Additional Performance Information......................................................................................143
Management of the Company...............................................................................................148
Additional Information on the "Master Feeder" Fund Structure............................................................151
Investment Advisory & Administration Services...........................................................................152
Fund Expenses...........................................................................................................163
Distribution Arrangements...............................................................................................164
Determination of Net Asset Value........................................................................................168
Additional Information on the Purchase and Redemption of Shares.........................................................169
Portfolio Transactions..................................................................................................170
Additional Tax Considerations...........................................................................................173
Capital Stock of the Company & Principal Holders of Securities..........................................................176
Other Information.......................................................................................................179
Financial Statements....................................................................................................180
Appendix................................................................................................................B-1
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This Statement of Additional Information ("SAI") is not a prospectus and should be read in conjunction with the
Company's current Prospectus, dated March 1, 2000. A copy of the Company's Prospectus may be obtained by writing
to "American Skandia Advisor Funds, Inc." at P.O. Box 8012, Boston, Massachusetts 02266-8012 or by calling
1-800-SKANDIA.
GENERAL INFORMATION
American Skandia Advisor Funds, Inc. (the "Company") is an open-end management investment company
comprised of twenty-nine diversified investment portfolios (each a "Fund" and together the "Funds"). The Company
was established as a Maryland corporation on March 5, 1997, and had no business history prior to the Fund's
commencement of operations on July 28, 1997. Five of the Funds -- ASAF American Century International Growth
Fund (formerly, the ASAF T. Rowe Price International Equity Fund), ASAF Janus Capital Growth Fund, ASAF INVESCO
Equity Income Fund, ASAF Total Return Bond Fund and ASAF JPM Money Market Fund (each a "Feeder Fund" and together
the "Feeder Funds") -- invest all of their investable assets in a corresponding portfolio (each a "Portfolio" and
together the "Portfolios") of American Skandia Master Trust (the "Trust"), an open-end management investment
company comprised of five diversified investment portfolios. Each Portfolio of the Trust invests in securities
in accordance with an investment objective, investment policies and limitations identical to those of its
corresponding Feeder Fund. This "master/feeder" fund structure differs from that of the other Funds of the
Company and many other investment companies which directly invest and manage their own portfolio of securities.
Those Funds of the Company which currently are not organized under a "master/feeder" fund structure (the
"Non-Feeder Funds") retain the right to invest their assets in a corresponding Portfolio of the Trust in the
future. For additional information regarding the "master/feeder" fund structure, see the Company's Prospectus
under "Special Information on the 'Master Feeder' Fund Structure" and this SAI under "Additional Information on
the `Master Feeder' Fund Structure."
American Skandia Investment Services, Incorporated ("ASISI" or the "Investment Manager") acts as the
investment manager for both the Non-Feeder Funds and the Portfolios. Currently, ASISI engages the following
sub-advisors ("Sub-advisor(s)") for the investment management of each Non-Feeder Fund and Portfolio: (a) ASAF
Founders International Small Capitalization Fund: Founders Asset Management LLC; (b) ASAF AIM International
Equity Fund: A I M Capital Management, Inc.; (c) ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund: Janus Capital Corporation; (d)
ASMT American Century International Growth Portfolio (formerly, the ASMT T. Rowe Price International Equity
Portfolio); American Century Investment Management, Inc. (e) ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund: Janus Capital
Corporation; (f) ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund: Zurich Scudder Investments, Inc. (g) ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap
Value Fund: GAMCO Investors, Inc.; (h) ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund: Janus Capital Corporation; (i) ASAF
Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund: Neuberger Berman Management Inc.; (j) ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value
Fund: Neuberger Berman Management Inc.; (k) ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund: Fred Alger Management, Inc.; (l) ASAF
Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund: GAMCO Investors, Inc.; (m) ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund: INVESCO Funds Group, Inc.;
(n) ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund: INVESCO Funds Group, Inc. (o) ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund: Rydex Global
Advisors; (p) ASAF Alliance Growth Fund (formerly, the ASAF Oppenheimer Large-Cap Growth Fund); Alliance Capital
Management L.P.; (q) ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund: Marsico Capital Management, LLC.; (r) ASMT Janus Capital
Growth Portfolio: Janus Capital Corporation; (s) ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund: T. Rowe Price Associates,
Inc.; (t) ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth + Value Fund: Alliance Capital Management L.P. and Sanford C.
Bernstein & Co., LLP ; (u) ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund: Sanford C. Bernstein & Co., LLP; (v) ASAF
Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund (formerly, ASAF Bankers Trust Managed Index 500 Fund): Sanford C.
Bernstein & Co.; (w) ASAF Alliance Growth & Income Fund (formerly, ASAF Lord Abbett Growth and Income Fund):
Alliance Capital Management L.P.; (x) ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund: Massachusetts Financial Services
Company; (y) ASMT INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio: INVESCO Funds Group, Inc.; (z) ASAF American Century
Strategic Balanced Fund: American Century Investment Management, Inc.; (aa) ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund:
Federated Investment Counseling; (bb) ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond Portfolio: Pacific Investment Management
Company LLC; and (cc) ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio: J.P. Morgan Investment Management Inc.
INVESTMENT PROGRAMS OF THE FUNDS
The following information supplements, and should be read in conjunction with, the discussion in the
Prospectus of the investment objective and policies of each Fund and Portfolio. The investment objective of each
Fund or Portfolio and supplemental information regarding its investment policies are described below separately
for each Fund or Portfolio.
The investment objective and, unless otherwise specified, the investment policies and limitations of
each Fund and Portfolio are not "fundamental" policies and may be changed by the Directors of the Company or the
Trustees of the Trust, where applicable, without shareholder approval. Those investment policies specifically
labeled as "fundamental," including those described in the "Fundamental Investment Restrictions" section of this
SAI, may not be changed without shareholder approval. Fundamental investment policies of a Fund or Portfolio may
be changed only with the approval of at least the lesser of (1) 67% or more of the total units of beneficial
interest ("shares") of the Fund or Portfolio represented at a meeting at which more than 50% of the outstanding
shares of the Fund or Portfolio are represented, or (2) a majority of the outstanding shares of the Fund or
Portfolio.
Notwithstanding any other investment policy of a Fund, each Fund may invest all of its investable assets
(cash, securities, and receivables relating to securities) in an open-end management investment company having
substantially the same investment objective, policies and limitations as the Fund. Those Funds which currently
invest all of their investable assets in such a manner, the Feeder Funds, seek to meet their respective
investment objectives by investing all of their investable assets in a corresponding Portfolio of the Trust,
which in turn invests directly in a portfolio of securities in accordance with the investment objective, policies
and limitations of its Feeder Fund. The investment objective, policies and limitations of each Feeder Fund are
otherwise identical to those of its corresponding Portfolio. As such, the following discussion of the Feeder
Funds, including references to the Directors of the Company, apply equally to the Funds' corresponding Portfolios
and the Trustees of the Trust, respectively.
ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth.
Investment Policies:
Options On Stock Indices and Stocks. An option is a right to buy or sell a security at a specified
price within a limited period of time. The Fund may write ("sell") covered call options on any or all of its
portfolio securities. In addition, the Fund may purchase options on securities. The Fund may also purchase put
and call options on stock indices.
The Fund may write ("sell") options on any or all of its portfolio securities and at such time and from
time to time as the Sub-advisor shall determine to be appropriate. No specified percentage of the Fund's assets
is invested in securities with respect to which options may be written. The extent of the Fund's option writing
activities will vary from time to time depending upon the Sub-advisor's evaluation of market, economic and
monetary conditions.
When the Fund purchases a security with respect to which it intends to write an option, it is likely
that the option will be written concurrently with or shortly after purchase. The Fund will write an option on a
particular security only if the Sub-advisor believes that a liquid secondary market will exist on an exchange for
options of the same series, which will permit the Fund to enter into a closing purchase transaction and close out
its position. If the Fund desires to sell a particular security on which it has written an option, it will
effect a closing purchase transaction prior to or concurrently with the sale of the security.
The Fund may enter into closing purchase transactions to reduce the percentage of its assets against
which options are written, to realize a profit on a previously written option, or to enable it to write another
option on the underlying security with either a different exercise price or expiration time or both.
Options written by the Fund will normally have expiration dates between three and nine months from the
date written. The exercise prices of options may be below, equal to or above the current market values of the
underlying securities at the times the options are written. From time to time for tax and other reasons, the
Fund may purchase an underlying security for delivery in accordance with an exercise notice assigned to it,
rather than delivering such security from its portfolio.
A stock index measures the movement of a certain group of stocks by assigning relative values to the
stocks included in the index. The Fund purchases put options on stock indices to protect the portfolio against
decline in value. The Fund purchases call options on stock indices to establish a position in equities as a
temporary substitute for purchasing individual stocks that then may be acquired over the option period in a
manner designed to minimize adverse price movements. Purchasing put and call options on stock indices also
permits greater time for evaluation of investment alternatives. When the Sub-advisor believes that the trend of
stock prices may be downward, particularly for a short period of time, the purchase of put options on stock
indices may eliminate the need to sell less liquid stocks and possibly repurchase them later. The purpose of
these transactions is not to generate gain, but to "hedge" against possible loss. Therefore, successful hedging
activity will not produce net gain to the Fund. Any gain in the price of a call option is likely to be offset by
higher prices the Fund must pay in rising markets, as cash reserves are invested. In declining markets, any
increase in the price of a put option is likely to be offset by lower prices of stocks owned by the Fund.
The Fund may purchase only those put and call options that are listed on a domestic exchange or quoted
on the automatic quotation system of the National Association of Securities Dealers, Inc. ("NASDAQ"). Options
traded on stock exchanges are either broadly based, such as the Standard & Poor's 500 Stock Index and 100 Stock
Index, or involve stocks in a designated industry or group of industries. The Fund may utilize either broadly
based or market segment indices in seeking a better correlation between the indices and the Fund.
Transactions in options are subject to limitations, established by each of the exchanges upon which
options are traded, governing the maximum number of options which may be written or held by a single investor or
group of investors acting in concert, regardless of whether the options are held in one or more accounts. Thus,
the number of options the Fund may hold may be affected by options held by other advisory clients of the
Sub-advisor. As of the date of this SAI, the Sub-advisor believes that these limitations will not affect the
purchase of stock index options by the Fund.
One risk of holding a put or a call option is that if the option is not sold or exercised prior to its
expiration, it becomes worthless. However, this risk is limited to the premium paid by the Fund. Other risks of
purchasing options include the possibility that a liquid secondary market may not exist at a time when the Fund
may wish to close out an option position. It is also possible that trading in options on stock indices might be
halted at a time when the securities markets generally were to remain open. In cases where the market value of
an issue supporting a covered call option exceeds the strike price plus the premium on the call, the Fund will
lose the right to appreciation of the stock for the duration of the option. For an additional discussion of
options on stock indices and stocks and certain risks involved therein, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus
under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Futures Contracts. The Fund may enter into futures contracts (or options thereon) for hedging
purposes. U.S. futures contracts are traded on exchanges which have been designated "contract markets" by the
Commodity Futures Trading Commission (the "CFTC") and must be executed through a futures commission merchant (an
"FCM") or brokerage firm which is a member of the relevant contract market. Although futures contracts by their
terms call for the delivery or acquisition of the underlying commodities or a cash payment based on the value of
the underlying commodities, in most cases the contractual obligation is offset before the delivery date of the
contract by buying, in the case of a contractual obligation to sell, or selling, in the case of a contractual
obligation to buy, an identical futures contract on a commodities exchange. Such a transaction cancels the
obligation to make or take delivery of the commodities.
The acquisition or sale of a futures contract could occur, for example, if the Fund held or considered
purchasing equity securities and sought to protect itself from fluctuations in prices without buying or selling
those securities. For example, if prices were expected to decrease, the Fund could sell equity index futures
contracts, thereby hoping to offset a potential decline in the value of equity securities in the portfolio by a
corresponding increase in the value of the futures contract position held by the Fund and thereby prevent the
Fund's net asset value from declining as much as it otherwise would have. The Fund also could protect against
potential price declines by selling portfolio securities and investing in money market instruments. However,
since the futures market is more liquid than the cash market, the use of futures contracts as an investment
technique would allow the Fund to maintain a defensive position without having to sell portfolio securities.
Similarly, when prices of equity securities are expected to increase, futures contracts could be bought
to attempt to hedge against the possibility of having to buy equity securities at higher prices. This technique
is sometimes known as an anticipatory hedge. Since the fluctuations in the value of futures contracts should be
similar to those of equity securities, the Fund could take advantage of the potential rise in the value of equity
securities without buying them until the market had stabilized. At that time, the futures contracts could be
liquidated and the Fund could buy equity securities on the cash market.
The Fund may also enter into interest rate and foreign currency futures contracts. Interest rate
futures contracts currently are traded on a variety of fixed-income securities, including long-term U.S. Treasury
Bonds, Treasury Notes, Government National Mortgage Association modified pass-through mortgage-backed securities,
U.S. Treasury Bills, bank certificates of deposit and commercial paper. Foreign currency futures contracts
currently are traded on, among others, the British pound, Canadian dollar, Japanese yen, Swiss franc, West German
mark, Mexican peso, Australian dollar, Brazilian real and on Eurodollar deposits.
The Fund will not, as to any positions, whether long, short or a combination thereof, enter into futures
and options thereon for which the aggregate initial margins and premiums exceed 5% of the fair market value of
its total assets after taking into account unrealized profits and losses on options entered into. In the case of
an option that is "in-the-money," the in-the-money amount may be excluded in computing such 5%. In general a
call option on a future is "in-the-money" if the value of the future exceeds the exercise ("strike") price of the
call; a put option on a future is "in-the-money" if the value of the future which is the subject of the put is
exceeded by the strike price of the put. The Fund may use futures and options thereon solely for bona fide
hedging or for other non-speculative purposes. As to long positions which are used as part of the Fund's
strategies and are incidental to its activities in the underlying cash market, the "underlying commodity value"
of the Fund's futures and options thereon must not exceed the sum of (i) cash set aside in an identifiable
manner, or short-term U.S. debt obligations or other dollar-denominated high-quality, short-term money
instruments so set aside, plus sums deposited on margin; (ii) cash proceeds from existing investments due in 30
days; and (iii) accrued profits held at the futures commission merchant. The "underlying commodity value" of a
future is computed by multiplying the size of the future by the daily settlement price of the future. For an
option on a future, that value is the underlying commodity value of the future underlying the option.
Unlike the situation in which the Fund purchases or sells a security, no price is paid or received by
the Fund upon the purchase or sale of a futures contract. Instead, the Fund is required to deposit in a
segregated asset account an amount of cash or qualifying securities (currently U.S. Treasury bills), currently in
a minimum amount of $15,000. This is called "initial margin." Such initial margin is in the nature of a
performance bond or good faith deposit on the contract. However, since losses on open contracts are required to
be reflected in cash in the form of variation margin payments, the Fund may be required to make additional
payments during the term of a contract to its broker. Such payments would be required, for example, where,
during the term of an interest rate futures contract purchased by the Fund, there was a general increase in
interest rates, thereby making the Fund's securities less valuable. In all instances involving the purchase of
financial futures contracts by the Fund, an amount of cash together with such other securities as permitted by
applicable regulatory authorities to be utilized for such purpose, at least equal to the market value of the
future contracts, will be deposited in a segregated account with the Fund's custodian to collateralize the
position. At any time prior to the expiration of a futures contract, the Fund may elect to close its position by
taking an opposite position which will operate to terminate the Fund's position in the futures contract.
Because futures contracts are generally settled within a day from the date they are closed out, compared
with a settlement period of three business days for most types of securities, the futures markets can provide
superior liquidity to the securities markets. Nevertheless, there is no assurance a liquid secondary market will
exist for any particular futures contract at any particular time. In addition, futures exchanges may establish
daily price fluctuation limits for futures contracts and may halt trading if a contract's price moves upward or
downward more than the limit in a given day. On volatile trading days when the price fluctuation limit is
reached, it would be impossible for the Fund to enter into new positions or close out existing positions. If the
secondary market for a futures contract were not liquid because of price fluctuation limits or otherwise, the
Fund would not promptly be able to liquidate unfavorable futures positions and potentially could be required to
continue to hold a futures position until the delivery date, regardless of changes in its value. As a result,
the Fund's access to other assets held to cover its futures positions also could be impaired. For an additional
discussion of futures contracts and certain risks involved therein, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus
under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Options on Futures Contracts. The Fund may purchase put and call options on futures contracts. An
option on a futures contract provides the holder with the right to enter into a "long" position in the underlying
futures contract, in the case of a call option, or a "short" position in the underlying futures contract, in the
case of a put option, at a fixed exercise price to a stated expiration date. Upon exercise of the option by the
holder, a contract market clearing house establishes a corresponding short position for the writer of the option,
in the case of a call option, or a corresponding long position, in the case of a put option. In the event that
an option is exercised, the parties will be subject to all the risks associated with the trading of futures
contracts, such as payment of variation margin deposits.
A position in an option on a futures contract may be terminated by the purchaser or seller prior to
expiration by effecting a closing purchase or sale transaction, subject to the availability of a liquid secondary
market, which is the purchase or sale of an option of the same series (i.e., the same exercise price and
expiration date) as the option previously purchased or sold. The difference between the premiums paid and
received represents the trader's profit or loss on the transaction.
An option, whether based on a futures contract, a stock index or a security, becomes worthless to the
holder when it expires. Upon exercise of an option, the exchange or contract market clearing house assigns
exercise notices on a random basis to those of its members which have written options of the same series and with
the same expiration date. A brokerage firm receiving such notices then assigns them on a random basis to those
of its customers which have written options of the same series and expiration date. A writer therefore has no
control over whether an option will be exercised against it, nor over the time of such exercise.
The purchase of a call option on a futures contract is similar in some respects to the purchase of a
call option on an individual security. See "Options on Foreign Currencies" below. Depending on the pricing of
the option compared to either the price of the futures contract upon which it is based or the price of the
underlying instrument, ownership of the option may or may not be less risky than ownership of the futures
contract or the underlying instrument. As with the purchase of futures contracts, when the Fund is not fully
invested it could buy a call option on a futures contract to hedge against a market advance. The purchase of a
put option on a futures contract is similar in some respects to the purchase of protective put options on
portfolio securities. For example, the Fund would be able to buy a put option on a futures contract to hedge the
Fund against the risk of falling prices. For an additional discussion of options on futures contracts and
certain risks involved therein, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risks Factors and
Investment Methods."
Options on Foreign Currencies. The Fund may buy and sell options on foreign currencies for hedging
purposes in a manner similar to that in which futures on foreign currencies would be utilized. For example, a
decline in the U.S. dollar value of a foreign currency in which portfolio securities are denominated would reduce
the U.S. dollar value of such securities, even if their value in the foreign currency remained constant. In
order to protect against such diminutions in the value of portfolio securities, the Fund could buy put options on
the foreign currency. If the value of the currency declines, the Fund would have the right to sell such currency
for a fixed amount in U.S. dollars and would thereby offset, in whole or in part, the adverse effect on the Fund
which otherwise would have resulted. Conversely, when a rise is projected in the U.S. dollar value of a currency
in which securities to be acquired are denominated, thereby increasing the cost of such securities, the Fund
could buy call options thereon. The purchase of such options could offset, at least partially, the effects of
the adverse movements in exchange rates.
Options on foreign currencies traded on national securities exchanges are within the jurisdiction of the
Securities and Exchange Commission (the "SEC"), as are other securities traded on such exchanges. As a result,
many of the protections provided to traders on organized exchanges will be available with respect to such
transactions. In particular, all foreign currency option positions entered into on a national securities
exchange are cleared and guaranteed by the Options Clearing Corporation ("OCC"), thereby reducing the risk of
counterparty default. Further, a liquid secondary market in options traded on a national securities exchange may
be more readily available than in the over-the-counter market, potentially permitting the Fund to liquidate open
positions at a profit prior to exercise or expiration, or to limit losses in the event of adverse market
movements.
The purchase and sale of exchange-traded foreign currency options, however, is subject to the risks of
the availability of a liquid secondary market described above, as well as the risks regarding adverse market
movements, margining of options written, the nature of the foreign currency market, possible intervention by
governmental authorities, and the effects of other political and economic events. In addition, exchange-traded
options on foreign currencies involve certain risks not presented by the over-the-counter market. For example,
exercise and settlement of such options must be made exclusively through the OCC, which has established banking
relationships in applicable foreign countries for this purpose. As a result, the OCC may, if it determines that
foreign governmental restrictions or taxes would prevent the orderly settlement of foreign currency option
exercises, or would result in undue burdens on the OCC or its clearing member, impose special procedures on
exercise and settlement, such as technical changes in the mechanics of delivery of currency, the fixing of dollar
settlement prices, or prohibitions on exercise.
Risk Factors of Investing in Futures and Options. The successful use of the investment practices
described above with respect to futures contracts, options on futures contracts, and options on securities
indices, securities, and foreign currencies draws upon skills and experience which are different from those
needed to select the other instruments in which the Fund invests. Should interest or exchange rates or the
prices of securities or financial indices move in an unexpected manner, the Fund may not achieve the desired
benefits of futures and options or may realize losses and thus be in a worse position than if such strategies had
not been used. Unlike many exchange-traded futures contracts and options on futures contracts, there are no
daily price fluctuation limits with respect to options on currencies and negotiated or over-the-counter
instruments, and adverse market movements could therefore continue to an unlimited extent over a period of time.
In addition, the correlation between movements in the price of the securities and currencies hedged or used for
cover will not be perfect and could produce unanticipated losses.
The Fund's ability to dispose of its positions in the foregoing instruments will depend on the
availability of liquid markets in the instruments. Markets in a number of the instruments are relatively new and
still developing and it is impossible to predict the amount of trading interest that may exist in those
instruments in the future. Particular risks exist with respect to the use of each of the foregoing instruments
and could result in such adverse consequences to the Fund as the possible loss of the entire premium paid for an
option bought by the Fund and the possible need to defer closing out positions in certain instruments to avoid
adverse tax consequences. As a result, no assurance can be given that the Fund will be able to use those
instruments effectively for the purposes set forth above.
In addition, options on U.S. Government securities, futures contracts, options on futures contracts,
forward contracts and options on foreign currencies may be traded on foreign exchanges and over-the-counter in
foreign countries. Such transactions are subject to the risk of governmental actions affecting trading in or the
prices of foreign currencies or securities. The value of such positions also could be affected adversely by (i)
other complex foreign political and economic factors, (ii) lesser availability than in the United States of data
on which to make trading decisions, (iii) delays in the Fund's ability to act upon economic events occurring in
foreign markets during nonbusiness hours in the United States, (iv) the imposition of different exercise and
settlement terms and procedures and margin requirements than in the United States, and (v) low trading volume.
For an additional discussion of certain risks involved in investing in futures and options, see this SAI and the
Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Foreign Securities. Investments in foreign countries involve certain risks which are not typically
associated with U.S. investments. For a discussion of certain risks involved in foreign investing, see this SAI
and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Forward Contracts for Purchase or Sale of Foreign Currencies. The Fund generally conducts its foreign
currency exchange transactions on a spot (i.e., cash) basis at the spot rate prevailing in the foreign exchange
currency market. When the Fund purchases or sells a security denominated in a foreign currency, it may enter
into a forward foreign currency contract ("forward contract") for the purchase or sale, for a fixed amount of
dollars, of the amount of foreign currency involved in the underlying security transaction. A forward contract
involves an obligation to purchase or sell a specific currency at a future date, which may be any fixed number of
days from the date of the contract agreed upon by the parties, at a price set at the time of the contract. The
Fund generally will not enter into forward contracts with a term greater than one year. In this manner, the Fund
may obtain protection against a possible loss resulting from an adverse change in the relationship between the
U.S. dollar and the foreign currency during the period between the date the security is purchased or sold and the
date upon which payment is made or received. Although such contracts tend to minimize the risk of loss due to
the decline in the value of the hedged currency, at the same time they tend to limit any potential gain which
might result should the value of such currency increase. The Fund will not speculate in forward contracts.
Forward contracts are traded in the interbank market conducted directly between currency traders
(usually large commercial banks) and their customers. Generally a forward contract has no deposit requirement,
and no commissions are charged at any stage for trades. Although foreign exchange dealers do not charge a fee
for conversion, they do realize a profit based on the difference between the prices at which they buy and sell
various currencies. When the Sub-advisor believes that the currency of a particular foreign country may suffer a
substantial decline against the U.S. dollar (or sometimes against another currency), the Fund may enter into a
forward contract to sell, for a fixed dollar or other currency amount, foreign currency approximating the value
of some or all of the Fund's securities denominated in that currency. In addition, the Fund may engage in
"proxy-hedging," i.e., entering into forward contracts to sell a different foreign currency than the one in which
the underlying investments are denominated with the expectation that the value of the hedged currency will
correlate with the value of the underlying currency. The Fund will not enter into forward contracts or maintain
a net exposure to such contracts where the fulfillment of the contracts would require the Fund to deliver an
amount of foreign currency or a proxy currency in excess of the value of its portfolio securities or other assets
denominated in the currency being hedged. Forward contracts may, from time to time, be considered illiquid, in
which case they would be subject to the Fund's limitation on investing in illiquid securities.
At the consummation of a forward contract for delivery by the Fund of a foreign currency, the Fund may
either make delivery of the foreign currency or terminate its contractual obligation to deliver the foreign
currency by purchasing an offsetting contract obligating it to purchase, at the same maturity date, the same
amount of the foreign currency. If the Fund chooses to make delivery of the foreign currency, it may be required
to obtain such currency through the sale of portfolio securities denominated in such currency or through
conversion of other Fund assets into such currency.
Dealings in forward contracts by the Fund will be limited to the transactions described above. Of
course, the Fund is not required to enter into such transactions with regard to its foreign currency-denominated
securities and will not do so unless deemed appropriate by the Sub-advisor. It also should be realized that this
method of protecting the value of the Fund's securities against a decline in the value of a currency does not
eliminate fluctuations in the underlying prices of the securities. It simply establishes a rate of exchange
which can be achieved at some future point in time. Additionally, although such contracts tend to minimize the
risk of loss due to the decline in the value of the hedged currency, at the same time they tend to limit any
potential gain which might result should the value of such currency increase. For an additional discussion of
forward foreign currency contracts and certain risks involved therein, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus
under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Lower-Rated or Unrated Fixed-Income Securities. The Fund may invest up to 5% of its total assets in
fixed-income securities which are unrated or are rated below investment grade either at the time of purchase or
as a result of reduction in rating after purchase. (This limitation does not apply to convertible securities and
preferred stocks.) Investments in lower-rated or unrated securities are generally considered to be of high
risk. These debt securities, commonly referred to as junk bonds, are generally subject to two kinds of risk,
credit risk and market risk. Credit risk relates to the ability of the issuer to meet interest or principal
payments, or both, as they come due. The ratings given a security by Moody's Investors Service, Inc. ("Moody's")
and Standard & Poor's ("S&P") provide a generally useful guide as to such credit risk. For a description of
securities ratings, see the Appendix to this SAI. The lower the rating given a security by a rating service, the
greater the credit risk such rating service perceives to exist with respect to the security. Increasing the
amount of the Fund's assets invested in unrated or lower grade securities, while intended to increase the yield
produced by those assets, will also increase the risk to which those assets are subject.
Market risk relates to the fact that the market values of debt securities in which the Fund invests
generally will be affected by changes in the level of interest rates. An increase in interest rates will tend to
reduce the market values of such securities, whereas a decline in interest rates will tend to increase their
values. Medium and lower-rated securities (Baa or BBB and lower) and non-rated securities of comparable quality
tend to be subject to wider fluctuations in yields and market values than higher rated securities and may have
speculative characteristics. In order to decrease the risk in investing in debt securities, in no event will the
Fund ever invest in a debt security rated below B by Moody's or by S&P. Of course, relying in part on ratings
assigned by credit agencies in making investments will not protect the Fund from the risk that the securities in
which they invest will decline in value, since credit ratings represent evaluations of the safety of principal,
dividend, and interest payments on debt securities, and not the market values of such securities, and such
ratings may not be changed on a timely basis to reflect subsequent events.
Because investment in medium and lower-rated securities involves greater credit risk, achievement of the
Fund's investment objective may be more dependent on the Sub-advisor's own credit analysis than is the case for
funds that do not invest in such securities. In addition, the share price and yield of the Fund may fluctuate
more than in the case of funds investing in higher quality, shorter term securities. Moreover, a significant
economic downturn or major increase in interest rates may result in issuers of lower-rated securities
experiencing increased financial stress, which would adversely affect their ability to service their principal,
dividend, and interest obligations, meet projected business goals, and obtain additional financing. In this
regard, it should be noted that while the market for high yield debt securities has been in existence for many
years and from time to time has experienced economic downturns in recent years, this market has involved a
significant increase in the use of high yield debt securities to fund highly leveraged corporate acquisitions and
restructurings. Past experience may not, therefore, provide an accurate indication of future performance of the
high yield debt securities market, particularly during periods of economic recession. Furthermore, expenses
incurred in recovering an investment in a defaulted security may adversely affect the Fund's net asset value.
Finally, while the Sub-advisor attempts to limit purchases of medium and lower-rated securities to securities
having an established secondary market, the secondary market for such securities may be less liquid than the
market for higher quality securities. The reduced liquidity of the secondary market for such securities may
adversely affect the market price of, and ability of the Fund to value, particular securities at certain times,
thereby making it difficult to make specific valuation determinations. The Fund does not invest in any medium
and lower-rated securities which present special tax consequences, such as zero-coupon bonds or pay-in-kind
bonds. For an additional discussion of certain risks involved in lower-rated securities, see this SAI and the
Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
The Sub-advisor seeks to reduce the overall risks associated with the Fund's investments through
diversification and consideration of factors affecting the value of securities it considers relevant. No
assurance can be given, however, regarding the degree of success that will be achieved in this regard or that the
Fund will achieve its investment objective.
Convertible Securities. The Fund may buy securities convertible into common stock if, for example, the
Sub-advisor believes that a company's convertible securities are undervalued in the market. Convertible
securities eligible for purchase include convertible bonds, convertible preferred stocks, and warrants. A
warrant is an instrument issued by a corporation which gives the holder the right to subscribe to a specific
amount of the corporation's capital stock at a set price for a specified period of time. Warrants do not
represent ownership of the securities, but only the right to buy the securities. The prices of warrants do not
necessarily move parallel to the prices of underlying securities. Warrants may be considered speculative in that
they have no voting rights, pay no dividends, and have no rights with respect to the assets of a corporation
issuing them. Warrant positions will not be used to increase the leverage of the Fund; consequently, warrant
positions are generally accompanied by cash positions equivalent to the required exercise amount.
Temporary Defensive Investments. Up to 100% of the assets of the Fund may be invested temporarily in
U.S. government obligations, commercial paper, bank obligations, repurchase agreements, negotiable U.S.
dollar-denominated obligations of domestic and foreign branches of U.S. depository institutions, U.S. branches of
foreign depository institutions, and foreign depository institutions, in cash, or in other cash equivalents, if
the Sub-advisor determines it to be appropriate for purposes of enhancing liquidity or preserving capital in
light of prevailing market or economic conditions. U.S. government obligations include Treasury bills, notes and
bonds, and issues of United States agencies, authorities and instrumentalities. Some government obligations,
such as Government National Mortgage Association pass-through certificates, are supported by the full faith and
credit of the United States Treasury. Other obligations, such as securities of the Federal Home Loan Banks, are
supported by the right of the issuer to borrow from the United States Treasury; and others, such as bonds issued
by Federal National Mortgage Association (a private corporation), are supported only by the credit of the agency,
authority or instrumentality. The Fund also may invest in obligations issued by the International Bank for
Reconstruction and Development (IBRD or "World Bank"). For more information on mortgage-related securities, see
this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
not "fundamental" restrictions and may be changed by the Directors of the Company without shareholder approval.
The Fund will not:
1........Invest more than 15% of the market value of its net assets in securities which are not readily
marketable, including repurchase agreements maturing in over seven days;
2........Purchase securities of other investment companies except in compliance with the Investment
Company Act of 1940;
3........Purchase any securities on margin except to obtain such short-term credits as may be necessary
for the clearance of transactions (and, provided that margin payments and other deposits in connection with
transactions in options, futures and forward contracts shall not be deemed to constitute purchasing securities on
margin); or
4........Sell securities short.
In addition, in periods of uncertain market and economic conditions, as determined by the Sub-advisor,
the Fund may depart from its basic investment objective and assume a defensive position with up to 100% of its
assets temporarily invested in high quality corporate bonds or notes and government issues, or held in cash.
If a percentage restriction is adhered to at the time of investment, a later increase or decrease in
percentage beyond the specified limit that results from a change in values or net assets will not be considered a
violation.
ASAF AIM INTERNATIONAL EQUITY FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek long-term capital growth by investing in a
diversified portfolio of international equity securities the issuers of which are considered by the Sub-advisor
to have strong earnings momentum.
Investment Policies:
In managing the Fund, the Sub-advisor seeks to apply to the Fund the same investment strategy that it
applies to several of its other managed portfolios that have similar investment objectives but that invest
primarily in United States equities markets. The Fund will utilize to the extent practicable a fully managed
investment policy providing for the selection of securities which meet certain quantitative standards determined
by the Sub-advisor. The Sub-advisor reviews carefully the earnings history and prospects for growth of each
company considered for investment by the Fund. It is anticipated that common stocks will be the principal form
of investment of the Fund. The Fund is primarily comprised of securities of two basic categories of companies:
(a) "core" companies, which the Sub-advisor considers to have experienced above-average and consistent long-term
growth in earnings and to have excellent prospects for outstanding future growth, and (b) "earnings acceleration"
companies, which the Sub-advisor believes are currently enjoying a dramatic increase in earnings.
If a particular foreign company meets the quantitative standards determined by the Sub-advisor, its
securities may be acquired by the Fund regardless of the location of the company or the percentage of the Fund's
investments in the company's country or region. However, the Sub-advisor will also consider other factors in
making investment decisions for the Fund, including such factors as the prospects for relative economic growth
among countries or regions, economic and political conditions, currency exchange fluctuations, tax considerations
and the liquidity of a particular security.
The Sub-advisor recognizes that often there is less public information about foreign companies than is
available in reports supplied by domestic companies, that foreign companies are not subject to uniform accounting
and financial reporting standards, and that there may be greater delays experienced by the Fund in receiving
financial information supplied by foreign companies than comparable information supplied by domestic companies.
In addition, the value of the Fund's investments that are denominated in a foreign currency may be affected by
changes in currency exchange rates. For these and other reasons, the Sub-advisor from time to time may encounter
greater difficulty applying its disciplined stock selection strategy to an international equity investment
portfolio than to a portfolio of domestic equity securities.
Any income realized by the Fund will be incidental and will not be an important criterion in the
selection of portfolio securities.
Under normal market conditions the Fund will invest at least 70% of its total assets in marketable
equity securities, including common stock, preferred stock, and other securities having the characteristics of
stock (such as an equity or ownership interest in a company) of foreign companies that are listed on a recognized
foreign securities exchange or traded on a foreign over-the-counter market. The Fund may also satisfy the
foregoing requirement in part by investing in the securities of foreign issuers in the form of ADRs, EDRs, or
other securities representing underlying securities of foreign issuers. The Fund may also invest up to 20% of
its total assets in securities exchangeable for or convertible into equity securities of foreign companies that
are listed on a recognized foreign securities exchange or traded in a foreign over-the-counter market.
Under normal market conditions, the Fund intends to invest in a diversified portfolio that includes
companies located in at least four countries outside of the United States. The Fund will emphasize investment in
foreign companies in the developed countries of Western Europe (such as Germany, France, Switzerland, the
Netherlands and the United Kingdom) and the Pacific Basin (such as Japan, Hong Kong and Australia), but the
Portfolio may also invest in the securities of companies located in developing countries (such as Turkey,
Malaysia and Mexico) in various regions of the world. The risks of investment in the equity markets of
developing countries are described in more detail immediately below and in this Statement under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods."
Real Estate Investment Trusts ("REITs"). The Fund may invest in equity and/or debt securities issued by
REITs. Such investments will not exceed 5% of the total assets of the Fund.
REITs are trusts that sell equity or debt securities to investors and use the proceeds to invest in real
estate or interests therein. A REIT may focus on particular types of projects, such as apartment complexes, or
geographic regions, such as the Southeastern United States, or both.
To the extent that the Fund invests in REITs, it could conceivably own real estate directly as a result
of a default on the securities it owns. The Fund, therefore, may be subject to certain risks associated with the
direct ownership of real estate, including difficulties in valuing and trading real estate, declines in the value
of real estate, environmental liability risks, risks related to general and local economic conditions, adverse
change in the climate for real estate, increases in property taxes and operating expenses, changes in zoning
laws, casualty or condemnation losses, limitations on rents, changes in neighborhood values, the appeal of
properties to tenants, and increases in interest rates.
In addition to the risks described above, equity REITs may be affected by any changes in the value of
the underlying property owned by the trusts, while mortgage REITs may be affected by the quality of any credit
extended. Equity and mortgage REITs are dependent upon management skill, and are generally not diversified and
therefore are subject to the risk of financing single or a limited number of projects. Such trusts are also
subject to heavy cash flow dependency, defaults by borrowers, self-liquidation, and the possibility that the REIT
will fail to maintain its exemption from the 1940 Act. Changes in interest rates may also affect the value of
debt securities of REITs held by the Fund. By investing in REITs indirectly through the Fund, a shareholder will
bear not only his/her proportionate share of the expenses of the Fund, but also, indirectly, similar expenses of
the REITs.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements. The Fund may employ reverse repurchase agreements (i) for temporary
emergency purposes, such as to meet unanticipated net redemptions so as to avoid liquidating other portfolio
securities during unfavorable market conditions; (ii) to cover short-term cash requirements resulting from the
timing of trade settlements; or (iii) to take advantage of market situations where the interest income to be
earned from the from the investment of the proceeds of the transaction is greater than the interest expense of
the transaction. The Fund may enter into reverse repurchase agreements in amounts not exceeding 10% of the value
of its total assets. Reverse repurchase agreements involve the risk that the market value of securities retained
by the Fund in lieu of liquidation may decline below the repurchase price of the securities sold by the Fund that
it is obligated to repurchase. This risk could cause a reduction in the net asset value of the Fund's shares.
Additional information about reverse repurchase agreements and their risks are included in the Trust's
Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Lending of Portfolio Securities. While securities are being lent, the Fund will continue to receive the
equivalent of the interest or dividends paid by the issuer on the securities, as well as interest on the
investment of the collateral or a fee from the borrower. The Fund has the right to call its loans and obtain the
securities on three business days' notice or, in connection with securities trading on foreign markets, within
such longer period of time that coincides with the normal settlement period for purchases and sales of such
securities in such foreign markets. The risks in lending portfolio securities, as with other extensions of
secured credit, consist of possible delay in receiving additional collateral or in the recovery of the securities
or possible loss of rights in the collateral should the borrower fail financially. Additional information about
the lending of portfolio securities is included in this Statement and the Trust's Prospectus under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods."
Borrowings. The Fund may borrow money to a limited extent from banks for temporary or emergency
purposes subject to the limitations under the 1940 Act. In addition, the Fund does not intend to engage in
leverage; therefore, consistent with current interpretations of the SEC, the Fund will not purchase additional
securities while borrowings from banks exceed 5% of the Fund's total assets. Additional information about
borrowing is included in the Trust's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Securities Issued on a When-Issued or Delayed-Delivery Basis. The Fund may purchase securities on a
"when-issued" basis, that is, delivery of and payment for the securities is not fixed at the date of purchase,
but is set after the securities are issued (normally within forty-five days after the date of the transaction).
The Fund also may purchase or sell securities on a delayed-delivery basis. The payment obligation and the
interest rate that will be received on the delayed delivery-securities are fixed at the time the buyer enters
into the commitment. If the Fund purchases a when-issued security or enters into a delayed-delivery agreement,
the Fund's custodian bank will segregate cash or other liquid assets in an amount at least equal to the
when-issued commitment or delayed-delivery agreement commitment. Additional information about when-issued and
delayed-delivery transactions and their risks is included in this Statement and in the Trust's Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Short Sales "Against the Box." As described in the Trust's Prospectus, the Fund may from time to time
make short sales against the box. To secure its obligation to deliver the securities sold short, the Fund will
deposit in escrow in a separate account with its custodian an equal amount of the securities sold short or
securities convertible into or exchangeable for such securities. Because the Fund ordinarily will want to
continue to receive interest and dividend payments on securities in its portfolio that are convertible into the
securities sold short, the Fund will normally close out a short position covered by convertible securities by
purchasing and delivering an equal amount of the securities sold short, rather than by delivering the convertible
securities that it already holds.
The Fund will make a short sale, as a hedge, when it believes that the price of a security may decline,
causing a decline in the value of a security owned by the Fund or a security convertible into or exchangeable for
such security. In such case, any future losses in the Fund's long position should be reduced by a gain in the
short position. Conversely, any gain in the long position should be reduced by a loss in the short position.
The extent to which such gains or losses are reduced will depend upon the amount of the security sold short
relative to the amount the Fund owns, either directly or indirectly, and, in the case where the Fund owns
convertible securities, changes in the conversion premium. In determining the number of shares to be sold short
against the Fund's position in a convertible security, the anticipated fluctuation in the conversion premium is
considered. The Fund may also make short sales to generate additional income from the investment of the cash
proceeds of short sales. In no event may more than 10% of the value of the Fund's total assets be deposited or
pledged as collateral for short sales at any time.
Foreign Securities. The Fund normally invests primarily in foreign securities, including American
Depositary Receipts ("ADRs") and European Depositary Receipts ("EDRs"). Generally, ADRs, in registered form, are
designed for use in the United States securities markets, and EDRs, in bearer form, are designed for use in
European securities markets. ADRs and EDRs may be listed on stock exchanges, or traded in OTC markets in the
United States or Europe, as the case may be. ADRs, like other securities traded in the United States, will be
subject to negotiated commission rates.
To the extent the Fund invests in securities denominated in foreign currencies, the Fund bears the risk
of changes in the exchange rates between U.S. currency and the foreign currency, as well as the availability and
status of foreign securities markets. The Fund's investments in securities denominated in foreign currencies
generally will be marketable equity securities (including common and preferred stock, depositary receipts for
stock and fixed income or equity securities exchangeable for or convertible into stock) of foreign companies that
generally are listed on a recognized foreign securities exchange or traded in a foreign over-the-counter market.
The Fund may also invest in foreign securities listed on recognized U.S. securities exchanges or traded in the
U.S. over-the-counter market.
Investments by the Fund in foreign securities, whether denominated in U.S. currencies or foreign
currencies, may entail risks that are greater than those associated with domestic investments. The risks of
investing in foreign securities are discussed in detail in this Statement and the Trust's Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods." Investment by the Fund in ADRs, EDRs and similar securities also
may entail some or all or these risks. The Sub-advisor seeks to mitigate the risks associated with foreign
investment through diversification and active professional management.
Developing Countries. A developing country or emerging market country can be considered to be
a country that is in the initial stages of its industrialization cycle. Currently, emerging markets generally
include every country in the world other than the developed European countries (primarily in Western Europe), the
United States, Canada, Japan, Australia, New Zealand, Hong Kong and Singapore. The characteristics of markets
can change over time. Currently, the Sub-advisor believes that investing in many emerging markets is not
desirable or feasible because of the lack of adequate custody arrangements for the Fund's assets, overly
burdensome repatriation and similar restrictions, the lack of organized and liquid securities markets,
unacceptable political risks or other reasons. As desirable opportunities to invest in securities in emerging
markets develop, the Fund may expand and further broaden the group of emerging markets in which it invests.
Many of the risks relating to foreign securities generally will be greater for emerging markets than for
developed countries. Many emerging markets have experienced substantial rates of inflation for many years.
Inflation and rapid fluctuations in inflation rates have had and may continue to have very negative effects on
the economies and securities markets for certain developing markets. Economies in emerging markets generally are
heavily dependent upon international trade and accordingly, have been and may continue to be affected adversely
by trade barriers, exchange controls, managed adjustments in relative currency values and other protectionist
measures imposed or negotiated by the countries with which they trade. These economies also have been and may
continue to be affected adversely by economic conditions in the countries with which they trade. There also may
be a lower level of securities market monitoring and regulation of developing markets and the activities of
investors in such markets, and enforcement of existing regulations has been extremely limited. The possibility
of revolution and the dependence on foreign economic assistance may be greater in these countries than in
developed countries.
In addition, brokerage commissions, custodial services and other costs relating to investment in foreign
markets are often higher than the costs of investing in the United States; this is particularly true with respect
to emerging markets. Such markets have different settlement and clearance procedures. In certain markets there
have been times when settlements have been unable to keep pace with the volume of securities transactions, making
it difficult to conduct such transactions. Such settlement problems may cause emerging market securities to be
illiquid. The inability of the Fund to make intended securities purchases due to settlement problems could cause
the Fund to miss attractive investment opportunities. Inability to dispose of a portfolio security caused by
settlement problems could result in losses to the Fund due to subsequent declines in value of the portfolio
security or, if the Fund has entered into a contract to sell the security, could result in liability to the
purchaser. Certain emerging markets may lack clearing facilities equivalent to those in developed countries.
Accordingly, settlements can pose additional risks in such markets and ultimately can expose the Fund to the risk
of losses resulting from its inability to recover from a counterparty.
The risk also exists that an emergency situation may arise in one or more emerging markets as a result
of which trading of securities may cease or may be substantially curtailed and prices for the Fund's portfolio
securities in such markets may not be readily available. The Fund's portfolio securities in the affected markets
will be valued at fair value determined in good faith by or under the direction of the Company's Board of
Directors.
Portfolio Turnover. Any particular security will be sold, and the proceeds reinvested, whenever such
action is deemed prudent from the viewpoint of the Fund's investment objective, regardless of the holding period
of that security. Additional information about portfolio turnover is included in this Statement under "Portfolio
Transactions" and the Trust's Prospectus under "Portfolio Turnover."
Options, Futures and Currency Strategies. The Fund may use forward contracts, futures contracts,
options on securities, options on indices, options on currencies, and options on futures contracts to attempt to
hedge against the overall level of investment and currency risk normally associated with the Fund's investments.
These instruments are often referred to as "derivatives," which may be defined as financial instruments whose
performance is derived, at least in part, from the performance of another asset (such as a security, currency or
an index of securities).
General Risks of Options, Futures and Currency Strategies. The use by the Fund of options, futures
contracts and forward currency contracts involves special considerations and risks. For example, there might be
imperfect correlation, or even no correlation, between the price movements or an instrument (such as an option
contract) and the price movements of the investments being hedged. In these circumstances, if a "protective put"
is used to hedge a potential decline in a security and the security does decline in price, the put option's
increased value may not completely offset the loss in the underlying security. Such a lack of correlation might
occur due to factors unrelated to the value of the investments being hedged, such as changing interest rates,
market liquidity, and speculative or other pressures on the markets in which the hedging instrument is traded.
The Fund will not enter into a hedging transaction if the Sub-advisor determines that the cost of
hedging will exceed the potential benefit to the Fund.
Additional information on these instruments is included in this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods." Certain risks pertaining to particular strategies are described in
the sections that follow.
Cover. Transactions using forward contracts, futures contracts and options (other than options
purchased by a Fund) expose the Fund to an obligation to another party. A Fund will not enter into any such
transactions unless it owns either (1) an offsetting ("covered") position in securities, currencies, or other
options, forward contracts or futures contracts or (2) cash or liquid assets with a value sufficient at all times
to cover its potential obligations not covered as provided in (1) above. The Fund will comply with SEC
guidelines regarding cover for these instruments and, if the guidelines so require, set aside cash or liquid
securities.
Assets used as cover cannot be sold while the position in the corresponding forward contract, futures
contract or option is open, unless they are replaced with other appropriate assets. If a large portion of a
Fund's assets is used for cover or otherwise set aside, it could affect portfolio management or the Fund's ability
to meet redemption requests or other current obligations.
Writing Call Options. The Fund may write (sell) covered call options on securities, futures
contracts, forward contracts, indices and currencies. Writing call options can serve as a limited hedge because
declines in the value of the hedged investment would be offset to the extent of the premium received for writing
the option.
Writing Put Options. The Fund may write (sell) put options on securities, futures contracts,
forward contracts, indices and currencies. The Fund would write a put option at an exercise price that, reduced
by the premium received on the option, reflects the lower price it is willing to pay for the underlying security,
contract or currency. The risk in such a transaction would be that the market price of the underlying security,
contract or currency would decline below the exercise price less the premium received.
Purchasing Put Options. The Fund may purchase put options on securities, futures contracts,
forward contracts, indices and currencies. The Fund may enter into closing sale transactions with respect to
such options, exercise such option or permit such option to expire.
The Fund may also purchase put options on underlying securities, contracts or currencies against which
it has written other put options. For example, where the Fund has written a put option on an underlying
security, rather than entering a closing transaction of the written option, it may purchase a put option with a
different strike price and/or expiration date that would eliminate some or all of the risk associated with the
written put. Used in combinations, these strategies are commonly referred to as "put spreads." Likewise, the
Fund may write call options on underlying securities, contracts or currencies against which it has purchased
protective put options. This strategy is commonly referred to as a "collar."
Purchasing Call Options. The Fund may purchase covered call options on securities, futures
contracts, forward contracts, indices and currencies. The Fund may enter into closing sale transactions with
respect to such options, exercise such options or permit such options to expire.
The Fund may also purchase call options on underlying securities, contracts or currencies against which
it has written other call options. For example, where the Fund has written a call option on an underlying
security, rather than entering a closing transaction of the written option, it may purchase a call option with a
different strike price and/or expiration date that would eliminate some or all of the risk associated with the
written call. Used in combinations, these strategies are commonly referred to as "call spreads."
Options may be either listed on an exchange or traded in over-the-counter ("OTC") markets. Listed
options are third-party contracts (i.e., performance of the obligations of the purchaser and seller is guaranteed
by the exchange or clearing corporation) and have standardized strike prices and expiration dates. OTC options
are two-party contracts with negotiated strike prices and expiration dates. The Fund will not purchase an OTC
option unless it believes that daily valuations for such options are readily obtainable. OTC options differ from
exchange-traded options in that OTC options are transacted with dealers directly and not through a clearing
corporation (which would guarantee performance). Consequently, there is a risk of non-performance by the
dealer. Since no exchange is involved, OTC options are valued on the basis of an average of the last bid prices
obtained from dealers, unless a quotation from only one dealer is available, in which case only that dealer's
price will be used.
Index Options. The risks of investment in index options may be greater than options on
securities. Because index options are settled in cash, when the Fund writes a call on an index it cannot provide
in advance for its potential settlement obligations by acquiring and holding the underlying securities. The Fund
can offset some of the risk of writing a call index option position by holding a diversified portfolio of
securities similar to those on which the underlying index is based. However, the Fund cannot, as a practical
matter, acquire and hold a portfolio containing exactly the same securities as underlie the index and, as a
result, bears a risk that the value of the securities held will not be perfectly correlated with the value of the
index.
Limitations on Options. The Fund will not write options it, immediately after such sale, the
aggregate value of securities or obligations underlying the outstanding options exceeds 20% of the Fund's total
assets. The Fund will not purchase options if, at the time of the investment, the aggregate premiums paid for
the options will exceed 5% of the Fund's total assets.
Interest Rate, Currency and Stock Index Futures Contracts. The Fund may enter into interest
rate, currency or stock index futures contracts (collectively, "Futures" or "Futures Contracts") and options on
Futures as a hedge against changes in prevailing levels of interest rates, currency exchange rates or stock price
levels, respectively, in order to establish more definitely the effective return on securities or currencies held
or intended to be acquired by it. The Fund's hedging may include sales of Futures as an offset against the
effect of expected increases in interest rates, and decreases in currency exchange rates and stock prices, and
purchase of Futures as an offset against the effect of expected declines in interest rates, and increases in
currency exchange rates or stock prices.
A Futures Contract is a two party agreement to buy or sell a specified amount of a specified security or
currency (or deliver a cash settlement price, in the case of an index future) for a specified price at a
designated date, time and place. A stock index future provides for the delivery, at a designated date, time and
place, of an amount of cash equal to a specified dollar amount times the difference between the stock index value
at the close of trading on the contract and the price agreed upon in the Futures Contract; no physical delivery
of stocks comprising the index is made.
The Fund will only enter into Futures Contracts that are traded on futures exchanges and are
standardized as to maturity date and underlying financial instrument. Futures exchanges and trading thereon in
the United States are regulated under the Commodity Exchange Act and by the CFTC.
The Fund's Futures transactions will be entered into for hedging purposes only; that is, Futures will be
sold to protect against a decline in the price of securities or currencies that the Fund owns, or Futures will be
purchased to protect the Fund against an increase in the price of securities or currencies it has committed to
purchase or expects to purchase.
If the Fund were unable to liquidate a Future or an option on Futures position due to the absence of a
liquid secondary market or the imposition of price limits, it could incur substantial losses. The Fund would
continue to be subject to market risk with respect to the position. In addition, except in the case of purchased
options, the Fund might be required to maintain the position being hedged by the Future or option or to maintain
cash or securities in a segregated account.
Additional information on Futures, options on Futures, and their risks is included in this SAI and the
Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Forward Contracts. A forward contract is an obligation, usually arranged with a commercial
bank or other currency dealer, to purchase or sell a currency against another currency at a future date and price
as agreed upon by the parties. The Fund either may accept or make delivery of the currency at the maturity of
the forward contract. The Fund may also, if its contra party agrees prior to maturity, enter into a closing
transaction involving the purchase or sale of an offsetting contract. Forward contracts are traded
over-the-counter, and not on organized commodities or securities exchanges. As a result, it may be more
difficult to value such contracts, and it may be difficult to enter into closing transactions.
The cost to the Fund of engaging in forward contracts varies with factors such as the currencies
involved, the length of the contract period and the market conditions then prevailing. Because forward contracts
are usually entered into on a principal basis, no fees or commissions are involved. The use of forward contracts
does not eliminate fluctuations in the prices of the underlying securities the Fund owns or intends to acquire,
but it does establish a rate of exchange in advance.
Additional information on forward contracts and their risks is included in this SAI and the Company's
Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Other Investment Companies. The Fund may invest in other investment companies to the extent permitted
by the 1940 Act and rules and regulations thereunder, and, if applicable, exemptive orders granted by the SEC.
Investment Policy Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitation is
applicable to the ASAF AIM International Equity Fund. This limitation is not a "fundamental" restriction, and
may be changed by the Directors without shareholder approval. The Fund will not:
1. Make investments for the purpose of gaining control of a company's management.
ASAF JANUS OVERSEAS GROWTH FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund is to seek long-term
growth of capital.
Investment Policies:
Futures, Options and Other Derivative Instruments. The Fund may enter into futures contracts on
securities, financial indices, and foreign currencies and options on such contracts, and may invest in options on
securities, financial indices and foreign currencies, forward contracts and swaps. The Fund will not enter into
any futures contracts or options on futures contracts if the aggregate amount of the Fund's commitments under
outstanding futures contracts positions and options on futures contracts written by the Fund would exceed the
market value of the total assets of the Fund (i.e., no leveraging). The Fund may invest in forward currency
contracts with stated values of up to the value of the Fund's assets.
The Fund may buy or write options in privately negotiated transactions on the types of securities and
indices based on the types of securities in which the Fund is permitted to invest directly. The Fund will effect
such transactions only with investment dealers and other financial institutions (such as commercial banks or
savings and loan institutions) deemed creditworthy by the Sub-advisor, and only pursuant to procedures adopted by
the Sub-advisor for monitoring the creditworthiness of those entities. To the extent that an option bought or
written by the Fund in a negotiated transaction is illiquid, the value of an option bought or the amount of the
Fund's obligations under an option written by the Fund, as the case may be, will be subject to the Fund's
limitation on illiquid investments. In the case of illiquid options, it may not be possible for the Fund to
effect an offsetting transaction at a time when the Sub-advisor believes it would be advantageous for the Fund to
do so. For a description of these strategies and instruments and certain risks involved therein, see this SAI
and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Eurodollar Instruments. The Fund may make investments in Eurodollar instruments. Eurodollar instruments
are U.S. dollar-denominated futures contracts or options thereon which are linked to the London Interbank Offered
Rate ("LIBOR"), although foreign currency-denominated instruments are available from time to time. Eurodollar
futures contracts enable purchasers to obtain a fixed rate for the lending of funds and sellers to obtain a fixed
rate for borrowings. The Fund might use Eurodollar futures contracts and options thereon to hedge against changes
in LIBOR, to which many interest rate swaps and fixed-income instruments are linked.
Swaps and Swap-Related Products. The Fund may enter into interest rate swaps, caps and floors on either
an asset-based or liability-based basis, depending upon whether it is hedging its assets or its liabilities, and
will usually enter into interest rate swaps on a net basis (i.e., the two payment streams are netted out, with
the Fund receiving or paying, as the case may be, only the net amount of the two payments). The net amount of the
excess, if any, of the Fund's obligations over its entitlement with respect to each interest rate swap will be
calculated on a daily basis and an amount of cash or other liquid assets having an aggregate net asset value at
least equal to the accrued excess will be maintained in a segregated account by the custodian of the Fund. If the
Fund enters into an interest rate swap on other than a net basis, it would maintain a segregated account in the
full amount accrued on a daily basis of its obligations with respect to the swap. The Fund will not enter into
any interest rate swap, cap or floor transaction unless the unsecured senior debt or the claims-paying ability of
the other party thereto is rated in one of the three highest rating categories of at least one nationally
recognized statistical rating organization at the time of entering into such transaction. The Sub-advisor will
monitor the creditworthiness of all counterparties on an ongoing basis. If there is a default by the other party
to such a transaction, the Fund will have contractual remedies pursuant to the agreements related to the
transaction.
The swap market has grown substantially in recent years with a large number of banks and investment
banking firms acting both as principals and as agents utilizing standardized swap documentation. The Sub-advisor
has determined that, as a result, the swap market has become relatively liquid. Caps and floors are more recent
innovations for which standardized documentation has not yet been developed and, accordingly, they are less
liquid than swaps. To the extent the Fund sells (i.e., writes) caps and floors, it will segregate cash or other
liquid assets having an aggregate net asset value at least equal to the full amount, accrued on a daily basis, of
its obligations with respect to any caps or floors.
There is no limit on the amount of interest rate swap transactions that may be entered into by the Fund.
These transactions may in some instances involve the delivery of securities or other underlying assets by the
Fund or its counterparty to collateralize obligations under the swap. Under the documentation currently used in
those markets, the risk of loss with respect to interest rate swaps is limited to the net amount of the payments
that the Fund is contractually obligated to make. If the other party to an interest rate swap that is not
collateralized defaults, the Fund would risk the loss of the net amount of the payments that it contractually is
entitled to receive. The Fund may buy and sell (i.e., write) caps and floors without limitation, subject to the
segregation requirement described above. For an additional discussion of these strategies, see this SAI under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Investment Company Securities. From time to time, the Fund may invest in securities of other investment
companies, subject to the provisions of Section 12(d)(1) of the 1940 Act. The Fund may invest in securities of
money market funds managed by the Sub-advisor subject to the terms of an exemptive order obtained by the
Sub-advisor and the funds that are advised or sub-advised by the Sub-advisor. Under such order, the Fund will
limit its aggregate investment in a money market fund managed by the Sub-advisor to the greater of (i) 5% of its
total assets or (ii) $2.5 million, although the Company's Board of Directors may increase this limit up to 25% of
the Company's total assets.
Zero-Coupon, Pay-In-Kind and Step Coupon Securities. The Fund may invest up to 10% of its assets in
zero-coupon, pay-in-kind and step coupon securities. For a discussion of zero-coupon debt securities and the
risks involved therein, see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Pass-Through Securities. The Fund may invest in various types of pass-through securities, such as
mortgage-backed securities, asset-backed securities and participation interests. A pass-through security is a
share or certificate of interest in a pool of debt obligations that have been repackaged by an intermediary, such
as a bank or broker-dealer. The purchaser of a pass-through security receives an undivided interest in the
underlying pool of securities. The issuers of the underlying securities make interest and principal payments to
the intermediary which are passed through to purchasers, such as the Fund. For an additional discussion of
pass-through securities and certain risks involved therein, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Depositary Receipts. The Fund may invest in sponsored and unsponsored American Depositary Receipts
("ADRs"), which are receipts issued by an American bank or trust company evidencing ownership of underlying
securities issued by a foreign issuer. ADRs, in registered form, are designed for use in U.S. securities markets.
Unsponsored ADRs may be created without the participation of the foreign issuer. Holders of these ADRs generally
bear all the costs of the ADR facility, whereas foreign issuers typically bear certain costs in a sponsored ADR.
The bank or trust company depositary of an unsponsored ADR may be under no obligation to distribute shareholder
communications received from the foreign issuer or to pass through voting rights. The Fund may also invest in
European Depositary Receipts ("EDRs"), receipts issued by a European financial institution evidencing an
arrangement similar to that of ADRs, Global Depositary Receipts ("GDRs") and in other similar instruments
representing securities of foreign companies. EDRs, in bearer form, are designed for use in European securities
markets. GDRs are securities convertible into equity securities of foreign issuers.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements. The Fund may enter into reverse repurchase agreements. The Fund will
enter into such agreements only to provide cash to satisfy unusually heavy redemption requests and for other
temporary or emergency purposes, rather than to obtain cash to make additional investments. Pursuant to an
exemptive order granted by the SEC, the Fund and other funds advised or sub-advised by the Sub-advisor may invest
in repurchase agreements and other money market instruments through a joint trading account. For a discussion of
reverse repurchase agreements and the risks involved therein, see the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods."
Other Income-Producing Securities. Other types of income producing securities that the Fund may
purchase include, but are not limited to, the following types of securities:
Variable and Floating Rate Obligations. These types of securities are relatively long-term
instruments that often carry demand features permitting the holder to demand payment of principal at any time or
at specified intervals prior to maturity.
Standby Commitments. These instruments, which are similar to a put, give the Fund the option to
obligate a broker, dealer or bank to repurchase a security held by that Fund at a specified price.
Tender Option Bonds. Tender option bonds are relatively long-term bonds that are coupled with
the agreement of a third party (such as a broker, dealer or bank) to grant the holders of such securities the
option to tender the securities to the institution at periodic intervals.
Inverse Floaters. Inverse floaters are debt instruments whose interest bears an inverse
relationship to the interest rate on another security. The Fund will not invest more than 5% of its assets in
inverse floaters. The Fund will purchase standby commitments, tender option bonds and instruments with demand
features primarily for the purpose of increasing the liquidity of the Fund.
Investment Policies Which May be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
not "fundamental" restrictions and may be changed by the Directors of the Company without shareholder approval:
1. The Fund will not (i) enter into any futures contracts and related options for purposes other
than bona fide hedging transactions within the meaning of CFTC regulations if the aggregate initial margin and
premiums required to establish positions in futures contracts and related options that do not fall within the
definition of bona fide hedging transactions will exceed 5% of the fair market value of the Fund's net assets,
after taking into account unrealized profits and unrealized losses on any such contracts it has entered into; and
(ii) enter into any futures contracts if the aggregate amount of the Fund's commitments under outstanding futures
contracts positions would exceed the market value of its total assets.
2. The Fund does not currently intend to sell securities short, unless it owns or has the right to
obtain securities equivalent in kind and amount to the securities sold short without the payment of any
additional consideration therefor, and provided that transactions in futures, options, swaps and forward
contracts are not deemed to constitute selling securities short.
3. The Fund does not currently intend to purchase securities on margin, except that the Fund may
obtain such short-term credits as are necessary for the clearance of transactions, and provided that margin
payments and other deposits in connection with transactions in futures, options, swaps and forward contracts
shall not be deemed to constitute purchasing securities on margin.
4. The Fund does not currently intend to purchase securities of other investment companies, except
in compliance with the 1940 Act or the conditions of any order of exemption from the SEC regarding the purchase
of securities of money market funds managed by the Sub-advisor or its affiliates.
5. The Fund may not mortgage or pledge any securities owned or held by the Fund in amounts that
exceed, in the aggregate, 15% of the Fund's net asset value, provided that this limitation does not apply to
reverse repurchase agreements, deposits of assets to margin, guarantee positions in futures, options, swaps or
forward contracts, or the segregation of assets in connection with such contracts.
6. The Fund does not currently intend to purchase any security or enter into a repurchase
agreement if, as a result, more than 15% of its net assets would be invested in repurchase agreements not
entitling the holder to payment of principal and interest within seven days and in securities that are illiquid
by virtue of legal or contractual restrictions on resale or the absence of a readily available market. The
Directors of the Company, or the Sub-advisor acting pursuant to authority delegated by the Directors of the
Company, may determine that a readily available market exists for securities eligible for resale pursuant to Rule
144A under the Securities Act of 1933 ("Rule 144A Securities"), or any successor to such rule, and Section 4(2)
commercial paper. Accordingly, such securities may not be subject to the foregoing limitation.
7. The Fund may not invest in companies for the purpose of exercising control of management.
ASAF AMERICAN CENTURY INTERNATIONAL GROWTH FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth.
Investment Policies:
In general, within the restrictions outlined herein, the Fund has broad powers with respect to investing
funds or holding them uninvested. Investments are varied according to what is judged advantageous under changing
economic conditions. It will be the Sub-advisor's policy to retain maximum flexibility in management without
restrictive provisions as to the proportion of one or another class of securities that may be held, subject to
the investment restrictions described below. It is the Sub-advisor's intention that the Fund will generally
consist of common stocks. However, the Sub-advisor may invest the assets of the Fund in varying amounts in other
instruments and in senior securities, such as bonds, debentures, preferred stocks and convertible issues, when
such a course is deemed appropriate in order to attempt to attain its financial objective.
Forward Currency Exchange Contracts. The Fund conducts its foreign currency exchange transactions
either on a spot (i.e., cash) basis at the spot rate prevailing in the foreign currency exchange market, or
through entering into forward currency exchange contracts to purchase or sell foreign currencies.
The Fund expects to use forward contracts under two circumstances: (1) when the Sub-advisor wishes to
"lock in" the U.S. dollar price of a security when the Fund is purchasing or selling a security denominated in a
foreign currency, the Fund would be able to enter into a forward contract to do so ("transaction hedging"); (2)
when the Sub-advisor believes that the currency of a particular foreign country may suffer a substantial decline
against the U.S. dollar, the Fund would be able to enter into a forward contract to sell foreign currency for a
fixed U.S. dollar amount approximating the value of some or all of the Fund's securities either denominated in,
or whose value is tied to, such foreign currency ("portfolio hedging"). It's anticipated that the Fund will
enter into portfolio hedges much less frequently than transaction hedges.
As to transaction hedging, when the Fund enters into a trade for the purchase or sale of a security
denominated in a foreign currency, it may be desirable to establish (lock in) the U.S. dollar cost or proceeds.
By entering into forward contracts in U.S. dollars for the purchase or sale of a foreign currency involved in an
underlying security transaction, the Fund will be able to protect itself against a possible loss between trade
and settlement dates resulting from the adverse change in the relationship between the U.S. dollar and the
subject foreign currency.
Under portfolio hedging, when the Sub-advisor believes that the currency of a particular country may
suffer a substantial decline relative to the U.S. dollar, the Fund could enter into a forward contract to sell
for a fixed dollar amount the amount in foreign currencies approximating the value of some or all of its
portfolio securities either denominated in, or whose value is tied to, such foreign currency. The Fund will
place cash or high-grade liquid securities in a separate account with its custodian in an amount sufficient to
cover its obligation under the contract entered into under the second circumstance. If the value of the
securities placed in the separate account declines, additional cash or securities will be placed in the account
on a daily basis so that the value of the account equals the amount of the Fund's commitments with respect to
such contracts. At any given time, no more than 10% of the Fund's assets will be committed to a segregated
account in connection with portfolio hedging transactions.
The precise matching of forward contracts in the amounts and values of securities involved would not
generally be possible since the future values of such foreign currencies will change as a consequence of market
movements in the values of those securities between the date the forward contract is entered into and the date it
matures. Predicting short-term currency market movements is extremely difficult, and the successful execution of
short-term hedging strategy is highly uncertain. Normally, consideration of the prospect for currency parities
will be incorporated into the long-term investment decisions made with respect to overall diversification
strategies. However, the Sub-advisor believes that it is important to have flexibility to enter into such
forward contracts when it determines that the Fund's best interests may be served.
Generally, the Fund will not enter into a forward contract with a term of greater than one year. At the
maturity of the forward contract, the Fund may either sell the portfolio security and make delivery of the
foreign currency, or it may retain the security and terminate the obligation to deliver the foreign currency by
purchasing an "offsetting" forward contract with the same currency trader obligating the Fund to purchase, on the
same maturity date, the same amount of the foreign currency.
It is impossible to forecast with absolute precision the market value of portfolio securities at the
expiration of the forward contract. Accordingly, it may be necessary for the Fund to purchase additional foreign
currency on the spot market (and bear the expense of such purchase) if the market value of the security is less
than the amount of foreign currency the Fund is obligated to deliver and if a decision is made to sell the
security and make delivery of the foreign currency the Fund is obligated to deliver. For an additional
discussion of forward currency exchange contracts and the risks involved therein, see this Statement and the
Trust's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Derivative Securities. To the extent permitted by its investment objectives and policies discussed
elsewhere herein, the Fund may invest in securities that are commonly referred to as "derivative" securities.
Certain derivative securities are more accurately described as "index/structured" securities. Index/structured
securities are derivative securities whose value or performance is linked to other equity securities (such as
depositary receipts), currencies, interest rates, indices or other financial indicators ("reference indices").
Some "derivatives," such as mortgage-backed and other asset-backed securities, are in many respects like
any other investment, although they may be more volatile or less liquid than more traditional debt securities.
The Fund may not invest in a derivative security unless the reference index or the instrument to which
it relates is an eligible investment for the Fund. For example, a security whose underlying value is linked to
the price of oil would not be a permissible investment because the Fund may not invest in oil and gas leases or
futures.
The return on a derivative security may increase or decrease, depending upon changes in the reference
index or instrument to which it relates.
There is a range of risks associated with derivative investments, including:
o the risk that the underlying security, interest rate, market index or other financial asset will not
move in the direction the portfolio manager anticipates;
o the possibility that there may be no liquid secondary market, or the possibility that price fluctuation
limits may be imposed by the exchange, either of which may make it difficult or impossible to close out
a position when desired; and
o the risk that the counterparty will fail to perform its obligations.
The Sub-advisor will report to the Investment Manager on activity in derivative securities, and the Investment
Manager will report to the Company's Board of Directors as necessary. For additional information on derivatives
and their risks, see the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Futures and Options. The Fund may enter into futures contracts, options or options on futures
contracts. The Fund may not, however, enter into a futures transaction for speculative purposes. Generally,
futures transactions will be used to:
o protect against a decline in market value of the Fund's securities (taking a short futures position), or
o protect against the risk of an increase in market value for securities in which the Fund generally
invests at a time when the Fund is not fully-invested (taking a long futures position), or
o provide a temporary substitute for the purchase of an individual security that may be purchased in an
orderly fashion.
Some futures and options strategies, such as selling futures, buying puts and writing calls, hedge the Fund's
investments against price fluctuations. Other strategies, such as buying futures, writing puts and buying calls,
tend to increase market exposure.
Although other techniques may be used to control the Fund's exposure to market fluctuations, the use of
futures contracts may be a more effective means of hedging this exposure. While the Fund will pay brokerage
commissions in connection with opening and closing out futures positions, these costs are lower than the
transaction costs incurred in the purchase and sale of the underlying securities.
The Fund may engage in futures and options transactions based on securities indices that are consistent
with the Fund's investment objectives. Examples of indices that may be used include the Bond Buyer Index of
Municipal Bonds for fixed income funds, or the S&P 500 Index for equity funds. The Fund also may engage in
futures and options transactions based on specific securities, such as U.S. Treasury bonds or notes. Futures
contracts are traded on national futures exchanges. Futures exchanges and trading are regulated under the
Commodity Exchange Act by the CFTC, a U.S. government agency.
Unlike when the Fund purchases or sells a bond, no price is paid or received by the Fund upon the
purchase or sale of the future. Initially, the Fund will be required to deposit an amount of cash or securities
equal to a varying specified percentage of the contract amount. This amount is known as initial margin. The
margin deposit is intended to assure completion of the contract (delivery or acceptance of the underlying
security) if it is not terminated prior to the specified delivery date. Minimum initial margin requirements are
established by the futures exchanges and may be revised. In addition, brokers may establish margin deposit
requirements that are higher than the exchange minimums. Cash held in the margin account is not income
producing. Subsequent payments, called variation margin, to and from the broker, will be made on a daily basis
as the price of the underlying debt securities or index fluctuates, making the future more or less valuable, a
process known as marking the contract to market.
Futures and options prices can be volatile, and trading in these markets involves certain risks, which
are described in more detail in this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods." The Sub-advisor will seek to minimize these risks by limiting the contracts entered into on behalf of
the Fund to those traded on national futures exchanges and for which there appears to be a liquid secondary
market.
Options on Futures. By purchasing an option on a futures contract, the Fund obtains the right, but not
the obligation, to sell the futures contract (a put option) or to buy the contract (a call option) at a fixed
strike price. The Fund can terminate its position in a put option by allowing it to expire or by exercising the
option. If the option is exercised, the Fund completes the sale of the underlying instrument at the strike
price. Purchasing an option on a futures contract does not require the Fund to make margin payments unless the
option is exercised.
Although they do not currently intend to do so, the Fund may write (or sell) call options that obligate
it to sell (or deliver) the option's underlying instrument upon exercise of the option. While the receipt of
option premiums would mitigate the effects of price declines, the Fund would give up some ability to participate
in a price increase on the underlying instrument. If the Fund were to engage in options transactions, it would
own the futures contract at the time a call were written and would keep the contract open until the obligation to
deliver it pursuant to the call expired.
Investments in Companies with Limited Operating History. The Fund may invest in the securities of
issuers with limiting operating history. The Sub-advisor considers an issuer to have a limited operating history
if that issuer has a record of less than three years of continuous operation.
Investments in securities of issuers with limited operating history may involve greater risks than
investments in securities of more mature issuers. By their nature, such issuers present limited operating
history and financial information upon which the manager may base its investment decision on behalf of the Fund.
In addition, financial and other information regarding such issuers, when available, may be incomplete or
inaccurate.
The Fund will not invest more than 5% of its total assets in the securities of issuers with less than a
three-year operating history. The Sub-advisor will consider periods of capital formation, incubation,
consolidation, and research and development in determining whether a particular issuer has a record of three
years of continuous operation.
Short Sales. The Fund may engage in short sales if, at the time of the short sale, the Fund owns or has
the right to acquire an equal amount of the security being sold short at no additional cost.
In a short sale, the seller does not immediately deliver the securities sold and is said to have a short
position in those securities until delivery occurs. To make delivery to the purchaser, the executing broker
borrows the securities being sold short on behalf of the seller. While the short position is maintained, the
seller collateralizes its obligation to deliver the securities sold short in an amount equal to the proceeds of
the short sale plus an additional margin amount established by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve. If
the Fund engages in a short sale the collateral account will be maintained by the Fund's custodian. While the
short sale is open the Fund will maintain in a segregated custodial account an amount of securities convertible
into or exchangeable for such equivalent securities at no additional cost. These securities would constitute the
Fund's long position.
If the Fund sells short securities that it owns, any future gains or losses in the Fund's long position
should be reduced by a gain or loss in the short position. The extent to which such gains or losses are reduced
would depend upon the amount of the security sold short relative to the amount the Fund owns. There will be
certain additional transaction costs associated with short sales, but the Fund will endeavor to offset these
costs with income from the investment of the cash proceeds of short sales.
Sovereign Debt Obligations. The Fund may purchase sovereign debt instruments issued or guaranteed by
foreign governments or their agencies, including debt of emerging market countries. Sovereign debt may be in the
form of conventional securities or other types of debt instruments such as loans or loan participations.
Sovereign debt of developing countries may involve a high degree of risk and may present a risk of default or
renegotiation or rescheduling of debt payments.
Portfolio Turnover. The Sub-advisor will purchase and sell securities without regard to the length of
time the security has been held and, accordingly, it can be expected that the rate of portfolio turnover may be
substantial.
The Sub-advisor intends to purchase a given security whenever the Sub-advisor believes it will
contribute to the stated objective of the Fund, even if the same security has only recently been sold. The Fund
will sell a given security, no matter for how long or for how short a period it has been held, and no matter
whether the sale is at a gain or at a loss, if the Sub-advisor believes that such security is not fulfilling its
purpose, either because, among other things, it did not live up to the Sub-advisor's expectations, or because it
may be replaced with another security holding greater promise, or because it has reached its optimum potential,
or because of a change in the circumstances of a particular company or industry or in general economic
conditions, or because of some combination of such reasons.
When a general decline in security prices is anticipated, the Fund may decrease or eliminate entirely
its equity position and increase its cash position, and when a rise in price levels is anticipated, the Fund may
increase its equity position and decrease its cash position. However, it should be expected that the Fund will,
under most circumstances, be essentially fully invested in equity securities.
Since investment decisions are based on the anticipated contribution of the security in question to the
Fund's objectives, the rate of portfolio turnover is irrelevant when the Sub-advisor believes a change is in
order to achieve those objectives, and the Fund's annual portfolio turnover rate cannot be anticipated and may be
comparatively high. Since the Sub-advisor does not take portfolio turnover rate into account in making
investment decisions, (1) the Sub-advisor has no intention of accomplishing any particular rate of portfolio
turnover, whether high or low, and (2) the portfolio turnover rates should not be considered as a representation
of the rates that will be attained in the future.
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
applicable to the ASAF American Century International Growth Fund. These limitations are not "fundamental"
restrictions and may be changed by the Directors without shareholder approval. The Fund will not:
1. Invest more than 15% of its assets in illiquid investments;
2. Invest in the securities of other investment companies except in compliance with the 1940 Act;
3. Buy securities on margin or sell short (unless it owns or by virtue of its ownership of other
securities has the right to obtain securities equivalent in kind and amount to the securities sold); however, the
Fund may make margin deposits in connection with the use of any financial instrument or any transaction in
securities permitted under its investment policies;
4. Invest in oil, gas or other mineral leases;
5. Invest for control or for management.
ASAF JANUS SMALL-CAP GROWTH FUND:
Investment Objective: As stated in the Prospectus, the Fund's investment objective is capital appreciation.
Realization of income is not a significant investment consideration and any income realized on the Fund's
investments therefore will be incidental to the Fund's objective.
Investment Policies:
Investment Company Securities. From time to time, the Fund may invest in securities of other investment
companies, subject to the provisions of Section 12(d)(1) of the 1940 Act. The Fund may invest in securities of
money market funds managed by the Sub-advisor subject to the terms of an exemptive order obtained by the
Sub-advisor and the funds that are advised or sub-advised by the Sub-advisor. Under such order, the Fund will
limit its aggregate investment in a money market fund managed by the Sub-advisor to the greater of (i) 5% of its
total assets or (ii) $2.5 million, although the Company's Board of Directors may increase this limit up to 25% of
the Company's total assets.
Depositary Receipts. The Fund may invest in sponsored and unsponsored American Depositary Receipts
("ADRs"), which are described in the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Holders of unsponsored ADRs generally bear all the costs of the ADR facility, whereas foreign issuers typically
bear certain costs in a sponsored ADR. The bank or trust company depositary of an unsponsored ADR may be under
no obligation to distribute shareholder communications received from the foreign issuer or to pass through voting
rights. The Fund may also invest in European Depositary Receipts ("EDRs"), Global Depositary Receipts ("GDRs")
and in other similar instruments representing securities of foreign companies.
Income-Producing Securities. Types of income producing securities that the Fund may purchase include,
but are not limited to, (i) variable and floating rate obligations, which are securities having interest rates
that are adjusted periodically according to a specified formula, usually with reference to some interest rate
index or market interest rate, (ii) standby commitments, which are instruments similar to puts that give the
holder the option to obligate a broker, dealer or bank to repurchase a security at a specified price, and (iii)
tender option bonds, which are securities that are coupled with the option to tender the securities to a bank,
broker-dealer or other financial institution at periodic intervals and receive the face value of the bond. The
Fund will purchase standby commitments, tender option bonds and instruments with demand features primarily for
the purpose of increasing the liquidity of its portfolio. The Fund may also invest in inverse floaters, which
are debt instruments the interest on which varies in an inverse relationship to the interest rate on another
security. For example, certain inverse floaters pay interest at a rate that varies inversely to prevailing
short-term interest rates. Some inverse floaters have an interest rate reset mechanism that multiplies the
effects of changes in an underlying index. Such a mechanism may increase fluctuations in the security's market
value. The Fund will not invest more than 5% of its assets in inverse floaters.
High-Yield/High-Risk Securities. The Fund intends to invest less than 35% of its net assets in debt
securities that are rated below investment grade (e.g., securities rated BB or lower by Standard & Poor's Ratings
Services ("Standard & Poor's") or Ba or lower by Moody's Investors Service, Inc. ("Moody's")). Lower rated
securities involve a higher degree of credit risk, which is the risk that the issuer will not make interest or
principal payments when due. In the event of an unanticipated default, the Fund would experience a reduction in
its income, and could expect a decline in the market value of the securities so affected.
The Fund may also invest in unrated debt securities of foreign and domestic issuers. Unrated debt,
while not necessarily of lower quality than rated securities, may not have as broad a market. Sovereign debt of
foreign governments is generally rated by country. Because these ratings do not take into account individual
factors relevant to each issue and may not be updated regularly, the Sub-advisor may treat such securities as
unrated debt. Because of the size and perceived demand of the issue, among other factors, certain municipalities
may not incur the costs of obtaining a rating. The Sub-advisor will analyze the creditworthiness of the issuer,
as well as any financial institution or other party responsible for payments on the security, in determining
whether to purchase unrated municipal bonds. Unrated debt securities will be included in the 35% limit unless
the portfolio managers deem such securities to be the equivalent of investment grade securities.
The Fund may purchase defaulted securities subject to the above limits, but only when the Sub-advisor
believes, based upon its analysis of the financial condition, results of operations and economic outlook of an
issuer, that there is potential for resumption of income payments and that the securities offer an unusual
opportunity for capital appreciation. Notwithstanding the Sub-advisor's belief as to the resumption of income,
however, the purchase of any security on which payment of interest or dividends is suspended involves a high
degree of risk. Such risk includes, among other things, the following:
Financial and Market Risks. Investments in securities that are in default involve a high
degree of financial and market risks that can result in substantial or, at times, even total losses. Issuers of
defaulted securities may have substantial capital needs and may become involved in bankruptcy or reorganization
proceedings. Among the problems involved in investments in such issuers is the fact that it may be difficult to
obtain information about their condition. The market prices of securities of such issuers also are subject to
abrupt and erratic movements and above average price volatility, and the spread between the bid and asked prices
of such securities may be greater than normally expected.
Disposition of Portfolio Securities. Although the Fund generally will purchase securities for
which the Sub-advisor expects an active market to be maintained, defaulted securities may be less actively traded
than other securities and it may be difficult to dispose of substantial holdings of such securities at prevailing
market prices. The Fund will limit holdings of any such securities to amounts that the Sub-advisor believes
could be readily sold, and holdings of such securities would, in any event, be limited so as not to limit the
Fund's ability to readily dispose of securities to meet redemptions.
Other. Defaulted securities require active monitoring and may, at times, require participation
in bankruptcy or receivership proceedings on behalf of the Fund.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements. The Fund may use reverse repurchase agreements to provide cash to
satisfy unusually heavy redemption requests or for other temporary or emergency purposes without the necessity of
selling portfolio securities or to earn additional income on portfolio securities, such as Treasury bills or
notes. The Fund will enter into reverse repurchase agreements only with parties that the Sub-advisor deems
creditworthy. Using reverse repurchase agreements to earn additional income involves the risk that the interest
earned on the invested proceeds is less than the expense of the reverse repurchase agreement transaction. This
technique may also have a leveraging effect on the Fund, although the requirement for the Fund to segregate
assets in the amount of the reverse repurchase agreement minimizes this effect. Pursuant to an exemptive order
granted by the SEC, the Fund and other funds advised or sub-advised by the Sub-advisor may invest in repurchase
agreements and other money market instruments through a joint trading account.
For an additional discussion of reverse repurchase agreements and their risks, see the Company's
Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Futures, Options and Forward Contracts. The Fund may enter into futures contracts on securities,
financial indices, and foreign currencies and options on such contracts, and may invest in options on securities,
financial indices, and foreign currencies, and forward contracts. The Fund will not enter into any futures
contracts or options on futures contracts if the aggregate amount of the Fund's commitments under outstanding
futures contract positions and options on futures contracts written by the Fund would exceed the market value of
the Fund's total assets. The Fund may invest in forward currency contracts with stated values of up to the value
of the Fund's assets.
The Fund may buy or write options in privately negotiated transactions on the types of securities, and
on indices based on the types of securities, in which the Fund is permitted to invest directly. The Fund will
effect such transactions only with investment dealers and other financial institutions (such as commercial banks
or savings and loan institutions) deemed creditworthy by the Sub-advisor pursuant to procedures adopted by the
Sub-advisor for monitoring the creditworthiness of those entities. To the extent that an option purchased or
written by the Fund in a negotiated transaction is illiquid, the value of the option purchased or the amount of
the Fund's obligations under an option it has written, as the case may be, will be subject to the Fund's
limitation on illiquid investments. In the case of illiquid options, it may not be possible for the Fund to
effect an offsetting transaction when the Sub-advisor believes it would be advantageous for the Fund to do so.
For a description of these strategies and instruments and certain of their risks, see this SAI and the Company's
Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Eurodollar Instruments. The Fund may make investments in Eurodollar instruments. Eurodollar instruments
are U.S. dollar-denominated futures contracts or options thereon that are linked to the London Interbank Offered
Rate ("LIBOR"), although foreign currency-denominated instruments are available from time to time. Eurodollar
futures contracts enable purchasers to obtain a fixed rate for the lending of funds and sellers to obtain a fixed
rate for borrowings. The Fund might use Eurodollar futures contracts and options thereon to hedge against
changes in LIBOR, to which many interest rate swaps and fixed-income instruments are linked.
Swaps and Swap-Related Products. The Fund may enter into interest rate swaps, caps and floors on either
an asset-based or liability-based basis, depending upon whether it is hedging its assets or its liabilities, and
will usually enter into interest rate swaps on a net basis (i.e., the two payment streams are netted out, with
the Fund receiving or paying, as the case may be, only the net amount of the two payments). The net amount of
the excess, if any, of the Fund's obligations over its entitlement with respect to each interest rate swap will
be calculated on a daily basis and an amount of cash or other liquid assets having an aggregate net asset value
at least equal to the accrued excess will be maintained in a segregated account by the Fund's custodian. If the
Fund enters into an interest rate swap on other than a net basis, it would maintain a segregated account in the
full amount accrued on a daily basis of its obligations with respect to the swap. The Fund will not enter into
any interest rate swap, cap or floor transaction unless the unsecured senior debt or the claims-paying ability of
the other party thereto is rated in one of the three highest rating categories of at least one NRSRO at the time
of entering into such transaction. The Sub-advisor will monitor the creditworthiness of all counterparties on an
ongoing basis. If there is a default by the other party to such a transaction, the Fund will have contractual
remedies pursuant to the agreements related to the transaction.
The swap market has grown substantially in recent years, with a large number of banks and investment
banking firms acting both as principals and as agents utilizing standardized swap documentation. The Sub-advisor
has determined that, as a result, the swap market has become relatively liquid. Caps and floors are more recent
innovations for which standardized documentation has not yet been developed and, accordingly, are less liquid
than swaps. To the extent the Fund sells (i.e., writes) caps and floors, it will segregate cash or other liquid
assets having an aggregate net asset value at least equal to the full amount, accrued on a daily basis, of its
obligations with respect to any caps or floors.
There is no limit on the amount of interest rate swap transactions that may be entered into by the
Fund. These transactions may in some instances involve the delivery of securities or other underlying assets by
the Fund or its counterparty to collateralize obligations under the swap. The Fund bears the risk of loss of any
payments it is contractually obligated to make in connection with interest rate swaps. In addition, if the other
party to an interest rate swap that is not collateralized defaults, the Fund would risk the loss of the payments
that it contractually is entitled to receive. The Fund may buy and sell (i.e., write) caps and floors without
limitation, subject to the segregation requirement described above.
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
applicable to the ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund. These limitations are not "fundamental" restrictions, and
may be changed by the Directors without shareholder approval.
1. The Fund does not currently intend to sell securities short, unless it owns or has the right to
obtain securities equivalent in kind and amount to the securities sold short without the payment of any
additional consideration therefor, and provided that transactions in futures, options, swaps and forward
contracts are not deemed to constitute selling securities short.
2. The Fund does not currently intend to purchase securities on margin, except that the Fund may
obtain such short-term credits as are necessary for the clearance of transactions, and provided that margin
payments and other deposits in connection with transactions in futures, options, swaps and forward contracts
shall not be deemed to constitute purchasing securities on margin.
3. The Fund does not currently intend to purchase any security or enter into a repurchase
agreement if, as a result, more than 15% of its net assets would be invested in repurchase agreements not
entitling the holder to payment of principal and interest within seven days and in securities that are illiquid
by virtue of legal or contractual restrictions on resale or the absence of a readily available market. The
Directors, or the Fund's Sub-advisor acting pursuant to authority delegated by the Directors, may determine that
a readily available market exists for securities eligible for resale pursuant to Rule 144A under the Securities
Act of 1933 ("Rule 144A Securities"), or any successor to such rule, Section 4(2) commercial paper and municipal
lease obligations. Accordingly, such securities may not be subject to the foregoing limitation.
4. The Fund may not invest in companies for the purpose of exercising control of management.
ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek maximum appreciation of investors' capital
from a portfolio primarily of growth stocks of smaller companies.
Investment Policies:
Options. The Fund may write (sell) call options on securities as long as it owns the underlying
securities subject to the option, or an option to purchase the same underlying securities having an exercise
price equal to or less than the exercise price of the option, or will establish and maintain with the Fund's
custodian for the term of the option a segregated account consisting of cash or other liquid securities
("eligible securities") to the extent required by applicable regulation in connection with the optioned
securities. The Fund may write put options provided that, so long as the Fund is obligated as the writer of the
option, the Fund owns an option to sell the underlying securities subject to the option having an exercise price
equal to or greater than the exercise price of the option, or it deposits and maintains with the custodian in a
segregated account eligible securities having a value equal to or greater than the exercise price of the option.
The premium received for writing an option will reflect, among other things, the current market price of the
underlying security, the relationship of the exercise price to such market price, the price volatility of the
underlying security, the option period, supply and demand and interest rates. The Fund may write or purchase
spread options, which are options for which the exercise price may be a fixed dollar spread or yield spread
between the security underlying the option and another security that is used as a benchmark. The exercise price
of an option may be below, equal to or above the current market value of the underlying security at the time the
option is written. The Fund may write (sell) call and put options on up to 25% of net assets and may purchase
put and call options provided that no more than 5% of its net assets may be invested in premiums on such options.
If a secured put option expires unexercised, the writer realizes a gain from the amount of the premium,
plus the interest income on the securities in the segregated account. If the secured put writer has to buy the
underlying security because of the exercise of the put option, the secured put writer incurs an unrealized loss
to the extent that the current market value of the underlying security is less than the exercise price of the put
option. However, this would be offset in whole or in part by gain from the premium received and any interest
income earned on the securities in the segregated account.
For an additional discussion of investing in options and the risks involved therein, see this Statement
and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Over-the-Counter Options. The Fund may deal in over-the-counter traded options ("OTC
options"). Unlike exchange-traded options, OTC options are transacted directly with dealers and not with a
clearing corporation. Since there is no exchange, pricing is normally done by reference to information from
market makers, which information is carefully monitored by the Sub-advisor and verified in appropriate cases. In
writing OTC options, the Fund receives the premium in advance from the dealer. OTC options are available for a
greater variety of securities or other assets, and for a wider range of expiration dates and exercise prices,
than exchange-traded options.
The staff of the SEC takes the position that purchased OTC options and the assets used as "cover" for
written OTC options are illiquid securities. Accordingly, the Fund will only engage in OTC options transactions
with dealers that have been specifically approved by the Sub-advisor. The Sub-advisor believes that the approved
dealers should be able to enter into closing transactions if necessary and, therefore, present minimal credit
risks to the Fund. The Sub-advisor will monitor the creditworthiness of the approved dealers on an on-going
basis. The Fund currently will not engage in OTC options transactions if the amount invested by the Fund in OTC
options, plus a "liquidity charge" related to OTC options written by the Fund, plus the amount invested by the
Fund in other illiquid securities, would exceed 15% of the Fund's net assets. The "liquidity charge" referred to
above is computed as described below.
The Fund anticipates entering into agreements with dealers to which the Fund sells OTC options. Under
these agreements the Fund would have the absolute right to repurchase the OTC options from the dealer at any time
at a price no greater than a price established under the agreements (the "Repurchase Price"). The "liquidity
charge" referred to above for a specific OTC option transaction will be the Repurchase Price related to the OTC
option less the intrinsic value of the OTC option. The intrinsic value of an OTC call option for such purposes
will be the amount by which the current market value of the underlying security exceeds the exercise price. In
the case of an OTC put option, intrinsic value will be the amount by which the exercise price exceeds the current
market value of the underlying security. If there is no such agreement requiring a dealer to allow the Fund to
repurchase a specific OTC option written by the Fund, the "liquidity charge" will be the current market value of
the assets serving as "cover" for such OTC option.
Options on Securities Indices. The Fund, as part of its options transactions, may also use
options on securities indices in an attempt to hedge against market conditions affecting the value of securities
that the Fund owns or intends to purchase, and not for speculation. When the Fund writes an option on a
securities index, it will be required to deposit with its custodian and mark-to-market eligible securities to the
extent required by applicable regulation. Where the Fund writes a call option on a securities index at a time
when the contract value exceeds the exercise price, the Fund will also segregate and mark-to-market, until the
option expires or is closed out, cash or cash equivalents equal in value to such excess. The Fund may also
purchase and sell options on indices other than securities indices, as available, such as foreign currency
indices. Because index options are settled in cash, a call writer cannot determine the amount of its settlement
obligations in advance and, unlike call writing on specific securities, cannot cover its potential settlement
obligations by acquiring and holding the underlying securities. Index options involve risks similar to those
risks relating to transactions in financial futures contracts described below.
For an additional discussion of investing in OTC options and options on securities indices, and the
risks involved therein, see this Statement and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and
Investment Methods."
Financial Futures Contracts and Related Options. The Fund may enter into financial futures contracts.
This investment technique is designed primarily to hedge (i.e. protect) against anticipated future changes in
market conditions or foreign exchange rates which otherwise might affect adversely the value of securities or
other assets which the Fund holds or intends to purchase. For example, when the near-term market view is bearish
but the portfolio composition is judged satisfactory for the longer term, exposure to temporary declines in the
market may be reduced by entering into futures contracts to sell securities or the cash value of an index.
Conversely, where the near-term view is bullish, but the Fund is believed to be well positioned for the longer
term with a high cash position, the Fund can hedge against market increases by entering into futures contracts to
buy securities or the cash value of an index. In either case, the use of futures contracts would tend to
minimize portfolio turnover and facilitate the Portfolio's pursuit of its investment objective. Also, if the
Fund owned long-term bonds and interest rates were expected to rise, it could sell financial futures contracts.
If interest rates did increase, the value of the bonds held by the Fund would decline, but this decline would be
offset in whole or in part by an increase in the value of the Fund's futures contracts. If, on the other hand,
long-term interest rates were expected to decline, the Portfolio could hold short-term debt securities and
benefit from the income earned by holding such securities, while at the same time the Portfolio could purchase
futures contracts on long-term bonds or the cash value of a securities index. Thus, the Portfolio could take
advantage of the anticipated rise in the value of long-term bonds without actually buying them. The futures
contracts and short-term debt securities could then be liquidated and the cash proceeds used to buy long-term
bonds. At the time of delivery, in the case of a contract relating to fixed income securities, adjustments are
made to recognize differences in value arising from the delivery of securities with a different interest rate
than that specified in the contract. In some cases, securities to be delivered under a futures contract may not
have been issued at the time the contract was written.
The market prices of futures contracts may be affected by certain factors. If participants in the
futures market elect to close out their contracts through offsetting transactions rather than meet margin
requirements, distortions in the normal relationship between the assets and futures market could result. Price
distortions also could result if investors in futures contracts decide to make or take delivery of underlying
securities or other assets rather than engage in closing transactions because of the resultant reduction in the
liquidity of the futures market. In addition, because margin requirements in the futures market are less onerous
than margin requirements in the cash market, increased participation by speculators in the futures market could
cause temporary price distortions. Due to the possibility of these price distortions and because of the
imperfect correlation between movements in the prices of securities or other assets and movements in the prices
of futures contracts, a correct forecast of market trends by the Sub-advisor still may not result in a successful
hedging transaction.
The Fund may purchase and write call and put options on financial futures contracts. Options on futures
contracts involve risks similar to those risks relating to transactions in financial futures contracts. The Fund
will not enter into any futures contracts or options on futures contracts if the aggregate of the contract value
of the outstanding futures contracts of the Fund and futures contracts subject to outstanding options written by
the Fund would exceed 50% of the total assets of the Fund. For an additional discussion of investing in
financial futures contracts and options on financial futures contracts and the risks involved therein, see this
Statement and the Trust's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Section 4(2) Paper. The Fund may invest in commercial paper issued by major corporations under the
Securities Act of 1933 in reliance on the exemption from registration afforded by Section 3(a)(3) thereof. Such
commercial paper may be issued only to finance current transactions and must mature in nine months or less. Such
commercial paper is traded primarily by institutional investors through investment dealers, and individual
investor participation in the commercial paper market is very limited. The Fund also may invest in commercial
paper issued in reliance on the so-called "private placement" exemption from registration afforded by Section
4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933 ("Section 4(2) paper"). Section 4(2) paper is restricted as to disposition
under the federal securities laws, and generally is sold to institutional investors, such as the Fund, who agree
that they are purchasing the paper for investment and not with a view to public distribution. Any resale by the
purchaser must be in an exempt transaction. Section 4(2) paper normally is resold to other institutional
investors through or with the assistance of the issuer or investment dealers who make a market in the Section
4(2) paper, thus providing liquidity. Section 4(2) paper will be considered illiquid, and subject to the Fund's
limitation on investing in illiquid securities, unless the Sub-advisor determines such Section 4(2) paper to be
liquid under guidelines established by the Board of Directors of the Company.
Collateralized Obligations. The Fund may invest in asset-backed and mortgage-backed securities,
including interest only ("IO") and principal only ("PO") securities (collectively, "collateralized
obligations"). A collateralized obligation is a debt security issued by a corporation, trust or custodian, or by
a U.S. Government agency or instrumentality, that is collateralized by a portfolio or pool of mortgages, mortgage
pass-through securities, U.S. Government securities or other assets. Collateralized obligations, depending on
their structure and the rate of prepayments, can be volatile.
The Fund will currently invest in only those collateralized obligations that are fully collateralized
and would not materially alter the risk profile of the Fund. Fully collateralized means that the collateral will
generate cash flows sufficient to meet obligations to holders of the collateralized obligations under even the
most conservative prepayment and interest rate projections. Thus, the collateralized obligations are structured
to anticipate a worst case prepayment condition and to minimize the reinvestment rate risk for cash flows between
coupon dates for the collateralized obligations. A worst case prepayment condition generally assumes immediate
prepayment of all securities purchased at a premium and zero prepayment of all securities purchased at a
discount. Reinvestment rate risk may be minimized by assuming very conservative reinvestment rates and by other
means such as by maintaining the flexibility to increase principal distributions in a low interest rate
environment. The effective credit quality of the collateralized obligations in such instances is the credit
quality of the issuer of the collateral. The requirements as to collateralization are determined by the issuer
or sponsor of the collateralized obligation in order to satisfy rating agencies, if rated. The Fund does not
currently intend to invest more than 5% of its total assets in collateralized obligations.
Because some collateralized obligations are issued in classes with varying maturities and interest
rates, the investor may obtain greater predictability of maturity through these collateralized obligations than
through direct investments in mortgage pass-through securities. Classes with shorter maturities may have lower
volatility and lower yield while those with longer maturities may have higher volatility and higher yield.
Payments of principal and interest on the underlying collateral securities are not passed through directly to the
holders of these collateralized obligations. Rather, the payments on the underlying portfolio or pool of
obligations are used to pay interest on each class and to retire successive maturities in sequence. These
relationships may in effect "strip" the interest payments from principal payments of the underlying obligations
and allow for the separate purchase of either the interest or the principal payments, sometimes called interest
only ("IO") and principal only ("PO") securities. By investing in IOs and POs, an investor has the option to
select from a pool of underlying collateral the portion of the cash flows that most closely corresponds to the
investor's forecast of interest rate movements.
Collateralized obligations are designed to be retired as the underlying obligations are repaid. In the
event of prepayment on or call of such securities, the class of collateralized obligation first to mature
generally will be paid down first. Although in most cases the issuer of collateralized obligations will not
supply additional collateral in the event of such prepayment, there generally will be sufficient collateral to
secure collateralized obligations that remain outstanding. Governmentally-issued and privately-issued IO's and
PO's will be considered illiquid for purposes of the Fund's limitation on illiquid securities unless they are
determined to be liquid under guidelines established by the Board of Directors.
In reliance on an interpretation by the SEC, the Fund's investments in certain qualifying collateralized
obligations are not subject to the limitations in the 1940 Act regarding investments by a registered investment
company, such as the Fund, in another investment company.
Inverse Floaters. The Fund may also invest in "inverse floaters." These inverse floaters are more
volatile than conventional fixed or floating rate collateralized obligations, and their yield and value will
fluctuate in inverse proportion to changes in the index upon which rate adjustments are based. As a result, the
yield on an inverse floater will generally increase when market yields (as reflected by the index) decrease and
decrease when market yields increase. The extent of the volatility of inverse floaters depends on the extent of
anticipated changes in market rates of interest. Generally, inverse floaters provide for interest rate
adjustments based upon a multiple of the specified interest index, which further increases their volatility. The
degree of additional volatility will be directly proportional to the size of the multiple used in determining
interest rate adjustments. Currently, the Fund does not intend to invest more than 5% of its net assets in
inverse floaters.
For an additional discussion of investing in collateralized obligations and the risks involved therein,
see this Statement and the Trust's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are applicable
to the ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund. These limitations are not "fundamental" restrictions and may be
changed without shareholder approval. The Fund will not:
1. Invest for the purpose of exercising control or management of another issuer.
2. Purchase securities of other investment companies, except in compliance with the 1940 Act.
3. Invest more than 15% of its net assets in illiquid securities.
ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund (formerly, the ASAF T. Rowe Price Small Company Value
Fund) is to provide long-term capital growth by investing primarily in small-capitalization stocks that appear to
be undervalued.
Investment Policies:
Although primarily all of the Fund's assets are invested in common stocks, the Fund may invest in
convertible securities, corporate debt securities and preferred stocks. The fixed-income securities in which the
Fund may invest include, but are not limited to, those described below. See this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors
and Investment Methods," for an additional discussion of debt obligations.
U.S. Government Obligations. Bills, notes, bonds and other debt securities issued by the U.S.
Treasury. These are direct obligations of the U.S. Government and differ mainly in the length of their
maturities.
U.S. Government Agency Securities. Issued or guaranteed by U.S. Government sponsored enterprises and
federal agencies. These include securities issued by the Federal National Mortgage Association, Government
National Mortgage Association, Federal Home Loan Bank, Federal Land Banks, Farmers Home Administration, Banks for
Cooperatives, Federal Intermediate Credit Banks, Federal Financing Bank, Farm Credit Banks, the Small Business
Association, and the Tennessee Valley Authority. Some of these securities are supported by the full faith and
credit of the U.S. Treasury; and the remainder are supported only by the credit of the instrumentality, which may
or may not include the right of the issuer to borrow from the Treasury.
Bank Obligations. Certificates of deposit, bankers' acceptances, and other short-term debt
obligations. Certificates of deposit are short-term obligations of commercial banks. A bankers' acceptance is a
time draft drawn on a commercial bank by a borrower, usually in connection with international commercial
transactions. Certificates of deposit may have fixed or variable rates. The Fund may invest in U.S. banks,
foreign branches of U.S. banks, U.S. branches of foreign banks, and foreign branches of foreign banks.
Short-Term Corporate Debt Securities. Outstanding nonconvertible corporate debt securities (e.g., bonds
and debentures) which have one year or less remaining to maturity. Corporate notes may have fixed, variable, or
floating rates.
Commercial Paper. Short-term promissory notes issued by corporations primarily to finance short-term
credit needs. Certain notes may have floating or variable rates.
Foreign Government Securities. Issued or guaranteed by a foreign government, province, instrumentality,
political subdivision or similar unit thereof.
Savings and Loan Obligations. Negotiable certificates of deposit and other short-term debt obligations
of savings and loan associations.
Supranational Entities. The Fund may also invest in the securities of certain supranational entities,
such as the International Development Bank.
Lower-Rated Debt Securities. The Fund's investment program permits it to purchase below investment
grade securities, commonly referred to as "junk bonds." The Fund will not purchase a junk bond if immediately
after such purchase the Fund would have more than 5% of its total assets invested in such securities. Since
investors generally perceive that there are greater risks associated with investment in lower quality securities,
the yields from such securities normally exceed those obtainable from higher quality securities. However, the
principal value of lower-rated securities generally will fluctuate more widely than higher quality securities.
Lower quality investments entail a higher risk of default -- that is, the nonpayment of interest and principal by
the issuer than higher quality investments. Such securities are also subject to special risks, discussed below.
Although the Fund seeks to reduce risk by portfolio diversification, credit analysis, and attention to trends in
the economy, industries and financial markets, such efforts will not eliminate all risk. There can, of course,
be no assurance that the Fund will achieve its investment objective.
After purchase by the Fund, a debt security may cease to be rated or its rating may be reduced below the
minimum required for purchase by the Fund. Neither event will require a sale of such security by the Fund.
However, the Sub-advisor will consider such event in its determination of whether the Fund should continue to
hold the security. To the extent that the ratings given by Moody's or S&P may change as a result of changes in
such organizations or their rating systems, the Fund will attempt to use comparable ratings as standards for
investments in accordance with the investment policies contained in the Company's Prospectus.
Junk bonds are regarded as predominantly speculative with respect to the issuer's continuing ability to
meet principal and interest payments. Because investment in low and lower-medium quality bonds involves greater
investment risk, to the extent the Fund invests in such bonds, achievement of its investment objective will be
more dependent on the Sub-advisor's credit analysis than would be the case if the Fund was investing in higher
quality bonds. For a discussion of the special risks involved in low-rated bonds, see this SAI and the Company's
Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Writing Covered Call Options. The Fund may write (sell) American or European style "covered" call
options and purchase options to close out options previously written by the Fund. In writing covered call
options, the Fund expects to generate additional premium income which should serve to enhance the Fund's total
return and reduce the effect of any price decline of the security or currency involved in the option. Covered
call options will generally be written on securities or currencies which, in the Sub-advisor's opinion, are not
expected to have any major price increases or moves in the near future but which, over the long term, are deemed
to be attractive investments for the Fund.
The Fund will write only covered call options. This means that the Fund will own the security or
currency subject to the option or an option to purchase the same underlying security or currency, having an
exercise price equal to or less than the exercise price of the "covered" option, or will establish and maintain
with its custodian for the term of the option, an account consisting of cash or other liquid assets having a
value equal to the fluctuating market value of the optioned securities or currencies.
Portfolio securities or currencies on which call options may be written will be purchased solely on the
basis of investment considerations consistent with the Fund's investment objective. The writing of covered call
options is a conservative investment technique believed to involve relatively little risk (in contrast to the
writing of naked or uncovered options, which the Fund will not do), but capable of enhancing the Fund's total
return. When writing a covered call option, a fund, in return for the premium, gives up the opportunity for
profit from a price increase in the underlying security or currency above the exercise price, but conversely
retains the risk of loss should the price of the security or currency decline. Unlike one who owns securities or
currencies not subject to an option, the Fund has no control over when it may be required to sell the underlying
securities or currencies, since it may be assigned an exercise notice at any time prior to the expiration of its
obligation as a writer. If a call option which the Fund has written expires, the Fund will realize a gain in the
amount of the premium; however, such gain may be offset by a decline in the market value of the underlying
security or currency during the option period. If the call option is exercised, the Fund will realize a gain or
loss from the sale of the underlying security or currency. The Fund does not consider a security or currency
covered by a call to be "pledged" as that term is used in the Fund's policy which limits the pledging or
mortgaging of its assets.
Call options written by the Fund will normally have expiration dates of less than nine months from the
date written. The exercise price of the options may be below, equal to, or above the current market values of
the underlying securities or currencies at the time the options are written. From time to time, the Fund may
purchase an underlying security or currency for delivery in accordance with an exercise notice of a call option
assigned to it, rather than delivering such security or currency from its portfolio. In such cases, additional
costs may be incurred.
The premium received is the market value of an option. The premium the Fund will receive from writing a
call option will reflect, among other things, the current market price of the underlying security or currency,
the relationship of the exercise price to such market price, the historical price volatility of the underlying
security or currency, and the length of the option period. Once the decision to write a call option has been
made, the Sub-advisor, in determining whether a particular call option should be written on a particular security
or currency, will consider the reasonableness of the anticipated premium and the likelihood that a liquid
secondary market will exist for those options. The premium received by the Fund for writing covered call options
will be recorded as a liability of the Fund. This liability will be adjusted daily to the option's current
market value, which will be the latest sale price at the time at which the net asset value per share of the Fund
is computed (close of the New York Stock Exchange), or, in the absence of such sale, the latest asked price. The
option will be terminated upon expiration of the option, the purchase of an identical option in a closing
transaction, or delivery of the underlying security or currency upon the exercise of the option.
The Fund will realize a profit or loss from a closing purchase transaction if the cost of the
transaction is less or more than the premium received from the writing of the option. Because increases in the
market price of a call option will generally reflect increases in the market price of the underlying security or
currency, any loss resulting from the repurchase of a call option is likely to be offset in whole or in part by
appreciation of the underlying security or currency owned by the Fund.
The Fund will not write a covered call option if, as a result, the aggregate market value of all
portfolio securities or currencies covering call or put options exceeds 25% of the market value of the Fund's
total assets. In calculating the 25% limit, the Fund will offset, against the value of assets covering written
calls and puts, the value of purchased calls and puts on identical securities or currencies with identical
maturity dates.
Writing Covered Put Options. The Fund may write American or European style covered put options and
purchase options to close out options previously written by the Fund.
The Fund would write put options only on a covered basis, which means that the Fund would maintain in a
segregated account cash, U.S. government securities or other liquid high-grade debt obligations in an amount not
less than the exercise price or the Fund will own an option to sell the underlying security or currency subject
to the option having an exercise price equal to or greater than the exercise price of the "covered" option at all
times while the put option is outstanding. (The rules of a clearing corporation currently require that such
assets be deposited in escrow to secure payment of the exercise price.) The Fund would generally write covered
put options in circumstances where the Sub-advisor wishes to purchase the underlying security or currency for the
Fund at a price lower than the current market price of the security or currency. In such event the Fund would
write a put option at an exercise price which, reduced by the premium received on the option, reflects the lower
price it is willing to pay. Since the Fund would also receive interest on debt securities or currencies
maintained to cover the exercise price of the option, this technique could be used to enhance current return
during periods of market uncertainty. The risk in such a transaction would be that the market price of the
underlying security or currency would decline below the exercise price less the premiums received. Such a
decline could be substantial and result in a significant loss to the Fund. In addition, the Fund, because it
does not own the specific securities or currencies which it may be required to purchase in exercise of the put,
cannot benefit from appreciation, if any, with respect to such specific securities or currencies.
The Fund will not write a covered put option if, as a result, the aggregate market value of all
portfolio securities or currencies covering put or call options exceeds 25% of the market value of the Fund's
total assets. In calculating the 25% limit, the Fund will offset, against the value of assets covering written
puts and calls, the value of purchased puts and calls on identical securities or currencies with identical
maturity dates.
Purchasing Put Options. The Fund may purchase American or European style put options. As the holder of
a put option, the Fund has the right to sell the underlying security or currency at the exercise price at any
time during the option period (American style) or at the expiration of the option (European style). The Fund may
enter into closing sale transactions with respect to such options, exercise them or permit them to expire. The
Fund may purchase put options for defensive purposes in order to protect against an anticipated decline in the
value of its securities or currencies. An example of such use of put options is provided in this SAI under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
The premium paid by the Fund when purchasing a put option will be recorded as an asset of the Fund.
This asset will be adjusted daily to the option's current market value, which will be the latest sale price at
the time at which the net asset value per share of the Fund is computed (close of New York Stock Exchange), or,
in the absence of such sale, the latest bid price. This asset will be terminated upon expiration of the option,
the selling (writing) of an identical option in a closing transaction, or the delivery of the underlying
security or currency upon the exercise of the option.
Purchasing Call Options. The Fund may purchase American or European style call options. As the holder
of a call option, the Fund has the right to purchase the underlying security or currency at the exercise price at
any time during the option period (American style) or at the expiration of the option (European style). The Fund
may enter into closing sale transactions with respect to such options, exercise them or permit them to expire.
The Fund may purchase call options for the purpose of increasing its current return or avoiding tax consequences
which could reduce its current return. The Fund may also purchase call options in order to acquire the
underlying securities or currencies. Examples of such uses of call options are provided in this SAI under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
The Fund may also purchase call options on underlying securities or currencies it owns in order to
protect unrealized gains on call options previously written by it. A call option would be purchased for this
purpose where tax considerations make it inadvisable to realize such gains through a closing purchase
transaction. Call options may also be purchased at times to avoid realizing losses.
Dealer (Over-the-Counter) Options. The Fund may engage in transactions involving dealer options.
Certain risks are specific to dealer options. While the Fund would look to a clearing corporation to exercise
exchange-traded options, if the Fund were to purchase a dealer option, it would rely on the dealer from whom it
purchased the option to perform if the option were exercised. Failure by the dealer to do so would result in the
loss of the premium paid by the Fund as well as loss of the expected benefit of the transaction. For a
discussion of dealer options, see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Futures Contracts:
Transactions in Futures. The Fund may enter into futures contracts, including stock index,
interest rate and currency futures ("futures" or "futures contracts"). The Fund may also enter into futures on
commodities related to the types of companies in which it invests, such as oil and gold futures. Otherwise the
nature of such futures and the regulatory limitations and risks to which they are subject are the same as those
described below.
Stock index futures contracts may be used to attempt to hedge a portion of the Fund, as a cash
management tool, or as an efficient way for the Sub-advisor to implement either an increase or decrease in
portfolio market exposure in response to changing market conditions. The Fund may purchase or sell futures
contracts with respect to any stock index. Nevertheless, to hedge the Fund successfully, the Fund must sell
futures contacts with respect to indices or subindices whose movements will have a significant correlation with
movements in the prices of the Fund's securities.
Interest rate or currency futures contracts may be used to attempt to hedge against changes in
prevailing levels of interest rates or currency exchange rates in order to establish more definitely the
effective return on securities or currencies held or intended to be acquired by the Fund. In this regard, the
Fund could sell interest rate or currency futures as an offset against the effect of expected increases in
interest rates or currency exchange rates and purchase such futures as an offset against the effect of expected
declines in interest rates or currency exchange rates.
The Fund will enter into futures contracts which are traded on national or foreign futures
exchanges, and are standardized as to maturity date and underlying financial instrument. Futures exchanges and
trading in the United States are regulated under the Commodity Exchange Act by the CFTC. Although techniques
other than the sale and purchase of futures contracts could be used for the above-referenced purposes, futures
contracts offer an effective and relatively low cost means of implementing the Fund's objectives in these areas.
Regulatory Limitations. The Fund will engage in futures contracts and options thereon only for
bona fide hedging, yield enhancement, and risk management purposes, in each case in accordance with rules and
regulations of the CFTC.
The Fund may not purchase or sell futures contracts or related options if, with respect to
positions which do not qualify as bona fide hedging under applicable CFTC rules, the sum of the amounts of
initial margin deposits and premiums paid on those positions would exceed 5% of the net asset value of the Fund
after taking into account unrealized profits and unrealized losses on any such contracts it has entered into;
provided, however, that in the case of an option that is in-the-money at the time of purchase, the in-the-money
amount may be excluded in calculating the 5% limitation. For purposes of this policy options on futures
contracts and foreign currency options traded on a commodities exchange will be considered "related options."
This policy may be modified by the Directors of the Company without a shareholder vote and does not limit the
percentage of the Fund's assets at risk to 5%.
In instances involving the purchase of futures contracts or the writing of call or put options
thereon by the Fund, an amount of cash or other liquid assets equal to the market value of the futures contracts
and options thereon (less any related margin deposits), will be identified by the Fund to cover the position, or
alternative cover (such as owning an offsetting position) will be employed. Assets used as cover cannot be sold
while the position in the corresponding option or future is open, unless they are replaced with similar assets.
As a result, the commitment of a large portion of the Fund's assets as cover could impede portfolio management or
the Fund's ability to meet redemption requests or other current obligations.
Options on Futures Contracts. The Fund may purchase and sell options on the same types of futures in
which it may invest. As an alternative to writing or purchasing call and put options on stock index futures, the
Fund may write or purchase call and put options on financial indices. Such options would be used in a manner
similar to the use of options on futures contracts. From time to time, a single order to purchase or sell
futures contracts (or options thereon) may be made on behalf of the Fund and other mutual funds or portfolios of
mutual funds managed by the Sub-advisor or Rowe Price-Fleming International, Inc. Such aggregated orders would
be allocated among the Fund and such other portfolios managed by the Sub-advisor in a fair and non-discriminatory
manner. See this SAI and Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods" for a
description of certain risks in options and future contracts.
Additional Futures and Options Contracts. Although the Fund has no current intention of engaging in
futures or options transactions other than those described above, it reserves the right to do so. Such futures
and options trading might involve risks which differ from those involved in the futures and options described
above.
Foreign Futures and Options. The Fund is permitted to invest in foreign futures and options. For a
description of foreign futures and options and certain risks involved therein as well as certain risks involved
in foreign investing, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods."
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest in U.S. dollar-denominated and non-U.S. dollar-denominated
securities of foreign issuers. There are special risks in foreign investing. Certain of these risks are
inherent in any international mutual fund while others relate more to the countries in which the Fund will
invest. Many of the risks are more pronounced for investments in developing or emerging countries, such as many
of the countries of Southeast Asia, Latin America, Eastern Europe and the Middle East. For an additional
discussion of certain risks involved in investing in foreign securities, see this SAI and the Company's
Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Foreign Currency Transactions. A forward foreign currency exchange contract involves an obligation to
purchase or sell a specific currency at a future date, which may be any fixed number of days from the date of the
contract agreed upon by the parties, at a price set at the time of the contract. These contracts are principally
traded in the interbank market conducted directly between currency traders (usually large, commercial banks) and
their customers. A forward contract generally has no deposit requirement, and no commissions are charged at any
stage for trades.
The Fund may enter into forward contracts for a variety of purposes in connection with the management of
the foreign securities portion of its portfolio. The Fund's use of such contracts would include, but not be
limited to, the following: First, when the Fund enters into a contract for the purchase or sale of a security
denominated in a foreign currency, it may desire to "lock in" the U.S. dollar price of the security. Second,
when the Sub-advisor believes that one currency may experience a substantial movement against another currency,
including the U.S. dollar, it may enter into a forward contract to sell or buy the amount of the former foreign
currency, approximating the value of some or all of the Fund's securities denominated in such foreign currency.
Alternatively, where appropriate, the Fund may hedge all or part of its foreign currency exposure through the use
of a basket of currencies or a proxy currency where such currency or currencies act as an effective proxy for
other currencies. In such a case, the Fund may enter into a forward contract where the amount of the foreign
currency to be sold exceeds the value of the securities denominated in such currency. The use of this basket
hedging technique may be more efficient and economical than entering into separate forward contracts for each
currency held in the Fund. The precise matching of the forward contract amounts and the value of the securities
involved will not generally be possible since the future value of such securities in foreign currencies will
change as a consequence of market movements in the value of those securities between the date the forward
contract is entered into and the date it matures. The projection of short-term currency market movement is
extremely difficult, and the successful execution of a short-term hedging strategy is highly uncertain. Under
normal circumstances, consideration of the prospect for currency parities will be incorporated into the longer
term investment decisions made with regard to overall diversification strategies. However, the Sub-advisor
believes that it is important to have the flexibility to enter into such forward contracts when it determines
that the best interests of the Fund will be served.
The Fund may enter into forward contracts for any other purpose consistent with the Fund's investment
objective and policies. However, the Fund will not enter into a forward contract, or maintain exposure to any
such contract(s), if the amount of foreign currency required to be delivered thereunder would exceed the Fund's
holdings of liquid assets and currency available for cover of the forward contract(s). In determining the amount
to be delivered under a contract, the Fund may net offsetting positions.
At the maturity of a forward contract, the Fund may sell the portfolio security and make delivery of the
foreign currency, or it may retain the security and either extend the maturity of the forward contract (by
"rolling" that contract forward) or may initiate a new forward contract.
If the Fund retains the portfolio security and engages in an offsetting transaction, the Fund will incur
a gain or a loss (as described below) to the extent that there has been movement in forward contract prices. If
the Fund engages in an offsetting transaction, it may subsequently enter into a new forward contract to sell the
foreign currency. Should forward prices decline during the period between the Fund's entering into a forward
contract for the sale of a foreign currency and the date it enters into an offsetting contract for the purchase
of the foreign currency, the Fund will realize a gain to the extent the price of the currency it has agreed to
sell exceeds the price of the currency it has agreed to purchase. Should forward prices increase, the Fund will
suffer a loss to the extent of the price of the currency it has agreed to purchase exceeds the price of the
currency it has agreed to sell.
The Fund's dealing in forward foreign currency exchange contracts will generally be limited to the
transactions described above. However, the Fund reserves the right to enter into forward foreign currency
contracts for different purposes and under different circumstances. Of course, the Fund is not required to enter
into forward contracts with regard to its foreign currency-denominated securities and will not do so unless
deemed appropriate by the Sub-advisor. It also should be realized that this method of hedging against a decline
in the value of a currency does not eliminate fluctuations in the underlying prices of the securities. It simply
establishes a rate of exchange at a future date. Additionally, although such contracts tend to minimize the risk
of loss due to a decline in the value of the hedged currency, at the same time, they tend to limit any potential
gain which might result from an increase in the value of that currency.
Although the Fund values its assets daily in terms of U.S. dollars, it does not intend to convert its
holdings of foreign currencies into U.S. dollars on a daily basis. It will do so from time to time, and
investors should be aware of the costs of currency conversion. Although foreign exchange dealers do not charge a
fee for conversion, they do realize a profit based on the difference (the "spread") between the prices at which
they are buying and selling various currencies. Thus, a dealer may offer to sell a foreign currency to the Fund
at one rate, while offering a lesser rate of exchange should the Fund desire to resell that currency to the
dealer. For a discussion of certain risk factors involved in foreign currency transactions, see this SAI and the
Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Federal Tax Treatment of Options, Futures Contracts and Forward Foreign Exchange Contracts. The Fund
may enter into certain option, futures, and forward foreign exchange contracts, including options and futures on
currencies, which will be treated as Section 1256 contracts or straddles.
Transactions which are considered Section 1256 contracts will be considered to have been closed at the
end of the Fund's fiscal year and any gains or losses will be recognized for tax purposes at that time. Such
gains or losses from the normal closing or settlement of such transactions will be characterized as 60% long-term
capital gain (taxable at a maximum rate of 20%) or loss and 40% short-term capital gain or loss regardless of the
holding period of the instrument (or, in the case of foreign exchange contracts, entirely as entirely as ordinary
income or loss). The Fund will be required to distribute net gains on such transactions to shareholders even
though it may not have closed the transaction and received cash to pay such distributions.
Options, futures and forward foreign exchange contracts, including options and futures on currencies,
which offset a foreign dollar denominated bond or currency position may be considered straddles for tax purposes,
in which case a loss on any position in a straddle will be subject to deferral to the extent of unrealized gain
in an offsetting position. The holding period of the securities or currencies comprising the straddle will be
deemed not to begin until the straddle is terminated. The holding period of the security offsetting an
"in-the-money qualified covered call" option on an equity security will not include the period of time the option
is outstanding.
Losses on written covered calls and purchased puts on securities, excluding certain "qualified covered
call" options on equity securities, may be long-term capital loss, if the security covering the option was held
for more than twelve months prior to the writing of the option.
In order for the Fund to continue to qualify for federal income tax treatment as a regulated investment
company, at least 90% of its gross income for a taxable year must be derived from qualifying income, i.e.,
dividends, interest, income derived from loans of securities, and gains from the sale of securities or
currencies. Tax regulations could be issued limiting the extent that net gain realized from option, futures or
foreign forward exchange contracts on currencies is qualifying income for purposes of the 90% requirement.
As a result of the "Taxpayer Relief Act of 1997," entering into certain options, futures contracts, or
forward contracts may be deemed a "constructive sale" of offsetting securities, which could result in a taxable
gain from the sale being distributed to shareholders. The Fund would be required to distribute any such gain
even though it would not receive proceeds from the sale at the time the option, futures or forward position is
entered into.
Hybrid Instruments. Hybrid Instruments have been developed and combine the elements of futures
contracts, options or other financial instruments with those of debt, preferred equity or a depository
instrument (hereinafter "Hybrid Instruments). Hybrid Instruments may take a variety of forms, including, but not
limited to, debt instruments with interest or principal payments or redemption terms determined by reference to
the value of a currency or commodity or securities index at a future point in time, preferred stock with dividend
rates determined by reference to the value of a currency, or convertible securities with the conversion terms
related to a particular commodity. For a discussion of certain risks involved in investing in hybrid instruments
see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Reverse Repurchase Agreements. Although the Fund has no current intention, in the foreseeable future,
of engaging in reverse repurchase agreements, the Fund reserves the right to do so. Reverse repurchase
agreements are ordinary repurchase agreements in which a fund is the seller of, rather than the investor in,
securities, and agrees to repurchase them at an agreed upon time and price. Use of a reverse repurchase
agreement may be preferable to a regular sale and later repurchase of the securities because it avoids certain
market risks and transaction costs. A reverse repurchase agreement may be viewed as a type of borrowing by the
Fund.
Short Sales. The Fund may, from time to time, make short sales of securities it owns or has the right
to acquire through conversion or exchange of other securities it owns (short sales "against the box"). In a
short sale, the Fund does not immediately deliver the securities sold or receive the proceeds from the sale. The
Fund may make a short sale against the box in order to hedge against market risks when it believes that the price
of a security may decline, affecting the Fund directly if it owns that security or causing a decline in the value
of a security owned by the Fund that is convertible into the security sold short.
To secure its obligations to deliver the securities sold short, the Fund will segregate assets with its custodian
in an amount at least equal to the value of the securities sold short or the securities convertible into, or
exchangeable for, the securities. The Fund may close out a short position by purchasing and delivering an equal
amount of securities sold short, rather than by delivering securities already held by the Fund, because the Fund
may want to continue to receive interest and dividend payments on securities in its portfolio that are
convertible into the securities sold short.
Warrants. The Fund may acquire warrants. For a discussion of certain risks involved therein, see this
SAI under "Certain Risk Factor and Investment Methods."
Investment in Small, Unseasoned Companies. The Fund may invest in small, less well-known companies that
have operated for less than three years (including predecessors). The securities of such companies may have a
limited trading market, which may adversely affect their disposition and can result in their being priced lower
than might otherwise be the case. If other investment companies and investors who invest in such issuers trade
the same securities when the Fund attempts to dispose of its holdings, the Fund may receive lower prices than
might otherwise be obtained.
Corporate Reorganizations. In general, securities of companies engaged in reorganization transactions
sell at a premium to their historic market price immediately prior to the announcement of the tender offer or
reorganization proposal. However, the increased market price of such securities may also discount what the
stated or appraised value of the security would be if the contemplated transaction were approved or consummated.
Such investments may be advantageous when the discount significantly overstates the risk of the contingencies
involved, significantly undervalues the securities, assets or cash to be received by shareholders of the issuer
as a result of the contemplated transaction, or fails adequately to recognize the possibility that the offer or
proposal may be replaced or superseded by an offer or proposal of greater value. The evaluation of such
contingencies requires unusually broad knowledge and experience on the part of the Sub-advisor, which must
appraise not only the value of the issuer and its component businesses and the assets or securities to be
received as a result of the contemplated transaction, but also the financial resources and business motivation of
the offeror as well as the dynamic of the business climate when the offer or proposal is in progress.
In making such investments, the Fund will be subject to its diversification and other investment restrictions,
including the requirement that, except with respect to 25% of its assets, not more than 5% of its assets may be
invested in the securities of any issuer (see this SAI under "Fundamental Investment Restrictions"). Because
such investments are ordinarily short term in nature, they will tend to increase the Fund's portfolio turnover
rate, thereby increasing its brokerage and other transaction expenses. The Sub-advisor intends to select
investments of the type described that, in its view, have a reasonable prospect of capital growth that is
significant in relation to both the risk involved and the potential of available alternate investments.
Lending of Portfolio Securities. Securities loans are made to broker-dealers or institutional investors
or other persons, pursuant to agreements requiring that the loans be continuously secured by collateral at least
equal at all times to the value of the securities lent, marked to market on a daily basis. The collateral
received will consist of cash or U.S. government securities. While the securities are being lent, the Fund will
continue to receive the equivalent of the interest or dividends paid by the issuer on the securities, as well as
interest on the investment of the collateral or a fee from the borrower. The Fund has a right to call each loan
and obtain the securities on three business days' notice or, in connection with securities trading on foreign
markets, within such longer period of time which coincides with the normal settlement period for purchases and
sales of such securities in such foreign markets. The Fund will not have the right to vote securities while they
are being lent, but it will call a loan in anticipation of any important vote. The risks in lending portfolio
securities, as with other extensions of secured credit, consist of possible delay in receiving additional
collateral or in the recovery of the securities or possible loss of rights in the collateral should the borrower
fail financially. Loans will only be made to firms deemed to be of good standing and will not be made unless the
consideration to be earned from such loans would justify the risk.
When-Issued Securities and Forward Commitment Contracts. The Fund may purchase securities on a
"when-issued" or delayed delivery basis and may purchase securities on a forward commitment basis. Any or all of
the Fund's investments in debt securities may be in the form of when-issueds and forwards. The price of such
securities, which may be expressed in yield terms, is fixed at the time the commitment to purchase is made, but
delivery and payment take place at a later date. Normally, the settlement date occurs within 90 days of the
purchase for when-issueds, but may be substantially longer for forwards. The Fund will cover its commitments
with respect to these securities by maintaining cash and/or other liquid assets with its custodian bank equal in
value to these commitments during the time between the purchase and the settlement. Such segregated securities
either will mature or, if necessary, be sold on or before the settlement date. For a discussion of these
securities and the risks involved therein, see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Money Market Securities. The Fund will hold a certain portion of its assets in U.S. and foreign
dollar-denominated money market securities, including repurchase agreements, rated in the two highest rating
categories, maturing in one year or less.
Investment Opportunities and Related Limitations. Affiliates of the Sub-advisor may, in the ordinary
course of their business, acquire for their own account or for the accounts of their advisory clients,
significant (and possibly controlling) positions in the securities of companies that may also be suitable for
investment by the Fund. The securities in which the Fund might invest may thereby be limited to some extent.
For instance, many companies in the past several years have adopted so-called "poison pill" or other defensive
measures designed to discourage or prevent the completion of non-negotiated offers for control of the company.
Such defensive measures may have the effect of limiting the shares of the company that might otherwise be
acquired by the Fund if the affiliates of the Sub-advisor or their advisory accounts have or acquire a
significant position in the same securities. However, the Sub-advisor does not believe that the investment
activities of its affiliates will have a material adverse effect upon the Fund in seeking to achieve its
investment objectives. In addition, orders for the Fund generally are accorded priority of execution over orders
entered on behalf of accounts in which the Sub-advisor or its affiliates have a substantial pecuniary interest.
The Fund may invest in the securities of companies that are investment management clients of the Sub-advisor's
affiliates. In addition, portfolio companies or their officers or directors may be minority shareholders of the
Sub-advisor or its affiliates.
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
not "fundamental" restrictions and may be changed by the Directors of the Company without shareholder approval.
The Fund will not:
1. Purchase additional securities when money borrowed exceeds 5% of its total assets;
2. Invest in companies for the purpose of exercising management or control;
3. Purchase a futures contract or an option thereon if, with respect to positions in futures or
options on futures which do not represent bona fide hedging, the aggregate initial margin and premiums on such
options would exceed 5% of the Fund's net asset value;
4. Purchase illiquid securities if, as a result, more than 15% of its net assets would be invested
in such securities. Securities eligible for resale under Rule 144A of the 1933 Act may be subject to this 15%
limitation;
5. Purchase securities of open-end or closed-end investment companies except in compliance with
the Investment Company Act of 1940 or the conditions of any order of exemption from the SEC regarding the
purchase of securities of money market funds managed by the Sub-advisor or its affiliates;
6. Purchase securities on margin, except (i) for use of short-term credit necessary for clearance
of purchases of portfolio securities and (ii) the Fund may make margin deposits in connection with futures
contracts or other permissible investments;
7. Mortgage, pledge, hypothecate or, in any manner, transfer any security owned by the Fund as
security for indebtedness except as may be necessary in connection with permissible borrowings or investments and
then such mortgaging, pledging or hypothecating may not exceed 33 1/3% of the Fund's total assets at the time of
borrowing or investment;
8. Invest in puts, calls, straddles, spreads, or any combination thereof, except to the extent
permitted by the Company's Prospectus and this SAI;
9. Sell securities short, except that the Fund may make short sales if it owns the securities sold
short or has the right to acquire such securities through conversion or exchange of other securities it owns; or
10. Invest in warrants if, as a result thereof, more than 10% of the value of the net assets of the
Fund would be invested in warrants, except that this restriction does not apply to warrants acquired as a result
of the purchase of another security. For purposes of these percentage limitations, the warrants will be valued
at the lower of cost or market.
ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek long-term growth of capital.
Investment Policies:
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest up to 25% of its net assets in foreign securities denominated
in foreign currencies and not publicly traded in the United States. Investing in securities of foreign issuers
generally involves risks not ordinarily associated with investing in securities of domestic issuers. For a
discussion of the risks involved in foreign securities, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain
Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Depositary Receipts. The Fund may invest in sponsored and unsponsored American Depositary Receipts
("ADRs"), which are described in the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Holders of unsponsored ADRs generally bear all the costs of the ADR facility, whereas foreign issuers typically
bear certain costs in a sponsored ADR. The bank or trust company depositary of an unsponsored ADR may be under
no obligation to distribute shareholder communications received from the foreign issuer or to pass through voting
rights. The Fund may also invest in European Depositary Receipts ("EDRs"), Global Depositary Receipts ("GDRs")
and in other similar instruments representing securities of foreign companies.
Investment Company Securities. From time to time, the Fund may invest in securities of other investment
companies, subject to the provisions of Section 12(d)(1) of the 1940 Act. The Fund may invest in securities of
money market funds managed by the Sub-advisor in excess of the limitations of Section 12(d)(1) under the terms of
an SEC exemptive order obtained by the Sub-advisor and the funds that are advised or sub-advised by the
Sub-advisor.
Municipal Obligations. The Fund may invest in municipal obligations issued by states, territories and
possessions of the United States and the District of Columbia. The value of municipal obligations can be
affected by changes in their actual or perceived credit quality. The credit quality of municipal obligations can
be affected by among other things the financial condition of the issuer or guarantor, the issuer's future
borrowing plans and sources of revenue, the economic feasibility of the revenue bond project or general borrowing
purpose, political or economic developments in the region where the security is issued, and the liquidity of the
security. Because municipal securities are generally traded over-the-counter, the liquidity of a particular
issue often depends on the willingness of dealers to make a market in the security. The liquidity of some
municipal obligations may be enhanced by demand features, which would enable the Fund to demand payment on short
notice from the issuer or a financial intermediary.
Income-Producing Securities. Types of income-producing securities that the Fund may purchase include,
but are not limited to, (i) variable and floating rate obligations, which are securities having interest rates
that are adjusted periodically according to a specified formula, usually with reference to some interest rate
index or market interest rate, and (ii) tender option bonds, which are relatively long-term bonds that are
coupled with the agreement of a third party (such as a broker, dealer or bank) to grant the holders of such
securities the option to tender the securities to the institution at periodic intervals. Variable and floating
rate obligations often carry demand features permitting the holder to demand payment of principal at any time or
at specified intervals prior to maturity. The Fund may also acquire standby commitments, which are instruments
similar to puts that give the holder the option to obligate a broker, dealer or bank to repurchase a security at
a specified price. The Fund will purchase standby commitments, tender option bonds and instruments with demand
features primarily for the purpose of increasing the liquidity of its portfolio. The Fund may also invest in
inverse floaters, which are debt instruments the interest on which varies in an inverse relationship to the
interest rate on another security. If movements in interest rates are incorrectly anticipated, the Fund could
lose money or its net asset value could decline by the use of inverse floaters. The Fund will not invest more
than 5% of its assets in inverse floaters. The Fund may also invest in strip bonds, which are debt securities
that are stripped of their interest (usually by a financial intermediary) after the securities are issued. The
market value of these securities generally fluctuates more in response to changes in interest rates than
interest-paying securities of comparable maturity.
Zero Coupon, Step Coupon and Pay-In-Kind Securities. The Fund may invest up to 10% of its assets in
zero coupon, pay-in-kind and step coupon securities. Zero coupon bonds are described in this SAI under "Certain
Risk Factors and Investment Methods." Step coupon bonds trade at a discount from their face value and pay coupon
interest. The coupon rate is low for an initial period and then increases to a higher coupon rate thereafter.
The discount from the face amount or par value depends on the time remaining until cash payments begin,
prevailing interest rates, liquidity of the security and the perceived credit quality of the issuer. Pay-in-kind
bonds normally give the issuer an option to pay cash at a coupon payment date or give the holder of the security
a similar bond with the same coupon rate and a face value equal to the amount of the coupon payment that would
have been made.
Generally, the market prices of zero coupon, step coupon and pay-in-kind securities are more volatile
than the prices of securities that pay interest periodically and in cash and are likely to respond to changes in
interest rates to a greater degree than other types of debt securities having similar maturities and credit
quality. Additionally, the Fund may have to sell portfolio holdings so that it is able to distribute cash in
order to satisfy current federal tax law requirements to distribute income accrued, but not actually received, on
zero coupon, step coupon and pay-in-kind securities. This may cause the Fund to incur capital gains or losses on
such sales, as well as reduce the assets to which Fund expenses could be allocated and reduce the rate of return
for the Fund. For additional discussion of potential tax consequences of investing in zero coupon securities,
see this SAI under "Additional Tax Considerations."
High-Yield/High-Risk Securities. The Fund may invest up to 35% of its net assets in bonds that are
rated below investment grade. The Fund may also invest in unrated debt securities of foreign and domestic
issuers. Unrated debt, while not necessarily of lower quality than rated securities, may not have as broad a
market. Because of the size and perceived demand of the issue, among other factors, certain municipalities may
not incur the costs of obtaining a rating. The Sub-advisor will analyze the creditworthiness of the issuer, as
well as any financial institution or other party responsible for payments on the security, in determining whether
to purchase unrated municipal bonds. Unrated bonds will be included in the 35% limit unless the Sub-advisor
deems such securities to be the equivalent of investment grade securities. For a description of these securities
and a discussion of the risks involved therein, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods."
The Fund may purchase defaulted securities subject to the above limits, but only when the Sub-advisor
believes, based upon its analysis of the financial condition, results of operations and economic outlook of an
issuer, that there is potential for resumption of income payments and that the securities offer an unusual
opportunity for capital appreciation. Notwithstanding the Sub-advisor's belief as to the resumption of income,
however, the purchase of any security on which payment of interest or dividends is suspended involves a high
degree of risk. Such risk includes, among other things, the following:
Financial and Market Risks. Investments in securities that are in default involve a high
degree of financial and market risks that can result in substantial or, at times, even total losses. Issuers of
defaulted securities may have substantial capital needs and may become involved in bankruptcy or reorganization
proceedings. Among the problems involved in investments in such issuers is the fact that it may be difficult to
obtain information about their condition. The market prices of securities of such issuers also are subject to
abrupt and erratic movements and above average price volatility, and the spread between the bid and asked prices
of such securities may be greater than normally expected.
Disposition of Portfolio Securities. Although the Fund generally will purchase securities for
which the Sub-advisor expects an active market to be maintained, defaulted securities may be less actively traded
than other securities and it may be difficult to dispose of substantial holdings of such securities at prevailing
market prices. The Fund will limit holdings of any such securities to amounts that the Sub-advisor believes
could be readily sold, and holdings of such securities would, in any event, be limited so as not to limit the
Portfolio's ability to readily dispose of securities to meet redemptions.
Other. Defaulted securities require active monitoring and may, at times, require participation
in bankruptcy or receivership proceedings on behalf of the Fund.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements. The Fund may use reverse repurchase agreements to provide cash to
satisfy unusually heavy redemption requests or for other temporary or emergency purposes without the necessity of
selling portfolio securities, or to earn additional income on portfolio securities, such as Treasury bills or
notes. The Fund will enter into reverse repurchase agreements only with parties that the Sub-advisor deems
creditworthy. Using reverse repurchase agreements to earn additional income involves the risk that the interest
earned on the invested proceeds is less than the expense of the reverse repurchase agreement transaction. This
technique may also have a leveraging effect on the Fund, although the requirement for the Fund to segregate
assets in the amount of the reverse repurchase agreement minimizes this effect.
For an additional discussion of reverse repurchase agreements and their risks, see the Company's
Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Futures, Options and Forward Contracts. The Fund may enter into futures contracts on securities,
financial indices, and foreign currencies and options on such contracts, and may invest in options on securities,
financial indices, and foreign currencies, and forward contracts. The Fund will not enter into any futures
contracts or options on futures contracts if the aggregate amount of the Fund's commitments under outstanding
futures contract positions and options on futures contracts written by the Fund would exceed the market value of
the Fund's total assets. The Fund may invest in forward currency contracts with stated values of up to the value
of the Fund's assets.
The Fund may buy or write options that are traded on United States and foreign securities exchanges and
over-the-counter on the types of securities, and on indices based on the types of securities, in which the Fund
is permitted to invest directly. The Fund will effect over-the-counter options transactions only with investment
dealers and other financial institutions (such as commercial banks or savings and loan institutions) deemed
creditworthy by the Sub-advisor pursuant to procedures adopted by the Sub-advisor for monitoring the
creditworthiness of those entities. To the extent that an option purchased or written by the Fund in a
negotiated transaction is illiquid, the value of the option purchased or the amount of the Fund's obligations
under an option it has written, as the case may be, will be subject to the Fund's limitation on illiquid
investments. In the case of illiquid options, it may not be possible for the Fund to effect an offsetting
transaction when the Sub-advisor believes it would be advantageous for the Fund to do so. For a description of
these strategies and instruments and certain of their risks, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Eurodollar Instruments. The Fund may make investments in Eurodollar instruments. Eurodollar
instruments are U.S. dollar-denominated futures contracts or options thereon that are linked to the London
Interbank Offered Rate ("LIBOR"), although foreign currency-denominated instruments are available from time to
time. Eurodollar futures contracts enable purchasers to obtain a fixed rate for the lending of funds and sellers
to obtain a fixed rate for borrowings. The Fund might use Eurodollar futures contracts and options thereon to
hedge against changes in LIBOR, to which many interest rate swaps and fixed-income instruments are linked.
Swaps and Swap-Related Products. The Fund may enter into interest rate swaps, caps and floors on either
an asset-based or liability-based basis, depending upon whether it is hedging its assets or its liabilities, and
will usually enter into interest rate swaps on a net basis (i.e., the two payment streams are netted out, with
the Fund receiving or paying, as the case may be, only the net amount of the two payments). The net amount of
the excess, if any, of the Fund's obligations over its entitlement with respect to each interest rate swap will
be calculated on a daily basis and an amount of cash or other liquid assets having an aggregate net asset value
at least equal to the accrued excess will be maintained in a segregated account by the Fund's custodian. If the
Fund enters into an interest rate swap on other than a net basis, it would maintain a segregated account in the
full amount accrued on a daily basis of its obligations with respect to the swap. The Fund will not enter into
any interest rate swap, cap or floor transaction unless the unsecured senior debt or the claims-paying ability of
the other party thereto is rated in one of the three highest rating categories of at least one NRSRO at the time
of entering into such transaction. The Sub-advisor will monitor the creditworthiness of all counterparties on an
ongoing basis. If there is a default by the other party to such a transaction, the Fund will have contractual
remedies pursuant to the agreements related to the transaction.
The swap market has grown substantially in recent years with a large number of banks and investment
banking firms acting both as principals and as agents utilizing standardized swap documentation. The Sub-advisor
has determined that, as a result, the swap market has become relatively liquid. Caps and floors are more recent
innovations for which standardized documentation has not yet been developed and, accordingly, are less liquid
than swaps. To the extent the Fund sells (i.e., writes) caps and floors, it will segregate cash or other liquid
assets having an aggregate net asset value at least equal to the full amount, accrued on a daily basis, of its
obligations with respect to any caps or floors.
There is no limit on the amount of interest rate swap transactions that may be entered into by the
Fund. These transactions may in some instances involve the delivery of securities or other underlying assets by
the Fund or its counterparty to collateralize obligations under the swap. Under the documentation currently used
in those markets, the risk of loss with respect to interest rate swaps is limited to the net amount of the
payments that the Fund is contractually obligated to make. If the other party to an interest rate swap that is
not collateralized defaults, the Fund would risk the loss of the payments that it contractually is entitled to
receive. The Fund may buy and sell (i.e., write) caps and floors without limitation, subject to the segregation
requirement described above.
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
applicable to the ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund. These limitations are not "fundamental" restrictions, and may
be changed by the Directors without shareholder approval.
1. The Fund does not currently intend to sell securities short, unless it owns or has the right to
obtain securities equivalent in kind and amount to the securities sold short without the payment of any
additional consideration therefor, and provided that transactions in futures, options, swaps and forward
contracts are not deemed to constitute selling securities short.
2. The Fund does not currently intend to purchase securities on margin, except that the Fund may
obtain such short-term credits as are necessary for the clearance of transactions, and provided that margin
payments and other deposits in connection with transactions in futures, options, swaps and forward contracts
shall not be deemed to constitute purchasing securities on margin.
3. The Fund may not mortgage or pledge any securities owned or held by the Fund in amounts that
exceed, in the aggregate, 15% of the Fund's net asset value, provided that this limitation does not apply to
reverse repurchase agreements, margin and other deposits in connection with transactions in futures, options,
swaps or forward contracts, or the segregation of assets in connection with such contracts.
4. The Fund does not currently intend to purchase any security or enter into a repurchase
agreement if, as a result, more than 15% of its net assets would be invested in repurchase agreements not
entitling the holder to payment of principal and interest within seven days and in securities that are illiquid
by virtue of legal or contractual restrictions on resale or the absence of a readily available market. The
Directors, or the Fund's Sub-advisor acting pursuant to authority delegated by the Directors, may determine that
a readily available market exists for securities eligible for resale pursuant to Rule 144A under the Securities
Act of 1933 ("Rule 144A Securities"), or any successor to such rule, Section 4(2) commercial paper and municipal
lease obligations. Accordingly, such securities may not be subject to the foregoing limitation.
5. The Fund may not invest in companies for the purpose of exercising control of management.
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth.
Investment Policies:
Securities Loans. In order to realize income, the Fund may lend portfolio securities with a value not
exceeding 33-1/3% of its total assets to banks, brokerage firms, or institutional investors judged creditworthy
by the Sub-advisor. Borrowers are required continuously to secure their obligations to return securities on loan
from the Fund by depositing collateral, which will be marked to market daily, in a form determined to be
satisfactory by the Directors and equal to at least 100% of the market value of the loaned securities, which will
also be marked to market daily. The Sub-advisor believes the risk of loss on these transactions is slight
because, if a borrower were to default for any reason, the collateral should satisfy the obligation. However, as
with other extensions of secured credit, loans of portfolio securities involve some risk of loss of rights in the
collateral should the borrower fail financially.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements. In a reverse repurchase agreement, the Fund sells portfolio securities
subject to its agreement to repurchase the securities at a later date for a fixed price reflecting a market rate
of interest; these agreements are considered borrowings for purposes of the Fund's investment limitations and
policies concerning borrowings. There is a risk that the counterparty to a reverse repurchase agreement will be
unable or unwilling to complete the transaction as scheduled, which may result in losses to the Fund.
Covered Call Options. The Fund may write covered call options on securities it owns. Generally, the
purpose of writing those options is to reduce the effect of price fluctuations of securities held by the Fund on
the Fund's net asset value. Securities on which call options may be written by the Fund are purchased solely on
the basis of investment considerations consistent with the Fund's investment objectives.
When the Fund writes a call option, it is obligated to sell a security to a purchaser at a specified
price at any time until a certain date if the purchaser decides to exercise the option. The Fund receives a
premium for writing the call option. The Fund writes only "covered" call options on securities it owns. So long
as the obligation of the writer of the call option continues, the writer may be assigned an exercise notice,
requiring it to deliver the underlying security against payment of the exercise price. The Fund may be obligated
to deliver securities underlying a call option at less than the market price thereby giving up any additional
gain on the security.
When the Fund purchases a call option, it pays a premium for the right to purchase a security from the
writer at a specified price until a specified date. A call option would be purchased by the Fund to offset a
previously written call option.
The writing of covered call options is a conservative investment technique believed to involve
relatively little risk (in contrast to the writing of "naked" or uncovered call options, which the Fund will not
do), but is capable of enhancing the Fund's total return. When writing a covered call option, the Fund, in
return for the premium, gives up the opportunity for profit from a price increase in the underlying security
above the exercise price, but conversely retains the risk of loss should the price of the security decline. If a
call option that the Fund has written expires unexercised, the Fund will realize a gain in the amount of the
premium; however, that gain may be offset by a decline in the market value of the underlying security during the
option period. If the call option is exercised, the Fund will realize a gain or loss from the sale or purchase
of the underlying security.
The exercise price of an option may be below, equal to, or above the market value of the underlying
security at the time the option is written. Options normally have expiration dates between three and nine months
from the date written. The obligation under any option terminates upon expiration of the option or, at an
earlier time, when the writer offsets the option by entering into a "closing purchase transaction" to purchase an
option of the same series.
Options are traded both on national securities exchanges and in the over-the-counter ("OTC") market.
Exchange-traded options are issued by a clearing organization affiliated with the exchange on which the option is
listed; the clearing organization in effect guarantees completion of every exchange-traded option. In contrast,
OTC options are contracts between the Fund and its counter-party with no clearing organization guarantee. Thus,
when the Fund sells or purchases an OTC option, it generally will be able to "close out" the option prior to its
expiration only by entering into a "closing purchase transaction" with the dealer to whom or from whom the Fund
originally sold or purchased the option. The Sub-advisor monitors the creditworthiness of dealers with which the
Fund may engage in OTC options, and will limit counterparties in such transactions to dealers with a net worth of
at least $20 million as reported in their latest financial statements. For an additional discussion of OTC
options and their risks, see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
The premium received (or paid) by the Fund when it writes (or purchases) an option is the amount at
which the option is currently traded on the applicable exchange, less (or plus) a commission. The premium may
reflect, among other things, the current market price of the underlying security, the relationship of the
exercise price to the market price, the historical price volatility of the underlying security, the length of the
option period, the general supply of and demand for credit, and the general interest rate environment. The
premium received by the Fund for writing an option is recorded as a liability on the Fund's statement of assets
and liabilities. This liability is adjusted daily to the option's current market value.
The Fund pays the brokerage commissions in connection with purchasing or writing options, including
those used to close out existing positions. These brokerage commissions normally are higher than those
applicable to purchases and sales of portfolio securities.
From time to time, the Fund may purchase an underlying security for delivery in accordance with an
exercise notice of a call option assigned to it, rather than delivering the security from its portfolio. In
those cases, additional brokerage commissions are incurred.
For an additional discussion of options and their risks, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest in U.S. dollar-denominated equity and debt securities issued by
foreign issuers (including governments, quasi-governments and foreign banks) and foreign branches of U.S. banks,
including negotiable CDs and commercial paper. These investments are subject to the Fund's quality standards.
While investments in foreign securities are intended to reduce risk by providing further diversification, such
investments involve sovereign and other risks, in addition to the credit and market risks normally associated
with domestic securities.
The Fund may invest in equity, debt, or other income-producing securities that are denominated in or
indexed to foreign currencies, including, but not limited to (1) common and preferred stocks, (2) convertible
securities, (3) warrants, (4) CDs, commercial paper, fixed-time deposits, and bankers' acceptances issued by
foreign banks, (5) obligations of other corporations, and (6) obligations of foreign governments, or their
subdivisions, agencies, and instrumentalities, international agencies, and supranational entities. Risks of
investing in foreign currency denominated securities include (1) nationalization, expropriation, or confiscatory
taxation, (2) adverse changes in investment or exchange control regulations (which could prevent cash from being
brought back to the U.S.), and (3) expropriation or nationalization of foreign portfolio companies. Mail service
between the U.S. and foreign countries may be slower or less reliable than within the United States, thus
increasing the risk of delayed settlements of portfolio transactions or loss of certificates for portfolio
securities. For an additional discussion of the risks associated with foreign securities, whether denominated in
U.S. dollars or foreign currencies, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and
Investment Methods."
Prices of foreign securities and exchange rates for foreign currencies may be affected by the interest
rates prevailing in other countries. The interest rates in other countries are often affected by local factors,
including the strength of the local economy, the demand for borrowing, the government's fiscal and monetary
policies, and the international balance of payments. Individual foreign economies may differ favorably or
unfavorably from the U.S. economy in such respects as gross national product, rate of inflation, capital
reinvestment, resource self-sufficiency, and balance of payments position.
Foreign markets also have different clearance and settlement procedures, and in certain markets there
have been times when settlements have been unable to keep pace with the volume of securities transactions, making
it difficult to conduct such transactions. Such delays in settlement could result in temporary periods when a
portion of the assets of the Fund is uninvested and no return is earned thereon. The inability of the Fund to
make intended security purchases due to settlement problems could cause the Fund to miss attractive investment
opportunities. Inability to dispose of portfolio securities due to settlement problems could result either in
losses to the Fund due to subsequent declines in value of the portfolio securities, or, if the Fund has entered
into a contract to sell the securities, could result in possible liability to the purchaser.
The Fund may invest in foreign corporate bonds and debentures and sovereign debt instruments issued or
guaranteed by foreign governments, their agencies or instrumentalities. Foreign debt securities are subject to
risks similar to those of other foreign securities, as well as risks similar to those of other debt securities,
as discussed in this SAI and in the Company's Prospectus under "Investment Programs of the Funds" and "Certain
Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
In order to limit the risk inherent in investing in foreign currency-denominated securities, the Fund
may not purchase any such security if after such purchase more than 10% of its total assets (taken at market
value) would be invested in such securities. Within such limitation, however, the Fund is not restricted in the
amount it may invest in securities denominated in any one foreign currency.
Foreign Currency Transactions. The Fund may engage in foreign currency exchange transactions. Foreign
currency exchange transactions will be conducted either on a spot (i.e., cash) basis at the spot rate prevailing
----
in the foreign currency exchange market, or through entering into forward contracts to purchase or sell foreign
currencies ("forward contracts"). The Fund may enter into forward contracts in order to protect against
uncertainty in the level of future foreign currency exchange rates. The Fund may also use forward contracts for
non-hedging purposes.
A forward contract involves an obligation to purchase or sell a specific currency at a future date,
which may be any fixed number of days (usually less than one year) from the date of the contract agreed upon by
the parties, at a price set at the time of the contract. These contracts are traded in the interbank market
conducted directly between traders (usually large commercial banks) and their customers. A forward contract
generally has no deposit requirement, and no commissions are charged at any stage for trades. Although foreign
exchange dealers do not charge a fee for conversion, they do realize a profit based on the difference (the
spread) between the price at which they are buying and selling various currencies.
When the Fund enters into a contract for the purchase or sale of a security denominated in a foreign
currency, it may wish to "lock in" the U.S. dollar price of the security. By entering into a forward contract
for the purchase or sale, for a fixed amount of U.S. dollars, of the amount of foreign currency involved in the
underlying security transactions, the Fund will be able to protect itself against a possible loss. When the
Sub-advisor believes that the currency of a particular foreign country may suffer a substantial decline against
the U.S. dollar, it may also enter into a forward contract to sell the amount of foreign currency for a fixed
amount of dollars which approximates the value of some or all of a Fund's securities denominated in such foreign
currency.
The Fund may also engage in cross-hedging by using forward contracts in one currency to hedge against
fluctuations in the value of securities denominated in a different currency, when the Sub-advisor believes that
there is a pattern of correlation between the two currencies. The Fund may also purchase and sell forward
contracts for non-hedging purposes when the Sub-advisor anticipates that the foreign currency will appreciate or
depreciate in value, but securities in that currency do not present attractive investment opportunities and are
not held in the Fund's portfolio.
When the Fund engages in forward contracts for hedging purposes, it will not enter into forward
contracts to sell currency or maintain a net exposure to such contracts if their consummation would obligate the
Fund to deliver an amount of foreign currency in excess of the value of its portfolio securities or other assets
denominated in that currency. At the consummation of the forward contract, the Fund may either make delivery of
the foreign currency or terminate its contractual obligation to deliver by purchasing an offsetting contract
obligating it to purchase the same amount of such foreign currency at the same maturity date. If the Fund
chooses to make delivery of the foreign currency, it may be required to obtain such currency through the sale of
portfolio securities denominated in such currency or through conversion of other assets into such currency. If
the Fund engages in an offsetting transaction, it will incur a gain or a loss to the extent that there has been a
change in forward contract prices. Closing purchase transactions with respect to forward contracts are usually
made with the currency trader who is a party to the original forward contract.
The Fund is not required to enter into such transactions and will not do so unless deemed appropriate by
the Sub-advisor.
Using forward contracts to protect the value of the Fund's portfolio securities against a decline in the
value of a currency does not eliminate fluctuations in the underlying prices of the securities. It simply
establishes a rate of exchange which can be achieved at some future point in time. The precise projection of
short-term currency market movements is not possible, and short-term hedging provides a means of fixing the
dollar value of only a portion of the Fund's foreign assets.
While the Fund may enter forward contracts to reduce currency exchange rate risks, transactions in such
contracts involve certain other risks. Thus, while the Fund may benefit from such transactions, unanticipated
changes in currency prices may result in a poorer overall performance for the Fund than if it had not engaged in
any such transactions. Moreover, there may be imperfect correlation between the Fund's holdings of securities
denominated in a particular currency and forward contracts entered into by the Fund. Such imperfect correlation
may cause the Fund to sustain losses which will prevent it from achieving a complete hedge or expose it to risk
of foreign exchange loss.
The Fund generally will not enter into a forward contract with a term of greater than one year. The
Fund may experience delays in the settlement of its foreign currency transactions.
When the Fund engages in forward contracts for the sale or purchase of currencies, the Fund will either
cover its position or establish a segregated account. The Fund will consider its position covered if it has
securities in the currency subject to the forward contract, or otherwise has the right to obtain that currency at
no additional cost. In the alternative, the Fund will place cash, fixed income, or equity securities
(denominated in the foreign currency subject to the forward contract) in a separate account. The amounts in such
separate account will equal the value of the Fund's assets which are committed to the consummation of foreign
currency exchange contracts. If the value of the securities placed in the separate account declines, the Fund
will place additional cash or securities in the account on a daily basis so that the value of the account will
equal the amount of its commitments with respect to such contracts.
For an additional discussion of forward foreign currency exchange contracts and their risks, see this
SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Options on Foreign Currencies. The Fund may write and purchase covered call and put options on foreign
currencies in amounts not exceeding 5% of its net assets for the purpose of protecting against declines in the
U.S. dollar value of portfolio securities or increases in the U.S. dollar cost of securities to be acquired, or
to protect the dollar equivalent of dividend, interest, or other payment on those securities. A decline in the
dollar value of a foreign currency in which portfolio securities are denominated will reduce the dollar value of
such securities, even if their value in the foreign currency remains constant. In order to protect against such
decreases in the value of portfolio securities, the Fund may purchase put options on the foreign currency. If
the value of the currency declines, the Fund will have the right to sell such currency for a fixed amount of
dollars which exceeds the market value of such currency. This would result in a gain that may offset, in whole
or in part, the negative effect of currency depreciation on the value of the Fund's securities denominated in
that currency.
Conversely, if the dollar value of a currency in which securities to be acquired by the Fund are
denominated rises, thereby increasing the cost of such securities, the Fund may purchase call options on such
currency. If the value of such currency increases sufficiently, the Fund will have the right to purchase that
currency for a fixed amount of dollars which is less than the market value of that currency. Such a purchase
would result in a gain that may offset, at least partially, the effect of any currency-related increase in the
price of securities the Fund intends to acquire.
As in the case of other types of options transactions, however, the benefit the Fund derives from
purchasing foreign currency options will be reduced by the amount of the premium and related transaction costs.
In addition, if currency exchange rates do not move in the direction or to the extent anticipated, the Fund could
sustain losses on transactions in foreign currency options which would deprive it of a portion or all of the
benefits of advantageous changes in such rates.
The Fund may also write options on foreign currencies for hedging purposes. For example, if the
Sub-advisor anticipates a decline in the dollar value of foreign currency denominated securities because of
declining exchange rates, it could, instead of purchasing a put option, write a call option on the relevant
currency. If the expected decline occurs, the option will most likely not be exercised, and the decrease in
value of portfolio securities will be offset, at least in part, by the amount of the premium received by the Fund.
Similarly, the Fund could write a put option on the relevant currency, instead of purchasing a call
option, to hedge against an anticipated increase in the dollar cost of securities to be acquired. If exchange
rates move in the manner projected, the put option most likely will not be exercised, and such increased cost
will be offset, at least in part, by the amount of the premium received. However, as in the case of other types
of options transactions, the writing of a foreign currency option will constitute only a partial hedge up to the
amount of the premium, and only if rates move in the expected direction.
If unanticipated exchange rate fluctuations occur, a put or call option may be exercised and the Fund
could be required to purchase or sell the underlying currency at a loss which may not be fully offset by the
amount of the premium. As a result of writing options on foreign currencies, the Fund also may be required to
forego all or a portion of the benefits which might otherwise have been obtained from favorable movements in
currency exchange rates. Options on foreign currencies may be traded on U.S. or foreign exchanges, or
over-the-counter. Options on foreign currencies that are traded on the OTC market involve liquidity and credit
risks that may not be present in the case of exchange-traded currency options.
A call option written on foreign currency by the Fund is "covered" if the Fund owns the underlying
foreign currency subject to the call, or if it has an absolute and immediate right to acquire that foreign
currency without additional cash consideration. A call option is also covered if the Fund holds a call on the
same foreign currency for the same principal amount as the call written where the exercise price of the call held
is (a) equal to or less than the exercise price of the call written or (b) greater than the exercise price of the
call written if the amount of the difference is maintained by the Fund in cash, fixed income or equity securities
in a segregated account with its custodian.
The risks of currency options are similar to the risks of other options, as discussed above and in this
SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Cover for Options on Securities, Forward Contracts, and Options on Foreign Currencies ("Hedging
Instruments"). The Fund will comply with SEC staff guidelines regarding "cover" for Hedging Instruments and, if
the guidelines so require, set aside in a segregated account with its custodian the prescribed amount of cash,
fixed income, or equity securities. Securities held in a segregated account cannot be sold while the futures,
option, or forward strategy covered by those securities is outstanding, unless they are replaced with other
suitable assets. As a result, segregation of a large percentage of the Fund's assets could impede portfolio
management or the Fund's ability to meet current obligations. The Fund may be unable promptly to dispose of
assets that cover, or are segregated with respect to, an illiquid options or forward position; this inability may
result in a loss to the Fund.
Preferred Stock. The Fund may invest in preferred stock. Unlike interest payments on debt securities,
dividends on preferred stock are generally payable at the discretion of the issuer's board of directors, although
preferred shareholders may have certain rights if dividends are not paid. Shareholders may suffer a loss of
value if dividends are not paid, and generally have no legal recourse against the issuer. The market prices of
preferred stocks are generally more sensitive to changes in the issuer's creditworthiness than are the prices of
debt securities.
Fixed Income Securities. The Fund may invest in money market instruments, U.S. Government or Agency
securities, and corporate bonds and debentures receiving one of the four highest ratings from Standard & Poor's
Ratings Group ("S&P"), Moody's Investors Service, Inc. ("Moody's") or any other nationally recognized statistical
rating organization ("NRSRO"), or, if not rated by any NRSRO, deemed comparable by the Sub-advisor to such rated
securities ("Comparable Unrated Securities"). The ratings of an NRSRO represent its opinion as to the quality of
securities it undertakes to rate. Ratings are not absolute standards of quality; consequently, securities with
the same maturity, coupon, and rating may have different yields. Although the Fund may rely on the ratings of
any NRSRO, the Fund mainly refers to ratings assigned by S&P and Moody's, which are described in Appendix A to
this SAI.
Fixed income securities are subject to the risk of an issuer's inability to meet principal and interest
payments on the obligations ("credit risk") and also may be subject to price volatility due to such factors as
interest rate sensitivity, market perception of the creditworthiness of the issuer, and general market liquidity
("market risk"). Lower-rated securities are more likely to react to developments affecting market and credit
risk than are more highly rated securities, which react primarily to movements in the general level of interest
rates.
Changes in economic conditions or developments regarding the individual issuer are more likely to cause
price volatility and weaken the capacity of the issuer of such securities to make principal and interest payments
than is the case for higher-grade debt securities. An economic downturn affecting the issuer may result in an
increased incidence of default. The market for lower-rated securities may be thinner and less active than for
higher-rated securities. Pricing of thinly traded securities requires greater judgment than pricing of
securities for which market transactions are regularly reported.
If the quality of any fixed income securities held by the Fund deteriorates so that they no longer would
be eligible for purchase by the Fund, the Fund will engage in an orderly disposition of the securities to the
extent necessary to ensure that the Fund's holding of such securities will not exceed 5% of its net assets.
Convertible Securities. The Fund may invest in convertible securities of any quality. A convertible
security entitles the holder to receive interest paid or accrued on debt or the dividend paid on preferred stock
until the convertible security matures or is redeemed, converted or exchanged. Before conversion, convertible
securities ordinarily provide a stream of income with generally higher yields than those of common stocks of the
same or similar issuers, but lower than the yield on non-convertible debt. Convertible securities are usually
subordinated to comparable-tier nonconvertible securities but rank senior to common stock in a corporation's
capital structure. The value of a convertible security is a function of (1) its yield in comparison with the
yields of other securities of comparable maturity and quality that do not have a conversion privilege, and (2)
its worth, at market value, if converted into the underlying common stock. Convertible debt securities are
subject to the Fund's investment policies and limitations concerning fixed-income investments.
Convertible securities are typically issued by smaller companies whose stock prices may be volatile.
The price of a convertible security often reflects such variations in the price of the underlying common stock in
a way that nonconvertible debt does not. A convertible security may be subject to redemption at the option of
the issuer at a price established in the security's governing instrument. If a convertible security held by the
Fund is called for redemption, the Fund will be required to convert it into the underlying common stock, sell it
to a third party or permit the issuer to redeem the security. Any of these actions could have an adverse effect
on the Fund's ability to achieve its investment objective.
Commercial Paper. Commercial paper is a short-term debt security issued by a corporation, bank,
municipality, or other issuer, usually for purposes such as financing current operations. The Fund may invest
only in commercial paper receiving the highest rating from S&P (A-1) or Moody's (P-1), or deemed by the
Sub-advisor to be of equivalent quality.
The Fund may invest in commercial paper that cannot be resold to the public because it was issued under
the exception for private offerings in Section 4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933. While such securities
normally will be considered illiquid and subject to the Fund's 15% limitation on investments in illiquid
securities, the Sub-advisor may in certain cases determine that such paper is liquid under guidelines established
by the Board of Directors.
Banking and Savings Institution Securities. The Fund may invest in banking and savings institution
obligations, which include CDs, time deposits, bankers' acceptances, and other short-term debt obligations issued
by savings institutions. CDs are receipts for funds deposited for a specified period of time at a specified rate
of return; time deposits generally are similar to CDs, but are uncertificated; and bankers' acceptances are time
drafts drawn on commercial banks by borrowers, usually in connection with international commercial transactions.
The CDs, time deposits, and bankers' acceptances in which the Fund invests typically are not covered by deposit
insurance.
Investment Policies Which May be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
applicable to the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund. These limitations are not fundamental restrictions
and can be changed without shareholder approval.
1. The Fund may not purchase securities if outstanding borrowings, including any reverse
repurchase agreements, exceed 5% of its total assets.
2. Except for the purchase of debt securities and engaging in repurchase agreements, the Fund may
not make any loans other than securities loans.
3. The Fund may not purchase securities on margin from brokers, except that the Fund may obtain
such short-term credits as are necessary for the clearance of securities transactions. Margin payments in
connection with transactions in futures contracts and options on futures contracts shall not constitute the
purchase of securities on margin and shall not be deemed to violate the foregoing limitation.
4. The Fund may not sell securities short, unless it owns or has the right to obtain securities
equivalent in kind and amount to the securities sold without payment of additional consideration. Transactions
in futures contracts and options shall not constitute selling securities short.
5. The Fund may not purchase any security if, as a result, more than 15% of its net assets would
be invested in illiquid securities. Illiquid securities include securities that cannot be sold within seven days
in the ordinary course of business for approximately the amount at which the Fund has valued the securities, such
as repurchase agreements maturing in more than seven days.
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth.
Investment Policies:
Securities Loans. In order to realize income, the Fund may lend portfolio securities with a value not
exceeding 33-1/3% of its total assets to banks, brokerage firms, or institutional investors judged creditworthy
by the Sub-advisor. Borrowers are required continuously to secure their obligations to return securities on loan
from the Fund by depositing collateral, which will be marked to market daily, in a form determined to be
satisfactory by the Directors and equal to at least 100% of the market value of the loaned securities, which will
also be marked to market daily. The Sub-advisor believes the risk of loss on these transactions is slight
because, if a borrower were to default for any reason, the collateral should satisfy the obligation. However, as
with other extensions of secured credit, loans of portfolio securities involve some risk of loss of rights in the
collateral should the borrower fail financially.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements. In a reverse repurchase agreement, the Fund sells portfolio securities
subject to its agreement to repurchase the securities at a later date for a fixed price reflecting a market rate
of interest; these agreements are considered borrowings for purposes of the Fund's investment limitations and
policies concerning borrowings. There is a risk that the counterparty to a reverse repurchase agreement will be
unable or unwilling to complete the transaction as scheduled, which may result in losses to the Fund.
Covered Call Options. The Fund may write covered call options on securities it owns valued at up to 10%
of its net assets and may purchase call options in related closing transactions. Generally, the purpose of
writing these options is to reduce the effect of price fluctuations of securities held by the Fund on the Fund's
net asset value. Securities on which call options may be written by the Fund are purchased solely on the basis
of investment considerations consistent with the Fund's investment objectives.
When the Fund writes a call option, it is obligated to sell a security to a purchaser at a specified
price at any time until a certain date if the purchaser decides to exercise the option. The Fund receives a
premium for writing the call option. The Fund writes only "covered" call options on securities it owns. So long
as the obligation of the writer of the call option continues, the writer may be assigned an exercise notice,
requiring it to deliver the underlying security against payment of the exercise price. The Fund may be obligated
to deliver securities underlying a call option at less than the market price thereby giving up any additional
gain on the security.
When the Fund purchases a call option, it pays a premium for the right to purchase a security from the
writer at a specified price until a specified date. A call option would be purchased by the Fund to offset a
previously written call option.
The writing of covered call options is a conservative investment technique believed to involve
relatively little risk (in contrast to the writing of "naked" or uncovered call options, which the Fund will not
do), but is capable of enhancing the Fund's total return. When writing a covered call option, the Fund, in
return for the premium, gives up the opportunity for profit from a price increase in the underlying security
above the exercise price, but conversely retains the risk of loss should the price of the security decline. If a
call option that the Fund has written expires unexercised, the Fund will realize a gain in the amount of the
premium; however, that gain may be offset by a decline in the market value of the underlying security during the
option period. If the call option is exercised, the Fund will realize a gain or loss from the sale or purchase
of the underlying security.
The exercise price of an option may be below, equal to, or above the market value of the underlying
security at the time the option is written. Options normally have expiration dates between three and nine months
from the date written. The obligation under any option terminates upon expiration of the option or, at an
earlier time, when the writer offsets the option by entering into a "closing purchase transaction" to purchase an
option of the same series.
Options are traded both on national securities exchanges and in the over-the-counter ("OTC") market.
Exchange-traded options are issued by a clearing organization affiliated with the exchange on which the option is
listed; the clearing organization in effect guarantees completion of, every exchange-traded option. In contrast,
OTC options are contracts between the Fund and its counter-party with no clearing organization guarantee. Thus,
when the Fund sells or purchases an OTC option, it generally will be able to "close out" the option prior to its
expiration only by entering into a "closing purchase transaction" with the dealer to whom or from whom the Fund
originally sold or purchased the option. The Sub-advisor monitors the creditworthiness of dealers with which the
Fund may engage in OTC options, and will limit counterparties in such transactions to dealers with a net worth of
at least $20 million as reported in their latest financial statements. For an additional discussion of OTC
options and their risks, see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
The premium received (or paid) by the Fund when it writes (or purchases) an option is the amount at
which the option is currently traded on the applicable exchange, less (or plus) a commission. The premium may
reflect, among other things, the current market price of the underlying security, the relationship of the
exercise price to the market price, the historical price volatility of the underlying security, the length of the
option period, the general supply of and demand for credit, and the general interest rate environment. The
premium received by the Fund for writing an option is recorded as a liability on the Fund's statement of assets
and liabilities. This liability is adjusted daily to the option's current market value.
The Fund pays the brokerage commissions in connection with purchasing or writing options, including
those used to close out existing positions. These brokerage commissions normally are higher than those
applicable to purchases and sales of portfolio securities.
For an additional discussion of options and their risks, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest in U.S. dollar-denominated equity and debt securities issued by
foreign issuers (including governments and quasi-governments) and foreign branches of U.S. banks, including
negotiable CDs and commercial paper. These investments are subject to the Fund's quality standards. While
investments in foreign securities are intended to reduce risk by providing further diversification, such
investments involve sovereign and other risks, in addition to the credit and market risks normally associated
with domestic securities.
The Fund may invest in equity, debt, or other income-producing securities that are denominated in or
indexed to foreign currencies, including, but not limited to (1) common and preferred stocks, (2) convertible
securities, (3) CDs, commercial paper, fixed-time deposits, and bankers' acceptances issued by foreign banks, (4)
obligations of other corporations, and (5) obligations of foreign governments, or their subdivisions, agencies,
and instrumentalities, international agencies, and supranational entities. Risks of investing in foreign
currency denominated securities include (1) nationalization, expropriation, or confiscatory taxation, (2) adverse
changes in investment or exchange control regulations (which could prevent cash from being brought back to the
U.S.), and (3) expropriation or nationalization of foreign portfolio companies. Mail service between the U.S.
and foreign countries may be slower or less reliable than within the United States, thus increasing the risk of
delayed settlements of portfolio transactions or loss of certificates for portfolio securities. For an
additional discussion of the risks associated with foreign securities, whether denominated in U.S. dollars or
foreign currencies, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Prices of foreign securities and exchange rates for foreign currencies may be affected by the interest
rates prevailing in other countries. The interest rates in other countries are often affected by local factors,
including the strength of the local economy, the demand for borrowing, the government's fiscal and monetary
policies, and the international balance of payments. Individual foreign economies may differ favorably or
unfavorably from the U.S. economy in such respects as gross national product, rate of inflation, capital
reinvestment, resource self-sufficiency, and balance of payments position.
Foreign markets also have different clearance and settlement procedures, and in certain markets there
have been times when settlements have been unable to keep pace with the volume of securities transactions, making
it difficult to conduct such transactions. Such delays in settlement could result in temporary periods when a
portion of the assets of the Fund is uninvested and no return is earned thereon. The inability of the Fund to
make intended security purchases due to settlement problems could cause the Fund to miss attractive investment
opportunities. Inability to dispose of portfolio securities due to settlement problems could result either in
losses to the Fund due to subsequent declines in value of the portfolio securities, or, if the Fund has entered
into a contract to sell the securities, could result in possible liability to the purchaser.
The Fund may invest in foreign corporate bonds and debentures and sovereign debt instruments issued or
guaranteed by foreign governments, their agencies or instrumentalities. The Fund may invest in lower-rated
foreign debt securities subject to the Fund's 15% limitation on lower-rated debt securities. Foreign debt
securities are subject to risks similar to those of other foreign securities, as well as risks similar to those
of other debt securities, as discussed in this SAI and in the Company's Prospectus under "Investment Programs of
the Funds" and "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
In order to limit the risk inherent in investing in foreign currency-denominated securities, the Fund
may not purchase any such security if after such purchase more than 10% of its total assets (taken at market
value) would be invested in such securities. Within such limitation, however, the Fund is not restricted in the
amount it may invest in securities denominated in any one foreign currency.
Foreign Currency Transactions. The Fund may engage in foreign currency exchange transactions. Foreign
currency exchange transactions will be conducted either on a spot (i.e., cash) basis at the spot rate prevailing
----
in the foreign currency exchange market, or through entering into forward contracts to purchase or sell foreign
currencies ("forward contracts"). The Fund may enter into forward contracts in order to protect against
uncertainty in the level of future foreign currency exchange rates, and only in amounts not exceeding 5% of the
Fund's net assets.
A forward contract involves an obligation to purchase or sell a specific currency at a future date,
which may be any fixed number of days (usually less than one year) from the date of the contract agreed upon by
the parties, at a price set at the time of the contract. These contracts are traded in the interbank market
conducted directly between traders (usually large commercial banks) and their customers. A forward contract
generally has no deposit requirement, and no commissions are charged at any stage for trades. Although foreign
exchange dealers do not charge a fee for conversion, they do realize a profit based on the difference (the
spread) between the price at which they are buying and selling various currencies.
When the Fund enters into a contract for the purchase or sale of a security denominated in a foreign
currency, it may wish to "lock in" the U.S. dollar price of the security. By entering into a forward contract
for the purchase or sale, for a fixed amount of U.S. dollars, of the amount of foreign currency involved in the
underlying security transactions, the Fund will be able to protect itself against a possible loss. When the
Sub-advisor believes that the currency of a particular foreign country may suffer a substantial decline against
the U.S. dollar, it may also enter into a forward contract to sell the amount of foreign currency for a fixed
amount of dollars which approximates the value of some or all of a Fund's securities denominated in such foreign
currency. The Fund may also engage in cross-hedging by using forward contracts in one currency to hedge against
fluctuations in the value of securities denominated in a different currency, when the Sub-advisor believes that
there is a pattern of correlation between the two currencies.
When the Fund engages in forward contracts for hedging purposes, it will not enter into forward
contracts to sell currency or maintain a net exposure to such contracts if their consummation would obligate the
Fund to deliver an amount of foreign currency in excess of the value of its portfolio securities or other assets
denominated in that currency. At the consummation of the forward contract, the Fund may either make delivery of
the foreign currency or terminate its contractual obligation to deliver by purchasing an offsetting contract
obligating it to purchase the same amount of such foreign currency at the same maturity date. If the Fund
chooses to make delivery of the foreign currency, it may be required to obtain such currency through the sale of
portfolio securities denominated in such currency or through conversion of other assets into such currency. If
the Fund engages in an offsetting transaction, it will incur a gain or a loss to the extent that there has been a
change in forward contract prices. Closing purchase transactions with respect to forward contracts are usually
made with the currency trader who is a party to the original forward contract.
The Fund is not required to enter into such transactions and will not do so unless deemed appropriate by
the Sub-advisor.
Using forward contracts to protect the value of the Fund's portfolio securities against a decline in the
value of a currency does not eliminate fluctuations in the underlying prices of the securities. It simply
establishes a rate of exchange which can be achieved at some future point in time. The precise projection of
short-term currency market movements is not possible, and short-term hedging provides a means of fixing the
dollar value of only a portion of the Fund's foreign assets.
While the Fund may enter forward contracts to reduce currency exchange rate risks, transactions in such
contracts involve certain other risks. Thus, while the Fund may benefit from such transactions, unanticipated
changes in currency prices may result in a poorer overall performance for the Fund than if it had not engaged in
any such transactions. Moreover, there may be imperfect correlation between the Fund's holdings of securities
denominated in a particular currency and forward contracts entered into by the Fund. Such imperfect correlation
may cause the Fund to sustain losses which will prevent it from achieving a complete hedge or expose it to risk
of foreign exchange loss.
The Fund generally will not enter into a forward contract with a term of greater than one year. The
Fund may experience delays in the settlement of its foreign currency transactions.
When the Fund engages in forward contracts for the sale or purchase of currencies, the Fund will either
cover its position or establish a segregated account. The Fund will consider its position covered if it has
securities in the currency subject to the forward contract, or otherwise has the right to obtain that currency at
no additional cost. In the alternative, the Fund will place cash, fixed income, or equity securities
(denominated in the foreign currency subject to the forward contract) in a separate account. The amounts in such
separate account will equal the value of the Fund's assets which are committed to the consummation of foreign
currency exchange contracts. If the value of the securities placed in the separate account declines, the Fund
will place additional cash or securities in the account on a daily basis so that the value of the account will
equal the amount of its commitments with respect to such contracts.
For an additional discussion of forward foreign currency exchange contracts and their risks, see this
SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Options on Foreign Currencies. The Fund may write and purchase covered call and put options on foreign
currencies in amounts not exceeding 5% of its net assets for the purpose of protecting against declines in the
U.S. dollar value of portfolio securities or increases in the U.S. dollar cost of securities to be acquired, or
to protect the dollar equivalent of dividend, interest, or other payment on those securities. A decline in the
dollar value of a foreign currency in which portfolio securities are denominated will reduce the dollar value of
such securities, even if their value in the foreign currency remains constant. In order to protect against such
decreases in the value of portfolio securities, the Fund may purchase put options on the foreign currency. If
the value of the currency declines, the Fund will have the right to sell such currency for a fixed amount of
dollars which exceeds the market value of such currency. This would result in a gain that may offset, in whole
or in part, the negative effect of currency depreciation on the value of the Fund's securities denominated in
that currency.
Conversely, if the dollar value of a currency in which securities to be acquired by the Fund are
denominated rises, thereby increasing the cost of such securities, the Fund may purchase call options on such
currency. If the value of such currency increases sufficiently, the Fund will have the right to purchase that
currency for a fixed amount of dollars which is less than the market value of that currency. Such a purchase
would result in a gain that may offset, at least partially, the effect of any currency-related increase in the
price of securities the Fund intends to acquire.
As in the case of other types of options transactions, however, the benefit the Fund derives from
purchasing foreign currency options will be reduced by the amount of the premium and related transaction costs.
In addition, if currency exchange rates do not move in the direction or to the extent anticipated, the Fund could
sustain losses on transactions in foreign currency options which would deprive it of a portion or all of the
benefits of advantageous changes in such rates.
The Fund may also write options on foreign currencies for hedging purposes. For example, if the
Sub-advisor anticipates a decline in the dollar value of foreign currency denominated securities because of
declining exchange rates, it could, instead of purchasing a put option, write a call option on the relevant
currency. If the expected decline occurs, the option will most likely not be exercised, and the decrease in
value of portfolio securities will be offset, at least in part, by the amount of the premium received by the Fund.
Similarly, the Fund could write a put option on the relevant currency, instead of purchasing a call
option, to hedge against an anticipated increase in the dollar cost of securities to be acquired. If exchange
rates move in the manner projected, the put option most likely will not be exercised, and such increased cost
will be offset, at least in part, by the amount of the premium received. However, as in the case of other types
of options transactions, the writing of a foreign currency option will constitute only a partial hedge up to the
amount of the premium, and only if rates move in the expected direction.
If unanticipated exchange rate fluctuations occur, a put or call option may be exercised and the Fund
could be required to purchase or sell the underlying currency at a loss which may not be fully offset by the
amount of the premium. As a result of writing options on foreign currencies, the Fund also may be required to
forego all or a portion of the benefits which might otherwise have been obtained from favorable movements in
currency exchange rates. Certain options on foreign currencies are traded on the OTC market and involve
liquidity and credit risks that may not be present in the case of exchange-traded currency options.
A call option written on foreign currency by the Fund is "covered" if the Fund owns the underlying
foreign currency subject to the call, or if it has an absolute and immediate right to acquire that foreign
currency without additional cash consideration. A call option is also covered if the Fund holds a call on the
same foreign currency for the same principal amount as the call written where the exercise price of the call held
is (a) equal to or less than the exercise price of the call written or (b) greater than the exercise price of the
call written if the amount of the difference is maintained by the Fund in cash, fixed income or equity securities
in a segregated account with its custodian.
The risks of currency options are similar to the risks of other options, as discussed above and in this
SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Cover for Options on Securities, Forward Contracts, and Options on Foreign Currencies ("Hedging
Instruments"). The Fund will comply with SEC staff guidelines regarding "cover" for Hedging Instruments and, if
the guidelines so require, set aside in a segregated account with its custodian the prescribed amount of cash,
fixed income, or equity securities. Securities held in a segregated account cannot be sold while the futures,
option, or forward strategy covered by those securities is outstanding, unless they are replaced with other
suitable assets. As a result, segregation of a large percentage of the Fund's assets could impede portfolio
management or the Fund's ability to meet current obligations. The Fund may be unable promptly to dispose of
assets that cover, or are segregated with respect to, an illiquid options or forward position; this inability may
result in a loss to the Fund.
Preferred Stock. The Fund may invest in preferred stock. Unlike interest payments on debt securities,
dividends on preferred stock are generally payable at the discretion of the issuer's board of directors, although
preferred shareholders may have certain rights if dividends are not paid. Shareholders may suffer a loss of
value if dividends are not paid, and generally have no legal recourse against the issuer. The market prices of
preferred stocks are generally more sensitive to changes in the issuer's creditworthiness than are the prices of
debt securities.
Fixed Income Securities. The Fund may invest in money market instruments, U.S. Government or Agency
securities, and corporate bonds and debentures receiving one of the four highest ratings from Standard & Poor's
Ratings Group ("S&P"), Moody's Investors Service, Inc. ("Moody's") or any other nationally recognized statistical
rating organization ("NRSRO"), or, if not rated by any NRSRO, deemed comparable by the Sub-advisor to such rated
securities ("Comparable Unrated Securities"). In addition, the Fund may invest up to 15% of its net assets,
measured at the time of investment, in corporate debt securities rated below investment grade or Comparable
Unrated Securities. The ratings of an NRSRO represent its opinion as to the quality of securities it undertakes
to rate. Ratings are not absolute standards of quality; consequently, securities with the same maturity, coupon,
and rating may have different yields. Although the Fund may rely on the ratings of any NRSRO, the Fund mainly
refers to ratings assigned by S&P and Moody's, which are described in Appendix A to this SAI.
Fixed income securities are subject to the risk of an issuer's inability to meet principal and interest
payments on the obligations ("credit risk") and also may be subject to price volatility due to such factors as
interest rate sensitivity, market perception of the creditworthiness of the issuer, and general market liquidity
("market risk"). Lower-rated securities are more likely to react to developments affecting market and credit
risk than are more highly rated securities, which react primarily to movements in the general level of interest
rates.
Changes in economic conditions or developments regarding the individual issuer are more likely to cause
price volatility and weaken the capacity of the issuer of such securities to make principal and interest payments
than is the case for higher-grade debt securities. An economic downturn affecting the issuer may result in an
increased incidence of default. The market for lower-rated securities may be thinner and less active than for
higher-rated securities. Pricing of thinly traded securities requires greater judgment than pricing of
securities for which market transactions are regularly reported.
Convertible Securities. The Fund may invest in convertible securities. A convertible security entitles
the holder to receive interest paid or accrued on debt or the dividend paid on preferred stock until the
convertible security matures or is redeemed, converted or exchanged. Before conversion, convertible securities
ordinarily provide a stream of income with generally higher yields than those of common stocks of the same or
similar issuers, but lower than the yield on non-convertible debt. Convertible securities are usually
subordinated to comparable-tier nonconvertible securities but rank senior to common stock in a corporation's
capital structure. The value of a convertible security is a function of (1) its yield in comparison with the
yields of other securities of comparable maturity and quality that do not have a conversion privilege, and (2)
its worth, at market value, if converted into the underlying common stock. Convertible debt securities are
subject to the Fund's investment policies and limitations concerning fixed-income investments.
Convertible securities are typically issued by smaller companies whose stock prices may be volatile.
The price of a convertible security often reflects such variations in the price of the underlying common stock in
a way that nonconvertible debt does not. A convertible security may be subject to redemption at the option of
the issuer at a price established in the security's governing instrument. If a convertible security held by the
Fund is called for redemption, the Fund will be required to convert it into the underlying common stock, sell it
to a third party or permit the issuer to redeem the security. Any of these actions could have an adverse effect
on the Fund's ability to achieve its investment objective.
Commercial Paper. Commercial paper is a short-term debt security issued by a corporation, bank,
municipality, or other issuer, usually for purposes such as financing current operations. The Fund may invest
only in commercial paper receiving the highest rating from S&P (A-1) or Moody's (P-1), or deemed by the
Sub-advisor to be of equivalent quality.
The Fund may invest in commercial paper that cannot be resold to the public because it was issued under
the exception for private offerings in Section 4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933. While such securities
normally will be considered illiquid and subject to the Fund's 15% limitation on investments in illiquid
securities, the Sub-advisor may in certain cases determine that such paper is liquid under guidelines established
by the Board of Directors.
Zero Coupon Securities. The Fund may invest up to 5% of its net assets in zero coupon securities,
which are debt obligations that do not entitle the holder to any periodic payment of interest prior to maturity
or specify a future date when the securities begin paying current interest. Rather, they are issued and traded
at a discount from their face amount or par value, which discount varies depending on prevailing interest rates,
the time remaining until cash payments begin, the liquidity of the security, and the perceived credit quality of
the issuer.
The market prices of zero coupon securities generally are more volatile than the prices of securities
that pay interest periodically and are likely to respond to changes in interest rates to a greater degree than do
other types of debt securities having similar maturities and credit quality. For a discussion of potential tax
consequences of investing in zero coupon securities, see this SAI under "Additional Tax Considerations."
Investment Policies Which May be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
applicable to the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund. These limitations are not fundamental restrictions,
and can be changed without shareholder approval.
1. The Fund may not purchase securities if outstanding borrowings, including any reverse
repurchase agreements, exceed 5% of its total assets.
2. Except for the purchase of debt securities and engaging in repurchase agreements, the Fund may
not make any loans other than securities loans.
3. The Fund may not purchase securities on margin from brokers, except that the Fund may obtain
such short-term credits as are necessary for the clearance of securities transactions. Margin payments in
connection with transactions in futures contracts and options on futures contracts shall not constitute the
purchase of securities on margin and shall not be deemed to violate the foregoing limitation.
4. The Fund may not sell securities short, unless it owns or has the right to obtain securities
equivalent in kind and amount to the securities sold without payment of additional consideration. Transactions
in futures contracts and options shall not constitute selling securities short.
5. The Fund may not purchase any security if, as a result, more than 15% of its net assets would
be invested in illiquid securities. Illiquid securities include securities that cannot be sold within seven days
in the ordinary course of business for approximately the amount at which the Fund has valued the securities, such
as repurchase agreements maturing in more than seven days.
6. The Fund may not invest more than 10% of the value of its total assets in securities of foreign
issuers, provided that this limitation shall not apply to foreign securities denominated in U.S. dollars.
ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek long-term capital growth.
Investment Policies:
Cash Position. In order to afford the Fund the flexibility to take advantage of new opportunities for
investments in accordance with its investment objective or to meet redemptions, it may, under normal
circumstances, hold up to 15% of its total assets in money market instruments including, but not limited to,
certificates of deposit, time deposits and bankers' acceptances issued by domestic bank and thrift institutions,
U.S. Government securities, commercial paper and repurchase agreements. In addition, when the Sub-advisor's
analysis of economic and technical market factors suggests that common stock prices will decline sufficiently so
that a temporary defensive position is deemed advisable, the Fund may invest in cash, commercial paper,
high-grade bonds or cash equivalents, all without limitation.
U.S. Government Obligations. Obligations, bills, notes, bonds, and other debt securities issued by the
U.S. Treasury are direct obligations of the U.S. Government and differ mainly in the length of their maturities.
Short-term Corporate Debt Securities. These are outstanding nonconvertible corporate debt securities
(e.g., bonds and debentures) which have one year or less remaining to maturity. Corporate debt securities may
have fixed, variable, or floating rates. For additional discussion on Short-term Corporate Debt Securities see
this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Commercial Paper. These are short-term promissory notes issued by corporations primarily to finance
short-term credit needs.
Small Capitalization and Related Investments. Certain companies in which the Fund will invest may still
be in the developmental stage. Investing in smaller, newer issuers generally involves greater risk than
investing in larger, more established issuers. Such companies may have limited product lines, markets or
financial resources and may lack management depth. Their securities may have limited marketability and may be
subject to more abrupt or erratic price movements than securities of larger, more established companies or the
market averages in general. The Fund also may invest in older companies that appear to be entering a new stage
of growth progress owing to factors such as management changes or development of new technology, products or
markets, or companies providing products or services with a high unit volume growth rate. These companies may be
subject to many of the same risks as small-cap companies.
Convertible Securities, Warrants, and Rights. The Fund may invest in securities convertible into or
exchangeable for equity securities, including warrants and rights. A warrant is a type of security that entitles
the holder to buy a proportionate amount of common stock at a specified price, usually higher than the market
price at the time of issuance, for a period of years or to perpetuity. In contrast, rights, which also represent
the right to buy common shares, normally have a subscription price lower than the current market value of the
common stock and a life of two to four weeks. Warrants may be freely transferable and may be traded on the major
securities exchanges. For additional discussion about Convertible Securities, Warrants, and Rights and their
risks, see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Portfolio Depositary Receipts. To the extent otherwise consistent with applicable law, the Fund may
invest up to 5% of its total assets in Portfolio Depositary Receipts, which are exchange-traded shares issued by
investment companies, typically unit investment trusts, holding portfolios of common stocks designed to replicate
and, therefore, track the performance of various broadly-based securities indices or sectors of such indices.
For example, the Fund may invest in Standard & Poor's Depositary Receipts(R)(SPDRs), issued by a unit investment
trust whose portfolio tracks the S&P 500 Composite Stock Price Index, or Standard & Poor's MidCap 400 Depositary
Receipts(R)(MidCap SPDRs), which are similarly linked to the S&P MidCap 400 Index.
Lending of Portfolio Securities. By lending its securities, the Fund can increase its income by
continuing to receive interest or dividends on the loaned securities as well as by either investing the cash
collateral or by earning income in the form of interest paid by the borrower when U.S. Government securities are
used as collateral. The Fund will adhere to the following conditions whenever its securities are loaned: (a)
the Fund must receive at least 100 percent cash collateral or equivalent securities from the borrower, (b) the
borrower must increase this collateral whenever the market value of the loaned securities including accrued
interest exceeds the value of the collateral, (c) the Fund must receive reasonable interest on the loan, as well
as any dividends, interest or other distributions on the loaned securities and any increase in market value, (d)
the Fund may pay only reasonable custodian fees in connection with the loan. The Fund will not lend securities
to the Investment Manager, the Sub-advisor or their affiliates. For additional information on the lending of
portfolio securities and its risks see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and
Investment Methods."
Options. The Fund may purchase put and call options and write (sell) put and covered call options on
securities and securities indices to increase gain or to hedge against the risk of unfavorable price movements
although, as in the past, it does not currently intend to rely on these strategies extensively, if at all. The
Fund will purchase or write options only if such options are exchange-traded or traded on an automated quotation
system of a national securities association.
The Fund will only sell call options that are "covered." A call option written by the Fund on a
security is "covered" if the Fund owns the underlying security covered by the call or has an absolute and
immediate right to acquire that security without additional cash consideration (or for additional cash
consideration held in a segregated account) upon conversion or exchange of other securities held in its
portfolio. A call option is also covered if the Fund holds a call on the same security as the call written where
the exercise price of the call held is (a) equal to or less than the exercise price of the call written or (b)
greater than the exercise price of the call written if the difference is maintained by the Fund in cash or other
liquid assets in a segregated account. If the Fund writes a put option, the Fund will segregate cash or other
liquid assets with a value equal to the exercise price, or else hold a put on the same security as the put
written where the exercise price of the put held is equal to or greater than the exercise price of the put
written.
Although the Fund will generally not purchase or write options that appear to lack an active secondary
market, there is no assurance that a liquid secondary market on an exchange will exist for any particular
option. In such event it might not be possible to effect closing transactions in particular options, so that the
Fund would have to exercise its option in order to realize any profit and would incur brokerage commissions upon
the exercise of the options. If the Fund, as a covered call option writer, is unable to effect a closing
purchase transaction in a secondary market, it will not be able to sell the underlying security until the option
expires, until it delivers the underlying security upon exercise, or until it otherwise covers the position.
In addition to options on securities, the Fund may also purchase and sell call and put options on
securities indices. The Fund may offset its position in stock index options prior to expiration by entering into
a closing transaction on an exchange or it may let the option expire unexercised. The Fund will not purchase
these options unless the Sub-advisor is satisfied with the development, depth and liquidity of the market and the
Sub-advisor believes the options can be closed out.
The Fund will not purchase options if, as a result, the aggregate cost of all outstanding options
exceeds 10% of the Fund's total assets. No more than 5% of the Fund's total assets will be committed to options
transactions entered into for non-hedging (speculative) purposes.
Stock Index Futures and Options on Stock Index Futures. Futures are generally bought and sold on the
commodities exchanges where they are listed. A stock index future obligates the seller to deliver (and the
purchaser to take) an amount of cash equal to a specific dollar amount times the difference between the value of
a specific stock index at the close of the last trading day of the contract and the price at which the agreement
is made. No physical delivery of the underlying stocks in the index is made.
While incidental to its securities activities, the Fund may purchase index futures as a substitute for a
comparable market position in the underlying securities. Securities index futures might be sold to protect
against a general decline in the value of securities of the type that comprise the index. Put options on futures
might be purchased to protect against declines in the market values of securities occasioned by a decline in
stock prices.
In an effort to compensate for the imperfect correlation of movements in the price of the securities
being hedged and movements in the price of the stock index futures, the Fund may buy or sell stock index futures
contracts in a greater or lesser dollar amount than the dollar amount of the securities being hedged if the
historical volatility of the stock index futures has been less or greater than that of the securities. Such
"over hedging" or "under hedging" may adversely affect the Fund's net investment results if market movements are
not as anticipated when the hedge is established.
The Fund will sell options on stock index futures contracts only as part of closing transactions to
terminate options positions it has purchased. No assurance can be given that such closing transactions can be
effected.
The Fund's use, if any, of stock index futures and options thereon will in all cases be consistent with
applicable regulatory requirements and in particular the rules and regulations of the CFTC and will be entered
into only for bona fide hedging, risk management or other portfolio management purposes. If the Fund exercises
an option on a futures contract it will be obligated to post initial margin (and potential subsequent variation
margin) for the resulting futures position just as it would for any position. In order to cover its potential
obligations if the Fund enters into futures contracts or options thereon, the Fund will maintain a segregated
account which will contain only liquid assets in an amount equal to the total market value of such futures
contracts less the amount of initial margin on deposit for such contracts.
For additional information about futures contracts and related options, see this SAI and the Company's
Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Borrowing. The Fund may borrow from banks for temporary or emergency purposes. If asset coverage for
such borrowings should decline below the required 300% as a result of market fluctuations or other reasons, the
Fund may be required to sell some of its portfolio holdings to reduce the debt and restore the 300% asset
coverage, even though it may be disadvantageous from an investment standpoint to sell securities at that time.
Additional information about borrowings and its risks is included in the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods."
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
applicable to the ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund. These limitations are not "fundamental" restrictions and may
be changed by the Directors without shareholder approval. The Fund will not:
1. Purchase securities on margin, except (i) for use of short-term credit necessary for clearance of
purchases of portfolio securities and (ii) the Fund may take margin deposits in connection with futures contracts
or other permissible investments;
2. Mortgage, pledge, hypothecate or, in any manner, transfer any security owned by the Fund as security for
indebtedness except as may be necessary in connection with permissible borrowings or investments and then such
mortgaging, pledging or hypothecating may not exceed 33 1/3% of the Fund's total assets at the time of borrowing
or investment;
3. Invest in oil, gas or mineral leases.
4. Purchase securities of open-end or closed-end investment companies except in compliance with the 1940
Act.
5. The Fund may not invest more than 15% of the assets of the Fund (taken at the time of the investments)
in "illiquid securities," illiquid securities being defined to include securities subject to legal or contractual
restrictions on resale (which may include private placements, but other than Rule 144A securities deemed liquid
by the Board of Directors or under guidelines adopted by the Board of Directors), repurchase agreements maturing
in more than seven days, certain options traded over the counter that the Fund has purchased, securities being
used to cover options a Fund has written, securities for which market quotations are not readily available, or
other securities which legally or in the Sub-advisor's option may be deemed illiquid.
ASAF GABELLI ALL-CAP VALUE FUND
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth.
Investment Policies:
Convertible Securities. The Fund may invest in convertible securities when it appears to the Fund's
Sub-advisor that it may not be prudent to be fully invested in common stocks. In evaluating a convertible
security, the Sub-advisor places primary emphasis on the attractiveness of the underlying common stock and the
potential for capital growth through conversion. The Fund will normally purchase only investment grade
convertible debt securities having a rating of, or equivalent to, at least "BBB" (which securities may have
speculative characteristics) by Standard & Poor's Rating Service ("S&P") or, if unrated, judged by the
Sub-advisor to be of comparable quality. However, the Fund may also invest up to 25% of its assets in more
speculative convertible debt securities, provided such securities have a rating of, or equivalent to, at least B
by S&P.
Convertible securities may include corporate notes or preferred stock but are ordinarily a long-term
debt obligation of the issuer convertible at a stated exchange rate into common stock of the issuer. As with all
debt securities, the market value of convertible securities tends to decline as interest rates increase and,
conversely, to increase as interest rates decline. Convertible securities generally offer lower interest or
dividend yields than non-convertible securities of similar quality. However, when the market price of the common
stock underlying a convertible security exceeds the conversion price, the price of the convertible security tends
to reflect the value of the underlying common stock. As the market price of the underlying common stock
declines, the convertible security tends to trade increasingly on a yield basis, and thus may not depreciate to
the same extent as the underlying common stock. Convertible securities rank senior to common stocks in an
issuer's capital structure and consequently entail less risk than the issuer's common stock, although the extent
to which such risk is reduced depends in large measure upon the degree to which the convertible security sells
above its value as a fixed income security.
In selecting convertible securities for the Fund, the Sub-advisor relies primarily on its own evaluation
of the issuer and the potential for capital growth through conversion. It does not rely on the rating of the
security or sell the security because of a change in rating absent a change in its own evaluation of the
underlying common stock and the ability of the issuer to pay principal and interest or dividends when due without
disrupting its business goals. Interest or dividend yield is a factor only to the extent it is reasonably
consistent with prevailing rates for securities of similar quality and thereby provides a support level for the
market price of the security. The Fund will purchase the convertible securities of highly leveraged issuers only
when, in the judgment of the Sub-advisor, the risk of default is outweighed by the potential for capital growth.
The issuers of debt obligations having speculative characteristics may experience difficulty in paying
principal and interest when due in the event of a downturn in the economy or unanticipated corporate
developments. The market prices of such securities may become increasingly volatile in periods of economic
uncertainty. Moreover, adverse publicity or the perceptions of investors, over which the Sub-advisor has no
control and whether or not based on fundamental analysis, may decrease the market price and liquidity of such
investments. Although the Sub-advisor will attempt to avoid exposing the Fund to such risks, there is no
assurance that it will be successful or that a liquid secondary market will continue to be available for the
disposition of such securities.
Lower-rated Debt Securities. The Fund may invest up to 5% of its assets in low-rated and unrated
corporate debt securities (often referred to as "junk bonds"). Corporate debt securities that are either unrated
or have a predominantly speculative rating may present opportunities for significant long-term capital growth if
the ability of the issuer to repay principal and interest when due is underestimated by the market or the rating
organizations. Because of its perceived credit weakness, the issuer is generally required to pay a higher
interest rate and/or its debt securities may be selling at a significantly lower market price than the debt
securities of other issuers. If the inherent value of such securities is higher than was perceived and such
value is eventually recognized, the market value of the securities may appreciate significantly. The Sub-advisor
believes that its research on the credit and balance sheet strength of certain issuers may enable it to select a
limited number of corporate debt securities that, in certain markets, will better serve the objective of capital
growth than alternative investments in common stocks. Of course, there can be no assurance that the Sub-advisor
will be successful. In its evaluation, the Sub-advisor will not rely exclusively on ratings and the receipt of
income from these securities is only an incidental consideration.
The ratings of Moody's Investors Service, Inc. ("Moody's") and S&P generally represent the opinions of
those organizations as to the quality of the securities that they rate. Such ratings, however, are relative and
subjective, and are not absolute standards of quality. Although the Sub-advisor uses these ratings as a
criterion for the selection of securities for the Fund, the Sub-advisor also relies on its independent analysis
to evaluate potential investments for the Fund. The Fund does not intend to purchase debt securities for which a
liquid trading market does not exist, but there can be no assurance that such a market will exist for the sale of
such securities.
Additional information on lower-rated debt securities and their risks is included in this SAI and the
Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods." Additional information on corporate
bond ratings is included in the Appendix to this SAI.
Borrowing. The Fund may borrow subject to certain restrictions set forth in the Company's Prospectus
under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods" and in this SAI under "Fundamental Investment Restrictions."
The Fund may mortgage, pledge or hypothecate up to 20% of its assets to secure permissible borrowings. Money
borrowed will be subject to interest costs, which may or may not be recovered by appreciation if securities are
purchased with the proceeds of the borrowing.
Investments in Warrants and Rights. The Fund may invest in warrants and rights (in addition to those
acquired in units or attached to other securities), which entitle the holder to buy equity securities at a
specific price for or at the end of a specific period of time. The value of a right or warrant may decline
because of a decline in the value of the underlying security, the passage of time, changes in interest rates or
in the dividend or other policies of the issuer whose equity underlies the warrant, a change in the perception as
to the future price of the underlying security, or any combination thereof. Additional information about
warrants and rights and their risks is included in this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods."
Investment in Small, Unseasoned Companies and Illiquid Securities. The Fund may invest in small, less
well-known companies that have operated for less than three years (including predecessors). The securities of
such companies may have a limited trading market, which may adversely affect their disposition and can result in
their being priced lower than might otherwise be the case. If other investment companies and investors who invest
in such issuers trade the same securities when the Fund attempts to dispose of its holdings, the Fund may receive
lower prices than might otherwise be obtained.
The Fund will not invest, in the aggregate, more than 15% of its net assets in illiquid securities. The
continued liquidity of any Rule 144A securities purchased by the Fund is not as well assured as that of publicly
traded securities, and accordingly, the Sub-advisor will monitor their liquidity under the guidelines adopted by
the Directors of the Company. For additional information on illiquid securities and their risks, see the
Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Corporate Reorganizations. In general, securities of companies engaged in reorganization transactions
sell at a premium to their historic market price immediately prior to the announcement of the tender offer or
reorganization proposal. However, the increased market price of such securities may also discount what the
stated or appraised value of the security would be if the contemplated transaction were approved or consummated.
Such investments may be advantageous when the discount significantly overstates the risk of the contingencies
involved, significantly undervalues the securities, assets or cash to be received by shareholders of the issuer
as a result of the contemplated transaction, or fails adequately to recognize the possibility that the offer or
proposal may be replaced or superseded by an offer or proposal of greater value. The evaluation of such
contingencies requires unusually broad knowledge and experience on the part of the Sub-advisor, which must
appraise not only the value of the issuer and its component businesses and the assets or securities to be
received as a result of the contemplated transaction, but also the financial resources and business motivation of
the offeror as well as the dynamic of the business climate when the offer or proposal is in progress.
In making such investments, the Fund will be subject to its diversification and other investment
restrictions, including the requirement that, except with respect to 25% of its assets, not more than 5% of its
assets may be invested in the securities of any issuer (see this SAI under "Fundamental Investment
Restrictions"). Because such investments are ordinarily short term in nature, they will tend to increase the
Fund's portfolio turnover rate, thereby increasing its brokerage and other transaction expenses. The Sub-advisor
intends to select investments of the type described that, in its view, have a reasonable prospect of capital
growth that is significant in relation to both the risk involved and the potential of available alternate
investments.
When-Issued, Delayed-Delivery and Forward Commitment Transactions. The Fund may enter into forward
commitments for the purchase or sale of securities, including on a "when-issued" or "delayed-delivery" basis, in
excess of customary settlement periods for the type of securities involved. In some cases, the obligations of
the parties under a forward commitment may be conditioned upon the occurrence of a subsequent event, such as
approval and consummation of a merger, corporate reorganization or debt restructuring (i.e., a when, as and if
issued security). When such transactions are negotiated, the price is fixed at the time of the commitment, with
payment and delivery generally taking place a month or more after the date of the commitment. While the Fund
will only enter into a forward commitment with the intention of actually acquiring the security, the Fund may
sell the security before the settlement date if it is deemed advisable. The Fund will segregate with its
custodian cash or liquid securities in an aggregate amount at least equal to the amount of its outstanding
forward commitments. Additional information regarding when-issued, delayed-delivery and forward commitment
transactions and their risks is included in this Statement and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods."
Other Investment Companies. The Fund may invest up to 10% of its total assets in the securities of
other investment companies, including small business investment companies. (Not more than 5% of its total assets
may be invested in any one investment company, nor will the Fund purchase more than 3% of the securities of any
other investment company.) To the extent that the Fund invests in the securities of other investment companies,
shareholders in the Fund may be subject to duplicative management and administrative fees.
Short Sales. The Fund may, from time to time, make short sales of securities it owns or has the right
to acquire through conversion or exchange of other securities it owns (short sales "against the box"). In a
short sale, the Fund does not immediately deliver the securities sold or receive the proceeds from the sale. The
Fund may make a short sale against the box in order to hedge against market risks when it believes that the price
of a security may decline, affecting the Fund directly if it owns that security or causing a decline in the value
of a security owned by the Fund that is convertible into the security sold short.
To secure its obligations to deliver the securities sold short, the Fund will segregate assets with its
custodian in an amount at least equal to the value of the securities sold short or the securities convertible
into, or exchangeable for, the securities. The Fund may close out a short position by purchasing and delivering
an equal amount of securities sold short, rather than by delivering securities already held by the Fund, because
the Fund may want to continue to receive interest and dividend payments on securities in its portfolio that are
convertible into the securities sold short.
Options. The Fund may purchase or sell listed call or put options on securities as a means of achieving
additional return or of hedging the value of the Fund's portfolio. In addition to changes in the price of an
underlying security, other principal factors affecting the market value of a put or a call option include supply
and demand, interest rates, price volatility of the underlying security and the time remaining until the
expiration date.
The Fund will only write calls options if they are covered. A call option is covered if the Fund owns
the underlying security covered by the call or has an absolute and immediate right to acquire that security
without additional cash consideration (or for additional cash consideration if cash or other liquid assets with a
value equal to such additional consideration are segregated with the Fund's custodian) upon conversion or
exchange of other securities held in its portfolio. A call option is also covered if the Fund holds a call on
the same security as the call written where the exercise price of the call held is (1) equal to or less than the
exercise price of the call written or (2) greater than the exercise price of the call written if cash or other
liquid assets equal to the difference are segregated with the custodian. If the Fund writes a put option, the
Fund will segregate cash or other assets with a value equal to the exercise price of the option, or will hold a
put on the same security as the put written where the exercise price of the put held is equal to or greater than
the exercise price of the put written.
If the Fund has written an option, it may terminate its obligation by effecting a closing purchase
transaction. However, once the Fund has been assigned an exercise notice, the Fund will be unable to effect a
closing purchase transaction. Similarly, if the Fund is the holder of an option it may liquidate its position by
effecting a closing sale transaction. This is accomplished by selling an option of the same series as the option
previously purchased. There can be no assurance that either a closing purchase or sale transaction can be
effected when the Fund so desires. The Fund will realize a profit from a closing sale transaction if the price
of the transaction is more than the premium paid to purchase the option; the Fund will realize a loss from a
closing sale transaction if the price of the transaction is less than the premium paid to purchase the option.
The Fund will generally purchase or write only those options for which there appears to be an active
secondary market. If, however, there is no liquid secondary market when the Sub-advisor wishes to close out an
option the Fund has purchased, it might not be possible to effect a closing sale transaction, so that the Fund
would have to exercise its options in order to realize any profit and would incur brokerage commissions upon the
exercise of call options and upon the subsequent disposition of underlying securities for the exercise of put
options. If the Fund, as a covered call option writer, is unable to effect a closing purchase transaction in a
secondary market, it will not be able to sell the underlying security until the option expires or it delivers the
underlying security upon exercise or otherwise covers the position.
In addition to options on securities, the Fund may also purchase and sell call and put options on
securities indices. The Fund may offset its position in stock index options prior to expiration by entering into
a closing transaction on an exchange or it may let the option it has purchased expire unexercised. The Fund may
write put and call options on stock indices for the purposes of increasing its gross income, thereby partially
protecting its portfolio against declines in the value of the securities it owns or increases in the value of
securities to be acquired. In addition, the Fund may purchase put and call options on stock indices in order to
hedge its investments against a decline in value or to attempt to reduce the risk of missing a market or industry
segment advance. While one purpose of writing such options is to generate additional income for the Fund, the
Fund recognizes that it may be required to deliver an amount of cash in excess of the market value of a stock
index at such time as an option written by the Fund is exercised by the holder. Because options on securities
indices require settlement in cash, the Adviser may be forced to liquidate portfolio securities to meet
settlement obligations. The Fund will not purchase options on indices unless the Sub-advisor is satisfied with
the development, depth and liquidity of the market and believes that the options can be closed out.
Although the Sub-advisor will attempt to take appropriate measures to minimize the risks relating to the
Fund's writing of put and call options, there can be no assurance that the Fund will succeed in any
option-writing program it undertakes.
Additional information about options on securities and securities indices and their risks in included in
this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Futures Contracts and Options on Futures. The Fund may enter into futures contracts that are traded on
a U.S. exchange or board of trade. Although the Fund has no current intention of using options on futures
contracts, the Fund may at some future date enter into such options. Investments in futures contracts and
related options will be made by the Fund solely for the purpose of hedging against changes in the value of its
portfolio securities or in the value of securities it intends to purchase. Such investments will only be made if
they are economically appropriate to the reduction of risks involved in the management of the Fund. In this
regard, the Fund may enter into futures contracts or options on futures relating to securities indices or other
financial instruments, including but not limited to U.S. Government securities. Futures exchanges and trading in
the United States are regulated under the Commodity Exchange Act by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission.
Initial margin payments required in connection with futures contracts will range from approximately 1%
to 10% of the contract amount. Initial margin amounts are subject to change by the exchange or board of trade on
which the contract is traded, and brokers or members of such board of trade may charge higher amounts. At any
time prior to the expiration of a futures contract, the portfolio may elect to close the position by taking an
opposite position, which will operate to terminate the Fund's existing position in the contract. At expiration,
certain futures contracts, including stock and bond index futures, are settled on a net cash payment basis rather
than by the sale and delivery of the securities underlying the futures contracts.
The potential loss related to the purchase of an option on a futures contract is limited to the premium
paid for the option (plus transaction costs). There are no daily cash payments by the purchaser of an option on
a futures contract to reflect changes in the value of the underlying contract; however, the value of the option
does change daily and that change would be reflected in the net asset value of the Fund.
The Sub-advisor may use such instruments for the Fund depending upon market conditions prevailing at the
time and the perceived investment needs of the Fund. In the event the Fund enters into futures contracts or
writes related options, an amount of cash or other liquid assets equal to the market value of the contract will
be segregated with the Fund's custodian to collateralize the positions, thereby insuring that the use of the
contract is unleveraged.
The Sub-advisor may have difficulty selling or buying futures contracts and options when it chooses. In
addition, hedging practices may not be available, may be too costly to be used effectively, or may be unable to
be used for other reasons.
Additional information about futures contracts, options on futures contracts and their risks is included
in this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods.'
Investment Opportunities and Related Limitations. Affiliates of the Sub-advisor may, in the ordinary
course of their business, acquire for their own account or for the accounts of their advisory clients,
significant (and possibly controlling) positions in the securities of companies that may also be suitable for
investment by the Fund. The securities in which the Fund might invest may thereby be limited to some extent.
For instance, many companies in the past several years have adopted so-called "poison pill" or other defensive
measures designed to discourage or prevent the completion of non-negotiated offers for control of the company.
Such defensive measures may have the effect of limiting the shares of the company that might otherwise be
acquired by the Fund if the affiliates of the Sub-advisor or their advisory accounts have or acquire a
significant position in the same securities. However, the Sub-advisor does not believe that the investment
activities of its affiliates will have a material adverse effect upon the Fund in seeking to achieve its
investment objectives. In addition, orders for the Fund generally are accorded priority of execution over orders
entered on behalf of accounts in which the Sub-advisor or its affiliates have a substantial pecuniary interest.
The Fund may invest in the securities of companies that are investment management clients of the Sub-advisor's
affiliates. In addition, portfolio companies or their officers or directors may be minority shareholders of the
Sub-advisor or its affiliates.
Investment Policies Which May be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
applicable to the ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund. These limitations are not fundamental restrictions and can be
changed without shareholder approval. The Fund may not:
1. Purchase securities on margin, but it may obtain such short-term credits from banks as may be
necessary for the clearance of purchase and sales of securities;
2. Mortgage, pledge or hypothecate any of its assets except that, in connection with permissible
borrowings, not more than 20% of the assets of the Fund (not including amounts borrowed) may be used as
collateral;
3. Invest in the securities of other investment companies except in compliance with the Investment
Company Act of 1940;
4. Invest, in the aggregate, more than 15% of the value of its total assets in securities for
which market quotations are not readily available, securities that are restricted for public sale, or in
repurchase agreements maturing or terminable in more than seven days;
5. Sell securities short, except that the Fund may make short sales if it owns the securities sold
short or has the right to acquire such securities through conversion or exchange of other securities it owns; or
6. Invest in companies for the purpose of exercising control.
ASAF INVESCO TECHNOLOGY FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth by investing primarily in
the equity securities of companies engaged in technology-related industries.
Investment Policies:
Debt Securities. Debt securities include bonds, notes and other securities that give the holder the
right to receive fixed amounts of principal, interest, or both on a date in the future or on demand. Debt
securities are often referred to as fixed income securities, even if the rate of interest varies over the life of
the security. The Fund may also invest in stripped debt securities (i.e., interest only and principal only
securities).
Although the Fund may invest in debt securities assigned lower grade ratings by S&P or Moody's, the
Fund's investments will generally be limited to debt securities rated B or higher by either S&P or Moody's. Debt
securities rated lower than B by either S&P or Moody's are usually considered to be highly speculative. The
Sub-advisor will limit the Fund's investments to debt securities that it believes are not highly speculative and
that are rated at least CCC by S&P or Caa by Moody's. The Fund expects that most emerging country debt
securities in which it invests will not be rated by U.S. rating services.
A significant economic downturn or increase in interest rates may cause issuers of debt securities to
experience increased financial problems which could adversely affect their ability to pay principal and interest,
to meet projected business goals, and to obtain additional financing. These conditions more severely impact
issuers of lower-rated debt securities. The Sub-advisor attempts to limit purchases of lower-rated securities to
securities having an established secondary market.
Although bonds in the lowest investment grade debt category (those rated BBB by S&P, Baa by Moody's or
the equivalent) are regarded as having adequate capability to pay principal and interest, they have speculative
characteristics. Adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to lead to a weakened
capacity to make principal and interest payments than is the case for higher-rated bonds. Lower-rated bonds by
Moody's (categories Ba, B, or Caa) are of poorer quality and also have speculative characteristics. Bonds rated
Caa may be in default or there may be present elements of danger with respect to principal or interest.
Lower-rated bonds by S&P (categories BB, B, or CCC) include those that are regarded, on balance, as predominantly
speculative with respect to the issuer's capacity to pay interest and repay principal in accordance with their
terms. While such bonds likely will have some quality and protective characteristics, these are outweighed by
large uncertainties or major risk exposures to adverse conditions. Bonds having equivalent ratings from other
ratings services will have characteristics similar to those of the corresponding S&P and Moody's ratings. For a
more specific description of S&P and Moody's corporate bond rating categories, please refer to the Appendix to
this SAI. Additional information about the debt securities and their risks, including the risks of lower-rated
debt securities, is included in this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods."
Equity and Convertible Debt Securities. As discussed in the Company's Prospectus, the Fund may invest
in common, preferred and convertible preferred stocks, and securities whose values are tied to the price of
stocks, such as rights, warrants and convertible debt securities. Additional information about these types of
securities and their risks is included in the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods."
The Fund seeks to invest in stocks that will increase in market value and may be sold for more than the
Fund paid to buy them. Market value is based upon constantly changing investor perceptions of what the company
is worth compared to other companies. Dividends are a factor in the changing market value of stocks, but many
companies do not pay dividends, or pay comparatively small dividends. As discussed in the Prospectus, the
principal risk of investing in equity securities is that their market values fluctuate constantly, often due to
factors entirely outside the control of the Fund or the company issuing the stock. At any given time, the market
value of an equity security may be significantly higher or lower than the amount paid by a Fund to acquire it.
Owners of preferred stocks are entitled to dividends payable from the corporation's earnings, which in
some cases may be "cumulative" if prior dividends on the preferred stock have not been paid. Preferred stocks
may be "participating," which means that they may be entitled to dividends in excess of the stated dividend in
certain cases.
Rights and warrants are securities which entitle the holder to purchase the securities of a company
(usually, its common stock) at a specified price during a specified time period. The value of a right or warrant
is affected by many of the same factors that determine the prices of common stocks. Rights and warrants may be
purchased directly or acquired in connection with a corporate reorganization or exchange offer.
The Fund also may purchase convertible securities, including convertible debt obligations and
convertible preferred stock. A convertible security entitles the holder to exchange it for a fixed number of
shares of common stock (or other equity security), usually at a fixed price within a specified period of time.
Until conversion, the owner of convertible securities usually receives the interest paid on a convertible bond or
the dividend preference of a preferred stock.
A convertible security has an "investment value", which is a theoretical value determined by the yield
it provides in comparison with similar securities without the conversion feature. Investment value changes are
based upon prevailing interest rates and other factors. It also has a "conversion value," which is the market
value the convertible security would have if it were exchanged for the underlying equity security. Convertible
securities may be purchased at varying price levels above or below their investment values or conversion values.
Conversion value is a simple mathematical calculation that fluctuates directly with the price of the
underlying security. However, if the conversion value is substantially below investment value, the market value
of the convertible security is governed principally by its investment value. If the conversion value is near or
above investment value, the market value of the convertible security generally will rise above investment value.
In such cases, the market value of the convertible security may be higher than its conversion value, due to the
combination of the convertible security's right to interest (or dividend preference) and the possibility of
capital appreciation from the conversion feature. However, there is no assurance that any premium above
investment value or conversion value will be recovered because prices change and, as a result, the ability to
achieve capital appreciation through conversion may be eliminated.
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest in the securities of foreign companies, or companies that have
their principal business activities outside the United States, either directly or through American Depositary
Receipts ("ADRs"). An ADR entitles its holder to all dividends and capital gains on the underlying foreign
securities, less any fees paid to the sponsoring bank. Foreign securities involve certain risks not associated
with investment in U.S. companies, which are described in more detail in this SAI and the Company's Prospectus
under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods." In addition, foreign exchange markets for the currencies in
which the foreign securities may be traded are affected by the international balance of payments and other
economic and financial conditions, speculation and other factors, all of which are outside the control of the
Fund. Generally, the Fund's foreign currency exchange transactions will be conducted on a cash or "spot" basis
at the spot rate for purchasing or selling currency in the currency exchange markets.
Investment Company Securities. The Fund may invest in Standard & Poor's Depository Receipts ("SPDRs")
and shares of other investment companies. SPDRs are investment companies whose portfolios mirror the
compositions of specific S&P indices, such as the S&P 500 and the S&P 400. SPDRs are traded on the American
Stock Exchange. SPDR holders such as the Fund are paid a "Dividend Equivalent Amount" that corresponds to the
amount of cash dividends accruing to the securities held by the SPDR Trust, net of certain fees and expenses.
The 1940 Act limits investments in securities of other investment companies, such as SPDR Trusts. These
limitations include, among others, that, subject to certain exceptions, no more than 10% of the Fund's total
assets may be invested in securities of other investment companies and no more than 5% of its total assets may be
invested in the securities of any one investment company.
Additional information on investing in other investment companies and its risks is included in the
Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
U.S. Government Securities. The Fund may, from time to time, purchase debt securities issued by the
U.S. government. These securities include Treasury bills, notes and bonds. Treasury bills have a maturity of
one year or less, Treasury notes generally have a maturity of one to ten years, and Treasury bonds generally have
maturities of more than ten years.
U.S. government debt securities also include securities issued or guaranteed by agencies or
instrumentalities of the U.S. government. Some obligations of U.S. government agencies, such as Government
National Mortgage Association ("GNMA") participation certificates, are supported by the full faith and credit of
the U.S. Treasury. GNMA Certificates are mortgage-backed securities representing part ownership of a pool of
mortgage loans. These loans -- issued by lenders such as mortgage bankers, commercial banks and savings and loan
associations -- are either insured by the Federal Housing Administration or guaranteed by the Veterans
Administration. A "pool" or group of such mortgages is assembled and, after being approved by GNMA, is offered
to investors through securities dealers. Once approved by GNMA, the timely payment of interest and principal on
each mortgage is guaranteed by GNMA and backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government. (For
additional information on mortgage-backed securities and their risks, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus
under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods.")
Other United States government debt securities, such as securities of the Federal Home Loan Banks, are
supported by the right of the issuer to borrow from the Treasury. Others, such as bonds issued by Fannie Mae, a
federally chartered private corporation, are supported only by the credit of the corporation. In the case of
securities not backed by the full faith and credit of the United States, the Fund must look principally to the
agency issuing or guaranteeing the obligation in the event the agency or instrumentality does not meet its
commitments. The Fund will invest in securities of such instrumentalities only when its Sub-advisor is satisfied
that the credit risk with respect to any such instrumentality is comparatively minimal.
When-Issued and Delayed-Delivery Transactions. Ordinarily, the Fund buys and sells securities on an
ordinary settlement basis. That means that the buy or sell order is sent, and the Fund actually takes delivery
or gives up physical possession of the security on the "settlement date," which is three business days later.
However, the Fund also may purchase and sell securities on a when-issued or delayed-delivery basis.
When-issued or delayed-delivery transactions occur when securities are purchased or sold by the Fund and
payment and delivery take place at an agreed-upon time in the future. The Fund may engage in this practice in an
effort to secure an advantageous price and yield. However, the yield on a comparable security available when
delivery actually takes place may vary from the yield on the security at the time the when-issued or
delayed-delivery transaction was entered into.
Additional information on when-issued and delayed-delivery transactions and their risks is included in
this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Futures, Options and Other Financial Instruments.
General. As discussed in the Prospectus, the Sub-adviser may use various types of financial
instruments, some of which are derivatives, to attempt to manage the risk of the Fund's investments or, in
certain circumstances, for investment (e.g., as a substitute for investing in securities). These financial
instruments include options, futures contracts (sometimes referred to as "futures"), forward contracts, swaps,
caps, floors and collars (collectively, "Financial Instruments"). The policies in this section do not apply to
other types of instruments sometimes referred to as derivatives, such as indexed securities, and mortgage-backed
and other asset-backed securities.
Hedging strategies can be broadly categorized as "short" hedges and "long" or "anticipatory" hedges. A
short hedge involves the use of a Financial Instrument in order to partially or fully offset potential variations
in the value of one or more investments held in the Fund's portfolio. A long or anticipatory hedge involves the
use of a Financial Instrument in order to partially or fully offset potential increases in the acquisition cost
of one or more investments that the Fund intends to acquire. In an anticipatory hedge transaction, the Fund does
not already own a corresponding security. Rather, it relates to a security or type of security that the Fund
intends to acquire. If the Fund does not eliminate the hedge by purchasing the security as anticipated, the
effect on the Fund's portfolio generally is the same as if a long position in the security were entered into.
Financial Instruments may also be used, in certain circumstances, for investment (e.g., as a substitute for
investing in securities).
Financial Instruments on individual securities generally are used to attempt to hedge against price
movements in one or more particular securities positions that the Fund already owns or intends to acquire.
Financial instruments on indices, in contrast, generally are used to attempt to hedge all or a portion of a
portfolio against price movements of securities within a market sector in which the Fund has invested or expects
to invest.
The use of Financial Instruments is subject to applicable regulations of the SEC, the several exchanges
upon which they are traded, and the CFTC. In addition, the Fund's ability to use Financial Instruments may be
limited by tax considerations. See this SAI under "Additional Tax Considerations." In addition to the
instruments and strategies described below, the Sub-advisor may use other similar or related techniques to the
extent that they are consistent with the Fund's investment objective and permitted by its investment limitations
and applicable regulatory authorities.
Special Risks. Financial Instruments and their use involve special considerations and risks, certain of
which are described below.
(1) Financial Instruments may increase the volatility of the Fund. If the Sub-advisor employs a
Financial Instrument that correlates imperfectly with the Fund's investments, a loss could result, regardless of
whether or not the intent was to manage risk.
(2) There might be imperfect correlation between price movements of a Financial Instrument and price
movements of the investment(s) being hedged. For example, if the value of a Financial Instrument used in a short
hedge increased by less than the decline in value of the hedged investment(s), the hedge would not be fully
successful. This might be caused by certain kinds of trading activity that distorts the normal price
relationship between the security being hedged and the Financial Instrument.
The Fund is authorized to use options and futures contracts related to securities with issuers,
maturities or other characteristics different from the securities in which it typically invests. This involves a
risk that the options or futures position will not track the performance of the Fund's portfolio investments.
The direction of options and futures price movements can also diverge from the direction of the
movements of the prices of their underlying instruments, even if the underlying instruments match the Fund's
investments well. Options and futures prices are affected by such factors as current and anticipated short-term
interest rates, changes in volatility of the underlying instrument, and the time remaining until expiration of
the contract, which may not affect security prices the same way. Imperfect correlation may also result from
differing levels of demand in the options and futures markets and the securities markets, from structural
differences in how options and futures and securities are traded, or from imposition of daily price fluctuation
limits or trading halts. The Fund may take positions in options and futures contracts with a greater or lesser
face value than the securities it wishes to hedge or intends to purchase in order to attempt to compensate for
differences in volatility between the contract and the securities, although this may not be successful in all
cases.
(3) If successful, the above-discussed hedging strategies can reduce risk of loss by wholly or partially
offsetting the negative effect of unfavorable price movements of portfolio securities. However, such strategies
can also reduce opportunity for gain by offsetting the positive effect of favorable price movements. For
example, if the Fund entered into a short hedge because the Sub-advisor projected a decline in the price of a
security in the Fund's portfolio, and the price of that security increased instead, the gain from that increase
would likely be wholly or partially offset by a decline in the value of the short position in the Financial
Instrument. Moreover, if the price of the Financial Instrument declined by more than the increase in the price
of the security, the Fund could suffer a loss.
(4) As described below, the Fund is required to maintain assets as "cover," maintain segregated accounts
or make margin payments when they take positions in Financial Instruments involving obligations to third parties
(i.e., Financial Instruments other than purchased options). If the Fund is unable to close out its positions in
such Financial Instruments, it might be required to continue to maintain such assets or segregated accounts or
make such payments until the position expired.
Cover. Positions in Financial Instruments, other than purchased options, expose the Fund to an
obligation to another party. The Fund will not enter into any such transaction unless it owns (1) an offsetting
("covered") position in securities, currencies or other options, futures contracts or forward contracts, or (2)
cash or liquid assets with a value, market-to-market daily, sufficient to cover its obligations to the extent not
covered as provided in (1) above. The Fund will comply with SEC guidelines regarding cover for these instruments
and will, if the guidelines so require, designate the prescribed amount of cash or liquid assets as segregated.
Assets used as cover or held as segregated cannot be sold while the position in the corresponding
Financial Instrument is open unless they are replaced with other appropriate assets. As a result, the commitment
of a large portion of the Fund's assets to cover or to hold as segregated could impede portfolio management or
the Fund's ability to meet redemption requests or other current obligations.
Options. The Fund may engage in certain strategies involving options to attempt to manage the risk of
its investments or, in certain circumstances, for investment (e.g., as a substitute for investing in
securities).
The purchase of call options can serve as a hedge against a price rise of the underlying security or
instrument and the purchase of put options can serve as a hedge against a price decline of the underlying
security or instrument. Writing call options can serve as a limited short hedge because declines in the value of
the hedged investment would be offset to the extent of the premium received for writing the option. Writing put
options can serve as a limited long or anticipatory hedge because increases in the value of the hedged investment
would be offset to the extent of the premium received for writing the option.
The value of an option position will reflect, among other things, the current market value of the
underlying investment, the time remaining until expiration, the relationship of the exercise price to the market
price of the underlying investment, the price volatility of the underlying investment and general market and
interest rate conditions. Options that expire unexercised have no value.
The Fund may effectively terminate its right or obligation under an option by entering into a closing
transaction. For example, the Fund may terminate a position in a put or call option it had purchased by writing
an identical put or call option, which is known as a closing sale transaction. Closing transactions permit a
Fund to realize profits or limit losses on an option position prior to its exercise or expiration. If the Fund
were unable to effect a closing transaction for an option it had purchased, it would have to exercise the option
to realize any profit.
Risks of Options on Securities. Options embody the possibility of large amounts of exposure,
which will result in the Fund's net asset value being more sensitive to changes in the value of the related
investment. The Fund may purchase or write both exchange-traded and OTC options. Exchange-traded options in the
United States are issued by a clearing organization affiliated with the exchange on which the option is listed
that, in effect, guarantees completion of every exchange-traded option transaction. In contrast, OTC options are
contracts between a fund and its counterparty (usually a securities dealer or a bank) with no clearing
organization guarantee. Failure by the counterparty to make or take delivery of the underlying investment upon
exercise would result in the loss of any premium paid by the Fund as well as the loss of any expected benefit
from the transaction.
Options on Indices. The risks of purchasing and selling options on indices may be greater than
options on securities. Because index options are settled in cash, when the Fund writes a call on an index it
cannot fulfill its potential settlement obligations by delivering the underlying securities. The Fund can offset
some of the risk of writing a call index option by holding a diversified portfolio of securities similar to those
on which the underlying index is based. However, the Fund cannot, as a practical matter, acquire and hold a
portfolio containing exactly the same securities as underlie the index and, as a result, it bears a risk that the
value of the securities held will vary from the value of the index.
OTC Options. Unlike exchange-traded options, which are standardized with respect to the
underlying instrument, expiration date, contract size, and strike price, the terms of OTC options (options not
traded on exchanges) generally are established through negotiation with the other party to the option contract.
While this type of arrangement allows a Fund great flexibility to tailor the option to its needs, OTC options
generally involve greater risk than exchange-traded options, which are guaranteed by the clearing organization of
the exchange where they are traded. Generally, OTC foreign currency options used by the Fund are European-style
options.
Additional information about options transactions and their risks is included in this SAI and the
Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Futures Contracts and Options on Futures Contracts. The purchase of futures or call options on futures
can serve as a long or an anticipatory hedge, and the sale of futures or the purchase of put options on futures
can serve as a short hedge. Writing call options on futures contracts can serve as a limited short hedge, using
a strategy similar to that used for writing call options on securities or indices. Similarly, writing put
options on futures contracts can serve as a limited long or anticipatory hedge.
In addition, futures strategies can be used to manage the "duration" (a measure of anticipated
sensitivity to changes in interest rates, which is sometimes related to the weighted average maturity of a
portfolio) and associated interest rate risk of the Fund's fixed-income investments. If the Sub-advisor wishes
to shorten the duration of the Fund's fixed-income investments (i.e., reduce anticipated sensitivity), the Fund
may sell an appropriate debt futures contract or a call option thereon, or purchase a put option on that futures
contract. If the Sub-advisor wishes to lengthen the duration of the Fund's fixed-income investments (i.e.,
increase anticipated sensitivity), the Fund may buy an appropriate debt futures contract or a call option
thereon, or sell a put option thereon.
At the inception of a futures contract, the Fund will be required to deposit "initial margin" in an
amount generally equal to 10% or less of the contract value. Unlike margin in securities transactions, initial
margin on futures contracts and written options on futures contracts does not represent a borrowing on margin,
but rather is in the nature of a performance bond or good-faith deposit that is returned to the Fund at the
termination of the transaction if all contractual obligations have been satisfied. Under certain circumstances,
such as periods of high volatility, the Fund may be required to increase the level of initial margin deposits.
If the Fund were unable to liquidate a futures contract or an option on a futures contract position due
to the absence of a liquid market or the imposition of price limits, it could incur substantial losses. The Fund
would continue to be subject to market risk with respect to the position. In addition, except in the case of
purchased options, the Fund would continue to be required to make daily variation margin payments and might be
required to continue to maintain the position being hedged by the futures contract or option or to continue to
maintain cash or securities in a segregated account.
Risks of Futures Contracts and Options Thereon. The spreads at a given time between prices in
the cash and futures markets (including the options on futures markets), due to differences in the natures of
those markets, will fluctuate based on a number of factors. For instance, the liquidity of the futures market
depends on participants entering into offsetting transactions rather than making or taking delivery. To the
extent participants decide to make or take delivery, liquidity in the futures market could be reduced, thus
producing price distortion. Due to the possibility of distortion, a hedge may not be successful. Although stock
index futures contracts do not require physical delivery, under extraordinary market conditions, liquidity of
such futures contracts also could be reduced.
For additional information on futures contracts and options on futures and their risks, see this SAI and
the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Index Futures. The price of index futures may move proportionately more than or less than the
price of the securities being hedged. If the price of the index futures moves proportionately less than the
price of the securities that are the subject of the hedge, the hedge will not be fully effective. Assuming the
price of the securities being hedged has moved in an unfavorable direction, as anticipated when the hedge was put
into place, the Fund would be in a better position than if it had not hedged at all, but not as good as if the
price of the index futures moved in full proportion to that of the hedged securities. If the price of the
futures contract moves more than the price of the securities, the Fund will experience either a loss or a gain on
the futures contract that will not be completely offset by movements in the price of the securities that are the
subject of the hedge.
Where index futures are purchased in an anticipatory hedge, it is possible that the market may decline
instead. If the Fund then decides not to invest in the securities at that time because of concern as to possible
further market decline or for other reasons, it will realize a loss on the futures contract that is not offset by
a reduction in the price of the securities it had anticipated purchasing.
Foreign Currency Hedging Strategies -- Special Considerations. The Fund may use options and futures
contracts on foreign currencies, as mentioned previously, and forward currency contracts, as described below, to
attempt to hedge against movements in the values of the foreign currencies in which the Fund's securities are
denominated or, in certain circumstances, for investment (e.g., as a substitute for investing in securities
denominated in foreign currency). Currency hedges can protect against price movements in a security that the
Fund owns or intends to acquire that are attributable to changes in the value of the currency in which it is
denominated.
The Fund may seek to hedge against price movements in a particular currency by entering into
transactions using Financial Instruments on another currency or a basket of currencies, the value of which the
Sub-advisor believes will have a high degree of positive correlation to the value of the currency being hedged.
The risk that movements in the price of the Financial Instrument will not correlate perfectly with movements in
the price of the currency subject to the hedging transaction may be increased when this strategy is used.
The value of Financial Instruments on foreign currencies depends on the value of the underlying currency
relative to the U.S. dollar. Because foreign currency transactions occurring in the interbank market might
involve substantially larger amounts than those involved in the use of such Financial Instruments by the Fund,
the Fund could be disadvantaged by having to deal in the odd-lot market (generally consisting of transactions of
less than $1 million) for the underlying foreign currencies at prices that are less favorable than for round lots.
There is no systematic reporting of last sale information for foreign currencies or any regulatory
requirement that quotations available through dealers or other market sources be firm or revised on a timely
basis. Quotation information generally is representative of very large transactions in the interbank market and
thus might not reflect odd-lot transactions where rates might be less favorable. The interbank market in foreign
currencies is a global, round-the-clock market. To the extent the U.S. options or futures markets are closed
while the markets for the underlying currencies remain open, significant price and rate movements might take
place in the underlying markets that cannot be reflected in the markets for the Financial Instruments until they
reopen.
Settlement of hedging transactions involving foreign currencies might be required to take place within
the country issuing the underlying currency. Thus, the Fund might be required to accept or make delivery of the
underlying foreign currency in accordance with any U.S. or foreign regulations regarding the maintenance of
foreign banking arrangements by U.S. residents and might be required to pay any fees, taxes and charges
associated with such delivery assessed in the issuing country.
Forward Currency Contracts and Foreign Currency Deposits. The Fund may enter into forward currency
contracts to purchase or sell foreign currencies for a fixed amount of U.S. dollars or another foreign currency.
If the Fund uses forward currency contracts to hedge against a decline in the value of existing
investments denominated in foreign currency, such a hedge would tend to offset both positive and negative
currency fluctuations, but would not offset changes in security values caused by other factors. The Fund could
also hedge the position by entering into a forward currency contract to sell another currency (or a basket of
currencies) expected to perform similarly to the currency in which the Fund's existing investments are
denominated. This type of hedge could offer advantages in terms of cost, yield or efficiency, but may not hedge
currency exposure as effectively as a simple hedge against U.S. dollars. This type of hedge may result in losses
if the currency used to hedge does not perform similarly to the currency in which the hedged securities are
denominated.
The cost to the Fund of engaging in forward currency contracts will vary with factors such as the
currency involved, the length of the contract period and the market conditions then prevailing. When the Fund
enters into a forward currency contract, it relies on the counterparty to make or take delivery of the underlying
currency at the maturity of the contract. Failure by the counterparty to do so would result in the loss of some
or all of any expected benefit of the transaction.
As is the case with futures contracts, purchasers and sellers of forward currency contracts can enter
into offsetting closing transactions, similar to closing transactions on futures contracts, by selling or
purchasing, respectively, an instrument identical to the instrument purchased or sold. Secondary markets
generally do not exist for forward currency contracts, with the result that closing transactions generally can be
made for forward currency contracts only by negotiating directly with the counterparty. Thus, there can be no
assurance that the Fund will in fact be able to close out a forward currency contract at a favorable price prior
to maturity. In addition, in the event of insolvency of the counterparty, the Fund might be unable to close out
a forward currency contract. In either event, the Fund would continue to be subject to market risk with respect
to the position, and would continue to be required to maintain a position in securities denominated in the
foreign currency or to segregate cash or liquid assets.
Forward currency contracts may substantially change a fund's investment exposure to changes in currency
exchange rates and could result in losses to the Fund if currencies do not perform as the adviser anticipates.
There is no assurance that the Sub-advisor's use of forward currency contracts will be advantageous to the Fund
or that it will hedge at an appropriate time.
The Fund may also purchase and sell foreign currency and invest in foreign currency deposits. Currency
conversion involves dealer spreads and other costs, although commissions usually are not charged.
Additional information about forward currency contracts and other foreign currency transactions and
their risks is included in this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods."
Combined Positions. The Fund may purchase and write options or futures in combination with each other,
or in combination with futures or forward currency contracts, to manage the risk and return characteristics of
its overall position. For example, the Fund may purchase a put option and write a call option on the same
underlying instrument, in order to construct a combined position whose risk and return characteristics are
similar to selling a futures contract. Another possible combined position would involve writing a call option at
one strike price and buying a call option at a lower price, in order to reduce the risk of the written call
option in the event of a substantial price increase. Because combined options positions involve multiple trades,
they result in higher transaction costs.
Turnover. The Funds' options and futures activities may affect their turnover rates and brokerage
commission payments. The exercise of calls or puts written by the Fund, and the sale or purchase of futures
contracts, may cause it to sell or purchase related investments, thus increasing its turnover rate. Once the
Fund has received an exercise notice on an option it has written, it cannot effect a closing transaction in order
to terminate its obligation under the option and must deliver or receive the underlying securities at the
exercise price. The exercise of puts purchased by the Fund may also cause the sale of related investments,
increasing turnover. Although such exercise is within the Fund's control, holding a protective put might cause
it to sell the related investments for reasons that would not exist in the absence of the put. The Fund will pay
a brokerage commission each time it buys or sells a put or call or purchases or sells a futures contract. Such
commissions may be higher than those that would apply to direct purchases or sales.
Swaps, Caps, Floors and Collars. The Fund is authorized to enter into swaps, caps, floors and collars.
Additional information on swaps, caps and floors is included in this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and
Investment Methods." A collar combines elements of buying a cap and selling a floor.
Investment Policies Which May be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following
limitations are applicable to the ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund. These limitations are not fundamental
restrictions, and can be changed without shareholder approval.
1. The Fund may not sell securities short (unless it owns or has the right to obtain securities
equivalent in kind and amount to the securities sold short) or purchase securities on margin, except that (i)
this policy does not prevent the Fund from entering into short positions in foreign currency, futures contracts,
options, forward contracts, swaps, caps, floors, collars and other financial instruments, (ii) the Fund may
obtain such short-term credits as are necessary for the clearance of transactions, and (iii) the Fund may make
margin payments in connection with futures contracts, options, forward contracts, swaps, caps, floors, collars
and other financial instruments.
2. The Fund does not currently intend to purchase any security if, as a result, more than 15% of
its net assets would be invested in securities that are deemed to be illiquid because they are subject to legal
or contractual restrictions on resale or because they cannot be sold or disposed of in the ordinary course of
business at approximately the prices at which they are valued.
3. The Fund may invest in securities issued by other investment companies to the extent that such
investments are consistent with the Fund's investment objective and policies and permissible under the 1940 Act.
ASAF INVESCO HEALTH SCIENCES FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek growth. The Fund invests primarily in the
equity securities of companies that develop, produce or distribute products or services related to health care.
Investment Policies:
ADRs. American Depository Receipts, or ADRs, are securities issued by American banks. ADRs are receipts
for the shares of foreign corporations that are held by the bank issuing the receipt. An ADR entitles its holder
to all dividends and capital gains on the underlying foreign securities, less any fees paid to the bank.
Purchasing ADRs gives the Fund the ability to purchase the functional equivalent of foreign securities without
going to the foreign securities markets to do so. ADRs are bought and sold in U.S. dollars, not foreign
currencies. An ADR that is "sponsored" means that the foreign corporation whose shares are represented by the ADR
is actively involved in the issuance of the ADR, and generally provides material information about the
corporation to the U.S. market. An "unsponsored" ADR program means that the foreign corporation whose shares are
held by the bank is not obligated to disclose material information in the United States, and, therefore, the
market value of the ADR may not reflect important facts known only to the foreign company. Since they mirror
their underlying foreign securities, ADRs generally have the same risks as investing directly in the underlying
foreign securities.
Certificates of Deposit in Foreign Banks and U.S. Branches of Foreign Banks. The Fund may maintain time
deposits in and invest in U.S. dollar denominated CDs issued by foreign banks and U.S. branches of foreign banks.
The Fund limits investments in foreign bank obligations to U.S. dollar denominated obligations of foreign banks
which have more than $10 billion in assets, have branches or agencies in the U.S., and meet other criteria
established by the Company's Directors.
The Fund may also invest in bankers' acceptances, time deposits and certificates of deposit of U.S.
branches of foreign banks and foreign branches of U.S. banks. Investments in instruments of U.S. branches of
foreign banks will be made only with branches that are subject to the same regulations as U.S. banks. Investments
in instruments issued by a foreign branch of a U.S. bank will be made only if the investment risk associated with
such investment is the same as that involving an investment in instruments issued by the U.S. parent, with the
U.S. parent unconditionally liable in the event that the foreign branch fails to pay on the investment for any
reason.
Commercial Paper. Commercial paper is the term for short-term promissory notes issued by domestic
corporations to meet current working capital needs. Commercial paper may be unsecured by the corporation's assets
but may be backed by a letter of credit from a bank or other financial institution. The letter of credit enhances
the paper's creditworthiness. The issuer is directly responsible for payment but the bank "guarantees" that if
the note is not paid at maturity by the issuer, the bank will pay the principal and interest to the buyer. The
Sub-advisor will consider the creditworthiness of the institution issuing the letter of credit, as well as the
creditworthiness of the issuer of the commercial paper, when purchasing paper enhanced by a letter of credit.
Commercial paper is sold either as interest-bearing or on a discounted basis, with maturities not exceeding 270
days.
Debt Securities. Debt securities include bonds, notes and other securities that give the holder the
right to receive fixed amounts of principal, interest, or both on a date in the future or on demand. Debt
securities also are often referred to as fixed-income securities, even if the rate of interest varies over the
life of the security.
Although the Fund may invest in debt securities assigned lower grade ratings by S&P or Moody's, the
Fund's investments have generally been limited to debt securities rated B or higher by either S&P or Moody's.
Debt securities rated lower than B by either S&P or Moody's are usually considered to be speculative. At the time
of purchase, the Sub-advisor will limit Fund investments to debt securities which the Sub-advisor believes are
not highly speculative and which are rated at least CCC by S&P or Caa by Moody's.
A significant economic downturn or increase in interest rates may cause issuers of debt securities to
experience increased financial problems which could adversely affect their ability to pay principal and interest
obligations, to meet projected business goals, and to obtain additional financing. These conditions more severely
impact issuers of lower-rated debt securities. The market for lower-rated straight debt securities may not be as
liquid as the market for higher-rated straight debt securities. Therefore, the Sub-advisor attempts to limit
purchases of lower-rated securities to securities having an established secondary market.
Although bonds in the lowest investment grade debt category (those rated BBB by S&P, Baa by Moody's or
the equivalent) are regarded as having adequate capability to pay principal and interest, they have speculative
characteristics. Adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to lead to a weakened
capacity to make principal and interest payments than is the case for higher-rated bonds. Lower-rated bonds by
Moody's (categories Ba, B or Caa) are of poorer quality and also have speculative characteristics. Bonds rated
Caa may be in default or there may be present elements of danger with respect to include those that are regarded,
on balance, as predominantly speculative with respect to the issuer's capacity to pay interest and repay
principal in accordance with their terms; BB indicates the lowest degree of speculation and CCC a high degree of
speculation. While such bonds likely will have some quality and protective characteristics, these are outweighed
by large uncertainties or major risk exposures to adverse conditions. Bonds having equivalent ratings from other
ratings services will have characteristics similar to those of the corresponding S&P and Moody's ratings.
The Fund may invest in zero coupon bonds, step-up bonds, mortgage-backed securities and asset-backed
securities. Step-up bonds initially make no (or low) cash interest payments but begin paying interest (or a
higher rate of interest) at a fixed time after issuance of the bond. The market values of step-up bonds generally
fluctuate more in response to changes in interest rates than interest-paying securities of comparable term and
quality. The Fund may be required to distribute income recognized on these bonds, even though no cash may be paid
to the Fund until the maturity or call date of a bond, in order for the Fund to maintain its qualification as a
regulated investment company. These required distributions could reduce the amount of cash available for
investment by the Fund.
Additional information about the debt securities, mortgage-backed securities, asset-backed securities
and zero coupon bonds and their risks, including the risks of lower-rated debt securities, is included in this
SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Domestic Bank Obligations. U.S. banks (including their foreign branches) issue certificates of deposit
(CDs) and bankers' acceptances which may be purchased by the Fund if an issuing bank has total assets in excess
of $5 billion and the bank otherwise meets the Fund's credit rating requirements. CDs are issued against deposits
in a commercial bank for a specified period and rate and are normally negotiable. Eurodollar CDs are certificates
issued by a foreign branch (usually London) of a U.S. domestic bank, and, as such, the credit is deemed to be
that of the domestic bank. Bankers' acceptances are short-term credit instruments evidencing the promise of the
bank (by virtue of the bank's "acceptance") to pay at maturity a draft which has been drawn on it by a customer
(the "drawer"). Bankers' acceptances are used to finance the import, export, transfer, or storage of goods and
reflect the obligation of both the bank and the drawer to pay the face amount. Both types of securities are
subject to the ability of the issuing bank to meet its obligations, and are subject to risks common to all debt
securities. In addition, banker's acceptances may be subject to foreign currency risk and certain other risks of
investment in foreign securities.
Equity and Convertible Debt Securities. The Fund may invest in common and preferred stocks, and
securities whose values are tied to the price of stocks, such as rights and warrants. Additional information
about these types of securities and their risks is included in the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods."
The Fund also may purchase convertible securities including convertible debt obligations and convertible
preferred stock. A convertible security entitles the holder to exchange it for a fixed number of shares of common
stock (or other equity security), usually at a fixed price within a specified period of time. Until conversion,
the owner of convertible securities usually receives the interest paid on a convertible bond or the dividend
preference of a preferred stock.
A convertible security has an "investment value" which is a theoretical value determined by the yield it
provides in comparison with similar securities without the conversion feature. Investment value changes are based
upon prevailing interest rates and other factors. It also has a "conversion value," which is the market value the
convertible security would have if it were exchanged for the underlying equity security. Convertible securities
may be purchased at varying price levels above or below their investment values or conversion values.
Conversion value is a simple mathematical calculation that fluctuates directly with the price of the
underlying security. However, if the conversion value is substantially below the investment value, the market
value of the convertible security is governed principally by its investment value. If the conversion value is
near or above investment value, the market value of the convertible security generally will rise above investment
value. In such cases, the market value of the convertible security may be higher than its conversion value, due
to the combination of the convertible security's right to interest (or dividend preference) and the possibility
of capital appreciation from the conversion feature. However, there is no assurance that any premium above
investment value or conversion value will be recovered because prices change and, as a result, the ability to
achieve capital appreciation through conversion may be eliminated.
Eurobonds and Yankee Bonds. The Fund may invest in bonds issued by foreign branches of U.S. banks
("Eurobonds") and bonds issued by a U.S. branch of a foreign bank and sold in the United States ("Yankee bonds").
These bonds are bought and sold in U.S. dollars, but generally carry with them the same risks as investing in
foreign securities.
Foreign Securities. Investments in the securities of foreign companies, or companies that have their
principal business activities outside the United States, involve certain risks not associated with investment in
U.S. companies. Foreign securities involve certain risks not associated with investment in U.S. companies, which
are described in more detail in this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods."
Foreign currency exchange rates are determined by supply and demand on the foreign exchange markets.
Foreign exchange markets are affected by the international balance of payments and other economic and financial
conditions, government intervention, speculation and other factors, all of which are outside the control of the
Fund. Generally, the Fund's foreign currency exchange transactions will be conducted on a cash or "spot" basis at
the spot rate for purchasing or selling currency in the foreign currency exchange markets.
Financial Instruments/Derivatives. The Sub-advisor may use various types of financial instruments, some
of which are derivatives, to attempt to manage the risk of the Fund's investments or, in certain circumstances,
for investment (e.g., as a substitute for investing in securities). These financial instruments include options,
futures contracts (sometimes referred to as "futures"), forward contracts, swaps, caps, floors and collars
(collectively, "Financial Instruments"). The policies in this section do not apply to other types of instruments
sometimes referred to as derivatives, such as indexed securities, mortgage-backed and other asset-backed
securities, and stripped interest and principal of debt.
Hedging strategies can be broadly categorized as "short" hedges and "long" or "anticipatory" hedges. A
short hedge involves the use of a Financial Instrument in order to partially or fully offset potential variations
in the value of one or more investments held in the Fund's portfolio. A long or anticipatory hedge involves the
use of a Financial Instrument in order to partially or fully offset potential increases in the acquisition cost
of one or more investments that the Fund intends to acquire. In an anticipatory hedge transaction, the Fund does
not already own a corresponding security. Rather, it relates to a security or type of security that the Fund
intends to acquire. If the Fund does not eliminate the hedge by purchasing the security as anticipated, the
effect on the Fund's portfolio is the same as if a long position were entered into.
Financial Instruments may also be used, in certain circumstances, for investment (e.g., as a substitute
for investing in securities). Financial Instruments on individual securities generally are used to attempt to
hedge against price movements in one or more particular securities positions that the Fund already owns or
intends to acquire. Financial Instruments on indexes, in contrast, generally are used to attempt to hedge all or
a portion of a portfolio against price movements of the securities within a market sector in which the Fund has
invested or expects to invest.
The use of Financial Instruments is subject to applicable regulations of the Securities and Exchange
Commission ("SEC"), the several exchanges upon which they are traded, and the Commodity Futures Trading
Commission ("CFTC"). In addition, the Fund's ability to use Financial Instruments will be limited by tax
considerations.
In addition to the instruments and strategies described below, the Sub-advisor may use other similar or
related techniques to the extent that they are consistent with the Fund's investment objective and permitted by
its investment limitations and applicable regulatory authorities.
Options. The Fund may engage in certain strategies involving options to attempt to manage the risk of
its investments or, in certain circumstances, for investment (e.g., as a substitute for investing in securities).
The purchase of call options can serve as a hedge against a price rise of the underlier and the purchase
of put options can serve as a hedge against a price decline of the underlier. Writing call options can serve as a
limited short hedge because declines in the value of the hedged investment would be offset to the extent of the
premium received for writing the option.
Writing put options can serve as a limited long or anticipatory hedge because increases in the value of
the hedged investment would be offset to the extent of the premium received for writing the option.
The value of an option position will reflect, among other things, the current market value of the
underlying investment, the time remaining until expiration, the relationship of the exercise price to the market
price of the underlying investment, the price volatility of the underlying investment and general market and
interest rate conditions. Options that expire unexercised have no value.
The Fund may effectively terminate its right or obligation under an option by entering into a closing
transaction. For example, the Fund may terminate its obligation under a call or put option that it had written by
purchasing an identical call or put option, which is known as a closing purchase transaction. Conversely, the
Fund may terminate a position in a put or call option it had purchased by writing an identical put or call
option, which is known as a closing sale transaction. Closing transactions permit the Fund to realize profits or
limit losses on an option position prior to its exercise or expiration.
Options on Indices. The risks of purchasing and selling options on indexes may be greater than options
on securities. Because index options are settled in cash, when the Fund writes a call on an index it cannot
fulfill its potential settlement obligations by delivering the underlying securities. The Fund can offset some of
the risk of writing a call index option by holding a diversified portfolio of securities similar to those on
which the underlying index is based. However, the Fund cannot, as a practical matter, acquire and hold a
portfolio containing exactly the same securities as underlie the index and, as a result, bears a risk that the
value of the securities held will vary from the value of the index.
OTC Options. Unlike exchange-traded options, which are standardized with respect to the underlying
instrument, expiration date, contract size, and strike price, the terms of OTC options (options not traded on
exchanges) generally are established through negotiation with the other party to the option contract. While this
type of arrangement allows the Fund great flexibility to tailor the option to its needs, OTC options generally
involve greater risk than exchange-traded options, which are guaranteed by the clearing organization of the
exchange where they are traded.
Additional information about options transactions and their risks is included in this SAI and the
Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Futures Contracts and Options on Futures Contracts. The purchase of futures or call options on futures
can serve as a long or an anticipatory hedge, and the sale of futures or the purchase of put options on futures
can serve as a short hedge. Writing call options on futures contracts can serve as a limited short hedge, using a
strategy similar to that used for writing call options on securities or indexes. Similarly, writing put options
on futures contracts can serve as a limited long or anticipatory hedge.
In addition, futures strategies can be used to manage the "duration" (a measure of anticipated
sensitivity to changes in interest rates, which is sometimes related to the weighted average maturity of a
portfolio) and associated interest rate risk of the Fund's fixed-income portfolio. If the Sub-Advisor wishes to
shorten the duration of the Fund's fixed-income portfolio (i.e., reduce anticipated sensitivity), the Fund may
sell an appropriate debt futures contract or a call option thereon, or purchase a put option on that futures
contract. If the Sub-advisor wishes to lengthen the duration of the Fund's fixed-income portfolio (i.e., increase
anticipated sensitivity), the Fund may buy an appropriate debt futures contract or a call option thereon, or sell
a put option thereon.
At the inception of a futures contract, the Fund is required to deposit "initial margin" in an amount
generally equal to 10% or less of the contract value. Initial margin must also be deposited when writing a call
or put option on a futures contract, in accordance with applicable exchange rules. Subsequent "variation margin"
payments are made to and from the futures broker daily as the value of the futures or written option position
varies, a process known as "marking-to-market." Unlike margin in securities transactions, initial margin on
futures contracts and written options on futures contracts does not represent a borrowing on margin, but rather
is in the nature of a performance bond or good-faith deposit that is returned to the Fund at the termination of
the transaction if all contractual obligations have been satisfied. Under certain circumstances, such as periods
of high volatility, the Fund may be required to increase the level of initial margin deposits.
If the Fund were unable to liquidate a futures contract or an option on a futures contract position due
to the absence of a liquid market or the imposition of price limits, it could incur substantial losses. The Fund
would continue to be subject to market risk with respect to the position. In addition, except in the case of
purchased options, the Fund would continue to be required to make daily variation margin payments and might be
required to continue to maintain the position being hedged by the futures contract or option or to continue to
maintain cash or securities in a segregated account.
Index Futures. For additional information on futures contracts and options on futures and their risks,
see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods." The price of the
index futures may move proportionately more than or less than the price of the securities being hedged. If the
price of the index futures moves proportionately less than the price of the securities that are the subject of
the hedge, the hedge will not be fully effective. Assuming the price of the securities being hedged has moved in
an unfavorable direction, as anticipated when the hedge was put into place, the Fund would be in a better
position than if it had not hedged at all, but not as good as if the price of the index futures moved in full
proportion to that of the hedged securities. However, if the price of the securities being hedged has moved in a
favorable direction, this advantage will be partially offset by movement of the price of the futures contract. If
the price of the futures contract moves more than the price of the securities, the Fund will experience either a
loss or a gain on the futures contract that will not be completely offset by movements in the price of the
securities that are the subject of the hedge.
Where index futures are purchased in an anticipatory hedge, it is possible that the market may decline
instead. If the Fund then decides not to invest in the securities at that time because of concern as to possible
further market decline or for other reasons, it will realize a loss on the futures contract that is not offset by
a reduction in the price of the securities it had anticipated purchasing.
Foreign Currency Hedging Strategies--Special Considerations. The Fund may use options and futures
contracts on foreign currencies, as mentioned previously, and forward currency contracts, as described below, to
attempt to hedge against movements in the values of the foreign currencies in which the Fund's securities are
denominated or, in certain circumstances, for investment (e.g., as a substitute for investing in securities
denominated in foreign currency). Currency hedges can protect against price movements in a security that the Fund
owns or intends to acquire that are attributable to changes in the value of the currency in which it is
denominated.
The Fund might seek to hedge against changes in the value of a particular currency when no Financial
Instruments on that currency are available or such Financial Instruments are more expensive than certain other
Financial Instruments. In such cases, the Fund may seek to hedge against price movements in that currency by
entering into transactions using Financial Instruments on another currency or a basket of currencies, the value
of which the Sub-advisor believes will have a high degree of positive correlation to the value of the currency
being hedged. The risk that movements in the price of the Financial Instrument will not correlate perfectly with
movements in the price of the currency subject to the hedging transaction may be increased when this strategy is
used.
The value of Financial Instruments on foreign currencies depends on the value of the underlying currency
relative to the U.S. dollar. Because foreign currency transactions occurring in the interbank market might
involve substantially larger amounts than those involved in the use of such Financial Instruments, the Fund could
be disadvantaged by having to deal in the odd-lot market (generally consisting of transactions of less than $1
million) for the underlying foreign currencies at prices that are less favorable than for round lots.
There is no systematic reporting of last sale information for foreign currencies or any regulatory
requirement that quotations available through dealers or other market sources be firm or revised on a timely
basis. Quotation information generally is representative of very large transactions in the interbank market and
thus might not reflect odd-lot transactions where rates might be less favorable. The interbank market in foreign
currencies is a global, round-the-clock market. To the extent the U.S. options or futures markets are closed
while the markets for the underlying currencies remain open, significant price and rate movements might take
place in the underlying markets that cannot be reflected in the markets for the Financial Instruments until they
reopen.
Settlement of hedging transactions involving foreign currencies might be required to take place within
the country issuing the underlying currency. Thus, the Fund might be required to accept or make delivery of the
underlying foreign currency in accordance with any U.S. or foreign regulations regarding the maintenance of
foreign banking arrangements by U.S. residents and might be required to pay any fees, taxes and charges
associated with such delivery assessed in the issuing country.
Forward Currency Contracts and Foreign Currency Deposits. The Fund may enter into forward currency
contracts to purchase or sell foreign currencies for a fixed amount of U.S. dollars or another foreign currency.
The Fund may also use forward currency contracts to hedge against a decline in the value of existing
investments denominated in foreign currency. Such a hedge would tend to offset both positive and negative
currency fluctuations, but would not offset changes in security values caused by other factors. The Fund could
also hedge the position by entering into a forward currency contract to sell another currency expected to perform
similarly to the currency in which the Fund's existing investments are denominated. This type of hedge could
offer advantages in terms of cost, yield or efficiency, but may not hedge currency exposure as effectively as a
simple hedge against U.S. dollars. This type of hedge may result in losses if the currency used to hedge does not
perform similarly to the currency in which the hedged securities are denominated.
The Fund may also use forward currency contracts in one currency or a basket of currencies to attempt to
hedge against fluctuations in the value of securities denominated in a different currency if the Sub-advisor
anticipates that there will be a positive correlation between the two currencies.
The cost to the Fund of engaging in forward currency contracts varies with factors such as the currency
involved, the length of the contract period and the market conditions then prevailing. Because forward currency
contracts are usually entered into on a principal basis, no fees or commissions are involved. When the Fund
enters into a forward currency contract, it relies on the counterparty to make or take delivery of the underlying
currency at the maturity of the contract. Failure by the counterparty to do so would result in the loss of some
or all of any expected benefit of the transaction.
As is the case with futures contracts, purchasers and sellers of forward currency contracts can enter
into offsetting closing transactions, similar to closing transactions on futures contracts, by selling or
purchasing, respectively, an instrument identical to the instrument purchased or sold. Secondary markets
generally do not exist for forward currency contracts, with the result that closing transactions generally can be
made for forward currency contracts only by negotiating directly with the counterparty. Thus, there can be no
assurance that the Fund will in fact be able to close out a forward currency contract at a favorable price prior
to maturity. In addition, in the event of insolvency of the counterparty, the Fund might be unable to close out a
forward currency contract. In either event, the Fund would continue to be subject to market risk with respect to
the position, and would continue to be required to maintain a position in securities denominated in the foreign
currency or to segregate cash or liquid assets.
Forward currency contracts may substantially change the Fund's investment exposure to changes in
currency exchange rates and could result in losses to the Fund if currencies do not perform as the Sub-advisor
anticipates. There is no assurance that the Sub-advisor's use of forward currency contracts will be advantageous
to the Fund or that it will hedge at an appropriate time.
The Fund may also purchase and sell foreign currency and invest in foreign currency deposits. Currency
conversion involves dealer spreads and other costs, although commissions usually are not charged.
Additional information about forward currency contracts and other foreign currency transactions and
their risks is included in this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods."
Combined Positions. The Fund may purchase and write options or futures in combination with each other,
or in combination with futures or forward currency contracts, to manage the risk and return characteristics of
its overall position. For example, the Fund may purchase a put option and write a call option on the same
underlying instrument, in order to construct a combined position whose risk and return characteristics are
similar to selling a futures contract. Another possible combined position would involve writing a call option at
one strike price and buying a call option at a lower price, in order to reduce the risk of the written call
option in the event of a substantial price increase. Because combined options positions involve multiple trades,
they result in higher transaction costs.
Turnover. The Fund's options and futures activities may affect their turnover rates and brokerage
commission payments. The exercise of calls or puts written by the Fund, and the sale or purchase of futures
contracts, may cause it to sell or purchase related investments, thus increasing its turnover rate. Once the Fund
has received an exercise notice on an option it has written, it cannot effect a closing transaction in order to
terminate its obligation under the option and must deliver or receive the underlying securities at the exercise
price. The exercise of puts purchased by the Fund may also cause the sale of related investments, increasing
turnover. Although such exercise is within the Fund's control, holding a protective put might cause it to sell
the related investments for reasons that would not exist in the absence of the put. The Fund will pay a brokerage
commission each time it buys or sells a put or call or purchases or sells a futures contract. Such commissions
may be higher than those that would apply to direct purchases or sales.
Swaps, Caps, Floors and Collars. The Fund is authorized to enter into swaps, caps, floors and collars.
Additional information about forward currency contracts and other foreign currency transactions and their risks
is included in this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods." A
collar combines elements of buying a cap and selling a floor.
Investment Company Securities. The Fund may invest in securities issued by other investment companies
that invest in short-term debt securities and seek to maintain a net asset value of $1.00 per share ("money
market funds"). The Fund also may invest in Standard & Poor's Depository Receipts ("SPDRs") and shares of other
investment companies. SPDRs are investment companies whose portfolios mirror the compositions of specific S&P
indices, such as the S&P 500 and the S&P 400. SPDRs are traded on the American Stock Exchange. SPDR holders such
as the Fund are paid a "Dividend Equivalent Amount" that corresponds to the amount of cash dividends accruing to
the securities held by the SPDR Trust, net of certain fees and expenses. The Investment Company Act of 1940, as
amended (the "1940 Act"), limits investments in securities of other investment companies, such as the SPDR Trust.
These limitations include, among others, that, subject to certain exceptions, no more than 10% of the Fund's
total assets may be invested in securities of other investment companies, no more than 5% of its total assets may
be invested in the securities of any one investment company, and the Fund may not own more than 3% of the
outstanding shares of any investment company.
Additional information on investing in other investment companies and its risks is included in the
Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
REITS -- Real Estate Investment Trusts are investment trusts that invest primarily in real estate and
securities of businesses connected to the real estate industry. A REIT is a managed portfolio of real estate
investments. Certain REITs holds equity positions in real estate and provides their shareholders with income
from the leasing of its properties and capital gains from any sales of properties. Other REITs specialize in
lending money to developers of properties and pass any interest income earned to their shareholders. REITs are
dependent upon management skills of their operators. REITs generally are not diversified, and are, therefore,
subject to the risk of financing a few projects or an unlimited number of projects. They are also subject to
heavy cash flow dependency, defaults by borrowers, and self-liquidation.
Securities Lending. The Fund may lend its portfolio securities. The advantage of lending portfolio
securities is that the Fund continues to have the benefits (and risks) of ownership of the loaned securities,
while at the same time receiving interest from the borrower of the securities. The primary risk in lending
portfolio securities is that a borrower may fail to return a portfolio security.
Sovereign Debt. In certain emerging countries, the central government and its agencies are the largest
debtors to local and foreign banks and others. Sovereign debt involves the risk that the government, as a result
of political considerations or cash flow difficulties, may fail to make scheduled payments of interest or
principal and may require holders to participate in rescheduling of payments or even to make additional loans. If
an emerging country government defaults on its sovereign debt, there is likely to be no legal proceeding under
which the debt may be ordered repaid, in whole or in part. The ability or willingness of a foreign sovereign
debtor to make payments of principal and interest in a timely manner may be influenced by, among other factors,
its cash flow, the magnitude of its foreign reserves, the availability of foreign exchange on the payment date,
the debt service burden to the economy as a whole, the debtor's then current relationship with the International
Monetary Fund and its then current political constraints. Some of the emerging countries issuing such instruments
have experienced high rates of inflation in recent years and have extensive internal debt. Among other effects,
high inflation and internal debt service requirements may adversely affect the cost and availability of future
domestic sovereign borrowing to finance government programs, and may have other adverse social, political and
economic consequences, including effects on the willingness of such countries to service their sovereign debt. An
emerging country government's willingness and ability to make timely payments on its sovereign debt also are
likely to be heavily affected by the country's balance of trade and its access to trade and other international
credits. If a country's exports are concentrated in a few commodities, such country would be more significantly
exposed to a decline in the international prices of one or more of such commodities. A rise in protectionism on
the part of its trading partners, or unwillingness by such partners to make payment for goods in hard currency,
could also adversely affect the country's ability to export its products and repay its debts. Sovereign debtors
may also be dependent on expected receipts from such agencies and others abroad to reduce principal and interest
arrearages on their debt. However, failure by the sovereign debtor or other entity to implement economic reforms
negotiated with multilateral agencies or others, to achieve specified levels of economic performance, or to make
other debt payments when due, may cause third parties to terminate their commitments to provide funds to the
sovereign debtor, which may further impair such debtor's willingness or ability to service its debts.
The Fund may invest in debt securities issued under the "Brady Plan" in connection with restructurings
in emerging country debt markets or earlier loans. These securities, often referred to as "Brady Bonds," are, in
some cases, denominated in U.S. dollars and collateralized as to principal by U.S. Treasury zero coupon bonds
having the same maturity. At least one year's interest payments, on a rolling basis, are collateralized by cash
or other investments. Brady Bonds are actively traded on an over-the-counter basis in the secondary market for
emerging country debt securities. Brady Bonds are lower-rated bonds and are highly volatile.
U.S. Government Securities. The Fund may, from time to time, purchase debt securities issued by the
U.S. government. These securities include Treasury bills, notes, and bonds. Treasury bills have a maturity of one
year or less, Treasury notes generally have a maturity of one to ten years, and Treasury bonds generally have
maturities of more than ten years.
U.S. government debt securities also include securities issued or guaranteed by agencies or
instrumentalities of the U.S. government. Some obligations of U.S. government agencies, which are established
under the authority of an act of Congress, such as Government National Mortgage Association ("GNMA")
Participation Certificates, are supported by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Treasury. GNMA Certificates
are mortgage-backed securities representing part ownership of a pool of mortgage loans. These loans -- issued by
lenders such as mortgage bankers, commercial banks and savings and loan associations -- are either insured by the
Federal Housing Administration or guaranteed by the Veterans Administration. A "pool" or group of such mortgages
is assembled and, after being approved by GNMA, is offered to investors through securities dealers. Once approved
by GNMA, the timely payment of interest and principal on each mortgage is guaranteed by GNMA and backed by the
full faith and credit of the U.S. government. The market value of GNMA Certificates is not guaranteed. GNMA
Certificates are different from bonds because principal is paid back monthly by the borrower over the term of the
loan rather than returned in a lump sum at maturity, as is the case with a bond. GNMA Certificates are called
"pass-through" securities because both interest and principal payments (including prepayments) are passed through
to the holder of the GNMA Certificate.
Other United States government debt securities, such as securities of the Federal Home Loan Banks, are
supported by the right of the issuer to borrow from the Treasury. Others, such as bonds issued by Fannie Mae, a
federally chartered private corporation, are supported only by the credit of the corporation. In the case of
securities not backed by the full faith and credit of the United States, the Fund must look principally to the
agency issuing or guaranteeing the obligation in the event the agency or instrumentality does not meet its
commitments. The Fund will invest in securities of such instrumentalities only when the Sub-advisor is satisfied
that the credit risk with respect to any such instrumentality is comparatively minimal.
When-Issued/Delayed Delivery. The Fund normally buys and sells securities on an ordinary settlement
basis. That means that the buy or sell order is sent, and the Fund actually takes delivery or gives up physical
possession of the security on the "settlement date," which is three business days later. However, the Fund also
may purchase and sell securities on a when-issued or delayed delivery basis.
When-issued or delayed delivery transactions occur when securities are purchased or sold by the Fund and
payment and delivery take place at an agreed-upon time in the future. The Fund may engage in this practice in an
effort to secure an advantageous price and yield. However, the yield on a comparable security available when
delivery actually takes place may vary from the yield on the security at the time the when-issued or delayed
delivery transaction was entered into. When the Fund engages in when-issued and delayed delivery transactions, it
relies on the seller or buyer to consummate the sale at the future date. If the seller or buyer fails to act as
promised, that failure may result in the Fund missing the opportunity of obtaining a price or yield considered to
be advantageous. No payment or delivery is made by the Fund until it receives delivery or payment from the other
party to the transaction. However, fluctuation in the value of the security from the time of commitment until
delivery could adversely affect the Fund.
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
not "fundamental" restrictions and may be changed by the Directors of the Company without shareholder approval.
The Fund will:
1. Not sell securities short (unless it owns or has the right to obtain securities equivalent in
kind and amount to the securities sold short) or purchase securities on margin, except that (i) this policy does
not prevent the Fund from entering into short positions in foreign currency, futures contracts, options, forward
contracts, swaps, caps, floors, collars and other financial instruments, (ii) the Fund may obtain such short-term
credits as are necessary for the clearance of transactions, and (iii) the Fund may make margin payments in
connection with futures contracts, options, forward contracts, swaps, caps, floors, collars and other financial
instruments.
2. Borrow money only from a bank or from an open-end management investment company managed by the
Sub-advisor or an affiliate or a successor thereof for temporary or emergency purposes (not for leveraging or
investing) or by engaging in reverse repurchase agreements with any party (reverse repurchase agreements will be
treated as borrowings for purposes of the Fund's fundamental limitation on borrowings.
3. Purchase any security if, as a result, more than 15% of its net assets would be invested in
securities that are deemed to be illiquid because they are subject to legal or contractual restrictions on resale
or because they cannot be sold or disposed of in the ordinary course of business at approximately the prices at
which they are valued.
4. Invest in securities issued by other investment companies only to the extent that such
investments are consistent with the Fund's investment objective and policies and permissible under the 1940 Act.
ASAF RYDEX MANAGED OTC FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to provide investment results that correspond to a
benchmark for securities that are traded in the over-the-counter market. The Fund's current benchmark is the
NASDAQ 100 Index.
Investment Policies:
Borrowing. The Fund may borrow money to facilitate management of the Fund's portfolio by enabling the
Fund to meet redemption requests when the liquidation of portfolio instruments would be inconvenient or
disadvantageous. Such borrowing is not for investment purposes and will be repaid by the Fund promptly.
As required by the 1940 Act, the Fund must maintain continuous asset coverage (total assets, including
assets acquired with borrowed funds, less liabilities exclusive of borrowings) of 300% of all amounts borrowed.
Maintenance of this percentage limitation may result in the sale of portfolio securities at a time when
investment considerations otherwise indicate that it would be disadvantageous to do so.
The Fund is authorized to pledge portfolio securities as the Sub-advisor deems appropriate in connection
with any borrowings. Additional information about borrowing is included in the Company's Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Other Investment Companies. The Fund may invest in other investment companies to the extent permitted
by the 1940 Act and rules and regulations thereunder, and, if applicable, exemptive orders granted by the SEC.
If a Fund invests in, and, thus, is a shareholder of, another investment company, the Fund's shareholders will
indirectly bear the Fund's proportionate share of the fees and expenses paid by such other investment company,
including advisory fees, in addition to both the management fees payable directly by the Fund to the Fund's
Investment Manager and the other expenses that the Fund bears directly in connection with the Fund's own
operations.
Lending of Portfolio Securities. Subject to the investment restrictions set forth below, the Fund may
lend portfolio securities to brokers, dealers, and financial institutions, provided that cash equal to at least
100% of the market value of the securities loaned is deposited by the borrower with the Fund and is maintained
each business day in a segregated account pursuant to applicable regulations. Loans would be subject to
termination by the borrower on one day's notice. Borrowed securities must be returned when the loan is
terminated. Any gain or loss in the market price of the borrowed securities which occurs during the term of the
loan inures to the Fund and the Fund's shareholders. The Fund may pay reasonable finders, borrowers,
administrative, and custodial fees in connection with a loan. For additional discussion about this practice, see
this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Options Transactions. The Fund may engage in options transactions as set forth below. A description of
and additional information on these instruments and their risks are included in this SAI and Company's Prospectus
under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods." Certain other information risks pertaining to these
investment strategies are described in the sections that follow.
Options on Securities. The Fund may buy call options and write (sell) put options on
securities for the purpose of realizing the Fund's investment objective.
Options on Security Indices. The Fund may purchase call options and write put options on
stock indices listed on national securities exchanges or traded in the over-the-counter market as an investment
vehicle for the purpose of realizing the Fund's investment objective.
When the Fund writes an option on an index, the Fund will be required to deposit and maintain with a
custodian cash or liquid securities equal in value to the aggregate exercise price of a put or call option
pursuant to the requirements and the rules of the applicable exchange. If, at the close of business on any day,
the market value of the deposited securities falls below the contract price, the Fund will deposit with the
custodian cash or liquid securities equal in value to the deficiency.
Stock Index Futures Contracts. The Fund may buy and sell stock index futures contracts and related
options (with respect to any stock index) that are traded on a recognized stock exchange or board of trade. When
the Fund purchases or sells a stock index futures contract, or sells an option thereon, the Fund "covers" its
position. To cover its position, the Fund may maintain with its custodian bank (and marked-to-market on a daily
basis), a segregated account consisting of cash or other liquid assets that, when added to any amounts deposited
with a futures commission merchant as initial margin, are equal to the market value of the futures contract. If
the Fund engages in the described securities trading practices and properly segregates assets, the segregated
account will function as a practical limit on the amount of leverage which the Fund may undertake and on the
potential increase in the speculative character of the Fund's outstanding portfolio securities. Additionally,
such segregated accounts will generally assure the availability of adequate funds to meet the obligations of the
Fund arising from such investment activities.
The Fund may cover its long position in a futures contract by purchasing a put option on the same
futures contract with a strike price (i.e., an exercise price) as high or higher than the price of the futures
contract. In the alternative, if the strike price of the put is less than the price of the futures contract, the
Fund will maintain in a segregated account cash or other liquid assets equal in value to the difference between
the strike price of the put and the price of the futures contract. The Fund may also cover its long position in
a futures contract by taking a short position in the instruments underlying the futures contract, or by taking
positions in instruments with prices which are expected to move relatively consistently with the futures
contract. A Fund may "cover" a short position in a futures contract by owning the instruments underlying the
contract (or, in the case of an index futures contract, a portfolio the value of which is expected to fluctuate
in a substantially similar manner to the index on which the futures contract is based), or by taking positions in
instruments with prices which are expected to move relatively consistently with the futures contract. The Fund
may also cover its short position in a futures contract by holding a call option permitting the Fund to purchase
the same futures contract at a price no higher than the price of the contract written by the Fund (or at a higher
price if the difference is maintained in liquid assets with the Fund's custodian).
The Fund may cover its sale of a call option on a futures contract by taking a long position in the
underlying futures contract at a price less than or equal to the strike price of the call option. In the
alternative, if the long position in the underlying futures contracts is established at a price greater than the
strike price of the written (sold) call, the Fund will maintain in a segregated account cash or other liquid
assets equal in value to the difference between the strike price of the call and the price of the futures
contract. The Fund may also cover its sale of a call option by taking positions in instruments with prices which
are expected to move relatively consistently with the call option. The Fund may cover its sale of a put option
on a futures contract by taking a short position in the underlying futures contract at a price greater than or
equal to the strike price of the put option, or, if the short position in the underlying futures contract is
established at a price less than the strike price of the written put, the Fund will maintain in a segregated
account cash or other liquid assets equal in value to the difference between the strike price of the put and the
price of the futures contract. The Fund may also cover its sale of a put option by taking positions in
instruments with prices which are expected to move relatively consistently with the put option. Additional
information on Futures and their risks is included in this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods."
Portfolio Turnover. The Fund's portfolio turnover rate to a great extent will depend on the purchase,
redemption, and exchange activity of the Fund, it is very difficult to estimate what the Fund's actual turnover
rate will be in the future. However, the Sub-advisor anticipates that the portfolio turnover may equal or exceed
100%. For an additional discussion of portfolio turnover, see this SAI under "Portfolio Transactions" and the
Company's Prospectus under "Portfolio Turnover."
Short Sales Against the Box. The Fund may engage in short sales "against the box". The Fund may make a
short sale when the Fund wants to sell the security the Fund owns at a current attractive price, in order to
hedge or limit the exposure of the Fund's position. For further information about this practice, please refer to
the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Tracking Error. Although the Fund does not expect that the returns over a year will deviate adversely
from its benchmark by more than ten percent, several factors may affect its ability to achieve this correlation.
Among these are: (1) Fund expenses, including brokerage (which may be increased by high portfolio turnover); (2)
less than all of the securities in the benchmark being held by the Fund and securities not included in the
benchmark being held by the Fund; (3) an imperfect correlation between the performance of instruments held by the
Fund, such as futures contracts and options, and the performance of the underlying securities in the cash market;
(4) bid-ask spreads (the effect of which may be increased by portfolio turnover); (5) the Fund holds instruments
traded in a market that has become illiquid or disrupted; (6) Fund share prices being rounded to the nearest
cent; (7) changes to the benchmark index that are not disseminated in advance; or (8) the need to conform the
Fund's portfolio holdings to comply with investment restrictions or policies or regulatory or tax law
requirements.
U.S. Government Securities. The Fund may invest in U.S. Government Securities. Securities issued or
guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies or instrumentalities include U.S. Treasury securities, which
are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Treasury and which differ only in their interest rates,
maturities, and times of issuance. U.S. Treasury bills have initial maturities of one year or less; U.S.
Treasury notes have initial maturities of one to ten years; and U.S. Treasury bonds generally have initial
maturities of greater than ten years. Certain U.S. Government Securities are issued or guaranteed by agencies
or instrumentalities of the U.S. Government including, but not limited to, Fannie Mae, the Government National
Mortgage Association, the Small Business Administration, the Federal Farm Credit Administration, the Federal Home
Loan Banks, Banks for Cooperatives (including the Central Bank for Cooperatives), the Federal Land Banks, the
Federal Intermediate Credit Banks, the Tennessee Valley Authority, the Export-Import Bank of the United States,
the Commodity Credit Corporation, the Federal Financing Bank, the Student Loan Marketing Association, and the
National Credit Union Administration.
Some obligations issued or guaranteed by U.S. Government agencies and instrumentalities, including, for
example, Government National Mortgage Association pass-through certificates, are supported by the full faith and
credit of the U.S. Treasury. Other obligations issued by or guaranteed by Federal agencies, such as those
securities issued by Fannie Mae, are supported by the discretionary authority of the U.S. Government to purchase
certain obligations of the Federal agency, while other obligations issued by or guaranteed by Federal agencies,
such as those of the Federal Home Loan Banks, are supported by the right of the issuer to borrow from the U.S.
Treasury. While the U.S. Government provides financial support to such U.S. Government-sponsored Federal
agencies, no assurance can be given that the U.S. Government will always do so, because the U.S. Government is
not so obligated by law. U.S. Treasury notes and bonds typically pay coupon interest semi-annually and repay the
principal at maturity.
When-Issued and Delayed-Delivery Securities. The Fund may purchase securities on a when-issued or
delayed-delivery basis (i.e., delivery and payment can take place between a month and 120 days after the date of
the transaction). At the time the Fund makes the commitment to purchase securities on a when-issued or
delayed-delivery basis, the Fund will record the transaction and thereafter reflect the value of the securities
each day in determining the Fund's net asset value. The Fund will not purchase securities on a when-issued or
delayed-delivery basis if, as a result, more than 15% of the Fund's net assets would be so invested. At the time
of delivery of the securities, the value of the securities may be more or less than the purchase price. The Fund
will also establish a segregated account with the Fund's custodian bank in which the Fund will maintain cash or
liquid securities equal to or greater in value than the Fund's purchase commitments for such when-issued or
delayed-delivery securities. The Sub-advisor does not believe that the Fund's net asset value or income will be
adversely affected by the Fund's purchase of securities on a when-issued or delayed-delivery basis. For more
information about when-issued securities, please see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods."
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
not "fundamental" restrictions and may be changed by the Directors of the Company without shareholder approval.
The Fund will not:
1. Invest in warrants.
2. Invest in real estate limited partnerships.
3. Invest in mineral leases.
4. Pledge, mortgage, or hypothecate the Fund's assets, except to the extent necessary to secure
permitted borrowings and to the extent related to the deposit of assets in escrow in connection with (i) the
writing of covered put and call options, (ii) the purchase of securities on a forward-commitment or
delayed-delivery basis, and (iii) collateral and initial or variation margin arrangements with respect to
currency transactions, options, futures contracts, including those relating to indices, and options on futures
contracts or indices.
5. Make short sales of portfolio securities or purchase any portfolio securities on margin, except for
such short-term credits as are necessary for the clearance of transactions. The deposit or payment by the Fund
of initial or variation margin in connection with futures or options transactions is not considered to be a
securities purchase on margin. The Fund may engage in short sales if, at the time of the short sale, the Fund
owns or has the right to acquire an equal amount of the security being sold at no additional cost ("selling
against the box").
ASAF ALLIANCE GROWTH FUND:
Investment Objective: The Fund's investment objective is to seek long-term growth of capital by investing
predominantly in the equity securities (common stocks, securities convertible into common stocks and rights and
warrants to subscribe for or purchase common stocks) of a limited number of large, carefully selected,
high-quality U.S. companies that, in the judgment of the Fund's Sub-advisor, are likely to achieve superior
earnings growth.
Investment Policies:
The Sub-advisor's research staff generally follows a primary research universe of approximately 500
companies that are considered by the Sub-advisor to have strong management, superior industry positions,
excellent balance sheets and the ability to demonstrate superior earnings growth. As one of the largest
multi-national investment firms, the Sub-advisor has access to considerable information concerning all of the
companies followed, an in-depth understanding of the products, services, markets and competition of these
companies and a good knowledge of the managements of most of the companies in its research universe.
The Sub-advisor's analysts prepare their own earnings estimates and financial models for each company
followed. While each analyst has responsibility for following companies in one or more identified sectors and/or
industries, the lateral structure of the Sub-advisor's research organization and constant communication among the
analysts result in decision-making based on the relative attractiveness of stocks among industry sectors. The
focus during this process is on the early recognition of change on the premise that value is created through the
dynamics of changing company, industry and economic fundamentals. Research emphasis is placed on the
identification of companies whose substantially above average prospective earnings growth is not fully reflected
in current market valuations.
The Sub-advisor continually reviews its primary research universe of approximately 500 companies to
maintain a list of favored securities, the "Alliance 100," considered by the Sub-advisor to have the most clearly
superior earnings potential and valuation attraction. The Sub-advisor's concentration on a limited universe of
companies allows it to devote its extensive resources to constant intensive research of these companies.
Companies are constantly added to and deleted from the Alliance 100 as their fundamentals and valuations change.
The Sub-advisor's Large Cap Growth Group, in turn, further refines, on a weekly basis, the selection process for
the Fund with each portfolio manager in the Group selecting 25 such companies that appear to the manager most
attractive at current prices. These individual ratings are then aggregated and ranked to produce a composite
list of the 25 most highly regarded stocks, the "Favored 25." Approximately 70% of the Fund's net assets will
usually be invested in the Favored 25 with the balance of the Fund's investment portfolio consisting principally
of other stocks in the Alliance 100. Fund emphasis upon particular industries or sectors is a by-product of the
stock selection process rather than the result of assigned targets or ranges.
The Sub-advisor expects the average weighted market capitalization of companies represented in the Fund
(i.e., the number of a company's shares outstanding multiplied by the price per share) to normally be in the
range of or exceed the average weighted market capitalization of companies comprising the Standard & Poor's 500
Composite Stock Price Index, a widely recognized unmanaged index of market activity based upon the aggregate
performance of a selected portfolio of publicly traded stocks, including monthly adjustments to reflect the
reinvestment of dividends and distributions. Investments will be made upon their potential for capital
appreciation.
Convertible Securities. The Fund may invest in convertible securities, which are convertible at a
stated exchange rate into common stock. Prior to their conversion, convertible securities have the same general
characteristics as non-convertible debt securities, as they provide a stable stream of income with generally
higher yields than those of equity securities of the same or similar issuers. As with all debt securities, the
market value of convertible securities tends to decline as interest rates increase and, conversely, to increase
as interest rates decline. Convertible securities generally offer lower interest or dividend yields than
non-convertible debt securities of similar quality. However, when the market price of the common stock
underlying a convertible security increases, the price of the convertible security increasingly reflects the
value of the underlying common stock and may rise accordingly. As the market price of the underlying common
stock declines, the convertible security tends to trade increasingly on a yield basis, and thus may not
depreciate to the same extent as the underlying common stock. Convertible securities rank senior to common
stocks on an issuer's capital structure. They are consequently of higher quality and entail less risk than the
issuer's common stock, although the extent to which such risk is reduced depends in large measure upon the degree
to which the convertible security sells above its value as a fixed income security. The Fund may invest up to
20% of its net assets in the convertible securities of companies whose common stocks are eligible for purchase by
the Fund under the investment policies described above. Additional information about convertible securities is
included in the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Rights and Warrants. The Fund may invest up to 5% of its net assets in rights or warrants, but will do
so only if the equity securities themselves are deemed appropriate by the Sub-advisor for inclusion in the Fund.
Rights and warrants may be more speculative than certain other types of investments in that they do not entitle a
holder to dividends or voting rights with respect to the securities which may be purchased nor do they represent
any rights in the assets of the issuing company. Also, the value of a right or warrant does not necessarily
change with the value of the underlying securities. Additional information about warrants is included in the
Trust's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest up to 15% of the value of its total assets in securities of
foreign issuers whose common stocks are eligible for purchase by the Fund under the investment policies described
above. For purposes of the Fund, foreign issuers are companies that (i) are organized outside the United States,
(ii) have their principal place of business outside the United States, and (iii) issue securities that are traded
principally in a foreign country. Companies that do not fall within this definition shall be deemed to be U.S.
companies. Additional information about foreign securities and their risks is included in this Statement and the
Trust's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Options and Futures:
While the Fund does not anticipate utilizing them on a regular basis, the Fund may from time to time may
engage in options and futures transactions as described below. Additional information about option, futures and
their risks is included in this Statement and the Trust's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods."
Options on Securities. The Fund may write exchange-traded call options on common stocks, and may
purchase and sell exchange-traded call and put options on common stocks written by others or combinations
thereof. The Fund will not write put options.
Generally, the opportunity for profit from the writing of options is higher, and consequently the risks
are greater, when the stocks involved are lower priced or volatile, or both. While an option that has been
written is in force, the maximum profit that may be derived from the optioned stock is the premium less brokerage
commissions and fees. The Fund will not write a call unless the Fund at all times during the option period owns
either (a) the optioned securities or has an absolute and immediate right to acquire that security without
additional cash consideration (or for additional cash consideration held in a segregated account by its
custodian) upon conversion or exchange of other securities held in its portfolio or (b) a call option on the same
security and in the same principal amount as the call written where the exercise price of the call held (i) is
equal to or less than the exercise price of the call written or (ii) is greater than the exercise price of the
call written if the difference is maintained by the Fund in liquid assets in a segregated account with its
Custodian.
Premiums received by the Fund in connection with writing call options will vary widely. Commissions,
stock transfer taxes and other expenses of the Fund must be deducted from such premium receipts. Calls written
by the Fund will ordinarily be sold either on a national securities exchange or through put and call dealers,
most, if not all, of whom are members of a national securities exchange on which options are traded, and will be
endorsed or guaranteed by a member of a national securities exchange or qualified broker-dealer, which may be
Sanford C. Bernstein & Co, LLC, an affiliate of the Sub-advisor. The endorsing or guaranteeing firm requires
that the option writer (in this case the Fund) maintain a margin account containing either corresponding stock or
other equity as required by the endorsing or guaranteeing firm.
The Fund will not sell a call option written by it if, as a result of the sale, the aggregate of the
Fund's portfolio securities subject to outstanding call options (valued at the lower of the option price or
market value of such securities) would exceed 15% of the Fund's total assets.
The Fund may purchase or write options on securities of the types in which it is permitted to invest in
privately negotiated (i.e., over-the-counter) transactions. The Sub-advisor has adopted procedures for
monitoring the creditworthiness of financial institutions with which over-the-counter options transactions are
effected.
In buying a call, the Fund would be in a position to realize a gain if, during the option period, the
price of the shares increased by an amount in excess of the premium paid and commissions payable on exercise. It
would realize a loss if the price of the security declined or remained the same or did not increase during the
period by more than the amount of the premium and commissions payable on exercise. In buying a put, the Fund
would realize a loss if the price of the security increased or remained the same or did not decrease during that
period by more than the amount of the premium and commissions payable on exercise. In addition, the Fund could
realize a gain or loss on such options by selling them.
The aggregate cost of all outstanding options purchased and held by the Fund, including options on
market indices as described below, will at no time exceed 10% of the Fund's total assets.
Options on Market Indices. The Fund may purchase and sell exchange-traded index options. Through the
purchase of listed index options, the portfolio could achieve many of the same objectives as through the use of
options on individual securities. Price movements in the Fund's securities probably will not correlate perfectly
with movements in the level of the index and, therefore, the Fund would bear a risk of loss on index options
purchased by it if favorable price movements of the hedged portfolio securities do not equal or exceed losses on
the options or if adverse price movements of the hedged portfolio securities are greater than gains realized from
the options.
Stock Index Futures. The Fund may purchase and sell stock index futures contracts. A stock index
futures contract is a bilateral agreement pursuant to which two parties agree to take or make delivery of an
amount of liquid assets equal to a specified dollar amount multiplied by the difference between the stock index
value at the close of the last trading day of the contract and the price at which the futures contract is
originally struck. No physical delivery of the underlying stocks in the index is made. The Fund will not
purchase or sell options on stock index futures contracts.
The Fund may not purchase or sell a stock index future if, immediately thereafter, more than 30% of its
total assets would be hedged by stock index futures. The Fund may not purchase or sell a stock index future if,
immediately thereafter, the sum of the amount of margin deposits on the Fund's existing futures positions would
exceed 5% of the market value of the Fund's total assets.
Currently, stock index futures contracts can be purchased or sold with respect to the Standard & Poor's
500 Stock Index on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, the New York Stock Exchange Composite Index on the New York
Futures Exchange and the Value Line Stock Index on the Kansas City Board of Trade. The Sub-advisor does not
believe that differences in composition of the three indices will create any differences in the price movements
of the stock index futures contracts in relation to the movements in such indices. However, such differences in
the indices may result in differences in correlation of the futures contracts with movements in the value of the
securities being hedged. The Fund reserves the right to purchase or sell stock index futures contracts that may
be created in the future.
The nature of initial margin in futures transactions is different from that of margin in security
transactions in that futures contract margin does not involve the borrowing of funds to finance transactions.
Rather, the initial margin is in the nature of a performance bond or good faith deposit on the contract which is
returned to the Fund upon termination of the futures contract, assuming all contractual obligations have been
satisfied.
There are several risks in connection with the use of stock index futures by the Fund as a hedging
device. One risk arises because of the imperfect correlation between movements in the price of the stock index
futures and movements in the price of the securities which are the subject of the hedge. The price of the stock
index futures may move more than or less than the price of the securities being hedged. If the price of the
stock index futures moves less than the price of the securities which are the subject of the hedge, the hedge
will not be fully effective but, if the price of the securities being hedged has moved in an unfavorable
direction, the Fund would be in a better position than if it had not hedged at all. If the price of the
securities being hedged has moved in a favorable direction, this advantage will be partially offset by the loss
on the index future. If the price of the future moves more than the price of the stock, the Fund will experience
either a loss or gain on the future which will not be completely offset by movements in the price of the
securities which are the subject of the hedge. To compensate for the imperfect correlation of movements in the
price of securities being hedged and movements in the price of the stock index futures, the Fund may buy or sell
stock index futures contracts in a greater dollar amount than the dollar amount of securities being hedged if the
volatility over a particular time period of the prices of such securities has been greater than the volatility
over such time period for the index, or if otherwise deemed to be appropriate by the Sub-advisor. Conversely,
the Fund may buy or sell fewer stock index futures contracts if the volatility over a particular time period of
the prices of the securities being hedged is less than the volatility over such time period of the stock index,
or if otherwise deemed to be appropriate by the Sub-advisor.
Where futures are purchased to hedge against a possible increase in the price of stock before the Fund
is able to invest its cash (or cash equivalents) in stocks (or options) in an orderly fashion, it is possible
that the market may decline instead. If the Sub-advisor then concludes not to invest in stock or options at that
time because of concern as to possible further market decline or for other reasons, the Fund will realize a loss
on the futures contract that is not offset by a reduction in the price of securities purchased.
The Fund's Sub-advisor intends to purchase and sell futures contracts on the stock index for which it
can obtain the best price with due consideration to liquidity.
Portfolio Turnover. The Fund's investment policies as described above are based on the Sub-advisor's
assessment of fundamentals in the context of changing market valuations. Therefore, they may under some
conditions involve frequent purchases and sales of shares of a particular issuer as well as the replacement of
securities. The Sub-advisor expects that more of its portfolio turnover will be attributable to increases and
decreases in the size of particular portfolio positions rather than to the complete elimination of a particular
issuer's securities from the Fund. For more information on portfolio turnover, see this SAI and the Company's
Prospectus under "Portfolio Turnover."
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
applicable to the ASAF Alliance Growth Fund. These limitations are not "fundamental" restrictions and may be
changed without shareholder approval. The Fund will not:
1. Invest in companies for the purpose of exercising control;
2. Purchase the securities of any other investment company or investment trust, except in
compliance with the 1940 Act;
3. Invest in interests in oil, gas or other mineral exploration or development programs, except
that it may purchase and sell securities of companies that deal in oil, gas or other mineral exploration or
development programs;
4. Make short sales of securities or purchase securities on margin except for such short-term
credits as may be necessary for the clearance of transactions;
5. Purchase illiquid securities if immediately after such investment more than 15% of the Fund's
net assets (taken at market value) would be so invested;
Whenever any investment restriction states a maximum percentage of the Fund's assets which may be invested in any
security or other asset, it is intended that such percentage be determined immediately after and as a result of
the Fund's acquisition of such securities or other assets. Accordingly, any later increase or decrease in
percentage beyond the specified limitation resulting from changes in values or net assets will not be considered
a violation of any such maximum.
ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth. Realization of income is
not an investment objective and any income realized on the Fund's investments, therefore, will be incidental to
the Fund's objective.
Investment Policies:
Futures, Options and Other Derivative Instruments. The Fund may enter into futures contracts on
securities, financial indices, and foreign currencies and options on such contracts, and may invest in options on
securities, financial indices and foreign currencies and forward contracts. The Fund will not use futures
contracts and options for leveraging purposes. The Fund will not enter into any futures contracts or options on
futures contracts if the aggregate amount of the Fund's commitments under outstanding futures contract positions
and options on futures contracts written by the Fund would exceed the market value of the total assets of the
Fund. The Fund may invest in forward currency contracts with stated values of up to the value of the Fund's
assets.
The Fund may buy or write options in privately negotiated transactions on the types of securities and on
indices based on the types of securities in which the Fund is permitted to invest directly. The Fund will effect
such transactions only with investment dealers and other financial institutions (such as commercial banks or
savings and loan institutions) deemed creditworthy by the Sub-advisor, and only pursuant to procedures adopted by
the Sub-advisor for monitoring the creditworthiness of those entities. To the extent that an option bought or
written by the Fund in a negotiated transaction is illiquid, the value of an option bought or the amount of the
Fund's obligations under an option written by the Fund, as the case may be, will be subject to the Fund's
limitation on illiquid investments. In the case of illiquid options, it may not be possible for the Fund to
effect an offsetting transaction at a time when the Sub-advisor believes it would be advantageous for the Fund to
do so. For a description of these strategies and instruments and certain risks involved therein, see this SAI
and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Interest Rate Swaps and Purchasing and Selling Interest Rate Caps and Floors. In addition to the
strategies noted above, the Fund, in order to attempt to protect the value of its investments from interest rate
or currency exchange rate fluctuations, may enter into interest rate swaps and may buy or sell interest rate caps
and floors. The Fund expects to enter into these transactions primarily to preserve a return or spread on a
particular investment or portion of its investments. The Fund also may enter into these transactions to protect
against any increase in the price of securities the Fund may consider buying at a later date. The Fund does not
intend to use these transactions as speculative investments. Interest rate swaps involve the exchange by the
Fund with another party of their respective commitments to pay or receive interest, e.g., an exchange of floating
rate payments for fixed rate payments. The exchange commitments can involve payments to be made in the same
currency or in different currencies. The purchase of an interest rate cap entitles the purchaser, to the extent
that a specified index exceeds a predetermined interest rate, to receive payments of interest on a contractually
based principal amount from the party selling the interest rate cap. The purchase of an interest rate floor
entitles the purchaser, to the extent that a specified index falls below a predetermined interest rate, to
receive payments of interest on a contractually based principal amount from the party selling the interest rate
floor.
The Fund may enter into interest rate swaps, caps and floors on either an asset-based or liability-based
basis, depending upon whether it is hedging its assets or its liabilities, and will usually enter into interest
rate swaps on a net basis, i.e., the two payment streams are netted out, with the Fund receiving or paying, as
the case may be, only the net amount of the two payments. The net amount of the excess, if any, of the Fund's
obligations over its entitlements with respect to each interest rate swap will be calculated on a daily basis and
an amount of cash or other liquid assets having an aggregate net asset value at least equal to the accrued excess
will be maintained in a segregated account by the Fund's custodian. If the Fund enters into an interest rate
swap on other than a net basis, the Fund would maintain a segregated account in the full amount accrued on a
daily basis of the Fund's obligations with respect to the swap. The Fund will not enter into any interest rate
swap, cap or floor transaction unless the unsecured senior debt or the claims-paying ability of the other party
thereto is rated in one of the three highest rating categories of at least one nationally recognized statistical
rating organization at the time of entering into such transaction. The Sub-advisor will monitor the
creditworthiness of all counterparties on an ongoing basis. If there is a default by the other party to such a
transaction, the Fund will have contractual remedies pursuant to the agreements related to the transaction.
The swap market has grown substantially in recent years with a large number of banks and investment
banking firms acting both as principals and as agents utilizing standardized swap documentation. The Sub-advisor
has determined that, as a result, the swap market has become relatively liquid. Caps and floors are more recent
innovations for which standardized documentation has not yet been developed and, accordingly, they are less
liquid than swaps. To the extent the Fund sells (i.e., writes) caps and floors, it will maintain in a segregated
account cash or other liquid assets having an aggregate net asset value at least equal to the full amount,
accrued on a daily basis, of the Fund's obligations with respect to any caps or floors.
There is no limit on the amount of interest rate swap transactions that may be entered into by the
Fund. These transactions may in some instances involve the delivery of securities or other underlying assets by
the Fund or its counterparty to collateralize obligations under the swap. Under the documentation currently used
in those markets, the risk of loss with respect to interest rate swaps is limited to the net amount of the
payments that the Fund is contractually obligated to make. If the other party to an interest rate swap that is
not collateralized defaults, the Fund would risk the loss of the net amount of the payments that the Fund
contractually is entitled to receive. The Fund may buy and sell (i.e., write) caps and floors without
limitation, subject to the segregated account requirement described above. For an additional discussion of these
strategies, see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Reverse Repurchase Agreements. Subject to guidelines promulgated by the Board of Directors of the
Company, the Fund may enter into reverse repurchase agreements. For a description of these investment
techniques, see the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
High-Yield/High-Risk Securities. High-yield/high-risk securities (or "junk" bonds) are debt securities
rated below investment grade by the primary rating agencies such as Standard & Poor's Rating Services ("Standard
& Poor's") and Moody's Investors Service, Inc. ("Moody's"). The Fund will not invest more than 5% of its total
assets in high-yield/high risk and mortgage- and asset-backed securities.
The value of lower quality securities generally is more dependent on the ability of the issuer to meet
interest and principal payments (i.e. credit risk) than is the case for higher quality securities. Conversely,
the value of higher quality securities may be more sensitive to interest rate movements than lower quality
securities. The Fund will not purchase debt securities rated below "CCC-" by Standard & Poor's or "Caa" by
Moody's. The Fund may also purchase unrated bonds of foreign and domestic issuers. For an additional discussion
of high-yield/high-risk and mortgage- and asset-backed securities, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus
under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Zero Coupon, Pay-in-Kind, and Step Coupon Bonds. The Fund may purchase zero coupon, pay-in-kind, and
step coupon bonds. Zero coupon bonds are debt securities that do not pay periodic interest, but are issued at a
discount from their face value. The discount approximates the total amount of interest the security will accrue
from the date of issuance to maturity. Pay-in-kind bonds normally give the issuer the option to pay cash at a
coupon payment date or give the holder of the security a similar bond with the same coupon rate and a face value
equal to the amount of the coupon payment that would have been made. Step coupon bonds begin to pay coupon
interest, or pay an increased rate of interest, at some time after they are issued. The discount at which step
coupon bonds trade depends on the time remaining until cash payments begin, prevailing interest rates, the
liquidity of the security and the perceived credit quality of the issuer. The market value of zero coupon,
pay-in-kind and step coupon bonds generally will fluctuate more in response to changes in interest rates than
will conventional interest-paying securities with comparable maturities. For an additional discussion of zero
coupon securities, see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
applicable to the ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund. These limitations are not "fundamental" restrictions, and
may be changed by the Directors without shareholder approval.
1. The Fund does not currently intend to sell securities short, unless it owns or has the right to
obtain securities equivalent in kind and amount to the securities sold short without the payment of any
additional consideration therefor, and provided that transactions in futures, options, swaps and forward
contracts are not deemed to constitute selling securities short.
2. The Fund does not currently intend to purchase securities on margin, except that the Fund may
obtain such short-term credits as are necessary for the clearance of transactions, and provided that margin
payments and other deposits in connection with transactions in futures, options, swaps and forward contracts
shall not be deemed to constitute purchasing securities on margin.
3. The Fund may not mortgage or pledge any securities owned or held by the Fund in amounts that
exceed, in the aggregate, 15% of the Fund's net asset value, provided that this limitation does not apply to (i)
reverse repurchase agreements; (ii) deposits of assets on margin; (iii) guaranteed positions in futures, options,
swaps or forward contracts; or (iv) the segregation of assets in connection with such contracts.
4. The Fund does not currently intend to purchase any securities or enter into a repurchase
agreement if, as a result, more than 15% of its net assets would be invested in repurchase agreements not
entitling the holder to payment of principal and interest within seven days and in securities that are illiquid
by virtue of legal or contractual restrictions on resale or the absence of a readily available market. The
Directors of the Company, or the Sub-advisor acting pursuant to authority delegated by the Directors, may
determine that a readily available market exists for securities eligible for resale pursuant to Rule 144A under
the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or any successor to such rule, and Section 4(2) commercial paper.
Accordingly, such securities may not be subject to the foregoing limitation.
5. The Fund may not invest in companies for the purpose of exercising control or management.
ASAF Janus Capital Growth Fund:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek growth of capital. Realization of income
is not a significant investment consideration and any income realized on the Fund's investments, therefore, will
be incidental to the Fund's objective.
Investment Policies:
Corporate Bonds and Debentures. The Fund may purchase corporate bonds and debentures, including bonds
rated below investment grade. The Fund will not invest more than 35% of its net assets in bonds rated below
investment grade by the primary rating agencies. For a discussion of lower rated securities, see this SAI and
the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Futures, Options and Other Derivative Instruments. The Fund may enter into futures contracts on
securities, financial indices, and foreign currencies and options on such contracts, and may invest in options on
securities, financial indices and foreign currencies, forward contracts and swaps. The Fund will not enter into
any futures contracts or options on futures contracts if the aggregate amount of the Fund's commitments under
outstanding futures contract positions and options on futures contracts written by the Fund would exceed the
market value of the total assets of the Fund (i.e., no leveraging). The Fund may invest in forward currency
contracts with stated values of up to the value of the Fund's assets.
The Fund may buy or write options in privately negotiated transactions on the types of securities and
indices based on the types of securities in which the Fund is permitted to invest directly. The Fund will effect
such transactions only with investment dealers and other financial institutions (such as commercial banks or
savings and loan institutions) deemed creditworthy by the Sub-advisor, and only pursuant to procedures adopted by
the Sub-advisor for monitoring the creditworthiness of those entities. To the extent that an option bought or
written by the Fund in a negotiated transaction is illiquid, the value of an option bought or the amount of the
Fund's obligations under an option written by the Fund, as the case may be, will be subject to the Fund's
limitation on illiquid investments. In the case of illiquid options, it may not be possible for the Fund to
effect an offsetting transaction at a time when the Sub-advisor believes it would be advantageous for the Fund to
do so. For a description of these strategies and instruments and certain risks involved therein, see this SAI
and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Interest Rate Swaps and Purchasing and Selling Interest Rate Caps and Floors. In addition to the
strategies noted above, the Fund, in order to attempt to protect the value of its investments from interest rate
or currency exchange rate fluctuations, may enter into interest rate swaps and may buy or sell interest rate caps
and floors. The Fund expects to enter into these transactions primarily to preserve a return or spread on a
particular investment or portion of its investments. The Fund also may enter into these transactions to protect
against any increase in the price of securities the Fund may consider buying at a later date. The Fund does not
intend to use these transactions as a speculative investments. Interest rate swaps involve the exchange by the
Fund with another party of their respective commitments to pay or receive interest, e.g., an exchange of floating
rate payments for fixed rate payments. The exchange commitments can involve payments to be made in the same
currency or in different currencies. The purchase of an interest rate cap entitles the purchaser, to the extent
that a specified index exceeds a predetermined interest rate, to receive payments of interest on a contractually
based principal amount from the party selling the interest rate cap. The purchase of an interest rate floor
entitles the purchaser, to the extent that a specified index falls below a predetermined interest rate, to
receive payments of interest on a contractually based principal amount from the party selling the interest rate
floor.
The Fund may enter into interest rate swaps, caps and floors on either an asset-based or liability-based
basis, depending upon whether it is hedging its assets or its liabilities, and will usually enter into interest
rate swaps on a net basis, i.e., the two payment streams are netted out, with the Fund receiving or paying, as
the case may be, only the net amount of the two payments. The net amount of the excess, if any, of the Fund's
obligations over its entitlements with respect to each interest rate swap will be calculated on a daily basis and
an amount of cash or other liquid assets having an aggregate net asset value at least equal to the accrued excess
will be maintained in a segregated account by the Fund's custodian. If the Fund enters into an interest rate
swap on other than a net basis, the Fund would maintain a segregated account in the full amount accrued on a
daily basis of the Fund's obligations with respect to the swap. The Fund will not enter into any interest rate
swap, cap or floor transaction unless the unsecured senior debt or the claims-paying ability of the other party
thereto is rated in one of the three highest rating categories of at least one nationally recognized statistical
rating organization at the time of entering into such transaction. The Sub-advisor will monitor the
creditworthiness of all counterparties on an ongoing basis. If there is a default by the other party to such a
transaction, the Fund will have contractual remedies pursuant to the agreements related to the transaction.
The swap market has grown substantially in recent years with a large number of banks and investment
banking firms acting both as principals and as agents utilizing standardized swap documentation. The Sub-advisor
has determined that, as a result, the swap market has become relatively liquid. Caps and floors are more recent
innovations for which standardized documentation has not yet been developed and, accordingly, they are less
liquid than swaps. To the extent the Fund sells (i.e., writes) caps and floors, it will maintain in a segregated
account cash or other liquid assets having an aggregate net asset value at least equal to the full amount,
accrued on a daily basis, of the Fund's obligations with respect to any caps or floors.
There is no limit on the amount of interest rate swap transactions that may be entered into by the
Fund. These transactions may in some instances involve the delivery of securities or other underlying assets by
the Fund or its counterparty to collateralize obligations under the swap. Under the documentation currently used
in those markets, the risk of loss with respect to interest rate swaps is limited to the net amount of the
payments that the Fund is contractually obligated to make. If the other party to an interest rate swap that is
not collateralized defaults, the Fund would risk the loss of the net amount of the payments that the Fund
contractually is entitled to receive. The Fund may buy and sell (i.e., write) caps and floors without
limitation, subject to the segregated account requirement described above. For an additional discussion of these
strategies, see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Investment Company Securities. From time to time, the Fund may invest in securities of other investment
companies, subject to the provisions of Section 12(d)(1) of the 1940 Act. The Fund may invest in securities of
money market funds managed by the Sub-advisor subject to the terms of an exemptive order obtained by the
Sub-advisor and the funds that are advised or sub-advised by the Sub-advisor. Under such order, the Fund will
limit its aggregate investment in a money market fund managed by the Sub-advisor to the greater of (i) 5% of its
total assets or (ii) $2.5 million, although the Company's Board of Directors may increase this limit up to 25% of
the Company's total assets.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements. Subject to guidelines promulgated by the Directors of the Company, the
Fund may enter into reverse repurchase agreements. Pursuant to an exemptive order granted by the SEC, the Fund
and other funds advised or sub-advised by the Sub-Advisor may invest in repurchase agreements and other money
market instruments through a joint trading account. For a description of these investment techniques, see the
Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Other Income-Producing Securities. Other types of income producing securities that the Fund may
purchase include, but are not limited to, the following types of securities:
Variable and Floating Rate Obligations. These types of securities are relatively long-term
instruments that often carry demand features permitting the holder to demand payment of principal at any time or
at specified intervals prior to maturity.
Standby Commitments. These instruments, which are similar to a put, give the Fund the option to
obligate a broker, dealer or bank to repurchase a security held by that Fund at a specified price.
Tender Option Bonds. Tender option bonds are relatively long-term bonds that are coupled with
the agreement of a third party (such as a broker, dealer or bank) to grant the holders of such securities the
option to tender the securities to the institution at periodic intervals.
Inverse Floaters. Inverse floaters are debt instruments whose interest bears an inverse
relationship to the interest rate on another security. The Fund will not invest more than 5% of its assets in
inverse floaters. The Fund will purchase standby commitments, tender option bonds and instruments with demand
features primarily for the purpose of increasing the liquidity of the Fund.
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
not "fundamental" investment restrictions and may be changed by the Directors of the Company without shareholder
approval. The Fund will not:
1. Purchase a security if as a result, more than 15% of its net assets in the aggregate, at market
value, would be invested in securities which cannot be readily resold because of legal or contractual
restrictions on resale or for which there is no readily available market, or repurchase agreements maturing in
more than seven days or securities used as a cover for written over-the-counter options, if any. The Directors
of the Company, the Investment Manager or the Sub-advisor acting pursuant to authority delegated by the
Directors, may determine that a readily available market exists for securities eligible for resale pursuant to
Rule 144A under the Securities Act of 1933, or any successor to such rule, and therefore that such securities are
not subject to the foregoing limitation;
2. Enter into any futures contracts or options on futures contracts for purposes other than bona
fide hedging transactions (as defined by the CFTC) if as a result the sum of the initial margin deposits and
premium required to establish positions in futures contracts and related options that do not fall within the
definition of bona fide hedging transactions would exceed 5% of the fair market value of the Fund's net assets;
3. Enter into any futures contracts if the aggregate amount of the Fund's commitments under
outstanding futures contracts positions of the Fund would exceed the market value of the total assets of the Fund;
4. Sell securities short, unless it owns or has the right to obtain securities equivalent in kind
and amount to the securities sold short, and provided that transactions in options, swaps and forward futures
contracts are not deemed to constitute selling securities short;
5. Mortgage or pledge any securities owned or held by the Fund in amounts that exceed, in the
aggregate, 15% of the Fund's net asset value, provided that this limitation does not apply to reverse repurchase
agreements or in the case of assets deposited to margin or guarantee positions in futures, options, swaps or
forward contracts or placed in a segregated account in connection with such contracts;
6. Invest in companies for the purpose of exercising management or control;
7. Purchase securities of open-end or closed-end investment companies except in compliance with
the Investment Company Act of 1940 or the conditions of any order of exemption from the SEC regarding the
purchase of securities of money market funds managed by the Sub-advisor or its affiliates; or
8. Purchase securities on margin, except (i) for use of short-term credit necessary for clearance
of purchases of portfolio securities and (ii) the Fund may make margin deposits in connection with futures
contracts or other permissible investments.
ASAF T. ROWE PRICE TAX MANAGED FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek attractive long-term capital appreciation
on an after tax basis. The Fund will normally invest primarily in common stocks. Assets of the Fund invested in
equity securities will be subject to all of the risks of investing in the stock market.
Investment Policies:
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest up to 25% of its total assets (excluding reserves) in U.S.
dollar-denominated and non-U.S. dollar-denominated securities of foreign issuers. These include
nondollar-denominated securities traded outside of the U.S. and dollar-denominated securities of foreign issuers
traded in the U.S. (such as ADRs). Such investments increase a portfolio's diversification and may enhance
return, but they also involve some special risks, such as exposure to potentially adverse local, political, and
economic developments; nationalization and exchange controls; potentially lower liquidity and higher volatility;
possible problems arising from accounting, disclosure, settlement, and regulatory practices that differ from U.S.
standards; and the chance that fluctuations in foreign exchange rates will decrease the investment's value
(favorable changes can increase its value). These risks are heightened for investments in developing countries,
and there is no limit on the amount of fund foreign investments that may be made in such countries.
Hybrid Instruments. Hybrid Instruments (a type of potentially high-risk derivative) can combine the
elements of futures contracts or options with those of debt, preferred equity, or a depository instrument
(hereinafter "Hybrid Instruments"). Thus, Hybrid Instruments may take a variety of forms, including, but not
limited to, debt instruments with interest or principal payments or redemption terms determined by reference to
the value of a currency or commodity or securities index at a future point in time, preferred stock with dividend
rates determined by reference to the value of a currency, or convertible securities with the conversion terms
related to a particular commodity. Hybrids can have volatile prices and limited liquidity and their use may be
unsuccessful. The Fund may invest up to 10% of its total assets in hybrid instruments.
For a discussion of certain risks involved in investing in hybrid instruments see this SAI under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Warrants. The Fund may acquire warrants. For a discussion of certain risks involved therein, see this
SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Futures Contracts:
Transactions in Futures. Futures contracts are a type of potentially high-risk derivative. The Fund
may enter into futures contracts including stock index, interest rate, and currency futures ("futures" or
"futures contracts").
Stock index futures contracts may be used to provide a hedge for a portion of the Fund's portfolio, as a
cash management tool, or as an efficient way for the Sub-advisor to implement either an increase or decrease in
portfolio market exposure in response to changing market conditions. The Fund may purchase or sell futures
contracts with respect to any stock index. Nevertheless, to hedge the Fund's portfolio successfully, the Fund
must sell futures contacts with respect to indices or subindices whose movements will have a significant
correlation with movements in the prices of the Fund's portfolio securities.
Interest rate or currency futures contracts may be used as a hedge against changes in prevailing levels
of interest rates or currency exchange rates in order to establish more definitely the effective return on
securities or currencies held or intended to be acquired by the Fund. In this regard, the Fund could sell
interest rate or currency futures as an offset against the effect of expected increases in interest rates or
currency exchange rates and purchase such futures as an offset against the effect of expected declines in
interest rates or currency exchange rates.
The Fund will enter into futures contracts which are traded on national and foreign futures exchanges,
and are standardized as to maturity date and underlying financial instrument. Futures exchanges and trading in
the United States are regulated under the Commodity Exchange Act by the CFTC. Although techniques other than the
sale and purchase of futures contracts could be used for the above-referenced purposes, futures contracts offer
an effective and relatively low cost means of implementing the Fund's objectives in these areas.
Regulatory Limitations. If the Fund purchases or sells futures contracts or related options which do not
qualify as bona fide hedging under applicable CFTC rules, the aggregate initial margin deposits and premium
required to establish those positions cannot exceed 5% of the liquidation value of the Fund after taking into
account unrealized profits and unrealized losses on any such contracts it has entered into; provided, however,
that in the case of an option that is in-the-money at the time of purchase, the in-the-money amount may be
excluded in calculating the 5% limitation. For purposes of this policy, options on futures contracts and foreign
currency options traded on a commodities exchange will be considered "related options." This policy may be
modified by the Directors of the Company without a shareholder vote and does not limit the percentage of the
Fund's assets at risk to 5%.
In instances involving the purchase of futures contracts or the writing of call or put options thereon
by the Fund, an amount of cash, liquid assets, or other suitable cover as permitted by the SEC, equal to the
market value of the futures contracts and options thereon (less any related margin deposits), will be identified
by the Fund to cover the position, or alternative cover (such as owning an offsetting position) will be
employed. Assets used as cover or held in an identified account cannot be sold while the position in the
corresponding option or future is open, unless they are replaced with similar assets. As a result, the
commitment of a large portion of the Fund's assets to cover or identified accounts could impede portfolio
management or the Fund's ability to meet redemption requests or other current obligations.
Options on Futures Contracts. The Fund may purchase and sell options on the same types of futures in
which it may invest. Writing a put option on a futures contract serves as a partial hedge against an increase in
the value of securities the Fund intends to acquire. If the futures price at expiration of the option is above
the exercise price, the Fund will retain the full amount of the premium which provides a partial hedge against
any increase that may have occurred in the price of the securities the Fund intends to acquire. If the futures
price when the option is exercised is below the exercise price, however, the Fund will incur a loss, which may be
wholly or partially offset by the decrease in the price of the securities the Fund intends to acquire.
As an alternative to writing or purchasing call and put options on stock index futures, the Fund may
write or purchase call and put options on stock indices. Such options would be used in a manner similar to the
use of options on futures contracts. From time to time a single order to purchase or sell futures contracts (or
options thereon) may be made on behalf of the Fund and other funds. Such aggregated orders would be allocated
among the Fund and the other funds in a fair and non-discriminatory manner. See this SAI and Company's
Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods" for a description of certain risks in options and
futures contracts.
Additional Futures and Options Contracts. Although the Fund has no current intention of engaging in
futures or options transactions other than those described above, it reserves the right to do so. Such futures
and options trading might involve risks which differ from those involved in the futures and options described
above.
Federal Tax Treatment of Options, Futures Contracts, and Forward Foreign Exchange Contracts. Although
the Fund invests almost exclusively in securities that generate income that is exempt from federal income taxes,
the Fund may enter into certain option, futures, and foreign exchange contracts, including options and futures on
currencies, which will be treated as Section 1256 contracts or straddles that are not exempt from such taxes.
Therefore, use of the investment techniques described above could result in taxable income to shareholders of the
Fund.
Transactions which are considered Section 1256 contracts will be considered to have been closed at the
end of the Fund's fiscal year and any gains or losses will be recognized for tax purposes at that time. Gains or
losses recognized from the normal closing or settlement of such transactions will be characterized as 60%
long-term capital gain or loss and 40% short-term capital gain or loss, without regard to the holding period of
the contract. The Fund will be required to distribute net gains on such transactions to shareholders even though
it may not have closed the transaction and received cash to pay such distributions.
Options, futures, and forward foreign exchange contracts, including options and futures on currencies,
which offset a foreign dollar-denominated bond or currency position may be considered straddles for tax purposes,
in which case a loss on any position in a straddle will be subject to deferral to the extent of unrealized gain
in an offsetting position. The holding period of the securities or currencies comprising the straddle will be
deemed not to begin until the straddle is terminated. The holding period of the security offsetting an
"in-the-money qualified covered call" option on an equity security will not include the period of time the option
is outstanding.
Losses on written covered calls and purchased puts on securities, excluding certain "qualified covered
call" options on equity securities, may be long-term capital losses, if the security covering the option was held
for more than 12 months prior to the writing of the option.
In order for the Fund to continue to qualify for federal income tax treatment as a regulated investment
company, at least 90% of its gross income for a taxable year must be derived from qualifying income, i.e.,
dividends, interest, income derived from loans of securities, and gains from the sale of securities or
currencies. Tax regulations could be issued limiting the extent that net gain realized from option, futures, or
foreign forward exchange contracts on currencies is qualifying income for purposes of the 90% requirement.
As a result of the "Taxpayer Relief Act of 1997," entering into certain options, futures contracts, or
forward contracts may result in the "constructive sale" of offsetting stocks or debt securities of the Fund.
Options on Securities
Writing Covered Call Options. The Fund may write (sell) American or European style "covered" call
options and purchase options to close out options previously written by the Fund. In writing covered call
options, the Fund expects to generate additional premium income which should serve to enhance the Fund's total
return and reduce the effect of any price decline of the security or currency involved in the option. Covered
call options will generally be written on securities or currencies which, in the Sub-advisor's opinion, are not
expected to have any major price increases or moves in the near future but which, over the long term, are deemed
to be attractive investments for the Fund.
The Fund generally will write only covered call options. This means that the Fund will either own the
security or currency subject to the option or an option to purchase the same underlying security or currency,
having an exercise price equal to or less than the exercise price of the "covered" option. From time to time,
the Fund will write a call option that is not covered as indicated above but where the Fund will establish and
maintain with its custodian for the term of the option, an account consisting of cash, U.S. government
securities, other liquid high-grade debt obligations, or other suitable cover as permitted by the SEC having a
value equal to the fluctuating market value of the optioned securities or currencies.
Portfolio securities or currencies on which call options may be written will be purchased solely on the
basis of investment considerations consistent with the Fund's investment objective. The writing of covered call
options is a conservative investment technique believed to involve relatively little risk (in contrast to the
writing of naked or uncovered options, which the Fund generally will not do), but capable of enhancing the Fund's
total return. When writing a covered call option, the Fund, in return for the premium, gives up the opportunity
for profit from a price increase in the underlying security or currency above the exercise price, but conversely
retains the risk of loss should the price of the security or currency decline. Unlike one who owns securities or
currencies not subject to an option, the Fund has no control over when it may be required to sell the underlying
securities or currencies, since it may be assigned an exercise notice at any time prior to the expiration of its
obligation as a writer. If a call option which the Fund has written expires, the Fund will realize a gain in the
amount of the premium; however, such gain may be offset by a decline in the market value of the underlying
security or currency during the option period. If the call option is exercised, the Fund will realize a gain or
loss from the sale of the underlying security or currency. The Fund does not consider a security or currency
covered by a call to be "pledged" as that term is used in the Fund's policy which limits the pledging or
mortgaging of its assets.
The premium received is the market value of an option. The premium the Fund will receive from writing a
call option will reflect, among other things, the current market price of the underlying security or currency,
the relationship of the exercise price to such market price, the historical price volatility of the underlying
security or currency, and the length of the option period. Once the decision to write a call option has been
made, the Sub-advisor, in determining whether a particular call option should be written on a particular security
or currency, will consider the reasonableness of the anticipated premium and the likelihood that a liquid
secondary market will exist for those options. The premium received by the Fund for writing covered call options
will be recorded as a liability of the Fund. This liability will be adjusted daily to the option's current
market value, which will be the latest sale price at the time at which the net asset value per share of the Fund
is computed (close of the New York Stock Exchange), or, in the absence of such sale, the latest asked price. The
option will be terminated upon expiration of the option, the purchase of an identical option in a closing
transaction, or delivery of the underlying security or currency upon the exercise of the option.
The Fund will realize a profit or loss from a closing purchase transaction if the cost of the
transaction is less or more than the premium received from the writing of the option. Because increases in the
market price of a call option will generally reflect increases in the market price of the underlying security or
currency, any loss resulting from the repurchase of a call option is likely to be offset in whole or in part by
appreciation of the underlying security or currency owned by the Fund.
The Fund will not write a covered call option if, as a result, the aggregate market value of all
portfolio securities or currencies covering written call or put options exceeds 25% of the market value of the
Fund's net assets. In calculating the 25% limit, the Fund will offset, against the value of assets covering
written calls and puts, the value of purchased calls and puts on identical securities or currencies with
identical maturity dates.
Writing Covered Put Options. The Fund may write American or European style covered put options and
purchase options to close out options previously written by the Fund.
The Fund would write put options only on a covered basis, which means that the Fund would maintain in a
segregated account cash, U.S. government securities, other liquid high-grade debt obligations, or other suitable
cover as determined by the SEC, in an amount not less than the exercise price or the Fund will own an option to
sell the underlying security or currency subject to the option having an exercise price equal to or greater than
the exercise price of the "covered" option at all times while the put option is outstanding. (The rules of a
clearing corporation currently require that such assets be deposited in escrow to secure payment of the exercise
price.)
The Fund would generally write covered put options in circumstances where the Sub-advisor wishes to
purchase the underlying security or currency for the Fund's portfolio at a price lower than the current market
price of the security or currency. In such event the Fund would write a put option at an exercise price which,
reduced by the premium received on the option, reflects the lower price it is willing to pay. Since the Fund
would also receive interest on debt securities or currencies maintained to cover the exercise price of the
option, this technique could be used to enhance current return during periods of market uncertainty. The risk in
such a transaction would be that the market price of the underlying security or currency would decline below the
exercise price less the premiums received. Such a decline could be substantial and result in a significant loss
to the Fund. In addition, the Fund, because it does not own the specific securities or currencies which it may be
required to purchase in exercise of the put, cannot benefit from appreciation, if any, with respect to such
specific securities or currencies.
The Fund will not write a covered put option if, as a result, the aggregate market value of all
portfolio securities or currencies covering put or call options exceeds 25% of the market value of the Fund's net
assets. In calculating the 25% limit, the Fund will offset, against the value of assets covering written puts
and calls, the value of purchased puts and calls on identical securities or currencies with identical maturity
dates.
Purchasing Put Options. The Fund may purchase American or European style put options. As the holder of
a put option, the Fund has the right to sell the underlying security or currency at the exercise price at any
time during the option period (American style) or at the expiration of the option (European style). The Fund may
enter into closing sale transactions with respect to such options, exercise them or permit them to expire. The
Fund may purchase put options for defensive purposes in order to protect against an anticipated decline in the
value of its securities or currencies.
The premium paid by the Fund when purchasing a put option will be recorded as an asset of the Fund.
This asset will be adjusted daily to the option's current market value, which will be the latest sale price at
the time at which the net asset value per share of the Fund is computed (close of New York Stock Exchange), or,
in the absence of such sale, the latest bid price. This asset will be terminated upon expiration of the option,
the selling (writing) of an identical option in a closing transaction, or the delivery of the underlying security
or currency upon the exercise of the option.
Purchasing Call Options. The Fund may purchase American or European style call options. As the holder
of a call option, the Fund has the right to purchase the underlying security or currency at the exercise price at
any time during the option period (American style) or at the expiration of the option (European style). The Fund
may enter into closing sale transactions with respect to such options, exercise them or permit them to expire.
The Fund may purchase call options for the purpose of increasing its current return or avoiding tax consequences
which could reduce its current return. The Fund may also purchase call options in order to acquire the
underlying securities or currencies.
The Fund will not commit more than 5% of its assets to premiums when purchasing call and put options.
The Fund may also purchase call options on underlying securities or currencies it owns in order to protect
unrealized gains on call options previously written by it. A call option would be purchased for this purpose
where tax considerations make it inadvisable to realize such gains through a closing purchase transaction. Call
options may also be purchased at times to avoid realizing losses.
Dealer (Over-the-Counter) Options. The Fund may engage in transactions involving dealer options.
Certain risks are specific to dealer options. While the Fund would look to a clearing corporation to exercise
exchange-traded options, if the Fund were to purchase a dealer option, it would rely on the dealer from whom it
purchased the option to perform if the option were exercised. Failure by the dealer to do so would result in the
loss of the premium paid by the Fund as well as loss of the expected benefit of the transaction. For a
discussion of dealer options, see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Lending of Portfolio Securities. Securities loans are made to broker-dealers, institutional investors,
or other persons, pursuant to agreements requiring that the loans be continuously secured by collateral at least
equal at all times to the value of the securities lent, marked to market on a daily basis. The collateral
received will consist of cash, U.S. government securities, letters of credit, or such other collateral as may be
permitted under its investment program. While the securities are being lent, the Fund will continue to receive
the equivalent of the interest or dividends paid by the issuer on the securities, as well as interest on the
investment of the collateral or a fee from the borrower. The Fund has a right to call each loan and obtain the
securities, within such period of time which coincides with the normal settlement period for purchases and sales
of such securities in the respective markets. The Fund will not have the right to vote on securities while they
are being lent, but it will call a loan in anticipation of any important vote. The risks in lending portfolio
securities, as with other extensions of secured credit, consist of possible delay in receiving additional
collateral or in the recovery of the securities or possible loss of rights in the collateral should the borrower
fail financially. Loans will only be made to firms deemed by the Sub-advisor to be of good standing and will not
be made unless, in the judgment of the Sub-advisor, the consideration to be earned from such loans would justify
the risk.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements. Although the Fund has no current intention of engaging in reverse
repurchase agreements, the Fund reserves the right to do so. Reverse repurchase agreements are ordinary
repurchase agreements in which the Fund is the seller of, rather than the investor in, securities, and agrees to
repurchase them at an agreed upon time and price. Use of a reverse repurchase agreement may be preferable to a
regular sale and later repurchase of the securities because it avoids certain market risks and transaction costs.
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
not "Fundamental" restrictions and may be changed by the Directors of the Company without shareholder approval.
The Fund will not:
1. Purchase additional securities when money borrowed exceeds 5% of its total assets;
2. Invest in companies for the purpose of exercising management or control;
3. Purchase a futures contract or an option thereon, if, with respect to positions in futures or
options on futures which do not represent bona fide hedging, the aggregate initial margin and premiums on such
options would exceed 5% of the Fund's net asset value;
4. Purchase illiquid securities if, as a result, more than 15% of its net assets would be invested in
such securities;
5. Purchase securities of open-end or closed-end investment companies except in compliance with the
Investment Company Act of 1940;
6. Purchase securities on margin, except (i) for use of short-term credit necessary for clearance of
purchases of portfolio securities and (ii) it may make margin deposits in connection with futures contracts or
other permissible investments;
7. Mortgage, pledge, hypothecate or, in any manner, transfer any security owned by the Fund as
security for indebtedness except as may be necessary in connection with permissible borrowings or investments and
then such mortgaging, pledging, or hypothecating may not exceed 33 1/3% of the Fund's total assets at the time of
borrowing or investment;
8. Purchase participations or other direct interests in, or enter into leases with respect to oil,
gas, or other mineral exploration or development programs if, as a result thereof, more than 5% of the value of
the total assets of the Fund would be invested in such programs;
9. Invest in puts, calls, straddles, spreads, or any combination thereof, except to the extent
permitted by the prospectus and Statement of Additional Information;
10. Effect short sales of securities; or
11. Invest in warrants if, as a result thereof, more than 10% of the value of the net assets of the
Fund would be invested in warrants.
ASAF ALLIANCE/BERNSTEIN 50/50 GROWTH + VALUE FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth by investing approximately
50% of its assets in growth stocks of large companies and 50% of its assets in value stocks of large companies.
Investment Policies:
Convertible Securities. The Fund may invest in convertible securities, which are convertible at a
stated exchange rate into common stock. Prior to their conversion, convertible securities have the same general
characteristics as non-convertible debt securities, as they provide a stable stream of income with generally
higher yields than those of equity securities of the same or similar issuers. As with all debt securities, the
market value of convertible securities tends to decline as interest rates increase and, conversely, to increase
as interest rates decline. Convertible securities generally offer lower interest or dividend yields than
non-convertible debt securities of similar quality. However, when the market price of the common stock
underlying a convertible security increases, the price of the convertible security increasingly reflects the
value of the underlying common stock and may rise accordingly. As the market price of the underlying common
stock declines, the convertible security tends to trade increasingly on a yield basis, and thus may not
depreciate to the same extent as the underlying common stock. Convertible securities rank senior to common
stocks on an issuer's capital structure. They are consequently of higher quality and entail less risk than the
issuer's common stock, although the extent to which such risk is reduced depends in large measure upon the degree
to which the convertible security sells above its value as a fixed income security. The Fund may invest up to
20% of the growth portion of its net assets in the convertible securities of companies whose common stocks are
eligible for purchase by the Fund under the investment policies described above. Additional information about
convertible securities is included in the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods."
Rights and Warrants. The Fund may invest up to 5% of the growth portion of its net assets in rights or
warrants, but will do so only if the equity securities themselves are deemed appropriate by the Sub-advisor for
inclusion in the Fund. Rights and warrants may be more speculative than certain other types of investments in
that they do not entitle a holder to dividends or voting rights with respect to the securities which may be
purchased nor do they represent any rights in the assets of the issuing company. Also, the value of a right or
warrant does not necessarily change with the value of the underlying securities. Additional information about
warrants is included in the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest up to 15% of the value of its total assets in foreign
securities. A foreign security is a security issued by a non-U.S. company which is defined as a company that (i)
is organized outside the United States; (ii) has their principal place of business outside the United States; and
(iii) issue securities traded principally in a foreign country. Companies that do not fall within the definition
of a non-U.S. company shall be considered a U.S. company for purposes of this definition. American Depository
Receipts (ADRs) are not considered foreign securities for the purposes of the 15% limitation on foreign
securities. Additional information about foreign securities and their risks is included in this Statement and
the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Options and Futures:
While the Fund does not anticipate utilizing them on a regular basis, the Fund may from time to time may engage
in options and futures transactions as described below. Additional information about option, futures and their
risks is included in this Statement and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods."
Options on Securities. The Fund may write exchange-traded call options on common stocks, and may
purchase and sell exchange-traded call and put options on common stocks written by others or combinations
thereof. The Fund will not write put options.
Generally, the opportunity for profit from the writing of options is higher, and consequently the risks
are greater, when the stocks involved are lower priced or volatile, or both. While an option that has been
written is in force, the maximum profit that may be derived from the optioned stock is the premium less brokerage
commissions and fees. The Fund will not write a call unless the Fund at all times during the option period owns
either (a) the optioned securities or has an absolute and immediate right to acquire that security without
additional cash consideration (or for additional cash consideration held in a segregated account by its
custodian) upon conversion or exchange of other securities held in its portfolio or (b) a call option on the same
security and in the same principal amount as the call written where the exercise price of the call held (i) is
equal to or less than the exercise price of the call written or (ii) is greater than the exercise price of the
call written if the difference is maintained by the Fund in liquid assets in a segregated account with its
Custodian.
Premiums received by the Fund in connection with writing call options will vary widely. Commissions,
stock transfer taxes and other expenses of the Fund must be deducted from such premium receipts. Calls written
by the Fund will ordinarily be sold either on a national securities exchange or through put and call dealers,
most, if not all, of whom are members of a national securities exchange on which options are traded, and will be
endorsed or guaranteed by a member of a national securities exchange or qualified broker-dealer. The endorsing or
guaranteeing firm requires that the option writer (in this case the Fund) maintain a margin account containing
either corresponding stock or other equity as required by the endorsing or guaranteeing firm.
The Fund will not sell a call option written by it if, as a result of the sale, the aggregate of the
Fund's portfolio securities subject to outstanding call options (valued at the lower of the option price or
market value of such securities) would exceed 15% of the growth portion of the Fund's total assets.
The Fund may purchase or write options on securities of the types in which it is permitted to invest in
privately negotiated (i.e., over-the-counter) transactions. The Sub-advisor has adopted procedures for
monitoring the creditworthiness of financial institutions with which over-the-counter options transactions are
effected.
In buying a call, the Fund would be in a position to realize a gain if, during the option period, the
price of the shares increased by an amount in excess of the premium paid and commissions payable on exercise. It
would realize a loss if the price of the security declined or remained the same or did not increase during the
period by more than the amount of the premium and commissions payable on exercise. In buying a put, the Fund
would realize a loss if the price of the security increased or remained the same or did not decrease during that
period by more than the amount of the premium and commissions payable on exercise. In addition, the Fund could
realize a gain or loss on such options by selling them.
The aggregate cost of all outstanding options purchased and held by the Fund, including options on
market indices as described below, will at no time exceed 10% of the growth portion of the Fund's total assets.
Options on Market Indices. The Fund may purchase and sell exchange-traded index options. Through the
purchase of listed index options, the portfolio could achieve many of the same objectives as through the use of
options on individual securities. Price movements in the Fund's securities probably will not correlate perfectly
with movements in the level of the index and, therefore, the Fund would bear a risk of loss on index options
purchased by it if favorable price movements of the hedged portfolio securities do not equal or exceed losses on
the options or if adverse price movements of the hedged portfolio securities are greater than gains realized from
the options.
Stock Index Futures. The Fund may purchase and sell stock index futures contracts. A stock index
futures contract is a bilateral agreement pursuant to which two parties agree to take or make delivery of an
amount of liquid assets equal to a specified dollar amount multiplied by the difference between the stock index
value at the close of the last trading day of the contract and the price at which the futures contract is
originally struck. No physical delivery of the underlying stocks in the index is made. The Fund will not
purchase or sell options on stock index futures contracts.
The Fund may not purchase or sell a stock index future if, immediately thereafter, more than 30% of its
total assets would be hedged by stock index futures. The Fund may not purchase or sell a stock index future if,
immediately thereafter, the sum of the amount of margin deposits on the Fund's existing futures positions would
exceed 5% of the market value of the Fund's total assets.
Currently, stock index futures contracts can be purchased or sold with respect to the Standard & Poor's
500 Stock Index on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, the New York Stock Exchange Composite Index on the New York
Futures Exchange and the Value Line Stock Index on the Kansas City Board of Trade. The Sub-advisor does not
believe that differences in composition of the three indices will create any differences in the price movements
of the stock index futures contracts in relation to the movements in such indices. However, such differences in
the indices may result in differences in correlation of the futures contracts with movements in the value of the
securities being hedged. The Fund reserves the right to purchase or sell stock index futures contracts that may
be created in the future.
The nature of initial margin in futures transactions is different from that of margin in security
transactions in that futures contract margin does not involve the borrowing of funds to finance transactions.
Rather, the initial margin is in the nature of a performance bond or good faith deposit on the contract which is
returned to the Fund upon termination of the futures contract, assuming all contractual obligations have been
satisfied.
There are several risks in connection with the use of stock index futures by the Fund as a hedging
device. One risk arises because of the imperfect correlation between movements in the price of the stock index
futures and movements in the price of the securities which are the subject of the hedge. The price of the stock
index futures may move more than or less than the price of the securities being hedged. If the price of the
stock index futures moves less than the price of the securities which are the subject of the hedge, the hedge
will not be fully effective but, if the price of the securities being hedged has moved in an unfavorable
direction, the Fund would be in a better position than if it had not hedged at all. If the price of the
securities being hedged has moved in a favorable direction, this advantage will be partially offset by the loss
on the index future. If the price of the future moves more than the price of the stock, the Fund will experience
either a loss or gain on the future which will not be completely offset by movements in the price of the
securities which are the subject of the hedge. To compensate for the imperfect correlation of movements in the
price of securities being hedged and movements in the price of the stock index futures, the Fund may buy or sell
stock index futures contracts in a greater dollar amount than the dollar amount of securities being hedged if the
volatility over a particular time period of the prices of such securities has been greater than the volatility
over such time period for the index, or if otherwise deemed to be appropriate by the Sub-advisor. Conversely,
the Fund may buy or sell fewer stock index futures contracts if the volatility over a particular time period of
the prices of the securities being hedged is less than the volatility over such time period of the stock index,
or if otherwise deemed to be appropriate by the Sub-advisor.
Where futures are purchased to hedge against a possible increase in the price of stock before the Fund
is able to invest its cash (or cash equivalents) in stocks (or options) in an orderly fashion, it is possible
that the market may decline instead. If the Sub-advisor then concludes not to invest in stock or options at that
time because of concern as to possible further market decline or for other reasons, the Fund will realize a loss
on the futures contract that is not offset by a reduction in the price of securities purchased.
The Fund's Sub-advisor intends to purchase and sell futures contracts on the stock index for which it
can obtain the best price with due consideration to liquidity.
Portfolio Turnover. The Fund's investment policies as described above are based on the Sub-advisor's
assessment of fundamentals in the context of changing market valuations. Therefore, they may under some
conditions involve frequent purchases and sales of shares of a particular issuer as well as the replacement of
securities. The Sub-advisor expects that more of its portfolio turnover will be attributable to increases and
decreases in the size of particular portfolio positions rather than to the complete elimination of a particular
issuer's securities from the Fund. It is anticipated that the growth portion of the Fund may have portfolio
turnover exceeding 100%. For more information on portfolio turnover, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus
under "Portfolio Turnover."
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
applicable to the ASAF Alliance Growth Fund. These limitations are not "fundamental" restrictions and may be
changed without shareholder approval. The Fund will not:
1. Invest in companies for the purpose of exercising control;
2. Purchase the securities of any other investment company or investment trust, except in
compliance with the 1940 Act;
3. Invest in interests in oil, gas or other mineral exploration or development programs, except
that it may purchase and sell securities of companies that deal in oil, gas or other mineral exploration or
development programs;
4. Make short sales of securities or purchase securities on margin except for such short-term
credits as may be necessary for the clearance of transactions;
5. Purchase illiquid securities if immediately after such investment more than 15% of the Fund's
net assets (taken at market value) would be so invested;
Whenever any investment restriction states a maximum percentage of the Fund's assets which may be
invested in any security or other asset, it is intended that such percentage be determined immediately after and
as a result of the Fund's acquisition of such securities or other assets. Accordingly, any later increase or
decrease in percentage beyond the specified limitation resulting from changes in values or net assets will not be
considered a violation of any such maximum.
ASAF SANFORD BERNSTEIN DEEP VALUE FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek long-term capital growth.
Investment Policies:
As a diversified fund, no more than 5% of the assets of the Fund may be invested in the securities of
one issuer (other than U.S. Government Securities), except that up to 25% of the Fund's assets may be invested
without regard to this limitation. The Fund will not invest more than 25% of its assets in the securities of
issuers in any one industry.
Short-Term Instruments. When the Fund experiences large cash inflows or anticipates substantial
redemption requests, the Fund may hold short-term investments for a limited time pending the purchase of equity
securities. The Fund's short-term instruments may consist of: (i) short-term obligations issued or guaranteed
by the U.S. government or any of its agencies or instrumentalities or by any of the states; (ii) other short-term
debt securities rated AA or higher by Standard & Poor's ("S&P") or Aa or higher by Moody's or, if unrated, of
comparable quality in the opinion of the Sub-advisor; (iii) commercial paper; (iv) bank obligations, including
negotiable certificates of deposit, time deposits and bankers' acceptances; and (v) repurchase agreements. At
the time the Fund invests in commercial paper, bank obligations or repurchase agreements, the issuer or the
issuer's parent must have outstanding debt rated AA or higher by S&P or Aa or higher by Moody's or outstanding
commercial paper or bank obligations rated A-1 by S&P or Prime-1 by Moody's; or, if no such ratings are
available, the instrument must be of comparable quality in the opinion of the Sub-advisor.
Certificates of Deposit and Bankers' Acceptances. Certificates of deposit are receipts issued by a
depository institution in exchange for the deposit of funds. The issuer agrees to pay the amount deposited plus
interest to the bearer of the receipt on the date specified on the certificate. The certificate usually can be
traded in the secondary market prior to maturity. Bankers' acceptances typically arise from short-term credit
arrangements designed to enable businesses to obtain funds to finance commercial transactions. Generally, an
acceptance is a time draft drawn on a bank by an exporter or an importer to obtain a stated amount of funds to
pay for specific merchandise. The draft is then "accepted" by a bank that, in effect, unconditionally guarantees
to pay the face value of the instrument on its maturity date. The acceptance may then be held by the accepting
bank as an asset or it may be sold in the secondary market at the going rate of discount for a specific
maturity. Although maturities for acceptances can be as long as 270 days, most acceptances have maturities of
six months or less.
Commercial Paper. Commercial paper consists of short-term (usually from 1 to 270 days) unsecured
promissory notes issued by corporations in order to finance their current operations. A variable amount master
demand note (which is a type of commercial paper) represents a direct borrowing arrangement involving
periodically fluctuating rates of interest under a letter agreement between a commercial paper issuer and an
institutional lender pursuant to which the lender may determine to invest varying amounts.
U.S. Government Obligations. The Fund may invest in obligations issued or guaranteed by U.S. Government
agencies or instrumentalities. These obligations may or may not be backed by the "full faith and credit" of the
United States. In the case of securities not backed by the full faith and credit of the United States, the Fund
must look principally to the federal agency issuing or guaranteeing the obligation for ultimate repayment, and
may not be able to assert a claim against the United States itself in the event the agency or instrumentality
does not meet its commitments. Government securities in which the Fund may invest that are not backed by the
full faith and credit of the United States include, but are not limited to, obligations of the Tennessee Valley
Authority, the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation and the U.S. Postal Service, each of which has the right to
borrow from the U.S. Treasury to meet its obligations, and obligations of the Federal Farm Credit System and the
Federal Home Loan Banks, both of whose obligations may be satisfied only by the individual credit of the issuing
agency. Securities that are backed by the full faith and credit of the United States include obligations of the
Government National Mortgage Association, the Farmers Home Administration, and the Export-Import Bank.
Equity Investments. The Fund may invest in equity securities listed on any domestic securities exchange
or traded in the over-the-counter markets, including ADRs and U.S. dollar denominated securities of foreign
issuers that trade on domestic exchanges and in the over-the-counter markets.. They may or may not pay dividends
or carry voting rights. Common stock occupies the most junior position in a company's capital structure.
Futures Contracts and Options on Futures Contracts.
Futures Contracts. The Fund may enter into securities index futures contracts. U.S. futures contracts
have been designed by exchanges which have been designated "contracts markets" by the CFTC, and must be executed
through a futures commission merchant, or brokerage firm, which is a member of the relevant contract market.
Futures contracts trade on a number of exchange markets, and, through their clearing corporations, the exchanges
guarantee performance of the contracts as between the clearing members of the exchange. These investments will
be made by the Fund solely for hedging purposes.
At the same time a futures contract is purchased or sold, the Fund must allocate cash or securities as a
deposit payment ("initial margin"). It is expected that the initial margin would be approximately 1 1/2% to 5%
of a contract's face value. Daily thereafter, the futures contract is valued and the payment of "variation
margin" may be required, because each day the Fund will provide or receive cash that reflects any decline or
increase in the contract's value.
Although futures contracts by their terms call for the actual delivery or acquisition of securities, in
most cases the contractual obligation is fulfilled before the date of the contract without having to make or take
delivery of the securities. The offsetting of a contractual obligation is accomplished by buying (or selling, as
the case may be) on a commodities exchange an identical futures contract calling for delivery in the same month.
Such a transaction, which is effected through a member of an exchange, cancels the obligation to make or take
delivery of the securities. Because transactions in the futures market are made, offset or fulfilled through a
clearinghouse associated with the exchange on which the contracts are traded, the Fund will incur brokerage fees
when it purchases or sells futures contracts. The liquidity of the futures market depends on participants
entering into offsetting transactions rather than making or taking delivery. To the extent participants decide
to make or take delivery, liquidity in the futures market could be reduced, thus producing distortion.
In addition, futures contracts entail other risks. Nonetheless, the Sub-advisor believes that use of
such contracts in certain circumstances will benefit the Fund. For an additional discussion of futures contracts
and the risks involved therein, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and
Investment Methods."
Options on Futures Contracts. The Fund may use stock index futures on a continual basis to "equitize"
cash so that the Fund may maintain 100% equity exposure. The Fund will not enter into any futures contracts or
options on futures contracts if immediately thereafter the amount of margin deposits on all the futures contracts
of the Fund and premiums paid on outstanding options on futures contracts owned by the Fund (other than those
entered into for bona fide hedging purposes) would exceed 5% of the market value of the total assets of the Fund.
A futures option gives the holder, in return for the premium paid, the right to buy (call) from or sell
(put) to the writer of the option a futures contract at a specified price at any time during the period of the
option. Upon exercise, the writer of the option is obligated to pay the difference between the cash value of the
futures contract and the exercise price. Like the buyer or seller of a futures contract, the holder, or writer,
of an option has the right to terminate its position prior to the scheduled expiration of the option by selling
or purchasing an option of the same series, at which time the person entering into the closing transaction will
realize a gain or loss. The Fund will be required to deposit initial margin and variation margin with respect to
put and call options on futures contracts written by it pursuant to brokers' requirements similar to those
described above. Net option premiums received will be included as initial margin deposits. In anticipation of
an increase in securities prices, the Fund may purchase call options on futures contracts as a substitute for the
purchase of futures contracts to hedge against a possible increase in the price of securities that the Fund
intends to purchase. Similarly, if the value of the securities held by the Portfolio is expected to decline, the
Fund might purchase put options or sell call options on futures contracts rather than sell futures contracts.
Investments in futures options involve some of the same considerations that are involved in connection
with investments in futures contracts (for example, the existence of a liquid secondary market). In addition,
the purchase or sale of an option also entails the risk that changes in the value of the underlying futures
contract will not correspond to changes in the value of the option purchased. Depending on the pricing of the
option compared to either the futures contract upon which it is based, or upon the price of the securities being
hedged, an option may or may not be less risky than ownership of the futures contract or such securities. In
general, the market prices of options can be expected to be more volatile than the market prices on the
underlying futures contract. Compared to the purchase or sale of futures contracts, however, the purchase of
call or put options on futures contracts may frequently involve less potential risk to the Fund because the
maximum amount at risk is the premium paid for the options (plus transaction costs). The writing of an option on
a futures contact involves risks similar to those risks relating to the sale of futures contracts.
Options on Securities Indices. The Fund may purchase and write (sell) call and put options on
securities indices. Such options give the holder the right to receive a cash settlement during the term of the
option based upon the difference between the exercise price and the value of the index.
Options on securities indices entail certain risks. The absence of a liquid secondary market to close
out options positions on securities indices may occur, although the Portfolio generally will only purchase or
write such an option if the Sub-advisor believes the option can be closed out.
Use of options on securities indices also entails the risk that trading in such options may be
interrupted if trading in certain securities included in the index is interrupted. The Fund will not purchase
such options unless the Sub-advisor believes the market is sufficiently developed such that the risk of trading
in such options is no greater than the risk of trading in options on securities.
For an additional discussion of options and the risks involved therein, see this SAI and the Company's
Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
not "fundamental" restrictions and may be changed by the Directors of the Company without shareholder approval.
The Fund will not:
1. Purchase any security or evidence of interest therein on margin, except that such short-term
credit as may be necessary for the clearance of purchases and sales of securities may be obtained and except that
deposits of initial deposit and variation margin may be made in connection with the purchase, ownership, holding
or sale of futures;
2. Invest for the purpose of exercising control or management;
3. Purchase securities of other investment companies except in compliance with the 1940 Act; or
4. Invest more than 15% of the Fund's net assets (taken at the greater of cost or market value) in
securities that are illiquid or not readily marketable, not including Rule 144A securities and commercial paper
that is sold under section 4(2) of the 1933 Act that have been determined to be liquid under procedures
established by the Board of Directors.
ASAF SANFORD BERNSTEIN MANAGED INDEX 500 FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund (formerly,
the ASAF Bankers Trust Managed Index 500 Fund) is to outperform the Standard & Poor's 500 Composite Stock Price
Index (the "S&P 500(R)") through stock selection resulting in different weightings of common stocks relative to the
index.
Investment Policies:
As a diversified fund, no more than 5% of the assets of the Fund may be invested in the securities of
one issuer (other than U.S. Government Securities), except that up to 25% of the Fund's assets may be invested
without regard to this limitation. The Fund will not invest more than 25% of its assets in the securities of
issuers in any one industry. In the unlikely event that the S&P 500 should concentrate to an extent greater than
that amount, the Fund's ability to achieve its objective may be impaired.
About the S&P 500. The Fund is not sponsored, endorsed, sold or promoted by Standard & Poor's, a
division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. ("S&P"). S&P makes no representation or warranty, express or
implied, to the shareholders of the Fund or any member of the public regarding the advisability of investing in
securities generally or in the Fund particularly or the ability of the S&P 500 to track general stock market
performance. S&P's only relationship to the Investment Manager or the Sub-advisor is a license provided to the
Investment Manager of certain trademarks and trade names of S&P and of the S&P 500 which is determined, composed
and calculated by S&P without regard to Investment Manager, Sub-advisor or the Fund. S&P has no obligation to
take the needs of the Investment Manager, Sub-advisor or the shareholders of the Fund into consideration in
determining, composing or calculating the S&P 500. S&P is not responsible for and has not participated in the
determination of the prices and amount of Fund's shares or the timing of the issuance or sale of the Fund's
shares, or in the determination or calculation of the Fund's net asset value. S&P has no obligation or liability
in connection with the administration, marketing or trading of the Fund.
S&P does not guarantee the accuracy and/or the completeness of the S&P 500 or any data included therein
and shall have no liability for any errors, omissions, or interruptions therein. S&P makes no warranty, express
or implied, as to the results to be obtained by the Fund, shareholders of the Fund, or any other person or entity
from the use of the S&P 500 or any data included therein. S&P makes no express or implied warranties and
expressly disclaims all warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose or use with respect to
the S&P 500 or any data included therein. Without limiting any of the foregoing, in no event shall S&P have any
liability for any special, punitive, indirect or consequential damages (including lost profits), even if notified
of the possibility of such damages.
Short-Term Instruments. When the Fund experiences large cash inflows or anticipates substantial
redemption requests, the Fund may hold short-term investments for a limited time pending the purchase of equity
securities. The Fund's short-term instruments may consist of: (i) short-term obligations issued or guaranteed
by the U.S. government or any of its agencies or instrumentalities or by any of the states; (ii) other short-term
debt securities rated AA or higher by S&P or Aa or higher by Moody's or, if unrated, of comparable quality in the
opinion of the Sub-advisor; (iii) commercial paper; (iv) bank obligations, including negotiable certificates of
deposit, time deposits and bankers' acceptances; and (v) repurchase agreements. At the time the Fund invests in
commercial paper, bank obligations or repurchase agreements, the issuer or the issuer's parent must have
outstanding debt rated AA or higher by S&P or Aa or higher by Moody's or outstanding commercial paper or bank
obligations rated A-1 by S&P or Prime-1 by Moody's; or, if no such ratings are available, the instrument must be
of comparable quality in the opinion of the Sub-advisor.
Certificates of Deposit and Bankers' Acceptances. Certificates of deposit are receipts issued by a
depository institution in exchange for the deposit of funds. The issuer agrees to pay the amount deposited plus
interest to the bearer of the receipt on the date specified on the certificate. The certificate usually can be
traded in the secondary market prior to maturity. Bankers' acceptances typically arise from short-term credit
arrangements designed to enable businesses to obtain funds to finance commercial transactions. Generally, an
acceptance is a time draft drawn on a bank by an exporter or an importer to obtain a stated amount of funds to
pay for specific merchandise. The draft is then "accepted" by a bank that, in effect, unconditionally guarantees
to pay the face value of the instrument on its maturity date. The acceptance may then be held by the accepting
bank as an asset or it may be sold in the secondary market at the going rate of discount for a specific
maturity. Although maturities for acceptances can be as long as 270 days, most acceptances have maturities of
six months or less.
Commercial Paper. Commercial paper consists of short-term (usually from 1 to 270 days) unsecured
promissory notes issued by corporations in order to finance their current operations. A variable amount master
demand note (which is a type of commercial paper) represents a direct borrowing arrangement involving
periodically fluctuating rates of interest under a letter agreement between a commercial paper issuer and an
institutional lender pursuant to which the lender may determine to invest varying amounts.
U.S. Government Obligations. The Fund may invest in obligations issued or guaranteed by U.S. Government
agencies or instrumentalities. These obligations may or may not be backed by the "full faith and credit" of the
United States. In the case of securities not backed by the full faith and credit of the United States, the Fund
must look principally to the federal agency issuing or guaranteeing the obligation for ultimate repayment, and
may not be able to assert a claim against the United States itself in the event the agency or instrumentality
does not meet its commitments. Government securities in which the Fund may invest that are not backed by the
full faith and credit of the United States include, but are not limited to, obligations of the Tennessee Valley
Authority, the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation and the U.S. Postal Service, each of which has the right to
borrow from the U.S. Treasury to meet its obligations, and obligations of the Federal Farm Credit System and the
Federal Home Loan Banks, both of whose obligations may be satisfied only by the individual credit of the issuing
agency. Securities that are backed by the full faith and credit of the United States include obligations of the
Government National Mortgage Association, the Farmers Home Administration, and the Export-Import Bank.
Equity Investments. The Fund may invest in equity securities listed on any domestic securities exchange
or traded in the over-the-counter market. They may or may not pay dividends or carry voting rights. Common
stock occupies the most junior position in a company's capital structure.
Warrants. Warrants entitle the holder to buy common stock from the issuer at a specific price (the
strike price) for a specific period of time. The strike price of warrants sometimes is much lower than the
current market price of the underlying securities, yet warrants are subject to similar price fluctuations. As a
result, warrants may be more volatile investments than the underlying securities.
Warrants do not entitle the holder to dividends or voting rights with respect to the underlying
securities and do not represent any rights in the assets of the issuing company. Also, the value of the warrant
does not necessarily change with the value of the underlying securities.
Convertible Securities. Convertible securities may be debt securities or preferred stocks that may be
converted into common stock or that carry the right to purchase common stock. Convertible securities entitle the
holder to exchange the securities for a specified number of shares of common stock, usually of the same company,
at specified prices within a certain period of time.
The terms of any convertible security determine its ranking in a company's capital structure. In the
case of subordinated convertible debentures, the holders' claims on assets and earnings are subordinated to the
claims of other creditors, and are senior to the claims of preferred and common shareholders. In the case of
convertible preferred stock, the holders' claims on assets and earnings are subordinated to the claims of all
creditors and are senior to the claims of common shareholders.
Futures Contracts and Options on Futures Contracts.
Futures Contracts. The Fund may enter into securities index futures contracts. U.S. futures contracts
have been designed by exchanges which have been designated "contracts markets" by the CFTC, and must be executed
through a futures commission merchant, or brokerage firm, which is a member of the relevant contract market.
Futures contracts trade on a number of exchange markets, and, through their clearing corporations, the exchanges
guarantee performance of the contracts as between the clearing members of the exchange. These investments will
be made by the Fund solely for hedging purposes. In this regard, the Fund may enter into futures contracts or
options on futures related to the S&P 500.
At the same time a futures contract is purchased or sold, the Fund must allocate cash or securities as a
deposit payment ("initial margin"). It is expected that the initial margin would be approximately 1 1/2% to 5%
of a contract's face value. Daily thereafter, the futures contract is valued and the payment of "variation
margin" may be required, because each day the Fund will provide or receive cash that reflects any decline or
increase in the contract's value.
Although futures contracts by their terms call for the actual delivery or acquisition of securities, in
most cases the contractual obligation is fulfilled before the date of the contract without having to make or take
delivery of the securities. The offsetting of a contractual obligation is accomplished by buying (or selling, as
the case may be) on a commodities exchange an identical futures contract calling for delivery in the same month.
Such a transaction, which is effected through a member of an exchange, cancels the obligation to make or take
delivery of the securities. Because transactions in the futures market are made, offset or fulfilled through a
clearinghouse associated with the exchange on which the contracts are traded, the Fund will incur brokerage fees
when it purchases or sells futures contracts. The liquidity of the futures market depends on participants
entering into offsetting transactions rather than making or taking delivery. To the extent participants decide
to make or take delivery, liquidity in the futures market could be reduced, thus producing distortion.
In addition, futures contracts entail other risks. Nonetheless, the Sub-advisor believes that use of
such contracts in certain circumstances will benefit the Fund. For an additional discussion of futures contracts
and the risks involved therein, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and
Investment Methods."
Options on Futures Contracts. The Fund may use stock index futures on a continual basis to "equitize"
cash so that the Fund may maintain 100% equity exposure. The Fund will not enter into any futures contracts or
options on futures contracts if immediately thereafter the amount of margin deposits on all the futures contracts
of the Fund and premiums paid on outstanding options on futures contracts owned by the Fund (other than those
entered into for bona fide hedging purposes) would exceed 5% of the market value of the total assets of the Fund.
A futures option gives the holder, in return for the premium paid, the right to buy (call) from or sell
(put) to the writer of the option a futures contract at a specified price at any time during the period of the
option. Upon exercise, the writer of the option is obligated to pay the difference between the cash value of the
futures contract and the exercise price. Like the buyer or seller of a futures contract, the holder, or writer,
of an option has the right to terminate its position prior to the scheduled expiration of the option by selling
or purchasing an option of the same series, at which time the person entering into the closing transaction will
realize a gain or loss. The Fund will be required to deposit initial margin and variation margin with respect to
put and call options on futures contracts written by it pursuant to brokers' requirements similar to those
described above. Net option premiums received will be included as initial margin deposits. In anticipation of
an increase in securities prices, the Fund may purchase call options on futures contracts as a substitute for the
purchase of futures contracts to hedge against a possible increase in the price of securities that the Fund
intends to purchase. Similarly, if the value of the securities held by the Fund is expected to decline, the Fund
might purchase put options or sell call options on futures contracts rather than sell futures contracts.
Investments in futures options involve some of the same considerations that are involved in connection
with investments in futures contracts (for example, the existence of a liquid secondary market). In addition,
the purchase or sale of an option also entails the risk that changes in the value of the underlying futures
contract will not correspond to changes in the value of the option purchased. Depending on the pricing of the
option compared to either the futures contract upon which it is based, or upon the price of the securities being
hedged, an option may or may not be less risky than ownership of the futures contract or such securities. In
general, the market prices of options can be expected to be more volatile than the market prices on the
underlying futures contract. Compared to the purchase or sale of futures contracts, however, the purchase of
call or put options on futures contracts may frequently involve less potential risk to the Fund because the
maximum amount at risk is the premium paid for the options (plus transaction costs). The writing of an option on
a futures contact involves risks similar to those risks relating to the sale of futures contracts.
Options on Securities Indices. The Fund may purchase and write (sell) call and put options on
securities indices. Such options give the holder the right to receive a cash settlement during the term of the
option based upon the difference between the exercise price and the value of the index.
Options on securities indices entail certain risks. The absence of a liquid secondary market to close
out options positions on securities indices may occur, although the Fund generally will only purchase or write
such an option if the Sub-advisor believes the option can be closed out.
Use of options on securities indices also entails the risk that trading in such options may be
interrupted if trading in certain securities included in the index is interrupted. The Fund will not purchase
such options unless the Sub-advisor believes the market is sufficiently developed such that the risk of trading
in such options is no greater than the risk of trading in options on securities.
For an additional discussion of options and the risks involved therein, see this SAI and the Company's
Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
not "fundamental" restrictions and may be changed by the Directors of the Company without shareholder approval.
The Fund will not:
1. Purchase any security or evidence of interest therein on margin, except that such short-term
credit as may be necessary for the clearance of purchases and sales of securities may be obtained and except that
deposits of initial deposit and variation margin may be made in connection with the purchase, ownership, holding
or sale of futures;
2. Invest for the purpose of exercising control or management;
3. Purchase securities of other investment companies except in compliance with the 1940 Act; or
4. Invest more than 15% of the Fund's net assets (taken at the greater of cost or market value) in
securities that are illiquid or not readily marketable, not including Rule 144A securities and commercial paper
that is sold under section 4(2) of the 1933 Act that have been determined to be liquid under procedures
established by the Board of Directors.
ASAF ALLIANCE GROWTH AND INCOME FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth and income through
investments primarily in dividend-paying common stocks of good quality.
Investment Policies:
It is the policy of the Fund to seek to balance the objectives of reasonable opportunity for capital
growth and reasonable current income through investments primarily in dividend-paying common stocks of good
quality. However, it may invest whenever the economic outlook is unfavorable for common stock investments in
other types of securities, such as bonds, convertible bonds, preferred stocks, and convertible preferred stocks.
Purchases and sales of portfolio securities are made at such times and in such amounts as deemed
advisable in light of market, economic and other conditions, irrespective of the degree of portfolio turnover.
The Fund engages primarily in holding securities for investment and not for trading purposes.
Covered Call Options. Subject to market conditions, the Fund may try to realize income by writing
covered call option contracts provided that the option is listed on a domestic securities exchange. The
Sub-advisor believes that the premiums the Fund will receive for writing options can increase the Fund's income
without subjecting it to substantial risks.
A security on which an option has been written will be held in escrow by the Fund's custodian until the
option expires, is exercised, or a closing purchase transaction is made. The Fund will purchase call options
only to close out a position in an option written by it. When a security is sold from the Fund against which a
call option has been written, the Fund will effect a closing purchase transaction so as to close out any existing
call option on that security.
The premium received by the Fund upon writing a call option will increase the Fund's assets, and a
corresponding liability will be recorded and subsequently adjusted from day to day to the current value of the
option written. For example, if the current value of the option exceeds the premium received, the excess would
be an unrealized loss and, conversely, if the premium exceeds the current value, such excess would be an
unrealized gain. The current value of the option will be the last sales price on the principal exchange on which
the option is traded or, in the absence of any transactions, the mean between the closing bid and asked price.
Except as stated above, the Fund will not purchase or sell puts or calls or combinations thereof.
Additional information on covered call options and their risks is included in this Statement and the
Trust's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Stock Index Futures. The Fund may purchase and sell stock index futures contracts. A stock index
futures contract is a bilateral agreement pursuant to which two parties agree to take or make delivery of an
amount of liquid assets equal to a specified dollar amount multiplied by the difference between the stock index
value at the close of the last trading day of the contract and the price at which the futures contract is
originally struck. No physical delivery of the underlying stocks in the index is made. The Fund will not
purchase or sell options on stock index futures contracts.
The Fund may not purchase or sell a stock index future if, immediately thereafter, more than 30% of its
total assets would be hedged by stock index futures. The Fund may not purchase or sell a stock index future if,
immediately thereafter, the sum of the amount of margin deposits on the Fund's existing futures positions would
exceed 5% of the market value of the Fund's total assets.
Currently, stock index futures contracts can be purchased or sold with respect to the Standard & Poor's
500 Stock Index on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, the New York Stock Exchange Composite Index on the New York
Futures Exchange and the Value Line Stock Index on the Kansas City Board of Trade. The Sub-advisor does not
believe that differences in composition of the three indices will create any differences in the price movements
of the stock index futures contracts in relation to the movements in such indices. However, such differences in
the indices may result in differences in correlation of the futures contracts with movements in the value of the
securities being hedged. The Fund reserves the right to purchase or sell stock index futures contracts that may
be created in the future.
The nature of initial margin in futures transactions is different from that of margin in security
transactions in that futures contract margin does not involve the borrowing of funds to finance transactions.
Rather, the initial margin is in the nature of a performance bond or good faith deposit on the contract which is
returned to the Fund upon termination of the futures contract, assuming all contractual obligations have been
satisfied.
There are several risks in connection with the use of stock index futures by the Fund as a hedging
device. One risk arises because of the imperfect correlation between movements in the price of the stock index
futures and movements in the price of the securities which are the subject of the hedge. The price of the stock
index futures may move more than or less than the price of the securities being hedged. If the price of the
stock index futures moves less than the price of the securities which are the subject of the hedge, the hedge
will not be fully effective but, if the price of the securities being hedged has moved in an unfavorable
direction, the Fund would be in a better position than if it had not hedged at all. If the price of the
securities being hedged has moved in a favorable direction, this advantage will be partially offset by the loss
on the index future. If the price of the future moves more than the price of the stock, the Fund will experience
either a loss or gain on the future which will not be completely offset by movements in the price of the
securities which are the subject of the hedge. To compensate for the imperfect correlation of movements in the
price of securities being hedged and movements in the price of the stock index futures, the Fund may buy or sell
stock index futures contracts in a greater dollar amount than the dollar amount of securities being hedged if the
volatility over a particular time period of the prices of such securities has been greater than the volatility
over such time period for the index, or if otherwise deemed to be appropriate by the Sub-advisor. Conversely,
the Fund may buy or sell fewer stock index futures contracts if the volatility over a particular time period of
the prices of the securities being hedged is less than the volatility over such time period of the stock index,
or if otherwise deemed to be appropriate by the Sub-advisor.
Where futures are purchased to hedge against a possible increase in the price of stock before the Fund
is able to invest its cash (or cash equivalents) in stocks (or options) in an orderly fashion, it is possible
that the market may decline instead. If the Fund then concludes not to invest in stock or options at that time
because of concern as to possible further market decline or for other reasons, the Fund will realize a loss on
the futures contract that is not offset by a reduction in the price of securities purchased.
The Fund's Sub-advisor intends to purchase and sell futures contracts on the stock index for which it
can obtain the best price with due consideration to liquidity.
For additional information regarding futures contracts and their risks, see this Statement and the
Trust's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest in foreign securities, but will not make any such investments
unless such securities are listed on a national securities exchange. The purchase of foreign securities entails
certain political and economic risks, and accordingly, the Fund has restricted its investments in securities in
this category to issues of high quality. Evidences of ownership of foreign securities may be held outside of the
U.S., and the Fund may be subject to the risks associated with the holding of such property overseas. Additional
information on foreign securities and their risks is included in this Statement and the Trust's Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Securities Ratings. The ratings of debt securities by S&P, Moody's, Duff & Phelps and Fitch are a
generally accepted barometer of credit risk. They are, however, subject to certain limitations from an
investor's standpoint. The rating of an issuer is heavily weighted by past developments and does not necessarily
reflect probable future conditions. There is frequently a lag between the time a rating is assigned and the time
it is updated. In addition, there may be varying degrees of difference in credit risk of securities within each
rating category.
A detailed description of the debt security ratings assigned by Moody's and S&P is included in Appendix
B to this Statement.
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
applicable to the ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund. These limitations are not "fundamental restrictions and
may be changed by the Directors without shareholder approval. The Fund may not:
1. Purchase the securities of any other investment company except in compliance with the 1940 Act;
and
2. Sell securities short.
ASAF MFS GROWTH WITH INCOME FUND:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek to provide reasonable current income and
long-term capital growth and income.
Investment Policies:
Corporate Debt Securities. The Fund may invest in debt securities, such as convertible and
non-convertible bonds, notes and debentures, issued by corporations, limited partnerships and similar entities.
Variable and Floating Rate Obligations. The Fund may invest in floating or variable rate securities.
Investments in variable or floating rate securities normally will involve industrial development or revenue bonds
which provide that the rate of interest is set as a specific percentage of a designated base rate, such as rates
on Treasury Bonds or Bills or the prime rate at a major commercial bank, and that a bondholder can demand payment
of the obligations on behalf of the Fund on short notice at par plus accrued interest, which amount may be more
or less than the amount of the bondholder paid for them. The maturity of floating or variable rate obligations
(including participation interests therein) is deemed to be the longer of (i) the notice period required before
the Fund is entitled to receive payment of the obligation upon demand or (ii) the period remaining until the
obligation's next interest rate adjustment. If not redeemed by the Fund through the demand feature, the
obligations mature on a specified date, which may range up to thirty years from the date of issuance.
Zero Coupon Bonds, Deferred Interest Bonds and PIK Bonds. The Fund may invest in zero coupon bonds,
deferred bonds and bonds on which the interest is payable in kind ("PIK bonds"). Zero coupon and deferred
interest bonds are debt obligations, which are issued at a significant discount from face value. The discount
approximates the total amount of interest the bonds will accrue and compound over the period until maturity or
the first interest payment date at a rate of interest reflecting the market rate of the security at the time of
issuance. While zero coupon bonds do not require the periodic payment of interest, deferred interest bonds do
provide for a period of delay before the regular payment of interest begins. PIK bonds are debt obligations,
which provide that the issuer may, at its option, pay interest on such bonds in cash or in the form of additional
debt obligations. Such investments benefit the issuer by mitigating its need for cash to meet debt service, but
also require a higher rate of return to attract investors who are willing to defer receipt of such cash. Such
investments may experience greater volatility in market value than debt obligations, which make regular payments
of interest. The Fund will accrue income on such investments for tax and accounting purposes, which are
distributable to shareholders and which, because no cash is received at the time of accrual, may require the
liquidation of other portfolio securities to satisfy the Fund's distribution obligations.
Equity Securities. The Fund may invest in all types of equity securities, including the following:
common stocks, preferred stocks and preference stocks; securities such as bonds, warrants or rights that are
convertible into stocks; and depository receipts for those securities. These securities may be listed on
securities exchanges, traded in various over-the-counter markets or have no organized market.
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest in dollar-denominated and non-dollar denominated foreign
securities. Investing in securities of foreign issuers generally involves risks not ordinarily associated with
investing in securities of domestic issuers. For a discussion of the risks involved in foreign securities, see
this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Depository Receipts. The Fund may invest in American Depository Receipts ("ADRs"), Global Depository
Receipts ("GDRs") and other types of depository receipts. ADRs are certificates by a U.S. depository (usually a
bank) and represent a specified quantity of shares of an underlying non-U.S. stock on deposit with a custodian
bank as collateral. GDRs and other types of depository receipts are typically issued by foreign banks or trust
companies and evidence ownership of underlying securities issued by either a foreign or a U.S. company.
Generally, ADRs are in registered form and are designed for use in U.S. securities markets and GDRs are in bearer
form and are designed for use in foreign securities markets. For the purposes of the Fund's policy to invest a
certain percentage of its assets in foreign securities, the investments of the Fund in ADRs, GDRs and other types
of depository receipts are deemed to be investments in the underlying securities.
ADRs may be sponsored or unsponsored. A sponsored ADR is issued by a depository which has an exclusive
relationship with the issuer of the underlying security. An unsponsored ADR may be issued by any number of U.S.
depositories. Under the terms of most sponsored arrangements, depositories agree to distribute notices of
shareholder meetings and voting instructions, and to provide shareholder communications and other information to
the ADR holders at the request of the issuer of the deposited securities. The depository of an unsponsored ADR,
on the other hand, is under no obligation to distribute shareholder communications received from the issuer of
the deposited securities or to pass through voting rights to ADR holders in respect of the deposited securities.
The Fund may invest in either type of ADR. Although the U.S. investor holds a substitute receipt of ownership
rather than direct stock certificates, the use of the depository receipts in the United Sates can reduce costs
and delays as well as potential currency exchange and other difficulties. The Fund may purchase securities in
local markets and direct delivery of these shares to the local depositary of an ADR agent bank in the foreign
country. Simultaneously, the ADR agents create a certificate which settles at the Fund's custodian in five days.
The Fund may also execute trades on the U.S. markets using existing ADRs. A foreign issuer of the security
underlying an ADR is generally not subject to the same reporting requirements in the United States as a domestic
issuer. Accordingly, information available to a U.S. investor will be limited to the information the foreign
issuer is required to disclose in its country and the market value of an ADR may not reflect undisclosed material
information concerning the issuer of the underlying security. ADRs may also be subject to exchange rate risks if
the underlying foreign securities are denominated in a foreign currency.
Emerging Markets. The Fund may invest in securities of government, government-related, supranational
and corporate issuers located in emerging markets. Such investments entail significant risks as described below.
Company Debt. Governments of many emerging market countries have exercised and continue to exercise
substantial influence over many aspects of the private sector through the ownership or control of many companies,
including some of the largest in any given country. As a result, government actions in the future could have a
significant effect on economic conditions in emerging markets, which in turn, may adversely affect companies in
the private sector, general market conditions and prices and yields of certain of the securities in the Fund's
portfolio. Expropriation, confiscatory taxation, nationalization, political, economic or social instability or
other similar developments have occurred frequently over the history of certain emerging markets and could
adversely affect the Fund's assets should these conditions recur.
Foreign currencies. Some emerging market countries may have managed currencies, which are not free
floating against the U.S. dollar. In addition, there is risk that certain emerging market countries may restrict
the free conversion of their currencies into other currencies. Further, certain emerging market currencies may
not be internationally traded. Certain of these currencies have experienced a steep devaluation relative to the
U.S. dollar. Any devaluations in the currencies in which a Fund's portfolio securities are denominated may have
a detrimental impact on the Fund's et asset value.
Inflation. Many emerging markets have experienced substantial, and in some periods extremely high,
rates of inflation for many years. Inflation and rapid fluctuations in inflation rates have had and may continue
to have adverse effects on the economies and securities markets of certain emerging market countries. In an
attempt to control inflation, wage and price controls have been imposed in certain countries. Of these
countries, some, in recent years, have begun to control inflation through prudent economic policies.
Liquidity; Trading Volume; Regulatory Oversight. The securities markets of emerging market countries
are substantially smaller, less developed, less liquid and more volatile than the major securities markets in the
U.S. Disclosure and regulatory standards are in many respects less stringent than U.S. standards. Furthermore ,
there is a lower level of monitoring and regulation of the markets and the activities of investors in such
markets.
The limited size of many emerging market securities markets and limited trading volume in the securities
of emerging market issuers compared to volume of trading in the securities of U.S. issuers could cause prices to
be erratic for reasons apart from factors that affect the soundness and competitiveness of the securities
issuers. For example, limited market size may cause prices to be unduly influenced by traders who control large
positions. Adverse publicity and investors' perceptions, whether or not based on in-depth fundamental analysis,
may decrease the value and liquidity of portfolio securities.
The risk also exists that an emergency situation may arise in one or more emerging markets, as a result
of which trading of securities may cease or may be substantially curtailed and prices for the Fund's securities
in such markets may not be readily available. The Fund may suspend redemption of its shares for any period
during which an emergency exists, as determined by the SEC. If market prices are not readily available, the
Fund's securities in the affected markets will be valued at fair value determined in good faith by or under the
direction of the Board of Directors.
Withholding. Income from securities held by the Fund could be reduced by a withholding tax on the
source or other taxes imposed by the emerging market countries in which the Fund makes its investments. The
Fund's net asset value may also be affected by changes in the rates or methods of taxation applicable to the Fund
or to entities in which the Fund has invested. The Sub-advisor will consider the cost of any taxes in
determining whether to acquire any particular investments, but can provide no assurance that the taxes will not
be subject to change.
Forward Contracts. The Fund may enter into contracts for the purchase or sale of a specific currency at
a future date at a price at the time the contract is entered into (a "Forward Contract"), for hedging purposes
(e.g., to protect its current or intended investments from fluctuations in currency exchange rates) as well as
for non-hedging purposes).
The Fund does not presently intend to hold Forward Contracts entered into until maturity, at which time
it would be required to deliver or accept delivery of the underlying currency, but will seek in most instances to
close out positions in such Contracts by entering into offsetting transactions, which will serve to fix the
Fund's profit or loss based upon the value of the Contracts at the time the offsetting transactions is executed.
The Fund will also enter into transactions in Forward Contracts for other than hedging purposes, which
presents greater profit potential but also involves increased risk. For example, the Fund may purchase a given
foreign currency through a Forward Contract if, in the judgement of the Sub-advisor, the value of such currency
is expected to rise relative to the U.S. dollar. Conversely, the Fund may sell the currency through a Forward
Contract if the Sub-advisor believes that its value will decline relative to the dollar.
For an additional discussion of Forward Contracts see this SAI and the Company Prospectus under "Certain
Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Futures Contracts. The Fund may purchase and sell futures contracts ("Future Contracts") on stock
indices, foreign currencies, interest rates or interest-rate related instruments, indices of foreign currencies
or commodities. The Fund also may purchase and sell Futures Contracts on foreign or domestic fixed income
securities or indices of such securities including municipal bond indices and any other indices of foreign or
domestic fixed income securities that may become available for trading. Such investment strategies will be used
for hedging purposes and for non-hedging purposes, subject to applicable law.
Futures Contracts differ from options in that they are bilateral agreements, with both the purchaser and
the seller equally obligated to complete the transaction. Futures Contracts call for settlement only on the
expiration date and cannot be exercised at any other time during their term.
Purchases or sales of stock index futures contracts are used to attempt to protect the Fund's current or
intended stock investments from broad fluctuations in stock prices. For example, the Fund may sell stock index
futures contracts in anticipations of or during market decline to attempt to offset the decrease in market value
of the Fund's securities portfolio that might otherwise result. If such decline occurs, the loss in value of
portfolio securities may be offset, in whole or in part, by gains on the futures position. When the Fund is not
fully invested in the securities market and anticipates a significant market advance, it may purchase stock index
futures in order to gain rapid market exposure that may, in part or entirely, offset increases in the cost of
securities that the Fund intends to purchase. As such purchases are made, the corresponding positions in stock
index futures contracts will be closed out. In a substantial majority of these transactions, the Fund will
purchase such securities upon termination of the futures position, but under unusual market conditions, a long
futures position may be terminated without a related purchase of securities.
The Fund may purchase and sell foreign currency futures contracts for hedging purposes, to attempt to
protect its current or intended investments from fluctuations in currency exchange rates. Such fluctuations
could reduce the dollar value of portfolio securities denominated in foreign currencies, or increase the dollar
cost of foreign-denominated securities, or increase the dollar cost of foreign-denominated securities to be
acquired, even if the value of such securities in the currencies in which they are denominated remains constant.
The Fund may sell futures contracts on a foreign currency, for example, where it holds securities denominated in
such currency and it anticipates a decline in the value of such currency relative to the dollar. In the event
such decline occurs, the resulting adverse effect on the value of foreign-denominated securities may be offset,
in whole or in part, by gains on the futures contracts.
Conversely, the Fund could protect against a rise in the dollar cost of foreign-denominated securities
to be acquired by purchasing futures contracts on the relevant security, which could offset, in whole or in part,
the increased cost of such securities resulting from the rise in the dollar value of the underlying currencies.
Where the Fund purchases futures contracts under such circumstances, however, and the prices of securities to be
acquired instead decline, the Fund will sustain losses on its futures position which could reduce or eliminate
the benefits of the reduced cost of portfolio securities to be acquired.
For further information on Futures Contracts, see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods."
Investment in Other Investment Companies. The Fund may invest other investment companies, including
both open-end and closed-end companies. Investments in closed-end investment companies may involve the payment
of substantial premiums above the value of such investment companies' portfolio securities.
Options. The Fund may invest in the following types of options, which involves the risks described
below under the caption "Special Risk Factors."
Options on Foreign Currencies. The Fund may purchase and write options on foreign currencies for
hedging and non-hedging purposes in a manner similar to that in which Futures Contracts on foreign currencies, or
Forward Contracts, will be utilized. For example, where a rise in the dollar value of a currency in which
securities to be acquired are denominated is projected, thereby increasing the cost of such securities, the Fund
may purchase call options thereon. The purchase of such options could offset, at least partially, the effect of
the adverse movements in exchange rates.
Similarly, instead of purchasing a call option to hedge against an anticipated increase in the dollar
cost of securities to be acquired, the Fund could write a put option on the relevant currency which, if rates
move in the manner projected, will expire unexercised and allow the Fund to hedge such increased cost up to the
amount of the premium. Foreign currency options written by the Fund will generally be covered in a manner
similar to the covering of other types of options.
Options on Futures Contracts. The Fund may also purchase and write options to buy or sell those Futures
Contracts in which it may invest as described above under "Futures Contracts." Such investment strategies will
be used for hedging purposes and for non-hedging purposes, subject to applicable law.
Options on Futures Contracts that are written or purchased by the Fund on U.S. Exchanges are traded on
the same contract market as the underlying Futures Contract, an, like Futures Contracts, are subject to the
regulation by the CFTC and the performance guarantee of the exchange clearinghouse. In addition, Options on
Futures Contracts may be traded on foreign exchanges. The Fund may cover the writing of call Options on Futures
Contracts (a) through purchases of the underlying Futures Contract, (b) through ownership of the instrument, or
instruments included in the index, underlying the Futures Contract, or (c) through the holding of a call on the
same Futures Contract and in the same principal amount as the call written where the exercise price of the call
held (I) is equal to or less than the exercise price of the call written or (ii) is greater than the exercise
price of the call written if the Fund owns liquid and unencumbered assets equal to the difference. The Fund may
cover the writing of put Options on Futures Contracts (a) through sales of the underlying Futures Contract, (b)
through the ownership of liquid and unencumbered assets equal to the value of the security or index underlying
the Futures Contract, or (c) through the holding of a put on the same Futures Contract and in the same principal
amount as the put written where the exercise price of the put held (i) is equal to or greater than the exercise
price of the put written if where the exercise price of the put held (ii) is less than the exercise price of the
put written of the Fund owns liquid and unencumbered assets equal to the difference. Put and call Options on
Futures Contracts may also be covered in such other manner as may be in accordance with the rules of the exchange
on which the option is traded and applicable laws and regulations. Upon the exercise of a call Option on a
Futures Contract written by the Fund, the Fund will be required to sell the underlying Futures Contract which, if
the Fund has covered its obligation through the purchase of such Contract, will serve to liquidate its futures
position. Similarly, where a put Option on a Futures Contract written by the Fund is exercised, the Fund will be
required to purchase the underlying Futures Contract which, if the Fund has covered its obligation through the
sale of such Contract, will close out its futures position.
Depending on the degree of correlation between changes in the value of its portfolio securities and the
changes in the value of its futures positions, the Fund's losses from existing Options on Futures Contracts may
to some extent be reduced or increased by changes in the value of portfolio securities.
Options on Securities. The Fund may write (sell) covered put and call options, and purchase put and
call options, on securities.
A call option written by the Fund is "covered" if the Fund owns the security underlying the call or has
an absolute and immediate right to acquire that security without additional cash consideration (or for additional
cash consideration if the Fund owns liquid and unencumbered assets equal to the amount of cash consideration)
upon conversion or exchange of other securities held in its portfolio. A call option is also covered if the Fund
holds a call on the same security and in the same principal amount as the call written where the exercise price
of the call held (a) is equal to or less than the exercise price of the call written or (b) is greater than the
exercise price of the call written if the Fund owns liquid and unencumbered assets equal to the difference. If
the portfolio writes a put option it must segregate liquid and unencumbered assets with a value equal to the
exercise price, or else holds a put on the same security and in the same principal amount as the put written
where the exercise price of the put held is equal to or greater than the exercise price of the put written or
where the exercise price of the put held is less than the exercise price of the put written if the Fund owns
liquid and unencumbered assets equal to the difference. Put and call options written by the Fund may also be
covered in such other manner as may be in accordance with the requirements of the exchange on which, or the
counterparty with which, the option is traded, and applicable laws and regulations.
Effecting a closing transaction in the case of a written call option will permit the Fund to write
another call option on the underlying security with either a different exercise price or expiration date or both,
or in the case of a written put option will permit the Fund to write another put option to the extent that the
Fund owns liquid and unencumbered assets. Such transactions permit the Fund to generate additional premium
income, which will partially offset declines in the value of portfolio securities or increases in the cost of
securities to be acquired. Also, effecting a closing transaction will permit the cash or proceeds from the
concurrent sale of any securities subject to the option to be used for other investments of the Fund, provided
that another option on such security is not written. If the Fund desires to sell a particular security from its
portfolio on which it has written a call option, it will effect a closing transaction in connection with the
option prior to or concurrent with the sale of the security.
The Fund may write options in connection with buy-and-write transactions; that is, the Fund may purchase
a security and then write a call option against that security. The exercise price of the call option the Fund
determines to write will depend upon the expected price movement of the underlying security. The exercise price
of a call option may be below ("in-the-money"), equal to ("at-the-money") or above ("out-of-the-money") the
current value of the underlying security at the time the option is written. Buy-and-write transactions using
in-the-money call options may be used when it is expected that the price of the underlying security will decline
moderately during the option period. Buy-and-write transactions using out-of-the-money call options may be used
when it is expected that the premiums received from writing the call option plus the appreciation in the market
price of the underlying security up to the exercise price will be greater than the appreciation in the price of
the underlying security alone. If the call options are exercised in such transactions, the Fund's' maximum gain
will be the premium received by it for writing the option, adjusted upwards or downwards by the difference
between the Fund's' purchase price of the security and the exercise price, less related transaction costs. If
the options are not exercised and the price of the underlying security declines, the amount of such decline will
be offset in part, or entirely, by the premium received.
The writing of covered put options is similar in terms of risk/return characteristics to buy-and-write
transactions. If the market price or the underlying security rises or otherwise is above the exercise price, the
put option will expire worthless and the Fund's' gain will be limited to the premium received, less related
transaction costs. If the market price of the underlying security declines or otherwise is below the exercise
price, the Fund may elect to close the position or retain the option until it is exercised, at which time the
Fund will be required to take delivery of the security at the exercise price; the Fund' return will be the
premium received from the put option minus the amount by which the market price of the security is below the
exercise price, which could result in a loss. Out-of-the-money, at-the-money and in-the-money put options may be
used by the Fund in the same market environments that call options are used in equivalent buy-and-write
transactions.
The Fund may also write combinations of put and call options on the same security, known as "straddles"
with the same exercise price and expiration date. By writing a straddle, the Fund undertakes a simultaneous
obligation to sell and purchase the same security in the event that one of the options is exercised. If the
price of the security subsequently rises sufficiently above the exercise price to cover the amount of the premium
and transaction costs, the call will likely be exercised and the Fund will be required to sell the underlying
security at a below market price. This loss may be offset, however, in whole or in part, by the premiums
received on the writing of the two options. Conversely, if the price of the security declines by a sufficient
amount, the put will likely be exercised. The writing of straddles will likely be effective, therefore, only
where the price of the security remains stable and neither the call nor the put is exercised. In those instances
where one of the options is exercised, the loss on the purchase or sale of the underlying security may exceed the
amount of the premiums received.
The writing of options on securities will not be undertaken by the Fund solely for hedging purposes, and
could involve certain risks which are not present in the case of hedging transactions. Moreover, even where
options are written for hedging purposes, such transactions constitute only a partial hedge against declines in
the value of portfolio securities or against increases in the value of securities to be acquired, up to the
amount of the premium. The Fund may also purchase options for hedging purposes or to increase its return.
The Fund may also purchase call options to hedge against an increase in the price of securities that the
Fund anticipates purchasing in the future. If such increase occurs, the call option will permit the Fund to
purchase the securities at the exercise price, or to close out the options at a profit.
Options on Stock Indices. The Fund may write (sell) covered call and put options and purchase call and
put options on stock indices. The Fund may cover written call options on stock indices by owning securities
whose price changes, in the opinion of the Sub-advisor, are expected to be similar to those of the underlying
index, or by having an absolute and immediate right to acquire such securities without additional cash
consideration (or for additional cash consideration if the Fund owns liquid and unencumbered assets equal to the
amount of cash consideration) upon conversion or exchange of other securities in its portfolio. The Fund may
also cover call options on stock indices by holding a call on the same index and in the same principal amount as
the call written where the exercise price of the call held (a) is equal to or less than the exercise price of the
call written or (b) is greater than the exercise price of the call written if the Fund own liquid and
unencumbered assets equal to the difference. If the Portfolio writes put options on stock indices, it must
segregate liquid and unencumbered assets with a value equal to the exercise price, or hold a put on the same
stock index and in the same principal amount as the put written where the exercise price of the put held (a) is
equal to or greater than the exercise price of the put written or (b) is less than the exercise price of the put
written if the Fund owns liquid and unencumbered assets equal to the difference. Put and call options on stock
indices may also be covered in such other manner as may be in accordance with the rules of the exchange on which,
or the counterparty with which, the option is traded and applicable laws and regulations.
The purchase of call options on stock indices may be used by the Fund to attempt to reduce the risk of
missing a broad market advance, or an advance in an industry or market segment, at a time when the Fund holds
uninvested cash or short-term debt securities awaiting investment. When purchasing call options for this
purpose, the Fund will also bear the risk of losing all or a portion of the premium paid it the value of the
index does not rise. The purchase of call options on stock indices when the Fund is substantially fully invested
is a form of leverage, up to the amount of the premium and related transaction costs, and involves risks of loss
and of increased volatility similar to those involved in purchasing calls on securities the Fund owns.
The index underlying a stock index option may be a "broad-based" index, such as the Standard & Poor's
500 Index or the New York Stock Exchange Composite Index, the changes in value of which ordinarily will reflect
movements in the stock market in general. In contrast, certain options may be based on narrower market indices,
such as the Standard & Poor's 100 Index, or on indices of securities of particular industry groups, such as those
of oil and gas or technology companies. A stock index assigns relative values to the stocks included in the
index and the index fluctuates with changes in the market values of the stocks so included. The composition of
the index is changed periodically.
For an additional discussion of options, see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods."
Special Risk Factors.
Risk of Imperfect Correlation of Hedging Instruments with the Fund's Portfolio. The use of derivatives
for "cross hedging" purposes (such as a transaction in a Forward Contract on one currency to hedge exposure to a
different currency) may involve greater correlation risks. Consequently, the Fund bears the risk that the price
of the portfolio securities being hedged will not move in the same amount or direction as the underlying index or
obligation.
It should be noted that stock index futures contracts or options based upon a narrower index of
securities, such as those of a particular industry group, may present greater risk than options or futures based
on a broad market index. This is due to the fact that a narrower index is more susceptible to rapid and extreme
fluctuations as a result of changes in the value of a small number of securities. Nevertheless, where the Fund
enters into transactions in options or futures on narrowly-based indices for hedging purposes, movements in the
value of the index should, if the hedge is successful, correlate closely with the portion of the Fund' portfolio
or the intended acquisitions being hedged.
The trading of derivatives for hedging purposes entails the additional risk of imperfect correlation
between movements in the price of the derivative and the price of the underlying index or obligation. The
anticipated spread between the prices may be distorted due to the difference in the nature of the markets such as
differences in margin requirements, the liquidity of such markets and the participation of speculators in the
derivatives markets. In this regard, trading by speculators in derivatives has in the past occasionally resulted
in market distortions, which may be difficult or impossible to predict, particularly near the expiration of such
instruments.
The trading of Options on Futures Contracts also entails the risk that changes in the value of the
underlying Futures Contracts will not be fully reflected in the value of the option. The risk of imperfect
correlation, however, generally tends to diminish as the maturity date of the Futures Contract or expiration date
of the option approaches.
Further, with respect to options on securities, options on stock indices, options on currencies and
Options on Futures Contracts, the Fund is subject to the risk of market movements between the time that the
option is exercised and the time of performance thereunder. This could increase the extent of any loss suffered
by the Fund in connection with such transactions.
In writing a covered call option on a security, index or futures contract, the Fund also incurs the risk
that changes in the value of the instruments used to cover the position will not correlate closely with changes
in the value of the option or underlying index or instrument. For example, where the Fund covers a call option
written on a stock index through segregation of securities, such securities may not match the composition of the
index, and the Fund may not be fully covered. As a result, the Fund could be subject to risk of loss in the
event of adverse market movements.
Risks of Non-Hedging Transactions. The Fund may enter transactions in derivatives for non-hedging
purposes as well as hedging purposes. Non-hedging transactions in such instruments involve greater risks and may
result in losses which may not be offset by increases in the value of portfolio securities or declines in the
cost of securities to be acquired. Nevertheless, the method of covering an option employed by the Fund may not
fully protect it against risk of loss and, in any event, the Fund could suffer losses on the option position
which might not be offset by corresponding portfolio gains. The Fund may also enter into futures, Forward
Contracts for non-hedging purposes. For example, the Fund may enter into such a transaction as an alternative to
purchasing or selling the underlying instrument or to obtain desired exposure to an index or market. In such
instances, the Fund will be exposed to the same economic risks incurred in purchasing or selling the underlying
instrument or instruments. However, transactions in futures, Forward Contracts may be leveraged, which could
expose the Fund to greater risk of loss than such purchases or sales. Entering into transactions in derivatives
for other than hedging purposes, therefore, could expose the Fund to significant risk of loss if the prices,
rates or values of the underlying instruments or indices do not move in the direction or to the extent
anticipated.
With respect to the writing of straddles on securities, the Fund incurs the risk that the price of the
underlying security will not remain stable, that one of the options written will be exercised and that the
resulting loss will not be offset by the amount of the premiums received. Such transactions, therefore, create
an opportunity for increased return by providing the Fund with two simultaneous premiums on the same security,
but involve additional risk, since the Fund may have an option exercised against it regardless of whether the
price of the security increases or decreases.
Risk of a Potential Lack of a Liquid Secondary Market. Prior to exercise or expiration, a futures or
option position can only be terminated by entering into a closing purchase or sale transaction. In that event,
it may not be possible to close out a position held by the Fund, and the Fund could be required to purchase or
sell the instrument underlying an option, make or receive a cash settlement or meet ongoing variation margin
requirements. Under such circumstances, if the Fund has insufficient cash available to meet margin requirements,
it will be necessary to liquidate portfolio securities or other assets at a time when it is disadvantageous to do
so. The inability to close out options and futures positions, therefore, could have an adverse impact on the
Fund' ability effectively to hedge its portfolio, and could result in trading losses.
The trading of Futures Contracts and options is also subject to the risk of trading halts, suspensions,
exchange or clearinghouse equipment failures, government intervention, insolvency of a brokerage firm or
clearinghouse or other disruptions of normal trading activity, which could at times make it difficult or
impossible to liquidate existing positions or to recover excess variation margin payments.
Potential Bankruptcy of a Clearinghouse or Broker. When the Fund enters into transactions in
exchange-traded futures or options, it is exposed to the risk of the potential bankruptcy of the relevant
exchange clearinghouse or the broker through which the Fund has effected the transaction. In that event, the
Fund might not be able to recover amounts deposited as margin, or amounts owed to the Fund in connection with its
transactions, for an indefinite period of time, and could sustain losses of a portion or all of such amounts.
Moreover, the performance guarantee of an exchange clearinghouse generally extends only to its members and the
Fund could sustain losses, notwithstanding such guarantee, in the event of the bankruptcy of its broker.
Trading and Position Limits. The exchanges on which futures and options are traded may impose
limitations governing the maximum number of positions on the same side of the market and involving the same
underlying instrument which may be held by a single investor, whether acting alone or in concert with others
(regardless of whether such contracts are held on the same or different exchanges or held or written in one or
more accounts or through one or more brokers.) Further, the CFTC and the various contract markets have
established limits referred to as "speculative position limits" on the maximum net long or net short position
which any person may hold or control in a particular futures or option contract. An exchange may order the
liquidation of positions found to be in violation of these limits and it may impose other sanctions or
restrictions. The Adviser does not believe that these trading and position limits will have any adverse impact
on the strategies for hedging the portfolios of the Fund.
Risks of Options on Futures Contracts. The amount of risk the Fund assumes when it purchases an Option
on a Futures Contract is the premium paid for the option, plus related transaction costs. In order to profit
from an option purchased, however, it may be necessary to exercise the option and to liquidate the underlying
Futures Contract, subject to the risks of the availability of a liquid offset market described herein. The
writer of an Option on a Futures Contract is subject to the risks of commodity futures trading, including the
requirement of initial and variation margin payments, as well as the additional risk that movements in the price
of the option may not correlate with movements in the price of the underlying security, index, currency or
Futures Contract.
Risks of Transactions in Foreign Currencies and Over-the-Counter Derivatives and Other Transactions Not
Conducted on U.S. Exchanges. Transactions in Forward Contracts on foreign currencies, as well as futures and
options on foreign currencies and transactions executed on foreign exchanges, are subject to all of the
correlation, liquidity and other risks outlined above. In addition, however, such transactions are subject to
the risk of governmental actions affecting trading in or the prices of currencies underlying such contracts,
which could restrict or eliminate trading and could have a substantial adverse effect on the value of positions
held by the Fund. Further, the value of such positions could be adversely affected by a number of other complex
political and economic factors applicable to the countries issuing the underlying currencies.
Further, unlike trading in most other types of instruments, there is no systematic reporting of last
sale information with respect to the foreign currencies underlying contracts thereon. As a result, the available
information on which trading systems will be based may not be as complete as the comparable data on which the
Fund makes investment and trading decisions in connection with other transactions. Moreover, because the foreign
currency market is a global, 24-hour market, events could occur in that market which will not be reflected in the
forward, futures or options market until the following day, thereby making it more difficult for the Fund to
respond to such events in a timely manner.
Settlements of exercises of over-the-counter Forward Contracts or foreign currency options generally
must occur within the country issuing the underlying currency, which in turn requires traders to accept or make
delivery of such currencies in conformity with any U.S. or foreign restrictions and regulations regarding the
maintenance of foreign banking relationships, fees, taxes or other charges.
Unlike transactions entered into by the Fund in Futures Contracts and exchange-traded options, on
foreign currencies, Forward Contracts, over-the-counter options on securities, swaps and other over-the-counter
derivatives are not traded on contract markets regulated by the CFTC or (with the exception of certain foreign
currency options) the SEC. To the contrary, such instruments are traded through financial institutions acting as
market-makers, although foreign currency options are also traded on certain national securities exchanges, such
as the Philadelphia Stock Exchange and the Chicago Board Options Exchange, subject to SEC regulation. In an
over-the-counter trading environment, many of the protections afforded to exchange participants will not be
available. For example, there are no daily price fluctuation limits, and adverse market movements could
therefore continue to an unlimited extent over a period of time. Although the purchaser of an option cannot lose
more than the amount of the premium plus related transaction costs, this entire amount could be lost. Moreover,
the option writer and a trader of Forward Contracts could lose amounts substantially in excess of their initial
investments, due to the margin and collateral requirements associated with such positions.
In addition, over-the-counter transactions can only be entered into with a financial institution willing
to take the opposite side, as principal, of the Fund's position unless the institution acts as broker and is able
to find another counterparty willing to enter into the transaction with the Fund. Where no such counterparty is
available, it will not be possible to enter into a desired transaction.
Further, over-the-counter transactions are not subject to the guarantee of an exchange clearinghouse,
and the Fund will therefore be subject to the risk of default by, or the bankruptcy of, the financial institution
serving as its counterparty. One or more of such institutions also may decide to discontinue their role as
market-makers in a particular currency or security, thereby restricting the Fund's ability to enter into desired
hedging transactions.
Options on securities, options on stock indices, Futures Contracts, Options on Futures Contracts and
options on foreign currencies may be traded on exchanges located in foreign countries. Such transactions may not
be conducted in the same manner as those entered into on U.S. exchanges, and may be subject to different margin,
exercise, settlement or expiration procedures. As a result, many of the risks of over-the-counter trading may be
present in connection with such transactions.
Options on foreign currencies traded on national securities exchanges are within the jurisdiction of the
SEC, as are other securities traded on such exchanges. As a result, many of the protections provided to traders
on organized exchanges will be available with respect to such transactions. In particular, all foreign currency
option positions entered into on a national securities exchange are cleared and guaranteed by the Options
Clearing Corporation (the "OCC"), thereby reducing the risk of counterparty default.
The purchase and sale of exchange-traded foreign currency options, is subject to the risks regarding
adverse market movements, margining of options written, the nature of the foreign currency market, possible
intervention by governmental authorities and the effects of other political and economic events. In addition,
exchange-traded options on foreign currencies involve certain risks not presented by the over-the-counter
market. For example, exercise and settlement of such options must be made exclusively through the OCC, which has
established banking relationships in applicable foreign countries for this purpose. As a result, the OCC may, if
it determines that foreign governmental restrictions or taxes would prevent the orderly settlement of foreign
currency option exercises, or would result in undue burdens on the OCC or its clearing member, impose special
procedures on exercise and settlement, such as technical changes in the mechanics of delivery of currency, the
fixing of dollar settlement prices or prohibitions on exercise.
Short Sales Against The Box. The Fund may make short sales "against the box." If the Fund enters into
a short sales against the box, it is required to segregate securities equivalent in kind and amount to the
securities sold short (or securities convertible or exchangeable into such securities) and is required to hold
such securities while the short sale is outstanding. The Fund will incur transaction costs, including interest,
in connection with opening, maintaining, and closing short sales against the box. For further information about
this practice, please refer to the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Short Term Instruments. The Fund may hold cash and invest in cash equivalents, such as short-term U.S.
Government Securities, commercial paper and bank instruments.
Temporary Defensive Positions. During periods of unusual market conditions when the Sub-advisor
believes that investing for temporary defensive purposes is appropriate, or in order to meet anticipated
redemption requests, a large portion or all of the assets of the Fund may be invested in cash (including foreign
currency) or cash equivalents, including, but not limited to, obligations of banks (including certificates of
deposit, bankers acceptances, time deposits and repurchase agreements), commercial paper, short-term notes, U.S.
Government securities and related repurchase agreements.
Warrants. The Fund may invest in warrants. The strike price of warrants typically is much lower than
the current market price of the underlying securities, yet they are subject to similar price fluctuations, in
absolute terms. As a result, warrants may be more volatile investments than the underlying securities and may
offer greater potential for capital appreciation as well as capital loss. Additional information regarding
warrants is included in this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk factors and Investment Methods."
"When-Issued" Securities. The Fund may purchase securities on a "when-issued," "forward commitment," or
"delayed delivery" basis. The commitment to purchase a security for which payment will be made on a future date
may be deemed a separate security. While awaiting delivery of securities purchased on such basis, the Fund will
identify liquid and unencumbered assets equal to its forward delivery commitment. For more information about
when-issued securities, please see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
ASAF INVESCO Equity Income Fund:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek high current income and capital growth
while following sound investment practices.
Investment Policies:
The Fund will pursue its objective by investing its assets in securities that are expected to produce
high levels of income and consistent, stable returns.
In pursuing its investment objective, the Fund normally invests at least 65% of its total assets in
dividend paying common and preferred stocks. Up to 30% of the Fund's assets may be invested in equity securities
that do not pay regular dividends. The remaining assets are invested in other income producing securities, such
as corporate bonds. Sometimes warrants are acquired when offered with income-producing securities, but the
warrants are disposed of at the first favorable opportunity. Acquiring warrants involves a risk that the Fund
will lose the premium it pays to acquire warrants if the Fund does not exercise a warrant before it expires. The
major portion of the investment portfolio normally consists of common stocks, convertible bonds and debentures,
and preferred stocks; however, there may also be substantial holdings of debt securities, including
non-investment grade and unrated debt securities.
Debt Securities. The debt securities in which the Fund invests are generally subject to two kinds of
risk, credit risk and market risk. The ratings given a debt security by Moody's and Standard & Poor's ("S&P")
provide a generally useful guide as to such credit risk. The lower the rating given a debt security by such
rating service, the greater the credit risk such rating service perceives to exist with respect to such
security. Increasing the amount of Fund assets invested in unrated or lower grade (Ba or less by Moody's, BB or
less by S&P) debt securities, while intended to increase the yield produced by the Fund's debt securities, will
also increase the credit risk to which those debt securities are subject.
Lower-rated debt securities and non-rated securities of comparable quality tend to be subject to wider
fluctuations in yields and market values than higher rated debt securities and may have speculative
characteristics. Although the Fund may invest in debt securities assigned lower grade ratings by S&P or Moody's,
the Fund's investments have generally been limited to debt securities rated B or higher by either S&P or
Moody's. Debt securities rated lower than B by either S&P or Moody's may be highly speculative. The Sub-advisor
intends to limit such portfolio investments to debt securities which are not believed by the Sub-advisor to be
highly speculative and which are rated at least CCC or Caa, respectively, by S&P or Moody's. In addition, a
significant economic downturn or major increase in interest rates may well result in issuers of lower-rated debt
securities experiencing increased financial stress which would adversely affect their ability to service their
principal and interest obligations, to meet projected business goals, and to obtain additional financing. While
the Sub-advisor attempts to limit purchases of lower-rated debt securities to securities having an established
retail secondary market, the market for such securities may not be as liquid as the market for higher rated debt
securities. For an additional discussion of certain risks involved in lower-rated or unrated securities, see
this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Lending Portfolio Securities. The Fund may lend its securities to qualified brokers, dealers, banks, or
other financial institutions. While voting rights may pass with the loaned securities, if a material event
(e.g., proposed merger, sale of assets, or liquidation) is to occur affecting an investment on loan, the loan
must be called and the securities voted. Loans of securities made by the Fund will comply with all other
applicable regulatory requirements, including the rules of the New York Stock Exchange and the requirements of
the Investment Company Act of 1940 and the Rules of the SEC thereunder.
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
not "fundamental" restrictions and may be changed by the Directors of the Company without shareholder approval.
The Fund will not:
1. Invest in companies for the purpose of exercising management or control;
2. Purchase securities of open-end or closed-end investment companies except in compliance with
the Investment Company Act of 1940;
3. Purchase securities on margin, except (i) for use of short-term credit necessary for clearance
of purchases of portfolio securities and (ii) the Fund may make margin deposits in connection with futures
contracts or other permissible investments;
4. Effect short sales of securities; or
5. Purchase any security or enter into a repurchase agreement, if as a result, more than 15% of
its net assets would be invested in repurchase agreements not entitling the holder to payment of principal and
interest within seven days and in securities that are illiquid by virtue of legal or contractual restrictions on
resale or the absence of a readily available market. The Directors of the Company, or the Investment Manager or
the Sub-advisor acting pursuant to authority delegated by the Directors, may determine that a readily available
market exists for securities eligible for resale pursuant to Rule 144A under the Securities Act of 1933, or any
successor to that rule, and therefore that such securities are not subject to the foregoing limitation.
ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek capital growth and current income.
Investment Policies:
In general, within the restrictions outlined herein, the Sub-advisor has broad powers with respect to
investing funds or holding them uninvested. Investments are varied according to what is judged advantageous
under changing economic conditions. It will be the policy of the Sub-advisor to retain maximum flexibility in
management without restrictive provisions as to the proportion of one or another class of securities that may be
held subject to the investment restrictions described below. However, the Sub-advisor may invest the assets of
the Fund in varying amounts in other instruments and in senior securities, such as bonds, debentures, preferred
stocks and convertible issues, when such a course is deemed appropriate in order to attempt to attain its
financial objectives. Senior securities that, in the opinion of the Sub-advisor, are high-grade issues may also
be purchased for defensive purposes.
The above statement of investment policy gives the Sub-advisor authority to invest in securities other
than common stocks and traditional debt and convertible issues. The Sub-advisor may invest in master limited
partnerships (other than real estate partnerships) and royalty trusts which are traded on domestic stock
exchanges when such investments are deemed appropriate for the attainment of the Fund's investment objectives.
The Sub-advisor will invest approximately 60% of the Fund in common stocks and the balance in fixed
income securities. Common stock investments are described above. The fixed income assets will be invested
primarily in investment grade securities. The Fund may invest up to 10% of its fixed income assets in high yield
securities. There are no credit or maturity restrictions on the fixed income securities in which the high yield
portion of the Fund may be invested. The Fund may invest in securities of the United States government and its
agencies and instrumentalities, corporate, sovereign government, municipal, mortgage-backed, and other
asset-backed securities. For purposes of determining the weighted average maturity of the fixed income portion
of the Fund, the Sub-advisor will use weighted average life as the measure of maturity for all mortgage-backed
and asset-backed securities. It can be expected that the Sub-advisor will invest from time to time in bonds and
preferred stock convertible into common stock.
Forward Currency Exchange Contracts. The Fund conducts its foreign currency exchange transactions
either on a spot (i.e., cash) basis at the spot rate prevailing in the foreign currency exchange market, or
through entering into forward foreign currency exchange contracts to purchase or sell foreign currencies.
The Fund expects to use forward contracts under two circumstances: (1) when the Sub-advisor wishes to
"lock in" the U.S. dollar price of a security when the Fund is purchasing or selling a security denominated in a
foreign currency, the Fund would be able to enter into a forward contract to do so ("transaction hedging"); (2)
when the Sub-advisor believes that the currency of a particular foreign country may suffer a substantial decline
against the U.S. dollar, the Fund would be able to enter into a forward contract to sell foreign currency for a
fixed U.S. dollar amount approximating the value of some or all of the Fund's securities either denominated in,
or whose value is tied to, such foreign currency ("portfolio hedging"). It is anticipated that the Fund will
enter into portfolio hedges much less frequently than transaction hedges.
As to transactional hedging, when the Fund enters into a trade for the purchase or sale of a security
denominated in a foreign currency, it may be desirable to establish (lock in) the U.S. dollar cost or proceeds.
By entering into forward contracts in U.S. dollars for the purchase or sale of a foreign currency involved in an
underlying security transaction, the Fund will be able to protect itself against a possible loss between trade
and settlement dates resulting from the adverse change in the relationship between the U.S. dollar at the subject
foreign currency.
Under portfolio hedging, when the Sub-advisor believes that the currency of a particular country may
suffer a substantial decline relative to the U.S. dollar, the Fund could enter into a foreign contract to sell
for a fixed dollar amount the amount in foreign currencies approximating the value of some or all of its
portfolio securities either denominated in, or whose value is tied to, such foreign currency. The Fund will
place cash or high-grade liquid securities in a separate account with its custodian in an amount sufficient to
cover its obligation under the contract. If the value of the securities placed in the separate account declines,
additional cash or securities will be placed in the account on a daily basis so that the value of the account
equals the amount of the Fund's commitments with respect to such contracts. At any given time, no more than 10%
of the Fund's assets will be committed to a segregated account in connection with portfolio hedging transactions.
The precise matching of forward contracts in the amounts and values of securities involved would not
generally be possible since the future values of such foreign currencies will change as a consequence of market
movements in the values of those securities between the date the forward contract is entered into and the date it
matures. Predicting short-term currency market movements is extremely difficult, and the successful execution of
short-term hedging strategy is highly uncertain. The Sub-advisor does not intend to enter into such contracts on
a regular basis. Normally, consideration of the prospect for currency parities will be incorporated into the
long-term investment decisions made with respect to overall diversification strategies. However, the Sub-advisor
believes that it is important to have flexibility to enter into such forward contracts when it determines that
the Fund 's best interests may be served.
Generally, the Fund will not enter into a forward contract with a term of greater than one year. At the
maturity of the forward contract, the Fund may either sell the portfolio security and make delivery of the
foreign currency, or it may retain the security and terminate the obligation to deliver the foreign currency by
purchasing an "offsetting" forward contract with the same currency trader obligating the Fund to purchase, on the
same maturity date, the same amount of the foreign currency.
It is impossible to forecast with absolute precision the market value of the Fund's securities at the
expiration of the forward contract. Accordingly, it may be necessary for the Fund to purchase additional foreign
currency on the spot market (and bear the expense of such purchase) if the market value of the security is less
than the amount of foreign currency the Fund is obligated to deliver and if a decision is made to sell the
security and make delivery of the foreign currency the Fund is obligated to deliver. For an additional
discussion of forward currency exchange contracts and certain risks involved therein, see this SAI and the
Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Derivative Securities. To the extent permitted by its investment objectives and policies discussed
elsewhere herein, the Fund may invest in securities that are commonly referred to as "derivative" securities.
Certain derivative securities are more accurately described as "index/structured" securities. Index/structured
securities are derivative securities whose value or performance is linked to other equity securities (such as
depositary receipts), currencies, interest rates, indices or other financial indicators ("reference indices").
Some "derivatives," such as mortgage-backed and other asset-backed securities, are in many respects like
any other investment, although they may be more volatile or less liquid than more traditional debt securities.
The Fund may not invest in a derivative security unless the reference index or the instrument to which
it relates is an eligible investment for the Fund. For example, a security whose underlying value is linked to
the price of oil would not be a permissible investment because the Fund may not invest in oil and gas leases or
futures.
The return on a derivative security may increase or decrease, depending upon changes in the reference
index or instrument to which it relates.
There is a range of risks associated with derivative investments, including:
o the risk that the underlying security, interest rate, market index or other financial asset will not
move in the direction the portfolio manager anticipates;
o the possibility that there may be no liquid secondary market, or the possibility that price fluctuation
limits may be imposed by the exchange, either of which may make it difficult or impossible to close out
a position when desired; and
o the risk that the counterparty will fail to perform its obligations.
The Sub-advisor will report to the Investment Manager on activity in derivative securities, and the Investment
Manager will report to the Trust's Board of Directors as necessary. For additional information on derivatives
and their risks, see the Trust's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Futures and Options. The Fund may enter into futures contracts, options or options on futures
contracts. The Fund may not, however, enter into a futures transaction for speculative purposes. Generally,
futures transactions will be used to:
o protect against a decline in market value of the Fund's securities (taking a short futures position), or
o protect against the risk of an increase in market value for securities in which the Fund generally
invests at a time
when the Fund is not fully-invested (taking a long futures position), or
o provide a temporary substitute for the purchase of an individual security that may be purchased in an
orderly fashion.
Some futures and options strategies, such as selling futures, buying puts and writing calls, hedge the
Fund's investments against price fluctuations. Other strategies, such as buying futures, writing puts and buying
calls, tend to increase market exposure.
Although other techniques may be used to control the Fund's exposure to market fluctuations, the use of
futures contracts may be a more effective means of hedging this exposure. While the Fund will pay brokerage
commissions in connection with opening and closing out futures positions, these costs are lower than the
transaction costs incurred in the purchase and sale of the underlying securities.
The Fund may engage in futures and options transactions based on securities indices that are consistent
with the Fund's investment objectives. Examples of indices that may be used include the Bond Buyer Index of
Municipal Bonds for fixed income funds, or the S&P 500 Index for equity funds. The Fund also may engage in
futures and options transactions based on specific securities, such as U.S. Treasury bonds or notes. Futures
contracts are traded on national futures exchanges. Futures exchanges and trading are regulated under the
Commodity Exchange Act by the CFTC, a U.S. government agency.
Unlike when the Fund purchases or sells a bond, no price is paid or received by the Fund upon the
purchase or sale of the future. Initially, the Fund will be required to deposit an amount of cash or securities
equal to a varying specified percentage of the contract amount. This amount is known as initial margin. The
margin deposit is intended to assure completion of the contract (delivery or acceptance of the underlying
security) if it is not terminated prior to the specified delivery date. Minimum initial margin requirements are
established by the futures exchanges and may be revised. In addition, brokers may establish margin deposit
requirements that are higher than the exchange minimums. Cash held in the margin account is not income
producing. Subsequent payments, called variation margin, to and from the broker, will be made on a daily basis
as the price of the underlying debt securities or index fluctuates, making the future more or less valuable, a
process known as marking the contract to market.
Futures and options prices can be volatile, and trading in these markets involves certain risks, which
are described in more detail in this Statement and the Trust's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and
Investment Methods." The Sub-advisor will seek to minimize these risks by limiting the contracts entered into on
behalf of the Fund to those traded on national futures exchanges and for which there appears to be a liquid
secondary market.
Options on Futures. By purchasing an option on a futures contract, the Fund obtains the right, but not
the obligation, to sell the futures contract (a put option) or to buy the contract (a call option) at a fixed
strike price. The Fund can terminate its position in a put option by allowing it to expire or by exercising the
option. If the option is exercised, the Fund completes the sale of the underlying instrument at the strike
price. Purchasing an option on a futures contract does not require the Fund to make margin payments unless the
option is exercised.
Although they do not currently intend to do so, the Fund may write (or sell) call options that obligate
it to sell (or deliver) the option's underlying instrument upon exercise of the option. While the receipt of
option premiums would mitigate the effects of price declines, the Fund would give up some ability to participate
in a price increase on the underlying instrument. If the Fund were to engage in options transactions, it would
own the futures contract at the time a call were written and would keep the contract open until the obligation to
deliver it pursuant to the call expired.
Portfolio Securities Lending. In order to realize additional income, the Fund may lend its portfolio
securities to persons not affiliated with it and who are deemed to be creditworthy by the Sub-advisor. Such
loans must be secured continuously by cash collateral maintained on a current basis in an amount at least equal
to the market value of the securities loaned, or by irrevocable letters of credit. During the existence of the
loan, the Fund must continue to receive the equivalent of the interest and dividends paid by the issuer on the
securities loaned and interest on the investment of the collateral. The Fund must have the right to call the
loan and obtain the securities loaned at any time on three days' notice, including the right to call the loan to
enable the Fund to vote the securities. Such loans may not exceed one-third of the Fund's total assets taken at
market. Interest on loaned securities may not exceed 10% of the annual gross income of the Fund (without offset
for realized capital gains).
Investments in Companies with Limited Operating History. The Fund may invest in the securities of
issuers with limiting operating history. The Sub-advisor considers an issuer to have a limited operating history
if that issuer has a record of less than three years of continuous operation.
Investments in securities of issuers with limited operating history may involve greater risks than
investments in securities of more mature issuers. By their nature, such issuers present limited operating
history and financial information upon which the manager may base its investment decision on behalf of the Fund.
In addition, financial and other information regarding such issuers, when available, may be incomplete or
inaccurate.
The Fund will not invest more than 5% of its total assets in the securities of issuers with less than a
three-year operating history. The Sub-advisor will consider periods of capital formation, incubation,
consolidation, and research and development in determining whether a particular issuer has a record of three
years of continuous operation.
Short Sales. The Fund may engage in short sales if, at the time of the short sale, the Fund owns or has
the right to acquire an equal amount of the security being sold short at no additional cost.
In a short sale, the seller does not immediately deliver the securities sold and is said to have a short
position in those securities until delivery occurs. To make delivery to the purchaser, the executing broker
borrows the securities being sold short on behalf of the seller. While the short position is maintained, the
seller collateralizes its obligation to deliver the securities sold short in an amount equal to the proceeds of
the short sale plus an additional margin amount established by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve. If
the Fund engages in a short sale, the collateral account will be maintained by the Fund's custodian. While the
short sale is open, the Fund will maintain in a segregated custodial account an amount of securities convertible
into, or exchangeable for, such equivalent securities at no additional cost. These securities would constitute
the Fund's long position.
When the Fund makes a short sale as described above, any future losses in the Fund's long position
should be reduced by a gain in the short position. The extent to which such gains or losses are reduced would
depend upon the amount of the security sold short relative to the amount the Fund owns. There will be certain
additional transaction costs associated with short sales, but the Fund will endeavor to offset these costs with
income from the investment of the cash proceeds of short sales.
Portfolio Turnover. The Sub-advisor will purchase and sell securities without regard to the length of
time the security has been held and, accordingly, it can be expected that the rate of portfolio turnover may be
substantial.
The Sub-advisor intends to purchase a given security whenever the Sub-advisor believes it will
contribute to the stated objective of the Fund, even if the same security has only recently been sold. The Fund
will sell a given security, no matter for how long or for how short a period it has been held, and no matter
whether the sale is at a gain or at a loss, if the Sub-advisor believes that it is not fulfilling its purpose,
either because, among other things, it did not live up to the Sub-advisor's expectations, or because it may be
replaced with another security holding greater promise, or because it has reached its optimum potential, or
because of a change in the circumstances of a particular company or industry or in general economic conditions,
or because of some combination of such reasons.
When a general decline in security prices is anticipated, the equity portion of the Fund may decrease or
eliminate entirely its equity position and increase its cash position, and when a rise in price levels is
anticipated, it may increase its equity position and decrease its cash position. However, it should be expected
that the Fund will, under most circumstances, be essentially fully invested in equity securities.
Since investment decisions are based on the anticipated contribution of the security in question to the
Fund's objectives, the rate of portfolio turnover is irrelevant when the Sub-advisor believes a change is in
order to achieve those objectives, and the Fund's annual portfolio turnover rate cannot be anticipated and may
be comparatively high. Since the Sub-advisor does not take portfolio turnover rate into account in making
investment decisions, (1) the Sub-advisor has no intention of accomplishing any particular rate of portfolio
turnover, whether high or low, and (2) the portfolio turnover rates in the past should not be considered as a
representation of the rates which will be attained in the future. For an additional discussion of portfolio
turnover, see this SAI under "Portfolio Transactions" and the Company's Prospectus under "Portfolio Turnover."
Collateralized Mortgage Obligations. The Fund may buy collateralized mortgage obligations ("CMOs"). The
Fund may buy CMOs that are: (i) collateralized by pools of mortgages in which payment of principal and interest
of each mortgage is guaranteed by an agency or instrumentality of the U.S. government; (ii) collateralized by
pools of mortgages in which payment of principal and interest are guaranteed by the issuer, and the guarantee is
collateralized by U.S. government securities; or (iii) securities in which the proceeds of the issue are invested
in mortgage securities and payments of principal and interest are supported by the credit of an agency or
instrumentality of the U.S. government. For a discussion of CMOs and the risks involved therein, see the
Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
not "fundamental" restrictions and may be changed by the Directors of the Company without shareholder approval.
The Fund will not:
1. Invest more than 15% of its assets in illiquid investments; or
2. Buy securities on margin or sell short (unless it owns, or by virtue of its ownership of, other
securities has the right to obtain securities equivalent in kind and amount to the securities sold); however, the
Fund may make margin deposits in connection with the use of any financial instrument or any transaction in
securities permitted under its investment policies;
3. Invest for control or for management; or
4. Invest in the securities of other investment companies except in compliance with the Investment
Company Act of 1940. Duplicate fees may result from such purchases.
ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek high current income by investing primarily
in fixed income securities. The fixed income securities in which the Fund intends to invest are lower-rated
corporate debt obligations.
Investment Policies:
Corporate Debt Securities. The Fund invests primarily in corporate debt securities. The corporate debt
obligations in which the Fund intends to invest are expected to be lower-rated. For a discussion of the special
risks associated with lower-rated securities, see the Company's Prospectus and this SAI under "Certain Risk
Factors and Investment Methods." Corporate debt obligations in which the Fund invests may bear fixed, floating,
floating and contingent, or increasing rates of interest. They may involve equity features such as conversion or
exchange rights, warrants for the acquisition of common stock of the same or a different issuer, participations
based on revenues, sales or profits, or the purchase of common stock in a unit transaction (where corporate debt
securities and common stock are offered as a unit).
U.S. Government Obligations. The types of U.S. government obligations in which the Fund may invest
include, but are not limited to, direct obligations of the U.S. Treasury (such as U.S. Treasury bills, notes, and
bonds) and obligations issued or guaranteed by U.S. government agencies or instrumentalities (such as the Federal
Home Loan Banks, Federal National Mortgage Association, Government National Mortgage Association, Federal Farm
Credit Banks, Tennessee Valley Authority, Export-Import Bank of the United States, Commodity Credit Corporation,
Federal Financing Bank, Student Loan Marketing Association, Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation, or National
Credit Union Administration). These securities may be backed by: the full faith and credit of the U.S. Treasury;
the issuer's right to borrow from the U.S. Treasury; the discretionary authority of the U.S. government to
purchase certain obligations of agencies or instrumentalities; or the credit of the agency or instrumentality
issuing the obligations. For an additional discussion of the types of U.S. government obligations in which the
Fund may invest, see the Company's Prospectus under "Investment Programs of the Funds."
Time and Savings Deposits and Bankers' Acceptances. The Fund may enter into time and savings deposits
(including certificates of deposit) and may purchase bankers' acceptances. The Fund may enter into time and
savings deposits (including certificates of deposit) in commercial or savings banks whose deposits are insured by
the Bank Insurance Fund ("BIF"), or the Savings Association Insurance Fund ("SAIF"), including certificates of
deposit issued by and other time deposits in foreign branches of BIF-insured banks. The Fund may also purchase
bankers' acceptances issued by a BIF-insured bank, or issued by the bank's Edge Act subsidiary and guaranteed by
the bank, with remaining maturities of nine months or less. The total acceptances of any bank held by the Fund
cannot exceed 0.25 of 1% of such bank's total deposits according to the bank's last published statement of
condition preceding the date of acceptance; and general obligations of any state, territory, or possession of the
United States, or their political subdivisions, so long as they are either (1) rated in one of the four highest
grades by nationally recognized statistical rating organizations or (2) issued by a public housing agency and
backed by the full faith and credit of the United States.
When-Issued and Delayed Delivery Transactions. The Fund may purchase fixed-income securities on a
when-issued or delayed delivery basis. The Fund may engage in when-issued and delayed delivery transactions only
for the purpose of acquiring portfolio securities consistent with the Fund's investment objective and policies,
not for investment leverage. These transactions are arrangements in which the Fund purchases securities with
payment and delivery scheduled for a future time. Settlement dates may be a month or more after entering into
these transactions, and the market values of the securities purchased may vary from the purchase prices. These
transactions are made to secure what is considered to be an advantageous price and yield for the Fund.
No fees or other expenses, other than normal transaction costs, are incurred. However, liquid assets of
the Fund sufficient to make payment for the securities to be purchased are segregated at the trade date. These
securities are marked to market daily and will maintain until the transaction is settled. For an additional
discussion of when-issued securities and certain risks involved therein, see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors
and Investment Methods."
Lending Portfolio Securities. In order to generate additional income, the Fund may lend its securities
to brokers/dealers, banks, or other institutional borrowers of securities. The Fund will only enter into loan
arrangements with broker/dealers, banks, or other institutions that have been determined to be creditworthy. The
collateral received when the Fund lends portfolio securities must be valued daily and, should the market value of
the loaned securities increase, the borrower must furnish additional collateral to the Fund. During the time
portfolio securities are on loan, the borrower pays the Fund any dividends or interest paid on such securities.
Loans are subject to termination at the option of the Fund or the borrower. The Fund may pay reasonable
administrative and custodial fees in connection with a loan and may pay a negotiated portion of the interest
earned on the cash or cash equivalent collateral to the borrower or placing broker. The Fund does not have the
right to vote securities on loan, but would terminate the loan and regain the right to vote if that were
considered important with respect to the investment.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements. The Fund may also enter into reverse repurchase agreements. When
effecting reverse repurchase agreements, liquid assets of the Fund, in a dollar amount sufficient to make payment
for the obligations to be purchased, are segregated at the trade date. These securities are marked to market
daily and are maintained until the transaction is settled. During the period any reverse repurchase agreements
are outstanding, but only to the extent necessary to ensure completion of the reverse repurchase agreements, the
Fund will restrict the purchase of portfolio instruments to money market instruments maturing on or before the
expiration date of the reverse repurchase agreements. For a discussion of reverse repurchase agreements and
certain risks involved therein, see the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Portfolio Turnover. The Fund may experience greater portfolio turnover than would be expected with a
portfolio of higher-rated securities. For an additional discussion of portfolio turnover, see this SAI under
"Portfolio Transactions" and the Company's Prospectus under "Portfolio Turnover."
Adverse Legislation. In 1989, legislation was enacted that required federally insured savings and loan
associations to divest their holdings of lower-rated bonds by 1994. This legislation also created the Resolution
Trust Corporation (the "RTC"), which disposed of a substantial portion of lower-rated bonds held by failed
savings and loan associations. The reduction of the number of institutions empowered to purchase and hold
lower-rated bonds, and the divestiture of bonds by these institutions and the RTC, have had an adverse impact on
the overall liquidity of the market for such bonds. Federal and state legislatures and regulators have and may
continue to propose new laws and regulations designed to limit the number or type of institutions that may
purchase lower-rated bonds, reduce the tax benefits to issuers of such bonds, or otherwise adversely impact the
liquidity of such bonds. The Fund cannot predict the likelihood that any of these proposals will be adopted, or
their potential impact on the liquidity of lower-rated bonds.
Foreign Securities. For a discussion of certain risks involved with investing in foreign securities,
including currency risks, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods."
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
not "fundamental" restriction and may be changed by the Directors of the Company without shareholder approval.
The Fund will not:
1. Invest more than 15% of the value of its net assets in securities that are not readily
marketable, including repurchase agreements providing for settlement in more than seven days after notice. The
Directors of the Company, or the Investment Manager or the Sub-advisor acting pursuant to authority delegated by
the Directors, may determine that a readily available market exists for certain securities eligible for resale
pursuant to Rule 144A under the Securities Act of 1933, or any successor to such rule, and therefore that such
securities are not subject to the foregoing limitation;
2. Purchase securities of open-end or closed-end investment companies except in compliance with
the Investment Company Act of 1940;
3. Purchase any securities on margin but may obtain such short-term credits as may be necessary
for the clearance of transactions;
4. Invest more than 10% of the value of its total assets in foreign securities which are not
publicly traded in the United States;
5. Make short sales of securities or maintain short positions, unless: during the time the short
position is open, it owns an equal amount of the securities sold or securities readily and freely convertible
into or exchangeable, without payment of additional consideration, for securities of the same issue as, and equal
in amount to, the securities sold short; and not more than 10% of the Fund's net assets (taken at current value)
is held as collateral for such sales at any one time; or
6. Purchase securities of a company for the purpose of exercising control or management. However,
the Fund may invest in up to 10% of the voting securities of any one issuer and may exercise its voting powers
consistent with the best interests of the Fund. From time to time, the Fund, together with other investment
companies advised by subsidiaries or affiliates of the Sub-advisor, may together buy and hold substantial amounts
of a company's voting stock. All such stock may be voted together. In some such cases, the Fund and the other
investment companies might collectively be considered to be in control of the company in which they have
invested. In some cases, directors, agents, employees, officers, or others affiliated with or acting for the
Fund, the Sub-advisor, or affiliated companies might possibly become directors of companies in which the Fund
holds stock.
ASAF PIMCO Total Return Bond Fund:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek to maximize total return, consistent with
preservation of capital. The Sub-advisor will seek to employ prudent investment management techniques,
especially in light of the broad range of investment instruments in which the Fund may invest.
Investment Policies:
Borrowing. The Fund may borrow for temporary administrative purposes. This borrowing may be
unsecured. The Investment Company Act of 1940 requires the Fund to maintain continuous asset coverage (that is,
total assets including borrowings, less liabilities exclusive of borrowings) of 300% of the amount borrowed. If
the 300% asset coverage should decline as a result of market fluctuations or other reasons, the Fund may be
required to sell some of its holdings within three days to reduce the debt and restore the 300% asset coverage,
even though it may be disadvantageous from an investment standpoint to sell securities at that time. Borrowing
will tend to exaggerate the effect on net asset value of any increase or decrease in the market value of the
Fund. Money borrowed will be subject to interest costs which may or may not be recovered by appreciation of the
securities purchased. The Fund also may be required to maintain minimum average balances in connection with such
borrowing or to pay a commitment or other fee to maintain a line of credit; either of these requirements would
increase the cost of borrowing over the stated interest rate.
In addition to the above, the Fund may enter into reverse repurchase agreements and mortgage dollar
rolls. A reverse repurchase agreement involves the sale of a portfolio-eligible security by the Fund, coupled
with its agreement to repurchase the instrument at a specified time and price. In a "dollar roll" transaction
the Fund sells a mortgage-related security (such as a GNMA security) to a dealer and simultaneously agrees to
repurchase a similar security (but not the same security) in the future at a pre-determined price. A "dollar
roll" can be viewed, like a reverse repurchase agreement, as a collateralized borrowing in which the Fund pledges
a mortgage-related security to a dealer to obtain cash. Unlike in the case of reverse repurchase agreements, the
dealer with which the Fund enters into a dollar roll transaction is not obligated to return the same securities
as those originally sold by the Fund, but only securities which are "substantially identical." To be considered
"substantially identical," the securities returned to the Fund generally must: (1) be collateralized by the same
types of underlying mortgages; (2) be issued by the same agency and be part of the same program; (3) have a
similar original stated maturity; (4) have identical net coupon rates; (5) have similar maturity: (4) have
identical net coupon rates; (5) have similar market yields (and therefore price); and (6) satisfy "good delivery"
requirements, meaning that the aggregate principal amounts of the securities delivered and received back must be
within 2.5% of the initial amount delivered. The Fund's obligations under a dollar roll agreement must be
covered by segregating cash or other liquid assets equal in value to the securities subject to repurchase by the
Fund.
Both dollar roll and reverse repurchase agreements will be subject to the Fund's limitations on
borrowings, which will restrict the aggregate of such transactions (plus any other borrowings) to 33 1/3% of the
Fund's total assets. Furthermore, because dollar roll transactions may be for terms ranging between one and six
months, dollar roll transactions may be deemed "illiquid" and subject to the Fund's overall limitations on
investments in illiquid securities.
Corporate Debt Securities. The Fund's investments in U.S. dollar- or foreign currency-denominated
corporate debt securities of domestic or foreign issuers are limited to corporate debt securities (corporate
bonds, debentures, notes and other similar corporate debt instruments, including convertible securities) which
meet the minimum ratings criteria set forth for the Fund, or, if unrated, are in the Sub-advisor's opinion
comparable in quality to corporate debt securities in which the Fund may invest. In the event that ratings
services assign different ratings to the same security, the Sub-advisor will determine which rating it believes
best reflects the security's quality and risk at that time, which may be the higher of the several assigned
ratings. The rate of return or return of principal on some debt obligations may be linked or indexed to the
level of exchange rates between the U.S. dollar and a foreign currency or currencies.
Among the corporate bonds in which the Fund may invest are convertible securities. A convertible
security is a bond, debenture, note, or other security that entitles the holder to acquire common stock or other
equity securities of the same or a different issuer. A convertible security generally entitles the holder to
receive interest paid or accrued until the convertible security matures or is redeemed, converted or exchanged.
Before conversion, convertible securities have characteristics similar to nonconvertible debt securities.
Convertible securities rank senior to common stock in a corporation's capital structure and, therefore, generally
entail less risk than the corporation's common stock, although the extent to which such risk is reduced depends
in large measure upon the degree to which the convertible security sells above its value as a fixed-income
security.
A convertible security may be subject to redemption at the option of the issuer at a predetermined
price. If a convertible security held by the Fund is called for redemption, the Fund will be required to permit
the issuer to redeem the security and convert it to underlying common stock, or will sell the convertible
security to a third party. The Fund generally would invest in convertible securities for their favorable price
characteristics and total return potential and would normally not exercise an option to convert.
Investments in securities rated below investment grade that are eligible for purchase by the Fund (i.e.,
rated B or better by Moody's or S&P) are described as "speculative" by both Moody's and S&P. Investment in
lower-rated corporate debt securities ("high yield securities") generally provides greater income and increased
opportunity for capital appreciation than investments in higher quality securities, but they also typically
entail greater price volatility and principal and income risk. These high yield securities are regarded as high
risk and predominantly speculative with respect to the issuer's continuing ability to meet principal and interest
payments. The market for these securities is relatively new, and many of the outstanding high yield securities
have not endured a major business recession. A long-term track record on default rates, such as that for
investment grade corporate bonds, does not exist for this market. Analysis of the creditworthiness of issuers of
debt securities that are high yield may be more complex than for issuers of higher quality debt securities.
High yield, high risk securities may be more susceptible to real or perceived adverse economic and
competitive industry conditions than investment grade securities. The price of high yield securities have been
found to be less sensitive to interest-rate adverse economic downturns or individual corporate developments. A
projection of an economic downturn or of a period of rising interest rates, for example, could cause a decline in
high yield security prices because the advent of a recession could lessen the ability of a highly leveraged
company to make principal and interest payments on its debt securities. If an issuer of high yield securities
defaults, in addition to risking payment of all or a portion of interest and principal, the Fund may incur
additional expenses to seek recovery. In the case of high yield securities structured as zero-coupon or
pay-in-kind securities, their market prices are affected to a greater extent by interest rate changes, and
therefore tend to be more volatile than securities which pay interest periodically and in cash.
The secondary market on which high yield, high risk securities are traded may be less liquid than the
market for higher grade securities. Less liquidity in the secondary trading market could adversely affect the
price at which the Fund could sell a high yield security, and could adversely affect the daily net asset value of
the shares. Adverse publicity and investor perceptions, whether or not based on fundamental analysis, may
decrease the values and liquidity of high yield securities especially in a thinly-traded market. When secondary
markets for high yield securities are less liquid than the market for higher grade securities, it may be more
difficult to value the securities because such valuation may require more research, and elements of judgment may
play a greater role in the valuation because there is less reliable, objective data available. The Sub-advisor
seeks to minimize the risks of investing in all securities through diversification, in-depth credit analysis and
attention to current developments in interest rates and market conditions. For an additional discussion of
certain risks involved in lower-rated debt securities, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain
Risk Factors and Investment Objectives."
Participation on Creditors Committees. The Fund may from time to time participate on committees formed
by creditors to negotiate with the management of financially troubled issuers of securities held by the Fund.
Such participation may subject the Fund to expenses such as legal fees and may make the Fund an "insider" of the
issuer for purposes of the federal securities laws, and therefore may restrict the Fund's ability to trade in or
acquire additional positions in a particular security when it might otherwise desire to do so. Participation by
the Fund on such committees also may expose the Fund to potential liabilities under the federal bankruptcy laws
or other laws governing the rights of creditors and debtors. The Fund will participate on such committees only
when the Sub-advisor believes that such participation is necessary or desirable to enforce the Fund's rights as a
creditor or to protect the value of securities held by the Fund.
Mortgage-Related Securities. The Fund may invest in mortgage-backed securities. Mortgage-related
securities are interests in pools of mortgage loans made to residential home buyers, including mortgage loans
made by savings and loan institutions, mortgage bankers, commercial banks and others. Pools of mortgage loans
are assembled as securities for sale to investors by various governmental, government-related and private
organizations (see "Mortgage Pass-Through Securities"). The Fund may also invest in debt securities which are
secured with collateral consisting of mortgage-related securities (see "Collateralized Mortgage Obligations"),
and in other types of mortgage-related securities.
Interests in pools of mortgage-related securities differ from other forms of debt securities, which
normally provide for periodic payment of interest in fixed amounts with principal payments at maturity or
specified call dates. Instead, these securities provide a monthly payment which consists of both interest and
principal payments. In effect, these payments are a "pass-through" of the monthly payments made by the
individual borrowers on their residential or commercial mortgage loans, net of any fees paid to the issuer or
guarantor of such securities. Additional payments are caused by repayments of principal resulting from the sale
of the underlying property, refinancing or foreclosure, net of fees or costs which may be incurred. Some
mortgage-related securities (such as securities issued by the Government National Mortgage Association) are
described as "modified pass-through." These securities entitle the holder to receive all interest and principal
payments owned on the mortgage pool, net of certain fees, at the scheduled payment dates regardless of whether or
not the mortgagor actually makes the payment.
The principal governmental guarantor of mortgage-related securities is the Government National Mortgage
Association ("GNMA"). GNMA is a wholly owned United States Government corporation within the Department of
Housing and Urban Development. GNMA is authorized to guarantee, with the full faith and credit of the United
States Government, the timely payment of principal and interest on securities issued by institutions approved by
GNMA (such as savings and loan institutions, commercial banks and mortgage bankers) and backed by pools of
FHA-insured or VA-guaranteed mortgages.
Government-related guarantors (i.e., not backed by the full faith and credit of the United States
Government) include the Federal National Mortgage Association ("FNMA") and the Federal Home Loan Mortgage
Corporation ("FHLMC"). FNMA is a government-sponsored corporation owned entirely by private stockholders. It is
subject to general regulation by the Secretary of Housing and Urban Development. FNMA purchases conventional
(i.e., not insured or guaranteed by any government agency) residential mortgages from a list of approved
seller/servicers which include state and federally chartered savings and loan associations, mutual savings banks,
commercial banks and credit unions and mortgage bankers. Pass-though securities issued by FNMA are guaranteed as
to timely payment of principal and interest by FNMA but are not backed by the full faith and credit of the United
States Government.
FHLMC was created by Congress in 1970 for the purpose of increasing the availability of mortgage credit
for residential housing. It is a government-sponsored corporation formerly owned by the twelve Federal Home Loan
Banks and now owned entirely by private stockholders. FHLMC issues Participation Certificates ("PC's") which
represent interests in conventional mortgages from FHLMC's national portfolio. FHLMC guarantees the timely
payment of interest and ultimate collection of principal, but PCs are not backed by the full faith and credit of
the United States Government.
Commercial banks, savings and loan institutions, private mortgage insurance companies, mortgage bankers
and other secondary market issuers also create pass-though pools of conventional residential mortgage loans.
Such issuers may, in addition, be the originators and/or servicers of the underlying mortgage loans as well as
the guarantors of the mortgage-related securities. Pools created by such nongovernmental issuers generally offer
a higher rate of interest than government and government-related pools because there are no direct or indirect
government or agency guarantees of payments in the former pools. However, timely payment of interest and
principal of these pools may be supported by various forms of insurance or guarantees, including individual loan,
title, pool and hazard insurance and letters of credit. The insurance and guarantees are issued by governmental
entities, private insurers and the mortgage poolers. Such insurance and guarantees and the creditworthiness of
the issuers thereof will be considered in determining whether a mortgage-related security meets the Company's and
the Trust's investment quality standards. There can be no assurance that the private insurers or guarantors can
meet their obligations under the insurance policies or guarantee arrangements. The Fund may buy mortgage-related
securities without insurance or guarantees if, through an examination of the loan experience and practices of the
originator/servicers and poolers, the Sub-advisor determines that the securities meet the Company's and the
Trust's quality standards. Although the market for such securities is becoming increasingly liquid, securities
issued by certain private organizations may not be readily marketable. The Fund will not purchase
mortgage-related securities or any other assets which in the Sub-advisor's opinion are illiquid if, as a result,
more than 15% of the value of the Fund's total assets will be illiquid.
Mortgage-backed securities that are issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or
instrumentalities, are not subject to the Fund's industry concentration restrictions, set forth in this SAI under
"Fundamental Investment Restrictions," by virtue of the exclusion from that test available to all U.S. Government
securities. In the case of privately issued mortgage-related securities, the Fund takes the position that
mortgage-related securities do not represent interests in any particular "industry" or group of industries. The
assets underlying such securities may be represented by a portfolio of first lien residential mortgages
(including both whole mortgage loans and mortgage participation interests) or portfolios of mortgage pass-through
securities issued or guaranteed by GNMA, FNMA or FHLMC. Mortgage loans underlying a mortgage-related security
may in turn be insured or guaranteed by the Federal Housing Administration or the Department of Veterans
Affairs. In the case of private issue mortgage-related securities whose underlying assets are neither U.S.
Government securities nor U.S. Government-insured mortgages, to the extent that real properties securing such
assets may be located in the same geographical region, the security may be subject to a greater risk of default
that other comparable securities in the event of adverse economic, political or business developments that may
affect such region and ultimately, the ability of residential homeowners to make payments of principal and
interest on the underlying mortgages.
Collateralized Mortgage Obligations (CMOs). A CMO is a hybrid between a mortgage-backed bond
and a mortgage pass-through security. Similar to a bond, interest and prepaid principal is paid, in most cases,
semiannually. CMOs may be collateralized by whole mortgage loans, but are more typically collateralized by
portfolios of mortgage pass-through securities guaranteed by GNMA, FHLMC, or FNMA, and their income streams.
CMOs are structured into multiple classes, each bearing a different stated maturity. Actual
maturity and average life will depend upon the prepayment experience of the collateral. CMOs provide for a
modified form of call protection through a de facto breakdown of the underlying pool of mortgages according to
--------
how quickly the loans are repaid. Monthly payment of principal received from the pool of underlying mortgages,
including prepayments, is first returned to investors holding the shortest maturity class. Investors holding the
longer maturity classes receive principal only after the first class has been retired. An investor is partially
guarded against a sooner than desired return or principal because of the sequential payments.
In a typical CMO transaction, a corporation ("issuer") issues multiple series (e.g., A, B, C,
Z) of the CMO bonds ("Bonds"). Proceeds of the Bond offering are used to purchase mortgages or mortgage
pass-through certificates ("Collateral"). The Collateral is pledged to a third party trustee as security for the
Bonds. Principal and interest payments from the Collateral are used to pay principal on the Bonds in the order
A, B, C, Z. The Series A, B, and C Bonds all bear current interest. Interest on the Series Z Bond is accrued
and added to principal and a like amount is paid as principal on the Series A, B, or C Bond currently being paid
off. When the Series A, B, and C Bonds are paid in full, interest and principal on the Series Z Bond begins to
be paid currently. With some CMOs, the issuer serves as a conduit to allow loan originators (primarily builders
or savings and loan associations) to borrow against their loan portfolios.
FHLMC Collateralized Mortgage Obligations. FHLMC CMOs are debt obligations of FHLMC issued in
multiple classes having different maturity dates which are secured by the pledge of a pool of conventional
mortgage loans purchased by FHLMC. Unlike FHLMC PCs, payments of principal and interest on the CMOs are made
semiannually, as opposed to monthly. The amount of principal payable on each semiannual payment date is
determined in accordance with FHLMC's mandatory sinking fund schedule, which, in turn, is equal to approximately
100% of FHA prepayment experience applied to the mortgage collateral pool. All sinking fund payments in the CMOs
are allocated to the retirement of the individual classes of bonds in the order of their stated maturities.
Payment of principal on the mortgage loans in the collateral pool in excess of the amount of FHLMC's minimum
sinking fund obligation for any payment date are paid to the holders of the CMOs as additional sinking fund
payments. Because of the "pass-through" nature of all principal payments received on the collateral pool in
excess of FHLMC's minimum sinking fund requirement, the rate at which principal of the CMOs is actually repaid is
likely to be such that each class of bonds will be retired in advance of its scheduled maturity date.
If collection of principal (including prepayments) on the mortgage loans during any semiannual
payment period is not sufficient to meet FHLMC's minimum sinking fund obligation on the next sinking fund payment
date, FHLMC agrees to make up the deficiency from its general funds.
Criteria for the mortgage loans in the pool backing the FHLMC CMOs are identical to those of
FHLMC PCs. FHLMC has the right to substitute collateral in the event of delinquencies and/or defaults. For an
additional discussion of mortgage-backed securities and certain risks involved therein, see this SAI and the
Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Other Mortgage-Related Securities. Other mortgage-related securities include securities other
than those described above that directly or indirectly represent a participation in, or are secured by and
payable from, mortgage loans on real property, including CMO residuals or stripped mortgage-backed securities.
Other mortgage-related securities may be equity or debt securities issued by agencies or instrumentalities of the
U.S. Government or by private originators of, or investors in, mortgage loans, including savings and loan
associations, homebuilders, mortgage banks, commercial banks, investment banks, partnerships, trusts and special
purpose entities of the foregoing.
CMO Residuals. CMO residuals are derivative mortgage securities issued by agencies or
instrumentalities of the U.S. Government or by private originators of, or investors in, mortgage loans, including
savings and loan associations, homebuilders, mortgage banks, commercial banks, investment banks and special
purpose entities of the foregoing.
The cash flow generated by the mortgage assets underlying a series of CMOs is applied first to
make required payments of principal and interest on the CMOs and second to pay the related administrative
expenses of the issuer. The residual in a CMO structure generally represents the interest in any excess cash
flow remaining after making the foregoing payments. Each payment of such excess cash flow to a holder of the
related CMO residual represents income and/or a return of capital. The amount of residual cash flow resulting
from a CMO will depend on, among other things, the characteristics of the mortgage assets, the coupon rate of
each class of CMO, prevailing interest rates, the amount of administrative expenses and the prepayment experience
on the mortgage assets. In particular, the yield to maturity on CMO residuals is extremely sensitive to
prepayments on the related underlying mortgage assets, in the same manner as an interest-only ("IO") class of
stripped mortgage-backed securities. See "Other Mortgage-Related Securities -- Stripped Mortgage-Backed
Securities." In addition, if a series of a CMO includes a class that bears interest at an adjustable rate, the
yield to maturity on the related CMO residual will also be extremely sensitive to changes in the level of the
index upon which interest rate adjustments are based. As described below with respect to stripped
mortgage-backed securities, in certain circumstances the Fund may fail to recoup fully its initial investment in
a CMO residual.
CMO residuals are generally purchased and sold by institutional investors through several
investment banking firms acting as brokers or dealers. The CMO residual market has only very recently developed
and CMO residuals currently may not have the liquidity of other more established securities trading in other
markets. Transactions in CMO residuals are generally completed only after careful review of the characteristics
of the securities in question. In addition, CMO residuals may or, pursuant to an exemption therefrom, may not
have been registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. CMO residuals, whether or not registered
under such Act, may be subject to certain restrictions on transferability, and may be deemed "illiquid" and
subject to the Fund's limitations on investment in illiquid securities.
Stripped Mortgage-Backed Securities. Stripped mortgage-backed securities ("SMBS") are
derivative multi-class mortgage securities. SMBS may be issued by agencies or instrumentalities of the U.S.
Government, or by private originators of, or investors in, mortgage loans, including savings and loan
associations, mortgage banks, commercial banks, investment banks and special purpose entities of the foregoing.
SMBS are usually structured with two classes that receive different proportions of the interest
and principal distributions on a pool of mortgage assets. A common type of SMBS will have one class receiving
some of the interest and most of the principal from the mortgage assets, which the other class will receive most
of the interest and the remainder of the principal. In the most extreme case, one class will receive all of the
interest (the IO class), while the other class will receive all of the principal (the principal-only or "PO"
class). The yield to maturity on an IO class is extremely sensitive to the rate of principal payments (including
prepayments) on the related underlying mortgage assets, and a rapid rate of principal payments may have a
material adverse effect on the Fund's yield to maturity from these securities. If the underlying mortgage assets
experience greater than anticipated prepayments of principal, the Fund may fail to fully recoup its initial
investment in these securities even if the security is in one of the highest rating categories.
Although SMBS are purchased and sold by institutional investors through several investment
banking firms acting as brokers or dealers, these securities were only recently developed. As a result,
established trading markets have not yet developed and, accordingly, these securities may be deemed "illiquid"
and subject to the Fund's limitations on investment in illiquid securities.
Other Asset-Backed Securities. Similarly, the Sub-advisor expects that other asset-backed
securities (unrelated to mortgage loans) will be offered to investors in the future. Several types of
asset-backed securities may be offered to investors, including Certificates for Automobile Receivables. For a
discussion of automobile receivables, see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Consistent with the Fund's investment objectives and policies, the Sub-advisor also may invest in other types of
asset-backed securities.
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest in U.S. dollar- or foreign currency-denominated corporate debt
securities of foreign issuers (including preferred or preference stock), certain foreign bank obligations (see
"Bank Obligations") and U.S. dollar- or foreign currency-denominated obligations of foreign governments or their
subdivisions, agencies and instrumentalities, international agencies and supranational entities. The Fund may
invest up to 20% of its assets in securities denominated in foreign currencies, and may invest beyond this limit
in U.S. dollar-denominated securities of foreign issuers. The Fund may invest up to 10% of its assets in
securities of issuers based in emerging market countries. Investing in the securities of foreign issuers
involves special risks and considerations not typically associated with investing in U.S. companies. For a
discussion of certain risks involved in foreign investments in general, and the special risks of investing in
developing countries, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods."
The Fund also may purchase and sell foreign currency options and foreign currency futures contracts and
related options (see ""Derivative Instruments"), and enter into forward foreign currency exchange contracts in
order to protect against uncertainty in the level of future foreign exchange rates in the purchase and sale of
securities.
A forward foreign currency contract involves an obligation to purchase or sell a specific currency at a
future date, which may be any fixed number of days from the date of the contract agreed upon by the parties, at a
price set at the tine of the contract. These contracts may be bought or sold to protect the Fund against a
possible loss resulting from an adverse change in the relationship between foreign currencies and the U.S. dollar
or, to increase exposure to a particular foreign currency. Open positions in forward contracts are covered by
the segregation with the Fund's custodian of cash or liquid assets and are marked to market daily. Although such
contracts are intended to minimize the risk of loss due to a decline on the value of the hedged currencies, at
the same time, they tend to limit any potential gain which might result should the value of such currencies
increase.
Brady Bonds. The Fund may invest in Brady Bonds. Brady Bonds are securities created through the
exchange of existing commercial bank loans to sovereign entities for new obligations in connection with debt
restructurings under a debt restructuring plan introduced by former U.S. Secretary of the Treasury, Nicholas F.
Brady (the "Brady Plan"). Brady Plan debt restructurings have been implemented in a number of countries,
including in Argentina, Bolivia, Bulgaria, Costa Rica, the Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Jordan, Mexico, Niger,
Nigeria, the Philippines, Poland, Uruguay, and Venezuela. In addition, Brazil has concluded a Brady-like plan.
It is expected that other countries will undertake a Brady Plan in the future.
Brady Bonds have been issued only recently, and accordingly do not have a long payment history. Brady
Bonds may be collateralized or uncollateralized, are issued in various currencies (primarily the U.S. dollar) and
are actively traded in the over-the-counter secondary market. U.S. dollar-denominated, collateralized Brady
Bonds, which may be fixed rate par bonds or floating rate discount bonds, are generally collateralized in full as
to principal by U.S. Treasury zero-coupon bonds having the same maturity as the Brady Bonds. Interest payments
on these Brady Bonds generally are collateralized on a one-year or longer rolling-forward basis by cash or
securities in an amount that, in the case of fixed rate bonds, is equal to at least one year of interest payments
or, in the case of floating rate bonds, initially is equal to at least one year's interest payments based on the
applicable interest rate at that time and is adjusted at regular intervals thereafter. Certain Brady Bonds are
entitled to "value recovery payments" in certain circumstances, which in effect constitute supplemental interest
payments but generally are not collateralized. Brady Bonds are often viewed as having three or four valuation
components: (i) the collateralized repayment of principal at final maturity; (ii) the collateralized interest
payments; (iii) the uncollateralized interest payments; and (iv) any uncollateralized repayment of principal at
maturity (these uncollateralized amounts constitute the "residual risk").
Most Mexican Brady Bonds issued to date have principal repayments at final maturity fully collateralized
by U.S. Treasury zero-coupon bonds (or comparable collateral denominated in other currencies) and interest coupon
payments collateralized on an 18-month rolling-forward basis by funds held in escrow by an agent for the
bondholders. A significant portion of the Venezuelan Brady Bonds and the Argentine Brady Bonds issued to date
have principal repayments at final maturity collateralized by U.S. Treasury zero-coupon bonds (or comparable
collateral denominated in other currencies) and/or interest coupon payments collateralized on a 14-month (for
Venezuela) or 12-month (for Argentina) rolling-forward basis by securities held by the Federal Reserve Bank of
New York as collateral agent.
Brady Bonds involve various risk factors including residual risk and the history of defaults with
respect to commercial bank loans by public and private entities of countries issuing Brady Bonds. There can be
no assurance that Brady Bonds in which the Fund may invest will not be subject to restructuring arrangements or
to requests for new credit, which may cause the Fund to suffer a loss of interest or principal on any of its
holdings.
Bank Obligations. Bank obligations in which the Funds invest include certificates of deposit, bankers'
acceptances, and fixed time deposits. Certificates of deposit are negotiable certificates issued against funds
deposited in a commercial bank for a definite period of time and earning a specified return. Bankers'
acceptances are negotiable drafts or bills of exchange, normally drawn by an importer or exporter to pay for
specific merchandise, which are "accepted" by a bank, meaning, in effect, that the bank unconditionally agrees to
pay the face value of the instrument on maturity. Fixed time deposits are bank obligations payable at a stated
maturity date and bearing interest at a fixed rate. Fixed time deposits may be withdrawn on demand by the
investor, but may be subject to early withdrawal penalties which vary depending upon market conditions and the
remaining maturity of the obligation. There are no contractual restrictions on the right to transfer a
beneficial interest in a fixed time deposit to a third party, although there is no market for such deposits. The
Fund will not invest in fixed time deposits which (1) are not subject to prepayment or (2) provide for withdrawal
penalties upon prepayment (other than overnight deposits) if, in the aggregate, more than 15% of its assets would
be invested in such deposits, repurchase agreements maturing in more than seven days and other illiquid assets.
The Fund will limit its investments in United States bank obligations to obligations of United States
bank (including foreign branches) which have more than $1 billion in total assets at the time of investment and
are member of the Federal Reserve System, are examined by the Comptroller of the Currency or whose deposits are
insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. The Fund also may invest in certificates of deposit of
savings and loan associations (federally or state chartered and federally insured) having total assets in excess
$1 billion.
The Fund will limit its investments in foreign bank obligations to United States dollar- or foreign
currency-denominated obligations of foreign banks (including United States branches of foreign banks) which at
the time of investment (i) have more than $10 billion, or the equivalent in other currencies, in total assets;
(ii) in terms of assets are among the 75 largest foreign banks in the world; (iii) have branches or agencies
(limited purpose offices which do not offer all banking services) in the United States; and (iv) in the opinion
of the Sub-advisor, are of an investment quality comparable to obligations of United States banks in which the
Fund may invest. Subject to the Fund's limitation on concentration of no more than 25% of its assets in the
securities of issuers in particular industry, there is no limitation on the amount of the Fund's assets which may
be invested in obligations of foreign banks which meet the conditions set forth herein.
Obligations of foreign banks involve somewhat different investment risks than those affecting
obligations of United States banks, including the possibilities that their liquidity could be impaired because of
future political and economic developments, that their obligations may be less marketable than comparable
obligations of United States banks, that a foreign jurisdiction might impose withholding taxes on interest income
payable on those obligations, that foreign deposits may be seized or nationalized, that foreign governmental
restrictions such as exchange controls may be adopted which might adversely affect the payment of principal and
interest on those obligations and that the selection of those obligations may be more difficult because there may
be less publicly available information concerning foreign banks or the accounting, auditing and financial
reporting standards, practices and requirements applicable to foreign banks may differ from those applicable to
United States banks. Foreign banks are not generally subject to examination by any United States Government
agency or instrumentality.
Derivative Instruments. In pursuing its individual objective, the Fund may, as described in the
Company's Prospectus, purchase and sell (write) both put options and call options on securities, securities
indices, and foreign currencies, and enter into interest rate, foreign currency and index futures contracts and
purchase and sell options on such futures contracts ("future options") for hedging purposes. The Fund also may
enter into swap agreements with respect to foreign currencies, interest rates and indices of securities. If
other types of financial instruments, including other types of options, futures contracts, or futures options are
traded in the future, the Fund may also use those instruments, provided that the Directors of the Company
determine that their use is consistent with the Fund's investment objective, and provided that their use is
consistent with restrictions applicable to options and futures contracts currently eligible for use by the Trust
(i.e., that written call or put options will be "covered" or "secured" and that futures and futures options will
be used only for hedging purposes).
Options on Securities and Indices. The Fund may purchase and sell both put and call options on debt or
other securities or indices in standardized contracts traded on foreign or national securities exchanges, boards
of trade, or similar entities, or quoted on NASDAQ or on a regulated foreign over-the-counter market, and
agreements sometimes called cash puts, which may accompany the purchase of a new issue of bonds from a dealer.
The Fund will write call options and put options only if they are "covered." In the case of a call
option on a security, the option is "covered" if the Fund owns the security underlying the call or has an
absolute and immediate right to acquire that security without additional cash consideration (or, if additional
cash consideration is required, cash or cash equivalents in such amount are segregated by the Fund) upon
conversion or exchange of other securities held by the Fund. For a call option on an index, the option is
covered if the Fund maintains with its custodian cash or cash equivalents equal to the contract value. A call
option is also covered if the Fund holds a call on the same security or index as the call written where the
exercise price of the call held is (i) equal to or less than the exercise price of the call written, or (ii)
greater than the exercise price of the call written, provided that cash or cash equivalents in the amount of the
difference are segregated by the Fund. A put option on a security or an index is "covered" if the Fund
segregates cash or cash equivalents equal to the exercise price. A put option is also covered if the Fund holds
a put on the same security or index as the put written where the exercise price of the put held is (i) equal to
or greater than the exercise price of the put written, or (ii) less than the exercise price of the put written,
provided that cash or cash equivalents in the amount of the difference are segregated by the Fund.
If an option written by the Fund expires, the Fund realizes a capital gain equal to the premium received
at the time the option was written. If an option purchased by the Fund expires unexercised, the Fund realizes a
capital loss equal to the premium paid.
Prior to the earlier of exercise or expiration, an option may be closed out by an offsetting purchase or
sale of an option of the same series (type, exchange, underlying security or index, exercise price, and
expiration). There can be no assurance, however, that a closing purchase or sale transaction can be effected
when the Fund desires.
The Fund will realize a capital gain from a closing purchase transaction if the cost of the closing
option is less than the premium received from writing the option, or if it is more, the Fund will realize a
capital loss. If the premium received from a closing sale transaction is more than the premium paid to purchase
the option, the Fund will realize a capital gain or, if it is less, the Fund will realize a capital loss. The
principal factors affecting the market value of a put or a call option include supply and demand, interest rates,
the current market price of the underlying security or index in relation to the exercise price of the option, the
volatility of the underlying security or index, and the time remaining until the expiration date.
The premium paid for a put or call option purchased by the Fund is an asset of the Fund. The premium
received for a option written by the Fund is recorded as a deferred credit. The value of an option purchased or
written is marked to market daily and is valued at the closing price on the exchange on which it is traded or, if
not traded on an exchange or no closing price is available, at the mean between the last bid and asked prices.
For a discussion of certain risks involved in options, see this SAI and the Company's Prospectus under "Certain
Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Foreign Currency Options. The Fund may buy or sell put and call options on foreign currencies either on
exchanges or in the over-the-counter market. A put option on a foreign currency gives the purchaser of the
option the right to sell a foreign currency at the exercise price until the option expires. Currency options
traded on U.S. or other exchanges may be subject to position limits which may limit the ability of the Fund to
reduce foreign currency risk using such options. Over-the-counter options differ from traded options in that
they are two-party contracts with price and other terms negotiated between buyer and seller, and generally do not
have as much market liquidity as exchange-traded options.
Futures Contracts and Options on Futures Contracts. The Fund may use interest rate, foreign currency or
index futures contracts, as specified in the Company's Prospectus. An interest rate, foreign currency or index
futures contract provides for the future sale by one party and purchase by another party of a specified quantity
of a financial instrument, foreign currency or the cash value of an index at a specified price and time. A
futures contract on an index is an agreement pursuant to which two parties agree to take or make delivery of an
amount of cash equal to the difference between the value of the index at the close of the last trading day of the
contract and the price at which the index contract was originally written. Although the value of an index might
be a function of the value of certain specified securities, no physical delivery of these securities is made.
The Fund may purchase and write call and put futures options. Futures options possess many of the same
characteristics as options on securities and indices (discussed above). A futures option gives the holder the
right, in return for the premium paid, to assume a long position (call) or short position (put) in a futures
contract at a specified exercise price at any time during the period of the option. Upon exercise of a call
option, the holder acquires a long position in the futures contract and the writer is assigned the opposite short
position. In the case of a put option, the opposite is true.
To comply with applicable rules of the CFTC under which the Company and the Fund avoid being deemed a
"commodity pool" or a "commodity pool operator," the Fund intends generally to limit its use of futures contracts
and futures options to "bona fide hedging" transactions, as such term is defined in applicable regulations,
interpretations and practice. For example, the Fund might use futures contracts to hedge against anticipated
changes in interest rates that might adversely affect either the value of the Fund's securities or the price of
the securities which the Fund intends to purchase. The Fund's hedging activities may include sales of futures
contracts as an offset against the effect or expected increases in interest rates, and purchases of futures
contracts as an offset against the effect of expected declines in interest rates. Although other techniques
could be used to reduce the Fund's exposure to interest rate fluctuations, the Fund may be able to hedge its
exposure more effectively and perhaps at a lower cost by using futures contracts and futures options.
The Fund will only enter into futures contracts and futures options which are standardized and traded on
a U.S. or foreign exchange, board of trade, or similar entity, or quoted on an automated quotation system.
When a purchase or sale of a futures contract is made by the Fund, the Fund is required to deposit with
its custodian (or broker, if legally permitted) a specified amount of cash or U.S. Government securities
("initial margin"). The margin required for a futures contract is set by the exchange on which the contract is
traded and may be modified during the term of the contract. The initial margin is in the nature of a performance
bond or good faith deposit on the futures contract which is returned to the Fund upon termination of the
contract, assuming all contractual obligations have been satisfied. The Fund expects to earn interest income on
its initial margin deposits. A futures contract held by the Fund is valued daily at the official settlement
price of the exchange on which it is traded. Each day the Fund pays or receives cash, called "variation margin,"
equal to the daily change in value of the futures contract. This process is known as "marking to market."
Variation margin does not represent a borrowing or loan by the Fund but is instead a settlement between the Fund
and the broker of the amount one would owe the other if the futures contract expired. In computing daily net
asset value, the Fund will mark to market its open futures positions.
The Fund is also required to deposit and maintain margin with respect to put and call options on futures
contracts written by it. Such margin deposits will vary depending on the nature of the underlying futures
contract (and the related initial margin requirements), the current market value of the option, and other futures
positions held by the Fund.
Although some futures contracts call for making or taking delivery of the underlying securities,
generally these obligations are closed out prior to delivery by offsetting purchases or sales of matching futures
contracts (same exchange, underlying security or index, and delivery month). If an offsetting purchase price is
less than the original sale price, the Fund realizes a capital gain, or if it is more, the Fund realizes a
capital loss. Conversely, if an offsetting sale price is more than the original purchase price, the Fund
realizes a capital gain, or if it is less, the Fund realizes a capital loss. The transaction costs must also be
included in these calculations.
Limitations on Use of Futures and Futures Options. In general, the Funds intend to enter into positions
in futures contracts and related options only for "bona fide hedging" purposes. With respect to positions in
futures and related options that do not constitute bona fide hedging positions, the Fund will not enter into a
futures contract or futures option contract if, immediately thereafter, the aggregate initial margin deposits
relating to such positions plus premiums paid by it for open futures option positions, less the amount by which
any such options are "in-the-money," would exceed 5% of the Fund's total assets. A call option is "in-the-money"
if the value of the futures contract that is the subject of the option exceeds the exercise price. A put option
is "in-the-money" if the exercise price exceeds the value of the futures contract that is the subject of the
option.
When purchasing a futures contract, the Fund will maintain with its custodian (and mark-to-market on a
daily basis) cash or other liquid assets that, when added to the amounts deposited with a futures commission
merchant as margin, are equal to the market value of the futures contract. Alternatively, the Fund may "cover"
its position by purchasing a put option on the same futures contract with a strike price as high or higher than
the price of the contract held by the Fund.
When selling a futures contract, the Fund will maintain with its custodian (and mark-to-market on a
daily basis) liquid assets that, when added to the amount deposited with a futures commission merchant as margin,
are equal to the market value of the instruments underlying the contract. Alternatively, the Fund may "cover"
its position by owning the instruments underlying the contract (or, in the case of an index futures contract, a
portfolio with a volatility substantially similar to that of the index on which the futures contract is based),
or by holding a call option permitting the Fund to purchase the same futures contract at a price no higher than
the price of the contract written by the Fund (or at a higher price if the difference is maintained in liquid
assets with the Fund's custodian).
When selling a call option on a futures contract, the Fund will maintain with its custodian (and
mark-to-market on a daily basis) cash or other liquid assets that, when added to the amounts deposited with a
futures commission merchant as margin, equal the total market value of the futures contract underlying the call
option. Alternatively, the Fund may cover its position by entering into a long position in the same futures
contract at a price no higher than the strike price of the call option, by owning the instruments underlying the
futures contract, or by holding a separate call option permitting the Fund to purchase the same futures contract
at a price not higher than the strike price of the call option sold by the Fund.
When selling a put option on a futures contract, the Fund will maintain with its custodian (and mark-to
market on a daily basis) cash or other liquid assets that equal the purchase price of the futures contract, less
any margin on deposit. Alternatively, the Fund may cover the position either by entering into a short position
in the same futures contract, or by owning a separate put option permitting it to sell the same futures contract
so long as the strike price of the purchased put option is the same or higher than the strike price of the put
option sold by the Fund.
Swap Agreements. The Fund may enter into interest rate, index and currency exchange rate swap
agreements for purposes of attempting to obtain a particular desired return at a lower cost to the Fund than if
the Fund had invested directly in an instrument that yielded that desired return. For a discussion of swap
agreements, see the Company's Prospectus under "Investment Programs of the Funds." The Fund's obligations under
a swap agreement will be accrued daily (offset against any amounts owing to the Fund) and any accrued but unpaid
net amounts owed to a swap counterparty will be covered by segregating cash or other liquid assets to avoid any
potential leveraging of the Fund's portfolio. The Fund will not enter into a swap agreement with any single
party if the net amount owned or to be received under existing contracts with that party would exceed 5% of the
Fund's assets.
Whether the Fund's use of swap agreements will be successful in furthering its investment objective of
total return will depend on the Sub-advisor's ability correctly to predict whether certain types of investments
are likely to produce greater returns than other investments. Because they are two party contracts and because
they may have terms of longer than seven days, swap agreements may be considered to be illiquid. Moreover, the
Fund bears the risk of loss of the amount expected to be received under a swap agreement in the event of the
default or bankruptcy of a swap agreement counterparty. The Sub-advisor will cause the Fund to enter into swap
agreements only with counterparties that would be eligible for consideration as repurchase agreement
counterparties under the Fund's repurchase agreement guidelines. Certain restrictions imposed on the Funds by
the Internal Revenue Code may limit the Funds' ability to use swap agreements. The swaps market is a relatively
new market and is largely unregulated. It is possible that developments in the swaps market, including potential
government regulation, could adversely affect the Fund's ability to terminate existing swap agreements or to
realize amounts to be received under such agreements.
Certain swap agreements are exempt from most provisions of the Commodity Exchange Act ("CEA") and,
therefore, are not regulated as futures or commodity option transactions under the CEA, pursuant to regulations
approved by the CFTC. To qualify for this exemption, a swap agreement must be entered into by "eligible
participants." To be eligible, natural persons and most other entities must have total assets exceeding $10
million; commodity pools and employee benefit plans must have assets exceeding $5 million. In addition, an
eligible swap transaction must meet three conditions. First, the swap agreement may not be part of a fungible
class of agreements that are standardized as to their material economic terms. Second, the creditworthiness of
parties with actual or potential obligations under the swap agreement must be a material consideration in
entering into or determining the terms of the swap agreement, including pricing, cost or credit enhancement
terms. Third, swap agreements may not be entered into and traded on or through a multilateral transaction
execution facility.
This exemption is not exclusive, and partnerships may continue to rely on existing exclusions for swaps,
such as the Policy Statement issued in July 1989 which recognized a safe harbor for swap transactions from
regulation as futures or commodity option transactions under the CEA or its regulations. The Policy Statement
applies to swap transactions settled in cash that (1) have individual tailored terms, (2) lack exchange-style
offset and the use of a clearing organization or margin system, (3) are undertaken in conjunction with a line of
business, and (4) are not marketed to the public.
Structured Notes. Structured notes are derivative debt securities, the interest rate or principal of
which is related to another economic indicator or financial market index. Indexed securities include structured
notes as well as securities other than debt securities, the interest rate or principal of which is determined by
such an unrelated indicator. Indexed securities may include a multiplier that multiplies the indexed element by
a specified factor and, therefore, the value of such securities may be very volatile. To the extent the Fund
invests in these securities, however, the Sub-advisor analyzes these securities in its overall assessment of the
effective duration of the Fund's portfolio in an effort to monitor the Fund's interest rate risk.
Foreign Currency Exchange-Related Securities. The Fund may invest in foreign currency warrants,
principal exchange rate linked securities and performance indexed paper. For a description of these instruments,
see this SAI under "Certain Risk Factor and Investment Methods."
Warrants to Purchase Securities. The Fund may invest in or acquire warrants to purchase equity or
fixed-income securities. Bonds with warrants attached to purchase equity securities have many characteristics of
convertible bonds and their prices may, to some degree, reflect the performance of the underlying stock. Bonds
also may be issued with warrants attached to purchase additional fixed-income securities at the same coupon
rate. A decline in interest rates would permit the Fund to buy additional bonds at the favorable rate or to sell
the warrants at a profit. If interest rates rise, the warrants would generally expire with no value.
Hybrid Instruments. The Fund may invest up to 5% of its assets in hybrid instruments. A hybrid
instrument can combine the characteristics of securities, futures, and options. Hybrids can be used as an
efficient means of pursuing a variety of investment goals, including currency hedging, duration management, and
increased total return. For an additional discussion of hybrid instruments and certain risks involved therein,
see the Company's SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Inverse Floaters. The Fund may also invest in inverse floating rate debt instruments ("inverse
floaters"). The interest rate on an inverse floater resets in the opposite direction from the market rate of
interest to which the inverse floater is indexed. An inverse floating rate security may exhibit greater price
volatility than a fixed rate obligation of similar credit quality. The Fund will not invest more than 5% of its
net assets in any combination of inverse floater, interest only, or principal only securities.
Loan Participations. The Fund may purchase participations in commercial loans. Such indebtedness may
be secured or unsecured. Loan participations typically represent direct participation in a loan to a corporate
borrower, and generally are offered by banks or other financial institutions or lending syndicates. When
purchasing loan participations, the Fund assumes the credit risk associated with the corporate borrower and may
assume the credit risk associated with an interposed bank or other financial intermediary. The participation
interests in which the Fund intends to invest may not be rated by any nationally recognized rating service.
A loan is often administered by an agent bank acting as agent for all holders. The agent bank
administers the terms of the loan, as specified in the loan agreement. In addition, the agent bank is normally
responsible for the collection of principal and interest payments from the corporate borrower and the
apportionment of these payments to the credit of all institutions which are parties to the loan agreement.
Unless, under the terms of the loan or other indebtedness, the Fund has direct recourse against the corporate
borrower, the Fund may have to rely on the agent bank or other financial intermediary to apply appropriate credit
remedies against a corporate borrower.
A financial institution's employment as agent bank might be terminated in the event that it fails to
observe a requisite standard of care or becomes insolvent. A successor agent bank would generally be appointed
to replace the terminated agent bank, and assets held by the agent bank under the loan agreement should remain
available to holders of such indebtedness. However, if assets held by the agent bank for the benefit of the Fund
were determined to be subject to the claims of the agent bank's general creditors, the Fund might incur certain
costs and delays in realizing payment on a loan or loan participation and could suffer a loss of principal and/or
interest. In situations involving other interposed financial institutions (e.g., an insurance company or
governmental agency) similar risks may arise.
Purchasers of loans and other forms of direct indebtedness depend primarily upon the creditworthiness of
the corporate borrower for payment of principal and interest. If the Fund does not receive scheduled interest or
principal payments on such indebtedness, the Fund's share price and yield could be adversely affected. Loans
that are fully secured offer the Fund more protection than an unsecured loan in the event of non-payment of
scheduled interest or principal. However, there is no assurance that the liquidation of collateral from a
secured loan would satisfy the corporate borrower's obligation, or that the collateral can be liquidated.
The Fund may invest in loan participations with credit quality comparable to that of issuers of its
securities investments. Indebtedness of companies whose creditworthiness is poor involves substantially greater
risks, and may be highly speculative. Some companies may never pay off their indebtedness, or may pay only a
small fraction of the amount owed. Consequently, when investing in indebtedness of companies with poor credit,
the Fund bears a substantial risk of losing the entire amount invested.
The Fund limits the amount of its total assets that it will invest in any one issuer or in issuers
within the same industry (see "Investment Restrictions"). For purposes of these limits, the Fund generally will
treat the corporate borrower as the "issuer" of indebtedness held by the Fund. In the case of loan
participations where a bank or other lending institution serves as a financial intermediary between the Fund and
the corporate borrower, if the participation does not shift to the Fund the direct debtor-creditor relationship
with the corporate borrower, SEC interpretations require the Fund to treat both the lending bank or other lending
institution and the corporate borrower as "issuers" for the purposes of determining whether the Fund has invested
more than 5% of its total assets in a single issuer. Treating a financial intermediary as an issuer of
indebtedness may restrict the Fund's ability to invest in indebtedness related to a single financial
intermediary, or a group of intermediaries engaged in the same industry, even if the underlying borrowers
represent many different companies and industries.
Loan and other types of direct indebtedness may not be readily marketable and may be subject to
restrictions on resale. In some cases, negotiations involved in disposing of indebtedness may require weeks to
complete. Consequently, some indebtedness may be difficult or impossible to dispose of readily at what the
Sub-advisor believes to be a fair price. In addition, valuation of illiquid indebtedness involves a greater
degree of judgment in determining the Fund's net asset value than if that value were based on available market
quotations, and could result in significant variations in the Fund's daily share price. At the same time, some
loan interests are traded among certain financial institutions and accordingly may be deemed liquid. As the
market for different types of indebtedness develops, the liquidity of these instruments is expected to improve.
In addition, the Fund currently intends to treat indebtedness for which there is no readily available market as
illiquid for purposes of the Fund's limitation on illiquid investments. Investments in loan participations are
considered to be debt obligations for purposes of the Company's investment restriction relating to the lending of
funds or assets by the Fund.
Investments in loans through a direct assignment of the financial institution's interests with respect
to the loan may involve additional risks to the Fund. For example, if a loan is foreclosed, the Fund could
become part owner of any collateral, and would bear the costs and liabilities associated with owning and
disposing of the collateral. In addition, it is conceivable that under emerging legal theories of lender
liability, the Fund could be held liable as co-lender. It is unclear whether loans and other forms of direct
indebtedness offer securities law protections against fraud and misrepresentation. In the absence of definitive
regulatory guidance, the Fund relies on the Sub-advisor's research in an attempt to avoid situations where fraud
or misrepresentation could adversely affect the Fund.
Delayed Funding Loans and Revolving Credit Facilities. The Fund may enter into, or acquire
participations in, delayed funding loans and revolving credit facilities. Delayed funding loans and revolving
credit facilities are borrowing arrangements in which the lender agrees to make loans up to a maximum amount upon
demand by the borrower during a specified term. These commitments may have the effect of requiring the Fund to
increase its investment in a company at a time when it might not otherwise decide to do so (including at a time
when the company's financial condition makes it unlikely that such amounts will be repaid). To the extent that
the Fund is committed to advance additional funds, it will at all times segregate liquid assets, determined to be
liquid by the Sub-advisor in accordance with procedures established by the Board of Directors, in an amount
sufficient to meet such commitments. The Fund may invest in delayed funding loans and revolving credit
facilities with credit quality comparable to that of issuers of its securities investments. Delayed funding
loans and revolving credit facilities may be subject to restrictions on transfer, and only limited opportunities
may exist to resell such instruments. As a result, the Fund may be unable to sell such investments at an
opportune time or may have to resell them at less than fair market value. The Fund currently intend to treat
delayed funding loans and revolving credit facilities for which there is no readily available market as illiquid
for purposes of the Fund's limitation on illiquid investments. Participation interests in revolving credit
facilities will be subject to the limitations discussed above under "Loan Participations." Delayed funding loans
and revolving credit facilities are considered to be debt obligations for purposes of the Company's investment
restriction relating to the lending of funds or assets by the Fund.
Lending Portfolio Securities. For the purpose of achieving income, the Fund may lend its portfolio
securities, provided (1) the loan is secured continuously by collateral consisting of U.S. Government securities
or cash or cash equivalents (cash, U.S. Government securities, negotiable certificates of deposit, bankers'
acceptances or letters of credit) maintained on a daily mark-to-market basis in an amount at least equal to the
current market value of the securities loaned, (2) the Fund may at any time call the loan and obtain the return
of securities loaned, (3) the Fund will receive any interest or dividends received on the loaned securities, and
(4) the aggregate value of the securities loaned will not at any time exceed one-third of the total assets of the
Fund.
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
not "fundamental" restrictions and may be changed by the Directors of the Company without shareholder approval.
The Fund will not:
1. Invest more than 15% of the assets of the Fund (taken at market value at the time of the
investment) in "illiquid securities;" illiquid securities being defined to include securities subject to legal or
contractual restrictions on resale (which may include private placements), repurchase agreements maturing in more
than seven days, certain options traded over the counter that the Fund has purchased, securities being used to
cover options the Fund has written, securities for which market quotations are not readily available, or other
securities which legally or in the Sub-advisor's option may be deemed illiquid;
2. Purchase securities for the Fund from, or sell portfolio securities to, any of the officers and
directors or trustees of the Company, the Trust, the Investment Manager or the Sub-advisor;
3. Invest more than 5% of the assets of the Fund (taken at market value at the time of investment)
in any combination of interest only, principal only, or inverse floating rate securities;
4. Invest in companies for the purpose of exercising management or control;
5. Purchase securities of open-end or closed-end investment companies except in compliance with
the Investment Company Act of 1940;
6. Purchase securities on margin, except (i) for use of short-term credit necessary for clearance
of purchases of portfolio securities and (ii) the Fund may make margin deposits in connection with futures
contracts or other permissible investments;
7. Purchase or sell oil, gas or other mineral programs;
8. Maintain a short position, or purchase, write or sell puts, calls, straddles, spreads or
combinations thereof, except as set forth in the Company's Prospectus and this SAI for transactions in options,
futures, and options on futures transactions arising under swap agreements or other derivative instruments; or
9. Pledge, mortgage or hypothecate its assets, except as may be necessary in connection with
permissible borrowings or investments; and then such pledging, mortgaging or hypothecating may not exceed 33 1/3%
of the Fund's total assets at the time of borrowing or investment. The deposit of assets in escrow in connection
with the writing of covered put and call options and the purchase of securities on a when-issued or delayed
delivery basis, collateral arrangements with respect to initial or variation margin deposits for future contracts
and commitments entered into under swap agreements or other derivative instruments, will not be deemed to be
pledges of the Portfolio's assets.
ASAF JPM Money Market Fund:
Investment Objective: The investment objective of the Fund is to seek high current income and maintain high
levels of liquidity.
Investment Policies:
Bank Obligations. The Fund will not invest in bank obligations for which any affiliate of the
Sub-advisor is the ultimate obligor or accepting bank.
Asset-Backed Securities. The asset-backed securities in which the Fund may invest are subject to the
Fund's overall credit requirements. However, asset-backed securities, in general, are subject to certain risks.
Most of these risks are related to limited interests in applicable collateral. For example, credit card
receivables are generally unsecured and the debtors are entitled to the protection of a number of state and
federal consumer credit laws, many of which give such debtors the right to set off certain amounts on credit card
debt thereby reducing the balance due. Additionally, if the letter of credit is exhausted, holders of
asset-backed securities may also experience delays in payments or losses if the full amounts due on underlying
sales contracts are not realized. Because asset-backed securities are relatively new, the market experience in
these securities is limited and the market's ability to sustain liquidity through all phases of the market cycle
has not been tested. For a discussion of asset-backed securities and the risks involved therein see the
Company's Prospectus and this SAI under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Synthetic Instruments. As may be permitted by current laws and regulations and if expressly permitted
by the Directors of the Company, the Fund may invest in certain synthetic instruments. Such instruments
generally involve the deposit of asset-backed securities in a trust arrangement and the issuance of certificates
evidencing interests in the trust. The certificates are generally sold in private placements in reliance on Rule
144A of the Securities Act of 1933 (without registering the certificates under such Act).
Reverse Repurchase Agreements. The Fund invests the proceeds of borrowings under reverse repurchase
agreements. The Fund will enter into a reverse repurchase agreement only when the interest income to be earned
from the investment of the proceeds is greater than the interest expense of the transaction. The Fund will not
invest the proceeds of a reverse repurchase agreement for a period which exceeds the duration of the reverse
repurchase agreement. The Fund may not enter into reverse repurchase agreements exceeding in the aggregate
one-third of the market value of its total assets, less liabilities other than the obligations created by reverse
repurchase agreements. The Fund will establish and maintain with its custodian a separate account with a
segregated portfolio of securities in an amount at least equal to its purchase obligations under its reverse
repurchase agreements. If interest rates rise during the term of a reverse repurchase agreement, such reverse
repurchase agreement may have a negative impact on the Fund's ability to maintain a net asset value of $1.00 per
share.
Foreign Securities. The Fund may invest in U.S. dollar-denominated foreign securities. Any foreign
commercial paper must not be subject to foreign withholding tax at the time of purchase. Foreign investments may
be made directly in securities of foreign issuers or in the form of American Depositary Receipts ("ADRs") and
European Depositary Receipts ("EDRs"). Generally, ADRs and EDRs are receipts issued by a bank or trust company
that evidence ownership of underlying securities issued by a foreign corporation and that are designed for use in
the domestic, in the case of ADRs, or European, in the case of EDRs, securities markets. For a discussion of
depositary receipts and the risks involved in investing in foreign securities, see the Company's Prospectus under
"Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods."
Lending Portfolio Securities. Loans will be subject to termination by the Fund in the normal settlement
time, generally three business days after notice. Borrowed securities must be returned when the loan is
terminated. The Fund may pay reasonable finders' and custodial fees in connection with a loan. In making a
loan, the Fund will consider the creditworthiness of the borrowing financial institution.
Investment Policies Which May Be Changed Without Shareholder Approval. The following limitations are
not "fundamental" restrictions and may be changed by the Directors of the Company without shareholder approval.
The Fund will not:
1. Invest in companies for the purpose of exercising management or control;
2. Purchase securities of open-end or closed-end investment companies except in compliance with
the Investment Company Act of 1940;
3. Purchase securities on margin, make short sales of securities, or maintain a short position,
provided that this restriction shall not be deemed to be applicable to the purchase or sale of when-issued
securities or of securities for delivery at a future date;
4. Acquire any illiquid securities, such as repurchase agreements with more than seven days to
maturity or fixed time deposits with a duration of over seven calendar days, if as a result thereof, more than
10% of the market value of the Fund's total assets would be in investments which are illiquid;
5. Mortgage, pledge or hypothecate any assets, except as may be necessary in connection with
permissible borrowings or investments; and then such mortgaging, pledging or hypothecating may not exceed 33 1/3%
of the Fund's total assets at the time of borrowing or investment;
6. Purchase or sell puts, calls, straddles, spreads, or any combination thereof, except to the
extent permitted by the Company's Prospectus and this SAI; or
7. Purchase or sell interests in oil, gas or other mineral exploration or development programs.
FUNDAMENTAL INVESTMENT RESTRICTIONS
Investment Restrictions. Each Fund and Portfolio has adopted the following fundamental investment
restrictions which may not be changed without shareholder approval.
1. Senior Securities. No Fund or Portfolio may issue senior securities, except as permitted under the
------------------
Investment Company Act of 1940 (the "1940 Act").
2. Borrowing. No Fund or Portfolio may borrow money, except that a Fund or Portfolio may (i) borrow
---------
money for non-leveraging, temporary or emergency purposes, and (ii) engage in reverse repurchase agreements and
make other investments or engage in other transactions, which may involve a borrowing, in a manner consistent
with the Fund or Portfolio's investment objective and policies; provided that the combination of (i) and (ii)
shall not exceed 33 1/3% of the value of the Fund or Portfolio's assets (including the amount borrowed) less
liabilities (other than borrowings) or such other percentage permitted by law. Any borrowings which come to
exceed this amount will be reduced in accordance with applicable law. Subject to the above limitations, the
Funds and Portfolios may borrow from banks or other persons to the extent permitted by applicable law.
3. Underwriting. No Fund or Portfolio may underwrite securities issued by other persons, except to the
------------
extent that the Fund or Portfolio may be deemed to be an underwriter (within the meaning of the Securities Act of
1933) in connection with the purchase and sale of portfolio securities.
4. Real Estate. No Fund or Portfolio may purchase or sell real estate unless acquired as a result of
-----------
the ownership of securities or other instruments; provided that this restriction shall not prohibit a Fund or
Portfolio from investing in securities or other instruments backed by real estate or in securities of companies
engaged in the real estate business.
5. Commodities. No Fund or Portfolio may purchase or sell physical commodities unless acquired as a
-----------
result of the ownership of securities or instruments; provided that this restriction shall not prohibit a Fund or
Portfolio from (i) engaging in permissible options and futures transactions and forward foreign currency
contracts in accordance with the Fund's or Portfolio's investment policies, or (ii) investing in securities of
any kind.
6. Lending. No Fund or Portfolio may make loans, except that a Fund or Portfolio may (i) lend
-------
portfolio securities in accordance with the Fund or Portfolio's investment policies in amounts up to 33 1/3% of
the total assets of the Fund or Portfolio taken at market value, (ii) purchase money market securities and enter
into repurchase agreements, and (iii) acquire publicly distributed or privately placed debt securities and
purchase debt.
7. Industry Concentration. No Fund or Portfolio other than the ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund may
-----------------------
purchase any security if, as a result, more than 25% of the value of the Fund or Portfolio's assets would be
invested in the securities of issuers having their principal business activities in the same industry; provided
that this restriction does not apply to investments in obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or
any of its agencies or instrumentalities (or repurchase agreements with respect thereto). The ASAF INVESCO
Technology Fund may invest more than 25% of the value of its assets in the securities of companies doing business
in one or more industries relating to technology.
8. Diversification. No Fund or Portfolio other than the ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Fund and the ASAF Rydex
---------------
Managed OTC Fund may, with respect to 75% of the value of its total assets, purchase the securities of any issuer
(other than securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or any of its agencies or instrumentalities)
if, as a result, (i) more than 5% of the value of the Fund's or Portfolio's total assets would be invested in the
securities of such issuer, or (ii) more than 10% of the outstanding voting securities of such issuer would be
held by the Fund or Portfolio. The ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Fund and the ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund may not, with
respect to 50% of its total assets, invest in the securities of any one issuer (other than the U.S. Government
and its agencies and instrumentalities), if immediately after and as a result of such investment more than 5% of
the total assets of the Portfolio would be invested in such issuer.
Notes to Investment Restrictions. The following notes should be read in conjunction with the above
fundamental investment restrictions. These notes are not fundamental policies and may be changed without
---
shareholder approval.
o Applicable to All Funds and Portfolios: If a restriction on a Fund's or Portfolio's investments is
---------------------------------------
adhered to at the time an investment is made, a subsequent change in the percentage of Fund or Portfolio assets
invested in certain securities or other instruments, or change in average duration of the Fund's or Portfolio's
investment portfolio, resulting from changes in the value of the Fund's or Portfolio's total assets, will not be
considered a violation of the restriction; provided, however, that the asset coverage requirement applicable to
borrowings shall be maintained in the manner contemplated by applicable law.
o Applicable to All Funds and Portfolios: With respect to investment restrictions (2) and (6), a Fund
--------------------------------------
or Portfolio will not borrow or lend to any other fund unless it applies for and receives an exemptive order from
the SEC, if so required, or the SEC issues rules permitting such transactions. There is no assurance the SEC
would grant any order requested by the Fund or Portfolio or promulgate any rules allowing the transactions.
o Applicable to All Funds and Portfolios. With respect to investment restriction (6), the
-------------------------------------------
restriction on making loans is not considered to limit a Fund or Portfolio's investments in loan participations
and assignments.
o Applicable Only to the ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund: With respect to
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
investment restriction (7), the Funds use industry classifications based, where applicable, on Baseline, Bridge
-------- -------
Information Systems, Reuters, the S&P Stock Guide published by Standard & Poor's, information obtained from
-------------------- ------- ---------------
Bloomberg L.P. and Moody's International, and/or the prospectus of the issuing company. Selection of an
appropriate industry classification resource will be made by the Sub-advisor in the exercise of its reasonable
discretion.
o Applicable Only to the ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund: With respect to investment restrictions
----------------------------------------------------------
(2) and (6), the Fund has no current intention of borrowing or lending to any other fund. For purposes of
investment restriction (6), the Fund will consider the acquisition of a debt security to include the execution of
a note or other evidence of an extension of credit with a term of more than nine months.
o Applicable only to the ASAF AIM International Equity Fund. With respect to investment restriction
-----------------------------------------------------------
(7), the Fund will not consider a bank-issued guaranty or financial guaranty insurance as a separate security for
purposes of determining the percentage of the Fund's assets invested in the securities of issuers in a particular
industry.
CERTAIN RISK FACTORS AND INVESTMENT METHODS
Some of the investment instruments, techniques and methods which may be used by one or more of the Funds
and the risks attendant thereto are described below. Other risk factors and investment methods may be described
in the Company's Prospectus under "Investment Programs of the Funds" and "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods," and in this SAI under "Investment Programs of the Funds." The risk factors and investment methods
described below only apply to those Funds or Portfolios that may invest in such securities or use such investment
methods. The below references to the investment methods used by the Feeder Funds apply equally to the Funds'
corresponding Portfolios.
Debt Obligations. Yields on short, intermediate, and long-term securities are dependent on a variety of
factors, including, the general conditions of the money and bond markets, the size of a particular offering, the
maturity of the obligation, and the rating of the issue. Debt securities with longer maturities tend to produce
higher yields and are generally subject to potentially greater capital appreciation and depreciation than
obligations with shorter maturities and lower yields. The market prices of debt securities usually vary,
depending upon available yields. An increase in prevailing interest rates will generally reduce the value of
debt investments, and a decline in interest rates will generally increase the value of debt investments. The
ability of a Fund to achieve its investment objective is also dependent on the continuing ability of the issuers
of the debt securities in which a Fund invests to meet their obligations for the payment of interest and
principal when due.
Special Risks Associated with Low-Rated and Comparable Unrated Securities. Low-rated and comparable
unrated securities, while generally offering higher yields than investment-grade securities with similar
maturities, involve greater risks, including the possibility of default or bankruptcy. They are regarded as
predominantly speculative with respect to the issuer's capacity to pay interest and repay principal. The special
risk considerations in connection with such investments are discussed below. See the Appendix of this SAI for a
discussion of securities ratings.
Effect of Interest Rates and Economic Changes. The low-rated and comparable unrated securities
market is relatively new, and its growth paralleled a long economic expansion. As a result, it is not clear how
this market may withstand a prolonged recession or economic downturn. Such a prolonged economic downturn could
severely disrupt the market for and adversely affect the value of such securities.
All interest-bearing securities typically experience appreciation when interest rates decline
and depreciation when interest rates rise. The market values of low-rated and comparable unrated securities tend
to reflect individual corporate developments to a greater extent than do higher-rated securities, which react
primarily to fluctuations in the general level of interest rates. Low-rated and comparable unrated securities
also tend to be more sensitive to economic conditions than are higher-rated securities. During an economic
downturn or a sustained period of rising interest rates, highly leveraged issuers of low-rated and comparable
unrated securities may experience financial stress and may not have sufficient revenues to meet their payment
obligations. The issuer's ability to service its debt obligations may also be adversely affected by specific
corporate developments, the issuer's inability to meet specific projected business forecasts, or the
unavailability of additional financing. The risk of loss due to default by an issuer of low-rated and comparable
unrated securities is significantly greater than issuers of higher-rated securities because such securities are
generally unsecured and are often subordinated to other creditors. Further, if the issuer of a low-rated and
comparable unrated security defaulted, a Fund might incur additional expenses to seek recovery. Periods of
economic uncertainty and changes would also generally result in increased fluctuation in the market prices of
low-rated and comparable unrated securities and thus in a Fund's net asset value.
As previously stated, the value of such a security will decrease in a rising interest rate
market and accordingly, so will a Fund's net asset value. If a Fund experiences unexpected net redemptions in
such a market, it may be forced to liquidate a portion of its portfolio securities without regard to their
investment merits. Due to the limited liquidity of some high-yield securities (discussed below), a Fund may be
forced to liquidate these securities at a substantial discount. Any such liquidation would reduce a Fund's asset
base over which expenses could be allocated and could result in a reduced rate of return for a Fund.
Payment Expectations. Low-rated and comparable unrated securities typically contain
redemption, call, or prepayment provisions which permit the issuer of securities containing such provisions to,
at their discretion, redeem the securities. During periods of falling interest rates, issuers of high-yield
securities are likely to redeem or prepay the securities and refinance them with debt securities with a lower
interest rate. To the extent an issuer is able to refinance the securities, or otherwise redeem them, a Fund may
have to replace the securities with a lower-yielding security, which would result in a lower return for a Fund.
Issuers of lower-rated securities are often highly leveraged, so that their ability to service
their debt obligations during an economic downturn or during sustained periods of rising interest rates may be
impaired. Such issuers may not have more traditional methods of financing available to them and may be unable to
repay outstanding obligations at maturity by refinancing. The risk of loss due to default in payment of interest
or repayment of principal by such issuers is significantly greater because such securities frequently are
unsecured and subordinated to the prior payment of senior indebtedness.
Credit Ratings. Credit ratings issued by credit-rating agencies attempt to evaluate the safety
of principal and interest payments of rated securities. They do not, however, evaluate the market value risk of
low-rated and comparable unrated securities and, therefore, may not fully reflect the true risks of an
investment. In addition, credit-rating agencies may or may not make timely changes in a rating to reflect
changes in the economy or in the condition of the issuer that affect the market value of the security.
Consequently, credit ratings may be used only as a preliminary indicator of investment quality. Investments in
low-rated and comparable unrated securities will be more dependent on the applicable Sub-advisor's credit
analysis than would be the case with investments in investment-grade debt securities. Such Sub-advisor may
employ its own credit research and analysis, which could include a study of existing debt, capital structure,
ability to service debt and to pay dividends, the issuer's sensitivity to economic conditions, its operating
history, and the current trend of earnings. The Sub-advisors continually monitor the investments in a Fund and
evaluate whether to dispose of or to retain low-rated and comparable unrated securities whose credit ratings or
credit quality may have changed.
Liquidity and Valuation. A Fund may have difficulty disposing of certain low-rated and
comparable unrated securities because there may be a thin trading market for such securities. There is no
established retail secondary market for many of these securities. A Fund anticipates that such securities could
be sold only to a limited number of dealers or institutional investors. To the extent a secondary trading market
does exist, it is generally not as liquid as the secondary market for higher-rated securities. The lack of a
liquid secondary market may have an adverse impact on the market price of the security. As a result, a Fund's
asset value and a Fund's ability to dispose of particular securities, when necessary to meet a Fund's liquidity
needs or in response to a specific economic event, may be impacted. The lack of a liquid secondary market for
certain securities may also make it more difficult for a Fund to obtain accurate market quotations for purposes
of valuing a portfolio. Market quotations are generally available on many low-rated and comparable unrated
issues only from a limited number of dealers and may not necessarily represent firm bids of such dealers or
prices for actual sales. During periods of thin trading, the spread between bid and asked prices is likely to
increase significantly. In addition, adverse publicity and investor perceptions, whether or not based on
fundamental analysis, may decrease the values and liquidity of low-rated and comparable unrated securities,
especially in a thinly-traded market.
Put and Call Options:
Writing (Selling) Call Options. A call option gives the holder (buyer) the "right to purchase"
a security or currency at a specified price (the exercise price), at expiration of the option (European style) or
at any time until a certain date (the expiration date) (American style). So long as the obligation of the writer
of a call option continues, he may be assigned an exercise notice by the broker-dealer through whom such option
was sold, requiring him to deliver the underlying security or currency against payment of the exercise price.
This obligation terminates upon the expiration of the call option, or such earlier time at which the writer
effects a closing purchase transaction by purchasing an option identical to that previously sold.
When writing a call option, a Fund, in return for the premium, gives up the opportunity for
profit from a price increase in the underlying security or currency above the exercise price, but conversely
retains the risk of loss should the price of the security or currency decline. Unlike one who owns securities or
currencies not subject to an option, a Fund has no control over when it may be required to sell the underlying
securities or currencies, since it may be assigned an exercise notice at any time prior to the expiration of its
obligation as a writer. If a call option which a Fund has written expires, the Fund will realize a gain in the
amount of the premium; however, such gain may be offset by a decline in the market value of the underlying
security or currency during the option period. If the call option is exercised, a Fund will realize a gain or
loss from the sale of the underlying security or currency.
Writing (Selling) Put Options. A put option gives the purchaser of the option the right to
sell, and the writer (seller) has the obligation to buy, the underlying security or currency at the exercise
price during the option period (American style) or at the expiration of the option (European style). So long as
the obligation of the writer continues, he may be assigned an exercise notice by the broker-dealer through whom
such option was sold, requiring him to make payment of the exercise price against delivery of the underlying
security or currency. The operation of put options in other respects, including their related risks and rewards,
is substantially identical to that of call options.
Premium Received from Writing Call or Put Options. A Fund will receive a premium from writing
a put or call option, which increases such Fund's return in the event the option expires unexercised or is closed
out at a profit. The amount of the premium will reflect, among other things, the relationship of the market
price of the underlying security to the exercise price of the option, the term of the option and the volatility
of the market price of the underlying security. By writing a call option, a Fund limits its opportunity to
profit from any increase in the market value of the underlying security above the exercise price of the option.
By writing a put option, a Fund assumes the risk that it may be required to purchase the underlying security for
an exercise price higher than its then current market value, resulting in a potential capital loss if the
purchase price exceeds the market value plus the amount of the premium received, unless the security subsequently
appreciates in value.
Closing Transactions. A Fund may terminate an option that it has written prior to its
expiration by entering into a closing purchase transaction in which it purchases an option having the same terms
as the option written. Closing transactions may be effected in order to realize a profit on an outstanding call
option, to prevent an underlying security or currency from being called, or, to permit the sale of the underlying
security or currency. A Fund will realize a profit or loss from such transaction if the cost of such transaction
is less or more than the premium received from the writing of the option. In the case of a put option, any loss
so incurred may be partially or entirely offset by the premium received from a simultaneous or subsequent sale of
a different put option. Because increases in the market price of a call option will generally reflect increases
in the market price of the underlying security, any loss resulting from the repurchase of a call option is likely
to be offset in whole or in part by unrealized appreciation of the underlying security owned by such Fund.
Furthermore, effecting a closing transaction will permit a Fund to write another call option on
the underlying security or currency with either a different exercise price or expiration date or both. If a Fund
desires to sell a particular security or currency from its portfolio on which it has written a call option, or
purchased a put option, it will seek to effect a closing transaction prior to, or concurrently with, the sale of
the security or currency. There is, of course, no assurance that a Fund will be able to effect such closing
transactions at a favorable price. If a Fund cannot enter into such a transaction, it may be required to hold a
security or currency that it might otherwise have sold. When a Fund writes a covered call option, it runs the
risk of not being able to participate in the appreciation of the underlying securities or currencies above the
exercise price, as well as the risk of being required to hold on to securities or currencies that are
depreciating in value. This could result in higher transaction costs. A Fund will pay transaction costs in
connection with the writing of options to close out previously written options. Such transaction costs are
normally higher than those applicable to purchases and sales of portfolio securities.
Purchasing Call Options. Call options may be purchased by a Fund for the purpose of acquiring
the underlying securities or currencies for its portfolio. Utilized in this fashion, the purchase of call
options enables a Fund to acquire the securities or currencies at the exercise price of the call option plus the
premium paid. At times the net cost of acquiring securities or currencies in this manner may be less than the
cost of acquiring the securities or currencies directly. This technique may also be useful to a Fund in
purchasing a large block of securities or currencies that would be more difficult to acquire by direct market
purchases. So long as it holds such a call option rather than the underlying security or currency itself, a Fund
is partially protected from any unexpected decline in the market price of the underlying security or currency and
in such event could allow the call option to expire, incurring a loss only to the extent of the premium paid for
the option.
Purchasing Put Options. A Fund may purchase a put option on an underlying security or currency
owned by the Fund (a "protective put") as a defensive technique in order to protect against an anticipated
decline in the value of the security or currency. Such hedge protection is provided only during the life of the
put option when the Fund, as the holder of the put option, is able to sell the underlying security or currency at
the put exercise price regardless of any decline in the underlying security's market price or currency's exchange
value. For example, a put option may be purchased in order to protect unrealized appreciation of a security or
currency where a Sub-advisor deems it desirable to continue to hold the security or currency because of tax
considerations. The premium paid for the put option and any transaction costs would reduce any capital gain
otherwise available for distribution when the security or currency is eventually sold.
If a Fund purchases put options at a time when the Fund does not own the underlying security or
currency, the Fund seeks to benefit from a decline in the market price of the underlying security or currency.
If the put option is not sold when it has remaining value, and if the market price of the underlying security or
currency remains equal to or greater than the exercise price during the life of the put option, a Fund will lose
its entire investment in the put option. In order for the purchase of a put option to be profitable, the market
price of the underlying security or currency must decline sufficiently below the exercise price to cover the
premium and transaction costs.
Dealer Options. Exchange-traded options generally have a continuous liquid market while dealer
options have none. Consequently, a Fund will generally be able to realize the value of a dealer option it has
purchased only by exercising it or reselling it to the dealer who issued it. Similarly, when a Fund writes a
dealer option, it generally will be able to close out the option prior to its expiration only by entering into a
closing purchase transaction with the dealer to which the Fund originally wrote the option. While a Fund will
seek to enter into dealer options only with dealers who will agree to and which are expected to be capable of
entering into closing transactions with the Fund, there can be no assurance that the Fund will be able to
liquidate a dealer option at a favorable price at any time prior to expiration. Until a Fund, as a covered
dealer call option writer, is able to effect a closing purchase transaction, it will not be able to liquidate
securities (or other assets) used as cover until the option expires or is exercised. In the event of insolvency
of the other party, a Fund may be unable to liquidate a dealer option. With respect to options written by a
Fund, the inability to enter into a closing transaction may result in material losses to a Fund. For example,
since a Fund must maintain a secured position with respect to any call option on a security it writes, a Fund may
not sell the assets which it has segregated to secure the position while it is obligated under the option. This
requirement may impair a Fund's ability to sell portfolio securities at a time when such sale might be
advantageous.
The Staff of the SEC has taken the position that purchased dealer options and the assets used
to secure the written dealer options are illiquid securities. A Fund may treat the cover used for written OTC
options as liquid if the dealer agrees that the Fund may repurchase the OTC option it has written for a maximum
price to be calculated by a predetermined formula. In such cases, the OTC option would be considered illiquid
only to the extent the maximum repurchase price under the formula exceeds the intrinsic value of the option. To
this extent, a Fund will treat dealer options as subject to a Fund's limitation on unmarketable or illiquid
securities. If the SEC changes its position on the liquidity of dealer options, a Fund will change its treatment
of such instrument accordingly.
Certain Risk Factors in Writing Call Options and in Purchasing Call and Put Options. During the option
period, a Fund, as writer of a call option has, in return for the premium received on the option, given up the
opportunity for capital appreciation above the exercise price should the market price of the underlying security
increase, but has retained the risk of loss should the price of the underlying security decline. The writer has
no control over the time when it may be required to fulfill its obligation as a writer of the option. The risk
of purchasing a call or put option is that a Fund may lose the premium it paid plus transaction costs. If a Fund
does not exercise the option and is unable to close out the position prior to expiration of the option, it will
lose its entire investment.
An exchange-traded option position may be closed out only on an exchange which provides a secondary
market. There can be no assurance that a liquid secondary market will exist for a particular option at a
particular time and that a Fund can close out its position by effecting a closing transaction. If a Fund is
unable to effect a closing purchase transaction, it cannot sell the underlying security until the option expires
or the option is exercised. Accordingly, a Fund may not be able to sell the underlying security at a time when
it might otherwise be advantageous to do so. Possible reasons for the absence of a liquid secondary market
include the following: (i) insufficient trading interest in certain options; (ii) restrictions on transactions
imposed by an exchange; (iii) trading halts, suspensions or other restrictions imposed with respect to particular
classes or series of options or underlying securities; (iv) inadequacy of the facilities of an exchange or the
clearing corporation to handle trading volume; and (v) a decision by one or more exchanges to discontinue the
trading of options or impose restrictions on orders. In addition, the hours of trading for options may not
conform to the hours during which the underlying securities are traded. To the extent that the options markets
close before the markets for the underlying securities, significant price and rate movements can take place in
the underlying markets that cannot be reflected in the options markets. The purchase of options is a highly
specialized activity which involves investment techniques and risks different from those associated with ordinary
portfolio securities transactions.
Each exchange has established limitations governing the maximum number of call options, whether or not
covered, which may be written by a single investor acting alone or in concert with others (regardless of whether
such options are written on the same or different exchanges or are held or written on one or more accounts or
through one or more brokers). An exchange may order the liquidation of positions found to be in violation of
these limits and it may impose other sanctions or restrictions.
Options on Stock Indices. Options on stock indices are similar to options on specific securities except
that, rather than the right to take or make delivery of the specific security at a specific price, an option on a
stock index gives the holder the right to receive, upon exercise of the option, an amount of cash if the closing
level of that stock index is greater than, in the case of a call, or less than, in the case of a put, the
exercise price of the option. This amount of cash is equal to such difference between the closing price of the
index and the exercise price of the option expressed in dollars multiplied by a specified multiple. The writer
of the option is obligated, in return for the premium received, to make delivery of this amount. Unlike options
on specific securities, all settlements of options on stock indices are in cash and gain or loss depends on
general movements in the stocks included in the index rather than price movements in particular stocks.
Risk Factors of Options on Indices. Because the value of an index option depends upon the movements in
the level of the index rather than upon movements in the price of a particular security, whether a Fund will
realize a gain or a loss on the purchase or sale of an option on an index depends upon the movements in the level
of prices in the market generally or in an industry or market segment rather than upon movements in the price of
the individual security. Accordingly, successful use of positions will depend upon a Sub-advisor's ability to
predict correctly movements in the direction of the market generally or in the direction of a particular
industry. This requires different skills and techniques than predicting changes in the prices of individual
securities.
Index prices may be distorted if trading of securities included in the index is interrupted. Trading in
index options also may be interrupted in certain circumstances, such as if trading were halted in a substantial
number of securities in the index. If this occurred, a Fund would not be able to close out options which it had
written or purchased and, if restrictions on exercise were imposed, might be unable to exercise an option it
purchased, which would result in substantial losses.
Price movements in portfolio securities will not correlate perfectly with movements in the level of the
index and therefore, a Fund bears the risk that the price of the securities may not increase as much as the level
of the index. In this event, the Fund would bear a loss on the call which would not be completely offset by
movements in the prices of the securities. It is also possible that the index may rise when the value of a
Fund's securities does not. If this occurred, a Fund would experience a loss on the call which would not be
offset by an increase in the value of its securities and might also experience a loss in the market value of its
securities.
Unless a Fund has other liquid assets which are sufficient to satisfy the exercise of a call on the
index, the Fund will be required to liquidate securities in order to satisfy the exercise. When a Fund has
written a call on an index, there is also the risk that the market may decline between the time the Fund has the
call exercised against it, at a price which is fixed as of the closing level of the index on the date of
exercise, and the time the Fund is able to sell securities. As with options on securities, the Sub-advisor will
not learn that a call has been exercised until the day following the exercise date, but, unlike a call on
securities where a Fund would be able to deliver the underlying security in settlement, a Fund may have to sell
part of its securities in order to make settlement in cash, and the price of such securities might decline before
they could be sold.
If a Fund exercises a put option on an index which it has purchased before final determination of the
closing index value for the day, it runs the risk that the level of the underlying index may change before
closing. If this change causes the exercised option to fall "out-of-the-money," the Fund will be required to pay
the difference between the closing index value and the exercise price of the option (multiplied by the applicable
multiplier) to the assigned writer. Although a Fund may be able to minimize this risk by withholding exercise
instructions until just before the daily cutoff time or by selling rather than exercising an option when the
index level is close to the exercise price, it may not be possible to eliminate this risk entirely because the
cutoff time for index options may be earlier than those fixed for other types of options and may occur before
definitive closing index values are announced.
Trading in Futures. A futures contract provides for the future sale by one party and purchase by
another party of a specified amount of a specific financial instrument (e.g., units of a stock index) at a
specified price, date, time and place designated at the time the contract is made. Brokerage fees are incurred
when a futures contract is bought or sold and margin deposits must be maintained. Entering into a contract to
buy is commonly referred to as buying or purchasing a contract or holding a long position. Entering into a
contract to sell is commonly referred to as selling a contract or holding a short position.
Unlike when a Fund purchases or sells a security, no price would be paid or received by a Fund upon the
purchase or sale of a futures contract. Upon entering into a futures contract, and to maintain a Fund's open
positions in futures contracts, a Fund would be required to deposit with its custodian in the name of the futures
broker an amount of cash, U.S. government securities, suitable money market instruments, or other liquid
securities, known as "initial margin." A margin deposit is intended to ensure a Fund's performance of the
futures contract. The initial margin required for a particular futures contract is set by the exchange on which
the contract is traded, and may be significantly modified from time to time by the exchange during the term of
the contract. Futures contracts are customarily purchased and sold on margins that may range upward from less
than 5% of the value of the contract being traded.
If the price of an open futures contract changes (by increase in the case of a sale or by decrease in
the case of a purchase) so that the loss on the futures contract reaches a point at which the margin on deposit
does not satisfy margin requirements, the broker will require an increase in the margin. However, if the value
of a position increases because of favorable price changes in the futures contract so that the margin deposit
exceeds the required margin, the broker will pay the excess to a Fund.
These subsequent payments, called "variation margin," to and from the futures broker are made on a daily
basis as the price of the underlying assets fluctuate making the long and short positions in the futures contract
more or less valuable, a process known as "marking to the market." A Fund may or may not earn interest income on
its margin deposits. Although certain futures contracts, by their terms, require actual future delivery of and
payment for the underlying instruments, in practice most futures contracts are usually closed out before the
delivery date. Closing out an open futures contract purchase or sale is effected by entering into an offsetting
futures contract purchase or sale, respectively, for the same aggregate amount of the identical securities and
the same delivery date. If the offsetting purchase price is less than the original sale price, a Fund realizes a
gain; if it is more, a Fund realizes a loss. Conversely, if the offsetting sale price is more than the original
purchase price, a Fund realizes a gain; if it is less, a Fund realizes a loss. The transaction costs must also
be included in these calculations. There can be no assurance, however, that a Fund will be able to enter into an
offsetting transaction with respect to a particular futures contract at a particular time. If a Fund is not able
to enter into an offsetting transaction, a Fund will continue to be required to maintain the margin deposits on
the futures contract.
A stock index futures contract is an agreement in which one party agrees to deliver to the other an
amount of cash equal to a specific amount multiplied by the difference between the value of a specific stock
index at the close of the last trading day of the contract and the price at which the agreement is made. No
physical delivery of securities is made. For example, one contract in the Financial Times Stock Exchange 100
Index future is a contract to buy 25 pounds sterling multiplied by the level of the UK Financial Times 100 Share
Index on a given future date. Settlement of a stock index futures contract may or may not be in the underlying
security. If not in the underlying security, then settlement will be made in cash, equivalent over time to the
difference between the contract price and the actual price of the underlying asset at the time the stock index
futures contract expires.
Options on futures are similar to options on underlying instruments except that options on futures give
the purchaser the right, in return for the premium paid, to assume a position in a futures contract (a long
position if the option is a call and a short position if the option is a put), rather than to purchase or sell
the futures contract, at a specified exercise price at any time during the period of the option. Upon exercise
of the option, the delivery of the futures position by the writer of the option to the holder of the option will
be accompanied by the delivery of the accumulated balance in the writer's futures margin account which represents
the amount by which the market price of the futures contract, at exercise, exceeds (in the case of a call) or is
less than (in the case of a put) the exercise price of the option on the futures contract. Alternatively,
settlement may be made totally in cash. Purchasers of options who fail to exercise their options prior to the
exercise date suffer a loss of the premium paid.
The writer of an option on a futures contract is required to deposit margin pursuant to requirements
similar to those applicable to futures contracts. Upon exercise of an option on a futures contract, the delivery
of the futures position by the writer of the option to the holder of the option will be accompanied by delivery
of the accumulated balance in the writer's margin account. This amount will be equal to the amount by which the
market price of the futures contract at the time of exercise exceeds, in the case of a call, or is less than, in
the case of a put, the exercise price of the option on the futures contract.
Although financial futures contracts by their terms call for actual delivery or acceptance of
securities, in most cases the contracts are closed out before the settlement date without the making or taking of
delivery. Closing out is accomplished by effecting an offsetting transaction. A futures contract sale is closed
out by effecting a futures contract purchase for the same aggregate amount of securities and the same delivery
date. If the sale price exceeds the offsetting purchase price, the seller immediately would be paid the
difference and would realize a gain. If the offsetting purchase price exceeds the sale price, the seller would
immediately pay the difference and would realize a loss. Similarly, a futures contract purchase is closed out by
effecting a futures contract sale for the same securities and the same delivery date. If the offsetting sale
price exceeds the purchase price, the purchaser would realize a gain, whereas if the purchase price exceeds the
offsetting sale price, the purchaser would realize a loss. Commissions on financial futures contracts and
related options transactions may be higher than those which would apply to purchases and sales of securities
directly.
A public market exists in interest rate futures contracts covering primarily the following financial
instruments: U.S. Treasury bonds; U.S. Treasury notes; Government National Mortgage Association ("GNMA") modified
pass-through mortgage-backed securities; three-month U.S. Treasury bills; 90-day commercial paper; bank
certificates of deposit; and Eurodollar certificates of deposit. It is expected that futures contracts trading
in additional financial instruments will be authorized. The standard contract size is generally $100,000 for
futures contracts in U.S. Treasury bonds, U.S. Treasury notes, and GNMA pass-through securities and $1,000,000
for the other designated futures contracts. A public market exists in futures contracts covering a number of
indices, including, but not limited to, the Standard & Poor's 500 Index, the Standard & Poor's 100 Index, the
NASDAQ 100 Index, the Value Line Composite Index and the New York Stock Exchange Composite Index.
Regulatory Matters Relating to Futures Contracts and Related Options. The Staff of the SEC has taken
the position that the purchase and sale of futures contracts and the writing of related options may give rise to
"senior securities" for the purposes of the restrictions contained in Section 18 of the 1940 Act on investment
companies' issuing senior securities. However, the Staff has taken the position that no senior security will be
created if a Fund segregates an amount of cash or other liquid assets at least equal to the amount of the Fund's
obligation under the futures contract or option. Each Fund will conduct its purchases and sales of any futures
contracts and writing of related options transactions in accordance with this requirement.
Certain Risks Relating to Futures Contracts and Related Options. There are special risks involved in
futures transactions.
Volatility and Leverage. The prices of futures contracts are volatile and are influenced,
among other things, by actual and anticipated changes in the market and interest rates, which in turn are
affected by fiscal and monetary policies and national and international policies and economic events.
Most United States futures exchanges limit the amount of fluctuation permitted in futures
contract prices during a single trading day. The daily limit establishes the maximum amount that the price of a
futures contract may vary either up or down from the previous day's settlement price at the end of a trading
session. Once the daily limit has been reached in a particular type of futures contract, no trades may be made
on that day at a price beyond that limit. The daily limit governs only price movement during a particular trading
day and therefore does not limit potential losses, because the limit may prevent the liquidation of unfavorable
positions. Futures contract prices have occasionally moved to the daily limit for several consecutive trading
days with little or no trading, thereby preventing prompt liquidation of futures positions and subjecting some
futures traders to substantial losses.
Because of the low margin deposits required, futures trading involves an extremely high degree
of leverage. As a result, a relatively small price movement in a futures contract may result in immediate and
substantial loss, as well as gain, to the investor. For example, if at the time of purchase, 10% of the value of
the futures contract is deposited as margin, a subsequent 10% decrease in the value of the futures contract would
result in a total loss of the margin deposit, before any deduction for the transaction costs, if the account were
then closed out. A 15% decrease would result in a loss equal to 150% of the original margin deposit, if the
contract were closed out. Thus, a purchase or sale of a futures contract may result in losses in excess of the
amount invested in the futures contract. However, a Fund would presumably have sustained comparable losses if,
instead of the futures contract, it had invested in the underlying instrument and sold it after the decline.
Furthermore, in the case of a futures contract purchase, in order to be certain that a Fund has sufficient assets
to satisfy its obligations under a futures contract, a Fund earmarks to the futures contract liquid assets equal
in value to the current value of the underlying instrument less the margin deposit.
Liquidity. A Fund may elect to close some or all of its futures positions at any time prior to
their expiration. A Fund would do so to reduce exposure represented by long futures positions or increase
exposure represented by short futures positions. A Fund may close its positions by taking opposite positions
which would operate to terminate the Fund's position in the futures contracts. Final determinations of variation
margin would then be made, additional cash would be required to be paid by or released to a Fund, and such Fund
would realize a loss or a gain.
Futures contracts may be closed out only on the exchange or board of trade where the contracts
were initially traded. Although a Fund may intend to purchase or sell futures contracts only on exchanges or
boards of trade where there appears to be an active market, there is no assurance that a liquid market on an
exchange or board of trade will exist for any particular contract at any particular time. In such event, it
might not be possible to close a futures contract, and in the event of adverse price movements, a Fund would
continue to be required to make daily cash payments of variation margin. However, in the event futures contracts
have been used to hedge the underlying instruments, a Fund would continue to hold the underlying instruments
subject to the hedge until the futures contracts could be terminated. In such circumstances, an increase in the
price of the underlying instruments, if any, might partially or completely offset losses on the futures
contract. However, as described below, there is no guarantee that the price of the underlying instruments will,
in fact, correlate with the price movements in the futures contract and thus provide an offset to losses on a
futures contract.
Hedging Risk. A decision of whether, when, and how to hedge involves skill and judgment, and
even a well-conceived hedge may be unsuccessful to some degree because of unexpected market behavior, market or
interest rate trends. There are several risks in connection with the use by a Fund of futures contracts as a
hedging device. One risk arises because of the imperfect correlation between movements in the prices of the
futures contracts and movements in the prices of the underlying instruments which are the subject of the hedge.
The Sub-advisor will, however, attempt to reduce this risk by entering into futures contracts whose movements, in
its judgment, will have a significant correlation with movements in the prices of a Fund's underlying instruments
sought to be hedged.
Successful use of futures contracts by a Fund for hedging purposes is also subject to a
Sub-advisor's ability to correctly predict movements in the direction of the market. It is possible that, when a
Fund has sold futures to hedge its portfolio against a decline in the market, the index, indices, or underlying
instruments on which the futures are written might advance and the value of the underlying instruments held in
the Fund's portfolio might decline. If this were to occur, a Fund would lose money on the futures and also would
experience a decline in value in its underlying instruments. However, while this might occur to a certain
degree, the Sub-advisor may believe that over time the value of a Fund's portfolio will tend to move in the same
direction as the market indices which are intended to correlate to the price movements of the underlying
instruments sought to be hedged. It is also possible that if a Fund were to hedge against the possibility of a
decline in the market (adversely affecting the underlying instruments held in its portfolio) and prices instead
increased, the Fund would lose part or all of the benefit of increased value of those underlying instruments that
it has hedged, because it would have offsetting losses in its futures positions. In addition, in such
situations, if a Fund had insufficient cash, it might have to sell underlying instruments to meet daily variation
margin requirements. Such sales of underlying instruments might be, but would not necessarily be, at increased
prices (which would reflect the rising market). A Fund might have to sell underlying instruments at a time when
it would be disadvantageous to do so.
In addition to the possibility that there might be an imperfect correlation, or no correlation
at all, between price movements in the futures contracts and the portion of the portfolio being hedged, the price
movements of futures contracts might not correlate perfectly with price movements in the underlying instruments
due to certain market distortions. First, all participants in the futures market are subject to margin deposit
and maintenance requirements. Rather than meeting additional margin deposit requirements, investors might close
futures contracts through offsetting transactions which could distort the normal relationship between the
underlying instruments and futures markets. Second, the margin requirements in the futures market are less
onerous than margin requirements in the securities markets, and as a result the futures market might attract more
speculators than the securities markets do. Increased participation by speculators in the futures market might
also cause temporary price distortions. Due to the possibility of price distortion in the futures market and
also because of the imperfect correlation between price movements in the underlying instruments and movements in
the prices of futures contracts, even a correct forecast of general market trends by the Sub-advisor might not
result in a successful hedging transaction over a very short time period.
Certain Risks of Options on Futures Contracts. A Fund may seek to close out an option position by
writing or buying an offsetting option covering the same index, underlying instruments, or contract and having
the same exercise price and expiration date. The ability to establish and close out positions on such options
will be subject to the maintenance of a liquid secondary market. Reasons for the absence of a liquid secondary
market on an exchange include the following: (i) there may be insufficient trading interest in certain options;
(ii) restrictions may be imposed by an exchange on opening transactions or closing transactions or both; (iii)
trading halts, suspensions or other restrictions may be imposed with respect to particular classes or series of
options, or underlying instruments; (iv) unusual or unforeseen circumstances may interrupt normal operations on
an exchange; (v) the facilities of an exchange or a clearing corporation may not at all times be adequate to
handle current trading volume; or (vi) one or more exchanges could, for economic or other reasons, decide or be
compelled at some future date to discontinue the trading of options (or a particular class or series of options),
in which event the secondary market on that exchange (or in the class or series of options) would cease to exist,
although outstanding options on the exchange that had been issued by a clearing corporation as a result of trades
on that exchange would continue to be exercisable in accordance with their terms. There is no assurance that
higher than anticipated trading activity or other unforeseen events might not, at times, render certain of the
facilities of any of the clearing corporations inadequate, and thereby result in the institution by an exchange
of special procedures which may interfere with the timely execution of customers' orders.
Foreign Futures and Options. Participation in foreign futures and foreign options transactions involves
the execution and clearing of trades on or subject to the rules of a foreign board of trade. Neither the
National Futures Association nor any domestic exchange regulates activities of any foreign boards of trade,
including the execution, delivery and clearing of transactions, or has the power to compel enforcement of the
rules of a foreign board of trade or any applicable foreign law. This is true even if the exchange is formally
linked to a domestic market so that a position taken on the market may be liquidated by a transaction on another
market. Moreover, such laws or regulations will vary depending on the foreign country in which the foreign
futures or foreign options transaction occurs. For these reasons, customers who trade foreign futures or foreign
options contracts may not be afforded certain of the protective measures provided by the Commodity Exchange Act,
the CFTC regulations and the rules of the National Futures Association and any domestic exchange, including the
right to use reparations proceedings before the CFTC and arbitration proceedings provided by the National Futures
Association or any domestic futures exchange. In particular, funds received from customers for foreign futures
or foreign options transactions may not be provided the same protections as funds received in respect of
transactions on United States futures exchanges. In addition, the price of any foreign futures or foreign
options contract and, therefore, the potential profit and loss thereon may be affected by any variance in the
foreign exchange rate between the time an order is placed and the time it is liquidated, offset or exercised.
Foreign Currency Contracts. A forward foreign currency exchange contract involves an obligation to
purchase or sell a specific currency at a future date, which may be any fixed number of days from the date of the
contract agreed upon by the parties, at a price set at the time of the contract. These contracts are principally
traded in the interbank market conducted directly between currency traders (usually large, commercial banks) and
their customers. A forward contract generally has no deposit requirement, and no commissions are charged at any
stage for trades.
Depending on the applicable investment policies and restrictions applicable to a Fund, a Fund may
generally enter into forward foreign currency exchange contracts under two circumstances. First, when a Fund
enters into a contract for the purchase or sale of a security denominated in a foreign currency, it may desire to
"lock in" the U.S. dollar price of the security. By entering into a forward contract for the purchase or sale,
for a fixed amount of dollars, of the amount of foreign currency involved in the underlying security
transactions, the Fund may be able to protect itself against a possible loss resulting from an adverse change in
the relationship between the U.S. dollar and the subject foreign currency during the period between the date the
security is purchased or sold and the date on which payment is made or received.
Second, when a Sub-advisor believes that the currency of a particular foreign country may suffer or
enjoy a substantial movement against another currency, including the U.S. dollar, it may enter into a forward
contract to sell or buy the amount of the former foreign currency, approximating the value of some or all of a
Fund's securities denominated in such foreign currency. Alternatively, where appropriate, a Fund may hedge all
or part of its foreign currency exposure through the use of a basket of currencies or a proxy currency where such
currencies or currency act as an effective proxy for other currencies. In such a case, a Fund may enter into a
forward contract where the amount of the foreign currency to be sold exceeds the value of the Fund's securities
denominated in such currency. The use of this basket hedging technique may be more efficient and economical than
entering into separate forward contracts for each currency held in a Fund. The precise matching of the forward
contract amounts and the value of the securities involved will not generally be possible since the future value
of such securities in foreign currencies will change as a consequence of market movements in the value of those
securities between the date the forward contract is entered into and the date it matures. The projection of
short-term currency market movement is extremely difficult, and the successful execution of a short-term hedging
strategy is highly uncertain.
As indicated above, it is impossible to forecast with absolute precision the market value of portfolio
securities at the expiration of the forward contract. Accordingly, it may be necessary for a Fund to purchase
additional foreign currency on the spot market (and bear the expense of such purchase) if the market value of the
security is less than the amount of foreign currency a Fund is obligated to deliver and if a decision is made to
sell the security and make delivery of the foreign currency. Conversely, it may be necessary to sell on the spot
market some of the foreign currency received upon the sale of the portfolio security if its market value exceeds
the amount of foreign currency a Fund is obligated to deliver. However, as noted, in order to avoid excessive
transactions and transaction costs, a Fund may use liquid assets denominated in any currency to cover the amount
by which the value of a forward contract exceeds the value of the securities to which it relates.
If a Fund retains the portfolio security and engages in an offsetting forward contract transaction, the
Fund will incur a gain or a loss (as described below) to the extent that there has been movement in forward
contract prices. If the Fund engages in an offsetting transaction, it may subsequently enter into a new forward
contract to sell the foreign currency. Should forward prices decline during the period between a Fund's entering
into a forward contract for the sale of a foreign currency and the date it enters into an offsetting contract for
the purchase of the foreign currency, the Fund will realize a gain to the extent the price of the currency it has
agreed to sell exceeds the price of the currency it has agreed to purchase. Should forward prices increase, a
Fund will suffer a loss to the extent of the price of the currency it has agreed to purchase exceeds the price of
the currency it has agreed to sell.
Currency Futures Contracts and Related Options. A currency futures contract sale creates an obligation
by a Fund, as seller, to deliver the amount of currency called for in the contract at a specified future time for
a special price. A currency futures contract purchase creates an obligation by a Fund, as purchaser, to take
delivery of an amount of currency at a specified future time at a specified price. Unlike forward foreign
currency exchange contracts, currency futures contracts are standardized as to amount and delivery period and are
traded on boards of trade and commodities exchanges. Although the terms of currency futures contracts specify
actual delivery or receipt, in most instances the contracts are closed out before the settlement date without the
making or taking of delivery of the currency. Closing out of a currency futures contract is effected by entering
into an offsetting purchase or sale transaction. Unlike a currency futures contract, which requires the parties
to buy and sell currency on a set date, an option on a currency futures contract entitles its holder to decide on
or before a future date whether to enter into such a contract. If the holder decides not to enter into the
contract, the premium paid for the option is fixed at the point of sale.
Interest Rate Swaps and Interest Rate Caps and Floors. Interest rate swaps involve the exchange by the
Fund with another party of their respective commitments to pay or receive interest, e.g., an exchange of floating
rate payments for fixed rate payments. The exchange commitments can involve payments to be made in the same
currency or in different currencies. The purchase of an interest rate cap entitles the purchaser, to the extent
that a specified index exceeds a predetermined interest rate, to receive payments of interest on a contractually
based principal amount from the party selling the interest rate cap. The purchase of an interest rate floor
entitles the purchaser, to the extent that a specified index falls below a predetermined interest rate, to
receive payments of interest on a contractually based principal amount from the party selling the interest rate
floor.
Hybrid Instruments:
Hybrid instruments combine the elements of futures contracts or options with those of debt, preferred
equity or a depository instrument. The risks of investing in hybrid instruments reflect a combination of the
risks from investing in securities, futures and currencies, including volatility and lack of liquidity.
Reference is made to the discussion of futures and forward contracts in this SAI for a discussion of these
risks. Further, the prices of the hybrid instrument and the related commodity or currency may not move in the
same direction or at the same time. Hybrid instruments may bear interest or pay preferred dividends at below
market (or even relatively nominal) rates. In addition, because the purchase and sale of hybrid instruments
could take place in an over-the-counter market or in a private transaction between a Fund and the seller of the
hybrid instrument, the creditworthiness of the other party to the transaction would be a risk factor which a Fund
would have to consider. Hybrid instruments also may not be subject to the regulation of the CFTC, which
generally regulates the trading of commodity futures by U.S. persons, the SEC, which regulates the offer and sale
of securities by and to U.S. persons, or any other governmental regulatory authority.
Foreign Currency Exchange-Related Securities. Certain Funds may invest in foreign currency warrants,
principal exchange rate linked securities and performance indexed paper.
Foreign Currency Warrants. Foreign currency warrants are warrants which entitle the holder to
receive from their issuer an amount of cash (generally, for warrants issued in the United States, in U.S.
dollars) which is calculated pursuant to a predetermined formula and based on the exchange rate between a
specified foreign currency and the U.S. dollar as of the exercise date of the warrant. Foreign currency warrants
generally are exercisable upon their issuance and expire as of a specified date and time. Foreign currency
warrants have been issued in connection with U.S. dollar-denominated debt offerings by major corporate issuers in
an attempt to reduce the foreign currency exchange risk which, from the point of view of prospective purchasers
of the securities, is inherent in the international fixed-income marketplace. Foreign currency warrants may
attempt to reduce the foreign exchange risk assumed by purchasers of a security by, for example, providing for a
supplemental payment in the event that the U.S. dollar depreciates against the value of a major foreign currency
such as the Japanese Yen. The formula used to determine the amount payable upon exercise of a foreign currency
warrant may make the warrant worthless unless the applicable foreign currency exchange rate moves in a particular
direction (e.g., unless the U.S. dollar appreciates or depreciates against the particular foreign currency to
which the warrant is linked or indexed). Foreign currency warrants are severable from the debt obligations with
which they may be offered, and may be listed on exchanges. Foreign currency warrants may be exercisable only in
certain minimum amounts, and an investor wishing to exercise warrants who possesses less than the minimum number
required for exercise may be required either to sell the warrants or to purchase additional warrants, thereby
incurring additional transaction costs. In the case of any exercise of warrants, there may be a time delay
between the time a holder of warrants gives instructions to exercise and the time the exchange rate relating to
exercise is determined, during which time the exchange rate could change significantly, thereby affecting both
the market and cash settlement values of the warrants being exercised. The expiration date of the warrants may
be accelerated if the warrants should be delisted from an exchange or if their trading should be suspended
permanently, which would result in the loss of any remaining "time value" of the warrants (i.e., the difference
between the current market value and the exercise value of the warrants), and, in the case the warrants were
"out-of-the-money," in a total loss of the purchase price of the warrants. Warrants are generally unsecured
obligations of their issuers and are not standardized foreign currency options issued by the Options Clearing
Corporation ("OCC"). Unlike foreign currency options issued by OCC, the terms of foreign exchange warrants
generally will not be amended in the event of governmental or regulatory actions affecting exchange rates or in
the event of the imposition of other regulatory controls affecting the international currency markets. The
initial public offering price of foreign currency warrants is generally considerably in excess of the price that
a commercial user of foreign currencies might pay in the interbank market for a comparable option involving
significantly larger amounts of foreign currencies. Foreign currency warrants are subject to significant foreign
exchange risk, including risks arising from complex political or economic factors.
Principal Exchange Rate Linked Securities. Principal exchange rate linked securities are debt
obligations the principal on which is payable at maturity in an amount that may vary based on the exchange rate
between the U.S. dollar and a particular foreign currency at or about that time. The return on "standard"
principal exchange rate linked securities is enhanced if the foreign currency to which the security is linked
appreciates against the U.S. dollar, and is adversely affected by increases in the foreign exchange value of the
U.S. dollar. "Reverse" principal exchange rate linked securities are like the "standard" securities, except that
their return is enhanced by increases in the value of the U.S. dollar and adversely impacted by increases in the
value of foreign currency. Interest payments on the securities are generally made in U.S. dollars at rates that
reflect the degree of foreign currency risk assumed or given up by the purchaser of the notes (i.e., at
relatively higher interest rates if the purchaser has assumed some of the foreign exchange risk, or relatively
lower interest rates if the issuer has assumed some of the foreign exchange risk, based on the expectations of
the current market). Principal exchange rate linked securities may in limited cases be subject to acceleration
of maturity (generally, not without the consent of the holders of the securities), which may have an adverse
impact on the value of the principal payment to be made at maturity.
Performance Indexed Paper. Performance indexed paper is U.S. dollar-denominated commercial
paper the yield of which is linked to certain foreign exchange rate movements. The yield to the investor on
performance indexed paper is established at maturity as a function of spot exchange rates between the U.S. dollar
and a designated currency as of or about that time (generally, the spot exchange rate two days prior to
maturity). The yield to the investor will be within a range stipulated at the time of purchase of the
obligation, generally with a guaranteed minimum rate of return that is below, and a potential maximum rate of
return that is above, market yields on U.S. dollar-denominated commercial paper, with both the minimum and
maximum rates of return on the investment corresponding to the minimum and maximum values of the spot exchange
rate two business days prior to maturity.
Zero-Coupon Securities. Zero-coupon securities pay no cash income and are sold at substantial discounts
from their value at maturity. When held to maturity, their entire income, which consists of accretion of
discount, comes from the difference between the issue price and their value at maturity. Zero-coupon securities
are subject to greater market value fluctuations from changing interest rates than debt obligations of comparable
maturities which make current distributions of interest (cash). Zero-coupon securities which are convertible
into common stock offer the opportunity for capital appreciation as increases (or decreases) in market value of
such securities closely follows the movements in the market value of the underlying common stock. Zero-coupon
convertible securities generally are expected to be less volatile than the underlying common stocks, as they
usually are issued with maturities of 15 years or less and are issued with options and/or redemption features
exercisable by the holder of the obligation entitling the holder to redeem the obligation and receive a defined
cash payment.
Zero-coupon securities include securities issued directly by the U.S. Treasury, and U.S. Treasury bonds
or notes and their unmatured interest coupons and receipts for their underlying principal ("coupons") which have
been separated by their holder, typically a custodian bank or investment brokerage firm. A holder will separate
the interest coupons from the underlying principal (the "corpus") of the U.S. Treasury security. A number of
securities firms and banks have stripped the interest coupons and receipts and then resold them in custodial
receipt programs with a number of different names, including Treasury Income Growth Receipts ("TIGRSTM") and
Certificate of Accrual on Treasuries ("CATSTM"). The underlying U.S. Treasury bonds and notes themselves are
held in book-entry form at the Federal Reserve Bank or, in the case of bearer securities (i.e., unregistered
securities which are owned ostensibly by the bearer or holder thereof), in trust on behalf of the owners
thereof. Counsel to the underwriters of these certificates or other evidences of ownership of the U.S. Treasury
securities have stated that, for federal tax and securities purposes, in their opinion purchasers of such
certificates, such as a Fund, most likely will be deemed the beneficial holder of the underlying U.S. Government
securities.
The U.S. Treasury has facilitated transfers of ownership of zero-coupon securities by accounting
separately for the beneficial ownership of particular interest coupon and corpus payments on Treasury securities
through the Federal Reserve book-entry record keeping system. The Federal Reserve program as established by the
Treasury Department is known as "STRIPS" or "Separate Trading of Registered Interest and Principal of
Securities." Under the STRIPS program, a Fund will be able to have its beneficial ownership of zero-coupon
securities recorded directly in the book-entry record-keeping system in lieu of having to hold certificates or
other evidences of ownership of the underlying U.S. Treasury securities.
When U.S. Treasury obligations have been stripped of their unmatured interest coupons by the holder, the
principal or corpus is sold at a deep discount because the buyer receives only the right to receive a future
fixed payment on the security and does not receive any rights to periodic interest (cash) payments. Once
stripped or separated, the corpus and coupons may be sold separately. Typically, the coupons are sold separately
or grouped with other coupons with like maturity dates and sold bundled in such form. Purchasers of stripped
obligations acquire, in effect, discount obligations that are economically identical to the zero-coupon
securities that the Treasury sells itself.
When-Issued Securities. The price of when-issued securities, which may be expressed in yield terms, is
fixed at the time the commitment to purchase is made, but delivery and payment for the when-issued securities
take place at a later date. Normally, the settlement date occurs within 90 days of the purchase. During the
period between purchase and settlement, no payment is made by a Fund to the issuer and no interest accrues to
such Fund. Forward commitments involve a risk of loss if the value of the security to be purchased declines
prior to the settlement date, which risk is in addition to the risk of decline in value of a Fund's other
assets. While when-issued securities may be sold prior to the settlement date, a Fund generally will purchase
such securities with the purpose of actually acquiring them unless a sale appears desirable for investment
reasons.
Mortgage-Backed Securities. When a Fund owns a mortgage-backed security, principal and interest
payments made on the mortgages in an underlying mortgage pool are passed through to a Fund. Unscheduled
prepayments of principal shorten the securities' weighted average life and may lower their total return. (When a
mortgage in the underlying mortgage pool is prepaid, an unscheduled principal prepayment is passed through to a
Fund. This principal is returned to a Fund at par. As a result, if a mortgage security were trading at a
premium, its total return would be lowered by prepayments, and if a mortgage security were trading at a discount,
its total return would be increased by prepayments.) The value of these securities also may change because of
changes in the market's perception of the creditworthiness of the federal agency that issued them. In addition,
the mortgage securities market in general may be adversely affected by changes in governmental regulation or tax
policies.
Asset-Backed Securities. Asset-backed securities directly or indirectly represent a participation
interest in, or are secured by and payable from, a stream of payments generated by particular assets such as
motor vehicle or credit card receivables. Payments of principal and interest may be guaranteed up to certain
amounts and for a certain time period by a letter of credit issued by a financial institution unaffiliated with
the entities issuing the securities. Asset-backed securities may be classified as pass-through certificates or
collateralized obligations.
Pass-through certificates are asset-backed securities which represent an undivided fractional ownership
interest in an underlying pool of assets. Pass-through certificates usually provide for payments of principal
and interest received to be passed through to their holders, usually after deduction for certain costs and
expenses incurred in administering the pool. Because pass-through certificates represent an ownership interest in
the underlying assets, the holders thereof bear directly the risk of any defaults by the obligors on the
underlying assets not covered by any credit support. See "Types of Credit Support" below.
Asset-backed securities issued in the form of debt instruments, also known as collateralized
obligations, are generally issued as the debt of a special purpose entity organized solely for the purpose of
owning such assets and issuing such debt. Such assets are most often trade, credit card or automobile
receivables. The assets collateralizing such asset-backed securities are pledged to a trustee or custodian for
the benefit of the holders thereof. Such issuers generally hold no assets other than those underlying the
asset-backed securities and any credit support provided. As a result, although payments on such asset-backed
securities are obligations of the issuers, in the event of defaults on the underlying assets not covered by any
credit support (see "Types of Credit Support"), the issuing entities are unlikely to have sufficient assets to
satisfy their obligations on the related asset-backed securities.
Methods of Allocating Cash Flows. While many asset-backed securities are issued with only one
class of security, many asset-backed securities are issued in more than one class, each with different payment
terms. Multiple class asset-backed securities are issued for two main reasons. First, multiple classes may be
used as a method of providing credit support. This is accomplished typically through creation of one or more
classes whose right to payments on the asset-backed security is made subordinate to the right to such payments of
the remaining class or classes. See "Types of Credit Support." Second, multiple classes may permit the issuance
of securities with payment terms, interest rates or other characteristics differing both from those of each other
and from those of the underlying assets. Examples include so-called "strips" (asset-backed securities entitling
the holder to disproportionate interests with respect to the allocation of interest and principal of the assets
backing the security), and securities with a class or classes having characteristics which mimic the
characteristics of non-asset-backed securities, such as floating interest rates (i.e., interest rates which
adjust as a specified benchmark changes) or scheduled amortization of principal.
Asset-backed securities in which the payment streams on the underlying assets are allocated in
a manner different than those described above may be issued in the future. A Fund may invest in such
asset-backed securities if such investment is otherwise consistent with its investment objectives and policies
and with the investment restrictions of the Fund.
Types of Credit Support. Asset-backed securities are often backed by a pool of assets
representing the obligations of a number of different parties. To lessen the effect of failures by obligors on
underlying assets to make payments, such securities may contain elements of credit support. Such credit support
falls into two classes: liquidity protection and protection against ultimate default by an obligor on the
underlying assets. Liquidity protection refers to the provision of advances, generally by the entity
administering the pool of assets, to ensure that scheduled payments on the underlying pool are made in a timely
fashion. Protection against ultimate default ensures ultimate payment of the obligations on at least a portion
of the assets in the pool. Such protection may be provided through guarantees, insurance policies or letters of
credit obtained from third parties, through various means of structuring the transaction or through a combination
of such approaches. Examples of asset-backed securities with credit support arising out of the structure of the
transaction include "senior-subordinated securities" (multiple class asset-backed securities with certain classes
subordinate to other classes as to the payment of principal thereon, with the result that defaults on the
underlying assets are borne first by the holders of the subordinated class) and asset-backed securities that have
"reserve funds" (where cash or investments, sometimes funded from a portion of the initial payments on the
underlying assets, are held in reserve against future losses) or that have been "over collateralized" (where the
scheduled payments on, or the principal amount of, the underlying assets substantially exceeds that required to
make payment of the asset-backed securities and pay any servicing or other fees). The degree of credit support
provided on each issue is based generally on historical information respecting the level of credit risk
associated with such payments. Delinquency or loss in excess of that anticipated could adversely affect the
return on an investment in an asset-backed security. Additionally, if a letter of credit is exhausted, holders
of asset-backed securities may also experience delays in payments or losses if the full amounts due on underlying
sales contracts are not realized.
Automobile Receivable Securities. Asset-backed securities may be backed by receivables from
motor vehicle installment sales contracts or installment loans secured by motor vehicles ("Automobile Receivable
Securities"). Since installment sales contracts for motor vehicles or installment loans related thereto
("Automobile Contracts") typically have shorter durations and lower incidences of prepayment, Automobile
Receivable Securities generally will exhibit a shorter average life and are less susceptible to prepayment risk.
Most entities that issue Automobile Receivable Securities create an enforceable interest in
their respective Automobile Contracts only by filing a financing statement and by having the servicer of the
Automobile Contracts, which is usually the originator of the Automobile Contracts, take custody thereof. In such
circumstances, if the servicer of the Automobile Contracts were to sell the same Automobile Contracts to another
party, in violation of its obligation not to do so, there is a risk that such party could acquire an interest in
the Automobile Contracts superior to that of the holders of Automobile Receivable Securities. Also although most
Automobile Contracts grant a security interest in the motor vehicle being financed, in most states the security
interest in a motor vehicle must be noted on the certificate of title to create an enforceable security interest
against competing claims of other parties. Due to the large number of vehicles involved, however, the
certificate of title to each vehicle financed, pursuant to the Automobile Contracts underlying the Automobile
Receivable Security, usually is not amended to reflect the assignment of the seller's security interest for the
benefit of the holders of the Automobile Receivable Securities. Therefore, there is the possibility that
recoveries on repossessed collateral may not, in some cases, be available to support payments on the securities.
In addition, various state and federal securities laws give the motor vehicle owner the right to assert against
the holder of the owner's Automobile Contract certain defenses such owner would have against the seller of the
motor vehicle. The assertion of such defenses could reduce payments on the Automobile Receivable Securities.
Credit Card Receivable Securities. Asset-backed securities may be backed by receivables from
revolving credit card agreements ("Credit Card Receivable Securities"). Credit balances on revolving credit card
agreements ("Accounts") are generally paid down more rapidly than are Automobile Contracts. Most of the Credit
Card Receivable Securities issued publicly to date have been Pass-Through Certificates. In order to lengthen the
maturity of Credit Card Receivable Securities, most such securities provide for a fixed period during which only
interest payments on the underlying Accounts are passed through to the security holder and principal payments
received on such Accounts are used to fund the transfer to the pool of assets supporting the related Credit Card
Receivable Securities of additional credit card charges made on an Account. The initial fixed period usually may
be shortened upon the occurrence of specified events which signal a potential deterioration in the quality of the
assets backing the security, such as the imposition of a cap on interest rates. The ability of the issuer to
extend the life of an issue of Credit Card Receivable Securities thus depends upon the continued generation of
additional principal amounts in the underlying accounts during the initial period and the non-occurrence of
specified events. An acceleration in cardholders' payment rates or any other event which shortens the period
during which additional credit card charges on an Account may be transferred to the pool of assets supporting the
related Credit Card Receivable Security could shorten the weighted average life and reduce the yield of the
Credit Card Receivable Security.
Credit card holders are entitled to the protection of a number of state and federal consumer
credit laws, many of which give such holder the right to set off certain amounts against balances owed on the
credit card, thereby reducing amounts paid on Accounts. In addition, unlike most other asset-backed securities,
Accounts are unsecured obligations of the cardholder.
Warrants. Warrants basically are options to purchase equity securities at a specific price valid for a
specific period of time. They do not represent ownership of the securities but only the right to buy them.
Investments in warrants are speculative in that warrants have no voting rights, pay no dividends, and have no
rights with respect to the assets of the corporation issuing them. Warrants differ from call options in that
warrants are issued by the issuer of the security which may be purchased on their exercise, whereas call options
may be written or issued by anyone. The prices of warrants do not necessarily move parallel to the prices of the
underlying securities.
Certain Risks of Foreign Investing:
Currency Fluctuations. Investment in securities denominated in foreign currencies involves
certain risks. A change in the value of any such currency against the U.S. dollar will result in a corresponding
change in the U.S. dollar value of a Fund's assets denominated in that currency. Such changes will also affect a
Fund's income. Generally, when a given currency appreciates against the dollar (the dollar weakens) the value of
a Fund's securities denominated in that currency will rise. When a given currency depreciates against the dollar
(the dollar strengthens), the value of a Fund's securities denominated in that currency would be expected to
decline.
Investment and Repatriation Restrictions. Foreign investment in the securities markets of
certain foreign countries is restricted or controlled in varying degrees. These restrictions may at times limit
or preclude investment in certain of such countries and may increase the cost and expenses of a Fund.
Investments by foreign investors are subject to a variety of restrictions in many developing countries. These
restrictions may take the form of prior governmental approval, limits on the amount or type of securities held by
foreigners, and limits on the types of companies in which foreigners may invest. Additional or different
restrictions may be imposed at any time by these or other countries in which a Fund invests. In addition, the
repatriation of both investment income and capital from several foreign countries is restricted and controlled
under certain regulations, including in some cases the need for certain government consents.
Market Characteristics. Foreign securities may be purchased in over-the-counter markets or on
stock exchanges located in the countries in which the respective principal offices of the issuers of the various
securities are located, if that is the best available market. Foreign stock markets are generally not as
developed or efficient as, and may be more volatile than, those in the United States. While growing in volume,
they usually have substantially less volume than U.S. markets and a Fund's securities may be less liquid and more
volatile than securities of comparable U.S. companies. Equity securities may trade at price/earnings multiples
higher than comparable U.S. securities and such levels may not be sustainable. Commissions on foreign stock
exchanges, which may be fixed, may generally be higher than negotiated commissions on U.S. exchanges, although a
Fund will endeavor to achieve the most favorable net results on its portfolio transactions. There is generally
less government supervision and regulation of foreign stock exchanges, brokers and listed companies than in the
United States. Moreover, settlement practices for transactions in foreign markets may differ from those in U.S.
markets, and may include delays beyond periods customary in the United States.
Political and Economic Factors. Individual foreign economies of certain countries may differ
favorably or unfavorably from the United States' economy in such respects as growth of gross national product,
rate of inflation, capital reinvestment, resource self-sufficiency and balance of payments position. The
internal politics of certain foreign countries are not as stable as in the United States. Moreover, as the
result of the prevailing political climate, the Fund may not be able to obtain legal remedies or enforce
judgements in foreign countries.
Governments in certain foreign countries continue to participate to a significant degree,
through ownership interest or regulation, in their respective economies. Action by these governments could have
a significant effect on market prices of securities and payment of dividends. The economies of many foreign
countries are heavily dependent upon international trade and are accordingly affected by protective trade
barriers and economic conditions of their trading partners. The enactment by these trading partners of
protectionist trade legislation could have a significant adverse effect upon the securities markets of such
countries.
Information and Supervision. There is generally less publicly available information about
foreign companies comparable to reports and ratings that are published about companies in the United States.
Foreign companies are also generally not subject to uniform accounting, auditing and financial reporting
standards, practices and requirements comparable to those applicable to U.S. companies.
Taxes. The dividends and interest payable on certain of a Fund's foreign securities may be
subject to foreign withholding taxes, thus reducing the net amount of income available for distribution to the
Fund's shareholders. A shareholder otherwise subject to U.S. federal income taxes may, subject to certain
limitations, be entitled to claim a credit or deduction for U.S. federal income tax purposes for his or her
proportionate share of such foreign taxes paid by the Fund.
Costs. Investors should understand that the expense ratio of a Fund investing primarily in
foreign securities can be expected to be higher than investment companies investing in domestic securities since
the cost of maintaining the custody of foreign securities and the rate of advisory fees paid by a Fund are higher.
Other. With respect to certain foreign countries, especially developing and emerging ones,
there is the possibility of adverse changes in investment or exchange control regulations, expropriation or
confiscatory taxation, limitations on the removal of funds or other assets of a Fund, political or social
instability, or diplomatic developments which could affect investments by U.S. persons in those countries.
Eastern Europe. Changes occurring in Eastern Europe and Russia today could have long-term
potential consequences. As restrictions fall, this could result in rising standards of living, lower
manufacturing costs, growing consumer spending, and substantial economic growth. However, investment in the
countries of Eastern Europe and Russia is highly speculative at this time. Political and economic reforms are too
recent to establish a definite trend away from centrally-planned economies and state owned industries. In many
of the countries of Eastern Europe and Russia, there is no stock exchange or formal market for securities. Such
countries may also have government exchange controls, currencies with no recognizable market value relative to
the established currencies of western market economies, little or no experience in trading in securities, no
financial reporting standards, a lack of a banking and securities infrastructure to handle such trading, and a
legal tradition which does not recognize rights in private property. In addition, these countries may have
national policies which restrict investments in companies deemed sensitive to the country's national interest.
Further, the governments in such countries may require governmental or quasi-governmental authorities to act as
custodian of a Fund's assets invested in such countries and these authorities may not qualify as a foreign
custodian under the 1940 Act and exemptive relief from such Act may be required. All of these considerations are
among the factors which could cause significant risks and uncertainties to investment in Eastern Europe and
Russia.
Latin America. The political history of certain Latin American countries has been
characterized by political uncertainty, intervention by the military in civilian and economic spheres, and
political corruption. Such developments, if they were to reoccur, could reverse favorable trends toward market
and economic reform, privatization and removal of trade barriers and result in significant disruption in
securities markets. Persistent levels of inflation or in some cases, hyperinflation, have led to high interest
rates, extreme measures by governments to keep inflation in check and a generally debilitating effect on economic
growth. Although inflation in many countries has lessened, there is no guarantee it will remain at lower
levels. In addition, of developing countries, a number of Latin American countries are also among the largest
debtors. There have been moratoria on, and reschedulings of, repayment with respect to these debts. Such events
can restrict the flexibility of these debtor nations in the international markets and result in the imposition of
onerous conditions on their economies.
Certain Latin American countries may have managed currencies which are maintained at artificial
levels to the U.S. dollar rather than at levels determined by the market. This type of system can lead to sudden
and large adjustments in the currency which, in turn, can have a disruptive and negative effect on foreign
investors. Certain Latin American countries also may restrict the free conversion of their currency into foreign
currencies, including the U.S. dollar. There is no significant foreign exchange market for certain currencies
and it would, as a result, be difficult for a Fund to engage in foreign currency transactions designed to protect
the value of the Fund's interests in securities denominated in such currencies.
Illiquid and Restricted Securities:
Subject to limitations discussed in the Company's Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment
Methods," the Funds generally may invest in illiquid securities. Illiquid securities include securities subject
to contractual or legal restrictions on resale (e.g., because they have not been registered under the Securities
Act of 1933, as amended (the "Securities Act")) and securities that are otherwise not readily marketable (e.g.,
because trading in the security is suspended or because market makers do not exist or will not entertain bids or
offers). Securities that have not been registered under the Securities Act are referred to as private placements
or restricted securities and are purchased directly from the issuer or in the secondary market. Foreign
securities that are freely tradable in their principal markets are not considered to be illiquid.
Restricted and other illiquid securities may be subject to the potential for delays on resale and
uncertainty in valuation. A Fund might be unable to dispose of illiquid securities promptly or at reasonable
prices and might thereby experience difficulty in satisfying redemption requests from shareholders. A Fund might
have to register restricted securities in order to dispose of them, resulting in additional expense and delay.
Adverse market conditions could impede such a public offering of securities.
A large institutional market exists for certain securities that are not registered under the Securities
Act, including foreign securities. The fact that there are contractual or legal restrictions on resale to the
general public or to certain institutions may not be indicative of the liquidity of such investments.
Rule 144A under the Securities Act allows such a broader institutional trading market for securities
otherwise subject to restrictions on resale to the general public. Rule 144A establishes a "safe harbor" from
the registration requirements of the Securities Act for resales of certain securities to qualified institutional
buyers. Rule 144A has produced enhanced liquidity for many restricted securities, and market liquidity for such
securities may continue to expand as a result of this regulation and the consequent existence of the PORTAL
system, which is an automated system for the trading, clearance and settlement of unregistered securities of
domestic and foreign issuers sponsored by the National Association of Securities Dealers, Inc.
Under guidelines adopted by the Company's Board of Directors, a Fund's Sub-Advisor may determine that
particular Rule 144A securities, and commercial paper issued in reliance on the private placement exemption from
registration afforded by Section 4(2) of the Securities Act, are liquid even though they are not registered. A
determination of whether such a security is liquid or not is a question of fact. In making this determination,
the Sub-Advisor will consider, as it deems appropriate under the circumstances and among other factors: (1) the
frequency of trades and quotes for the security; (2) the number of dealers willing to purchase or sell the
security; (3) the number of other potential purchasers of the security; (4) dealer undertakings to make a market
in the security; (5) the nature of the security (e.g., debt or equity, date of maturity, terms of dividend or
interest payments, and other material terms) and the nature of the marketplace trades (e.g., the time needed to
dispose of the security, the method of soliciting offers, and the mechanics of transfer); and (6) the rating of
the security and the financial condition and prospects of the issuer. In the case of commercial paper, the
Sub-advisor will also determine that the paper (1) is not traded flat or in default as to principal and interest,
and (2) is rated in one of the two highest rating categories by at least two Nationally Recognized Statistical
Rating Organizations ("NRSROs") or, if only one NRSRO rates the security, by that NRSRO, or, if the security is
unrated, the Sub-advisor determines that it is of equivalent quality.
Rule 144A securities and Section 4(2) commercial paper that have been deemed liquid as described above
will continue to be monitored by the Sub-advisor to determine if the security is no longer liquid as the result
of changed conditions. Investing in Rule 144A securities or Section 4(2) commercial paper could have the effect
of increasing the amount of a Fund's assets invested in illiquid securities if institutional buyers are unwilling
to purchase such securities.
Repurchase Agreements:
As stated in the Prospectus under "Certain Risk Factors and Investment Methods," certain of the Funds
may enter into repurchase agreements. In a repurchase agreement, an investor (such as the Fund) purchases a
security (known as the "underlying security") from a securities dealer or bank. Any such dealer or bank must be
deemed creditworthy by the Sub-advisor. At that time, the bank or securities dealer agrees to repurchase the
underlying security at a mutually agreed upon price on a designated future date. The repurchase price may be
higher than the purchase price, the difference being income to the Fund, or the purchase and repurchase prices
may be the same, with interest at an agreed upon rate due to the Fund on repurchase. In either case, the income
to the Fund generally will be unrelated to the interest rate on the underlying securities. Repurchase agreements
must be "fully collateralized," in that the market value of the underlying securities (including accrued
interest) must at all times be equal to or greater than the repurchase price. Therefore, a repurchase agreement
can be considered a loan collateralized by the underlying securities.
Repurchase agreements are generally for a short period of time, often less than a week, and will
generally be used by a Fund to invest excess cash or as part of a temporary defensive strategy. Repurchase
agreements that do not provide for payment within seven days will be treated as illiquid securities. In the
event of a bankruptcy or other default by the seller of a repurchase agreement, the Fund could experience both
delays in liquidating the underlying security and losses. These losses could result from: (a) possible decline
in the value of the underlying security while the Fund is seeking to enforce its rights under the repurchase
agreement; (b) possible reduced levels of income or lack of access to income during this period; and (c) expenses
of enforcing its rights.
Securities Lending:
The Company has made arrangements for the Funds to lend securities. While a Fund may earn additional
income from lending securities, such activity is incidental to the investment objective of the Fund. In addition
to the compensation payable by borrowers under securities loans, a Fund would also earn income from the
investment of cash collateral for such loans. Any cash collateral received by a Fund in connection with such
loans normally will be invested in high-quality money market securities. However, any losses resulting from the
investment of cash collateral would be borne by the lending Fund. There is no assurance that collateral for
loaned securities will be sufficient to provide for recovery of interest, dividends, or other distributions paid
in respect of loaned securities and not received by a Fund or to pay all expenses incurred by a Fund in arranging
the loans or in exercising rights in the collateral in the event that loaned securities are not returned.
ADDITIONAL PERFORMANCE INFORMATION
From time to time, a Fund's yield and total return may be included in advertisements, sales literature,
or shareholder reports. In addition, the Company may advertise the effective yield of the ASAF JPM Money Market
Fund. All figures are based upon historical earnings and are not intended to indicate future performance.
ASAF JPM MONEY MARKET FUND (the "Money Market Fund"):
In accordance with regulations prescribed by the SEC, the Company is required to compute the Money
Market Fund's current annualized yield for a seven-day period in accordance with a specified formula, which does
not take into consideration any realized or unrealized gains or losses on its portfolio securities. This current
annualized yield is computed by determining the net change (exclusive of realized gains and losses on the sale of
securities and unrealized appreciation and depreciation) in the value of a hypothetical account having a balance
of one share of the Money Market Fund at the beginning of such seven-day period, dividing such net change in
account value by the value of the account at the beginning of the period to determine the base period return and
annualizing this quotient on a 365-day basis.
The SEC also permits the Company to disclose the effective yield of the Money Market Fund for the same
seven-day period, which is the Fund's yield determined on a compounded basis. The effective yield is calculated
by compounding the unannualized base period return by adding one to the base period return, raising the sum to a
power equal to 365 divided by 7, and subtracting one from the result. The effective yield will be slightly
higher than the yield because of the compounding effect of this assumed reinvestment.
The yield on amounts held in the Money Market Fund normally will fluctuate on a daily basis. Therefore,
the disclosed yield for any given past period is not an indication or representation of future yields or rates of
return. The Money Market Fund's actual yield is affected by changes in interest rates on money market
securities, the average portfolio maturity of the corresponding Portfolio in which the Money Market Fund invests,
the types and quality of portfolio securities held by such Portfolio, and the Fund's and Portfolio's operating
expenses.
The current yield and effective yield calculations for each class of shares of the ASAF JPM Money Market
Fund are shown below for the seven day period ended April 30, 2000:
Class A Class B Class C Class X
Current Yield 4.16% 3.66% 3.66% 3.66%
Effective Yield 4.24% 3.72% 3.73% 3.73%
ALL OTHER FUNDS:
Standardized Average Annual Total Return Quotations. "Total return" is one of the primary methods used
to measure performance and represents the percentage change in value of a class of a Fund, or of a hypothetical
investment in a class of a Fund, over any period up to the lifetime of the class. Average annual total return
quotations for Class A, B, C and X shares are computed by finding the average annual compounded rates of return
that would cause a hypothetical investment made on the first day of a designated period to equal the ending
redeemable value of such hypothetical investment on the last day of the designated period in accordance with the
following formula:
P(1+T)n = ERV
Where: P = a hypothetical initial payment of $1,000
T = average annual total return
n = number of years
ERV = ending redeemable value of the hypothetical $1,000 initial payment made at the
beginning of the designated period (or fractional portion thereof)
The computation above assumes that the maximum sales charge applicable to a class of Fund shares is
deducted from the initial $1,000 payment, and that all dividends and distributions made by a Fund are reinvested
at net asset value ("NAV") during the designated period. The average annual total return quotation is determined
to the nearest 1/100 of 1%.
Total return percentages for periods longer than one year will usually be accompanied by total return
percentages for each year within the period and/or by the average annual compounded total return for the period.
The income and capital components of a given return may be separated and portrayed in a variety of ways in order
to illustrate their relative significance. Performance may also be portrayed in terms of cash or investment
values, without percentages. Past performance cannot guarantee any particular future result. In determining the
average annual total return (calculated as provided above), recurring fees, if any, that are charged to all
shareholder accounts are taken into consideration. For any account fees that vary with the size of the account,
the account fee used for purposes of the above computation is assumed to be the fee that would be charged to the
mean account size of a class of the Fund.
In addition, with respect to the Class X shares, a standardized return will reflect the impact of the
2.5% bonus shares. The impact of the bonus shares on total return is particularly pronounced for shorter periods
for which total return is measured, such as one and three years. You should take this into consideration in any
comparison of total return between the Funds and other mutual funds. For a discussion of the Class X bonus
shares, see the Company's Prospectus under "How to Buy Shares."
The total return of each class of shares of each Fund that had commenced operations prior to October 31,
2000, other than the JPM Money Market Fund, computed as of October 31, 2000, is shown below:
Total Return
-------------
Class A Class B Class C Class X
ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund1
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF AIM International Equity Fund4
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund2
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF American Century International Growth Fund1*
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund1**
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund5
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund1***
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund6
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund3
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund3
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund6
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund6
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund6
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund6
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Alliance Growth Fund2*+
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Marsico Growth Fund3
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Janus Capital Growth Fund1
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund4
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund2*++
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund4
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF INVESCO Equity Income Fund1
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund1
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund1
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
ASAF PIMCO Total Return Bond Fund1
One Year insert% insert% insert% insert%
Since Inception insert% insert% insert% insert%
1. Commenced operations July 28, 1997.
2. Commenced operations January 2, 1998.
3. Commenced operations August 19, 1998.
4. Commenced operations November 1, 1999.
5. Commenced operations March 1, 2000.
6. Commenced operations September 11, 2000.
* Prior to May 1, 2000, Rowe Price-Fleming International, Inc. served as Sub-advisor to the Fund. The
performance information provided in the above chart reflects that of the Fund for periods during which the Fund
was sub-advised by the prior Sub-advisor.
** Prior to January 1, 1999, Founders Asset Management LLC served as Sub-advisor to the Fund. The performance
information provided in the above chart reflects that of the Fund for periods during part of which the Fund was
sub-advised by the prior Sub-advisor.
*** Prior to September 11, 2000, T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc. served as Sub-advisor to the Fund. The
performance information provided in the above chart reflects that of the Fund for periods during part of which
the Fund was sub-advised by the prior Sub-advisor.
*+ Prior to December 31, 1998, Robertson, Stephens & Company Investment Management L.P. served as Sub-advisor to
the Fund. From December 31, 1998 to April 30, 2000, OppenheimerFunds, Inc. served as Sub-advisor to the Fund.
The performance information provided in the above chart reflects that of the Fund for periods during which the
Fund was sub-advised by the prior Sub-advisors.
*++ Prior to May 1, 2000, Lord, Abbett & Co. served as Sub-advisor to the Fund. The performance information
provided in the above chart reflects that of the Fund for periods during which the Fund was sub-advised by the
prior Sub-advisor.
Standardized Yield Quotations. The yield of a class of Fund shares is computed by dividing the class's
net investment income per share during a base period of 30 days, or one month, by the maximum offering price per
share of the class on the last day of such base period in accordance with the following formula:
YIELD = 2 [ (a - b + 1)6 - 1 ]
-----
cd
Where: a = net investment income earned during the period attributable to the subject class
b = net expenses accrued for the period attributable to the subject class
c = the average daily number of shares of the subject class outstanding during the
period that were entitled to receive dividends
d = the maximum offering price per share of the subject class
Net investment income will be determined in accordance with rules established by the SEC. The price per
share of Class A shares, other than shares of the ASAF JPM Money Market Fund, will include the maximum sales
charge imposed on purchases of Class A shares which decreases with the amount of shares purchased.
The yield for each class of shares of the ASAF Federated High Yield Fund and ASAF PIMCO Total Return
Bond Fund for the 30 day period ended April 30, 2000 is shown below:
Class A Class B Class C Class X
ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund 10.38% 10.34% 10.36% 10.35%
ASAF PIMCO Total Return Bond Fund 5.57% 5.31% 5.32% 5.31%
Non-Standardized Performance. In order to more completely represent a Fund's performance or more
accurately compare such performance to other measures of investment return, a Fund also may include in
advertisements, sales literature and shareholder reports other total return performance data ("Non-Standardized
Return"). Non-Standardized Return may be quoted for the same or different periods as those for which
standardized return is quoted; it may consist of an aggregate or average annual percentage rate of return, actual
year-by-year rates or any combination thereof. Non-Standardized Return may or may not take sales charges into
account; performance data calculated without taking the effect of sales charges into account will be higher than
data including the effect of such charges. Non-standardized performance will be advertised only if the standard
performance data for the same period, as well as for the required periods, is also presented.
Each Fund may also publish its distribution rate and/or its effective distribution rate. A Fund's
distribution rate is computed by dividing the most recent monthly distribution per share annualized, by the
current NAV per share. A Fund's effective distribution rate is computed by dividing the distribution rate by the
ratio used to annualize the most recent monthly distribution and reinvesting the resulting amount for a full year
on the basis of such ratio. The effective distribution rate will be higher than the distribution rate because of
the compounding effect of the assumed reinvestment. Unlike a Fund's yield, which is computed from the yields to
maturity of all debt obligations held by the Fund, the distribution rate is based on a Fund's last monthly
distribution. A Fund's monthly distribution tends to be relatively stable and may be more or less than the
amount of net investment income and short-term capital gain actually earned by the Fund during the month (see the
Company's Prospectus under "Dividends, Capital Gains and Taxes").
Other data that may be advertised or published about each Fund include the average portfolio quality,
the average portfolio maturity and the average portfolio duration.
Comparative Information. From time to time in advertisements or sales material, the Fund's performance
ratings or other information as published by recognized mutual fund statistical or rating services, such as
Lipper Analytical Services, Inc. or Morningstar, or by publications of general interest, such as Forbes or Money,
------ -----
may be discussed. The performance of the Funds may also be compared to that of other selected mutual funds,
mutual fund averages or recognized stock market indicators. Such performance ratings or comparisons may be made
with funds that may have different investment restrictions, objectives, policies or techniques than the Funds and
such other funds or market indicators may be comprised of securities that differ significantly from the Funds'
investments. Descriptions of some of the indices which may be used are listed below:
o The Standard & Poor's 500 Composite Stock Price Index is a well-diversified list of 500 large
capitalization companies representing the U.S. Stock Market.
o The Standard and Poor's Small Cap 600 index is designed to represent price movements in the small
cap U.S. equity market. It contains companies chosen by the Standard & Poor's Index Committee for their size,
industry characteristics, and liquidity. None of the companies in the S&P 600 overlap with the S&P 500 or the
S&P 400 (MidCap Index). The S&P 600 is weighted by market capitalization.
o The NASDAQ Composite OTC Price Index is a market value-weighted and unmanaged index showing the
changes in the aggregate market value of approximately 3,500 stocks.
o The Lehman Government Bond Index is a measure of the market value of all public obligations of the
U.S. Treasury; all publicly issued debt of all agencies of the U.S. Government and all quasi-federal
corporations; and all corporate debt guaranteed by the U.S. Government. Mortgage backed securities, bonds and
foreign targeted issues are not included in the Lehman Government Index.
o The Lehman Government/Corporate Bond Index is a measure of the market value of approximately 5,300
bonds with a face value currently in excess of $1.3 trillion. To be included in the Lehman Government/Corporate
Index, an issue must have amounts outstanding in excess of $1 million, have at least one year to maturity and be
rated "Baa" or its equivalent or higher ("investment grade") by a nationally recognized rating agency.
o The Russell 2000 Index represents the bottom two thirds of the largest 3000 publicly traded
companies domiciled in the U.S. Russell uses total market capitalization to determine the companies that are
included in the Index. Only common stocks are included in the Index.
o The Russell 2500 Index is a market value-weighted, unmanaged index showing total return (i.e.,
principal changes with income) in the aggregate market value of 2,500 stocks of publicly traded companies
domiciled in the United States. The Index includes stocks traded on the New York Stock Exchange and the American
Stock Exchange as well as in the over-the-counter market.
o The Morgan Stanley Capital International EAFE Index (the "EAFE Index") is an unmanaged index, which
includes over 1,000 companies representing the stock markets of Europe, Australia, New Zealand and the Far East.
The EAFE Index is typically shown weighted by the market capitalization. However, EAFE is also available
weighted by Gross Domestic Product ("GDP"). These weights are modified on July 1st of each year to reflect the
prior year's GDP.
o The Lehman Brothers High Yield BB Index is a measure of the market value of public debt issues with
a minimum par value of $100 million and rated Ba1-Ba3 by Moody's. All bonds within the index are U.S. dollar
denominated, non-convertible and have at least one year remaining to maturity.
In addition, the total return or yield of the Funds may be compared to the yield on U.S. Treasury obligations and
to the percentage change in the Consumer Price Index.
Each Fund's investment performance may be advertised in various financial publications, newspapers,
magazines, including: Across the Board, Advertising Age, Adviser's Magazine, Adweek, Agent, American Banker,
American Agent and Broker, Associated Press, Barron's, Best's Review, Bloomberg, Broker World, Business Daily,
Business Insurance, Business Marketing, Business Month, Business News Features, Business Week, Business Wire,
California Broker, Changing Times, Consumer Reports, Consumer Digest, Crain's, Dow Jones News Service, Economist,
Entrepreneur, Entrepreneurial Woman, Financial Planning, Financial Services Week, Financial Times, Financial
World, Forbes, Fortune, Hartford Courant, Inc., Independent Business, Institutional Investor, Insurance Forum,
Insurance Advocate Independent, Insurance Review Investor's, Insurance Times, Insurance Week, Insurance Product
News, Insurance Sales, Investment Dealers Digest, Investment Advisor, Journal of Commerce, Journal of
Accountancy, Journal of the American Society of CLU & ChFC, Kiplinger's Personal Finance, Knight-Ridder, Life
Association News, Life Insurance Selling, Life Times, LIMRA's MarketFacts, Lipper Analytical Services, Inc.,
MarketFacts, Medical Economics, Money, Morningstar, Inc., Nation's Business, National Underwriter, New Choices,
New England Business, New York Times, Pension World, Pensions & Investments, Professional Insurance Agents,
Professional Agent, Registered Representative, Reuter's, Rough Notes, Round the Table, Service, Success, The
Standard, The Boston Globe, The Washington Post, Tillinghast, Time, U.S. News & World Report, U.S. Banker, United
Press International, USA Today, Value Line, The Wall Street Journal, Wiesenberger Investment and Working Woman.
From time to time the Company may publish the sales of shares of one or more of the Funds on a gross or
net basis and for various periods of time, and compare such sales with sales similarly reported by other
investment companies.
MANAGEMENT OF THE COMPANY
The following table sets forth information concerning the officers and Directors of the Company,
including their addresses and principal business occupations for the last five years:
Name, Age and Address:(1) Position Held with the Company:(2) Principal Occupation:(3)`
--------------------- ------------------------------ --------------------
John Birch (50) Vice President Senior Vice President and Chief
Operating Officer:
American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated
December 1997 to present
Executive Vice President and
Chief Operating Officer:
International Fund Administration
Bermuda
August 1996 to October 1997
Senior Vice President and
Chief Administrative Officer:
Gabelli Funds, Inc.
Rye, New York
March 1995 to August 1996
Gordon C. Boronow (47) Vice President President & Chief Operating Officer:
American Skandia Life Assurance
Corporation
Jan R. Carendi (55)* President, Principal Executive Officer Deputy Chief Executive Officer:
and Director Skandia Insurance Company Ltd.
David E. A. Carson (66) Director Director
People's Bank People's Bank (January 2000 - present)
850 Main Street
Bridgeport, CT 06604 Chairman
People's Bank (January 1999-December
1999)
Chairman & Chief Executive Officer:
People's Bank (January 1998 to December
1998)
President, Chairman & Chief Executive
Officer:
People's Bank (1983 to January 1998)
Richard G. Davy, Jr. (52) Treasurer and Chief Financial and Vice President, Operations:
Accounting Officer American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated (January 1997 to present)
Controller:
American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated (September 1994 to January
1997)
Edward C. Macdonald (33) Secretary Senior Counsel, Securities, Counsel,
Securities, and Senior Associate
Counsel:
American Skandia, Incorporated (April
1999 to present)
Branch Chief, Senior Counsel and
Attorney:
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission
(October 1994 to April 1999)
Julian A. Lerner (76) Director Retired since 1995; Senior Vice
12850 Spurling Road President & Portfolio Manager of AIM
Suite 208 Charter Fund and AIM Summit Fund from
Dallas, TX 75230 1986 to 1995
Thomas M. Mazzaferro(47)* Director Executive Vice President and
Chief Financial Officer
American Skandia Life Assurance
Corporation
April 1988 to present
Thomas M. O'Brien (50) Director President & Chief Executive Officer
North Fork Bank Atlantic Bank (May 2000 to present)
275 Broad Hollow Road
Melville, NY 11747 Vice Chairman:
North Fork Bank (January 1997 to April
2000)
President & Chief Executive Officer:
North Side Savings Bank (December 1984
to December 1996)
John A. Pileski (61) Director Retired since June 2000
Tax Partner:
KPMG, LLP
757 Third Avenue
New York, NY 10017
(January 1995 to June 2000)
F. Don Schwartz (65) Director Management Consultant
6 Sugan Close Drive (April 1985 to present)
New Hope, PA 18938
* Indicates a Director of the Company who is an "interested person" within the meaning set forth in the 1940 Act.
(1) Unless otherwise indicated, the address of each officer and director listed above is One Corporate Drive,
Shelton, Connecticut 06484.
(2) All of the officers and Directors of the Company listed above serve in similar capacities for the Trust
and/or American Skandia Trust, both of which are also investment companies managed by the Investment Manager.
(3) Unless otherwise indicated, each officer and director listed above has held his principal occupation for at
least the last five years. In addition to the principal occupations noted above, the following officers and
Directors of the Company hold the following positions with American Skandia Life Assurance Corporation ("ASLAC"),
American Skandia Investment Services, Incorporated ("ASISI"), American Skandia Marketing, Incorporated ("ASM"),
American Skandia Information Services and Technology Corporation ("ASIST") or American Skandia, Incorporated
("ASI"): Mr. Boronow also serves as Executive Vice President, Chief Operating Officer and a Director of ASI, and
a Director of ASLAC, ASISI, ASM and ASIST; Mr. Carendi also serves as Chairman and a Director of ASI, and Chief
Executive Officer and a Director of ASLAC, ASISI and ASIST and a Director of ASM; Mssrs. Birch, Davy and also
serve as Directors of ASISI.
The Company's Articles of Incorporation provides that the Directors, officers and employees of the
Company may be indemnified by the Company to the fullest extent permitted by federal and state law, including
Maryland law. Neither the Articles of Incorporation nor the By-laws of the Company authorize the Company to
indemnify any director or officer against any liability to which he or she would otherwise be subject by reason
of or for willful misfeasance, bad faith, gross negligence or reckless disregard of such person's duties.
Under the Maryland General Corporation Law, a Director of the Company who is held liable for assenting
to a distribution made in violation of the Company's Articles of Incorporation is entitled to contribution from
each shareholder of the Company for the amount the shareholder accepted knowing the distribution was made in
violation of those provisions. Absent such knowledge, a shareholder will not be obligated to the Company or its
creditors in respect of shares held in the Company except to the extent of any unpaid portion of the subscription
price or purchase price for such shares.
The officers and Directors of the Company who are affiliates of the Investment Manager do not receive
compensation directly from the Company for serving in the capacities described above. Those officers and
Directors of the Company, however, who are affiliated with the Investment Manager may receive remuneration
indirectly from the Company for services provided in their respective capacities with the Investment Manager.
Each of the other Directors receives for his service on the Board of Directors an annual and "per-meeting" fee,
plus reimbursement for reasonable out-of-pocket expenses incurred in connection with attendance at Board
meetings. The following table sets forth information concerning the compensation paid by the Company to the
Directors in the fiscal year ended October 31, 2000. Neither the Company nor any investment company in the Fund
Complex offers any pension or retirement benefits to its directors or trustees.
Aggregate Compensation Total Compensation from the
Name of Director: from the Company: Company and Fund Complex:(1)
---------------- ---------------- ------------------------
Jan R. Carendi $ 0 $ 0
David E.A. Carson $insert $insert
Julian A. Lerner $insert $insert
Thomas M. Mazzaferro $ 0 $ 0
Thomas M. O'Brien $insert(2) $insert(2)
John A. Pileski $insert $insert
F. Don Schwartz $24,100 $81,300
(1) As of the date of this SAI, the "Fund Complex" consisted of the Company, the Trust and American Skandia
Trust. The amount indicated is the compensation paid to the Directors by the Fund Complex for the twelve month
period ending October 31, 2000.
(2) Mr. O'Brien deferred a portion of this compensation from the Company valued as of October 31, 2000 at
$insert and from the Fund Complex valued as of October 31, 2000 at $insert.
As of December 11, 2000, the Directors and officers of the Company owned, in the aggregate, less than 1% of each
class of the Company's shares.
Codes of Ethics. The Company, the Trust, the Investment Manager and the Distributor have adopted codes of ethics
under rule 17j-1 of the 1940 Act. While these codes contain provisions reasonably necessary to prevent personnel
subject to the codes from engaging in unlawful conduct, they do not prohibit investments in securities, including
securities that may be purchased or held by the Funds and Portfolios, by such personnel.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ON THE "MASTER FEEDER" FUND STRUCTURE
As previously discussed, certain Funds of the Company are organized under a "master feeder" structure.
The Trust's Agreement and Declaration of Trust provides that the Feeder Funds and any other entities permitted to
invest in a Portfolio of the Trust (e.g., other U.S. and foreign investment companies, and common and commingled
trust funds) will each be liable for all obligations of each such Portfolio in the event that the Trust fails to
satisfy such liabilities and obligations. However, the risk of an investor in a Portfolio (including a Feeder
Fund) incurring financial loss beyond the amount of its investment on account of such liability is limited to
circumstances in which the Portfolio had inadequate insurance and was unable to meet its obligations out of its
assets. Accordingly, the Trustees of the Trust believe that neither a Feeder Fund nor its shareholders will be
adversely affected by reason of the Fund investing in a corresponding Portfolio of the Trust.
The Directors of the Company and the Trustees of the Trust have oversight responsibility for the
operations of each Fund and Portfolio, respectively. As of the date of this Prospectus, each of the Directors of
the Company also serves as a Trustee of the Trust. The Directors of the Company and the Trustees of the Trust,
including a majority of the Directors and Trustees who are not "interested persons" (as defined in the 1940 Act)
of the Company or the Trust, respectively, have adopted written procedures designed to identify and reasonably
address any potential conflicts of interest which might arise as a result of an "overlap" of Directors and
Trustees, including, if necessary, the creation of a separate board of trustees of the Trust.
INVESTMENT ADVISORY & ADMINISTRATION SERVICES
THE INVESTMENT MANAGER:
American Skandia Investment Services, Incorporated ("ASISI," as previously defined) acts as investment
manager to each Non-Feeder Fund and Portfolio pursuant to separate investment management agreements with the
Company and the Trust, respectively (the "Management Agreements"). Unlike the Non-Feeder Funds, each of the
Feeder Funds invests all of its respective investable assets in a corresponding Portfolio of the Trust and thus
does not require an investment manager.
ASISI, a Connecticut corporation organized in 1991, is registered as an investment adviser with the SEC
and is a wholly-owned subsidiary of American Skandia, Incorporated, whose indirect parent is Skandia Insurance
Company Ltd. ("Skandia"). Skandia is a Swedish company that owns, directly or indirectly, a number of insurance
companies in many countries. The predecessor to Skandia commenced operations in 1855. In addition to serving as
investment manager to the Company and the Trust, ASISI currently serves as the investment manager to American
Skandia Trust, an open-end management investment company whose shares are made available to life insurance
companies writing variable annuity contracts and variable life insurance policies. Shares of American Skandia
Trust also may be offered directly to qualified pension and retirement plans. For a list of those officers and
Directors of the Company who also serve in similar capacities for the Investment Manager, see this SAI under
"Management of the Company."
The Management Agreements provide, in substance, that the Investment Manager will furnish each
Non-Feeder Fund and Portfolio with investment advice and investment management and administrative services
subject to the supervision of the Directors of the Company or the Trustees of the Trust, where applicable, and in
conformity with the stated investment objective, policies and limitations of the applicable Fund or Portfolio.
The Investment Manager is responsible for providing, at its expense, such personnel as is required by each
Non-Feeder Fund or Portfolio for the proper conduct of its affairs and may engage a sub-advisor to conduct the
investment program of the Fund or Portfolio pursuant to the Investment Manager's obligations under the Management
Agreements. The Investment Manager, not the Funds or Portfolios, is responsible for the expenses of conducting
the investment programs of the Funds and Portfolios.
The Management Agreements provide further that neither the Investment Manager nor its personnel shall be
liable for any act or omission in the course of, or connected with, rendering services under the agreements, or
for any losses that may be sustained in the purchase, holding or sale of any security on behalf of the Funds or
Portfolios, except for willful misfeasance, bad faith or gross negligence in the performance of its or their
duties or by reason of reckless disregard of its or their obligations and duties under the agreements. The
Management Agreements also permit the Investment Manager to render services to others.
Under the terms of the Management Agreements, each Non-Feeder Fund and Portfolio has agreed to pay ASISI
an investment management fee, which is accrued daily and paid monthly, equal on an annual basis to a stated
percentage of the respective Fund or Portfolio's average daily NAV. The Investment Manager, not any Fund or
Portfolio, is responsible for the payment of the sub-advisory fees to the Sub-advisors. For a discussion of the
fees payable to the Investment Manager and the Sub-advisors, as well as any applicable voluntary fee waiver
arrangements, see the Company's Prospectus under "Expense Information" and "Management of the Funds."
Investment Management Fees. ASISI receives a monthly fee from each Non-Feeder Fund and Portfolio for
the performance of its services. ASISI pays each Sub-advisor a portion of such fee for the performance of the
sub-advisory services at no additional cost to any Fund or Portfolio. Each Non-Feeder Fund and Portfolio's
investment management fee is accrued daily for the purposes of determining the offering and redemption price of
the Fund's shares. The fees payable to ASISI, based on a stated percentage of the Non-Feeder Fund or Portfolio's
average daily net assets, are as follows:
Fund/Portfolio: Annual Rate:
-------------- -----------
ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund: 1.10% of the first $100 million; plus 1.00
% of the amount over $100 million
ASAF AIM International Equity Fund: 1.10%
ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund: 1.10%
ASMT American Century International Growth Portfolio: 1.00%
ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund: 0.90%
ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund: 0.95%
ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund: 1.00%
ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund: 1.00%
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund: 0.90%
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund: 0.90%
ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund: 0.95%
ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund: 0.95%
ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund: 1.00%
ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund: Insert%
ASAF Rydex OTX Fund: 0.85%
ASAF Alliance Growth Fund: .90% of the first $1 billion;
plus .85% of the amount over $1 billion
ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund: 1.00%
ASMT Janus Capital Growth Portfolio: 1.00%
ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund Insert%
ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth + ValueFund: Insert%
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund: Insert%
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund: 0.80%
ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund: 1.00%
ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund: 1.00%
ASMT INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio: 0.75%
ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund: 0.90%
ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund: 0.70%
ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond Portfolio: 0.65%
ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio: 0.50%
Investment Management Fee Waivers. The Investment Manager may from time to time agree to voluntarily
waive or reduce its fees, while retaining their ability to be reimbursed for such fees prior to the end of each
fiscal year. Such voluntary fee waivers or reductions may be rescinded at any time and without notice to
investors.
The Investment Manager has voluntarily agreed to waive portions of its investment management fees equal
to .10% of the average daily net assets of the ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund and .20% of the average daily net
assets of the ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund.
The investment management fee paid for each of the past three fiscal years by each Fund and Portfolio
that was publicly offered prior to October 31, 2000 was as follows:
Year ended Year ended Year ended
----------- ----------- ----------
Name of Fund October 31, 1998 October 31, 1999 October 31, 2000
------------ ---------------- ---------------- ----------------
ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund $34,725 $103,320 $insert
ASAF AIM International Equity Fund $0 $0 $insert
ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund $146,239 $1,437,199 $insert
ASMT American Century International Growth Portfolio $94,058 $232,476 $insert
ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund $46,399 $562,158 $insert
ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund $0 $0 $insert
ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund $210,032 $554,991 $insert
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund $1,920 $227,545 $insert
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund $2,770 $187,273 $insert
ASAF Alliance Growth Fund $89,166 $368,003 $insert
ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund $43,773 $2,818,406 $insert
ASMT Janus Capital Growth Portfolio $578,304 $6,824,885 $insert
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund $0 $0 $insert
ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund $114,324 $808,859 $insert
ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund $0 $0 $insert
ASMT INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio $244,316 $990,476 $insert
ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund $81,420 $642,319 $insert
ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund $148,821 $627,368 $insert
ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond Portfolio $151,673 $762,481 $insert
ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio $83,674 $495,966 $insert
Fees for the Portfolios are based upon the total assets of each Portfolio, which include assets other
than those of the Feeder Funds. The Portfolios commenced operations in June 1997, while the ASAF Founders
International Small Capitalization Fund, ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund, ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund,
ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund, and ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund commenced operations on
July 28, 1997. The ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund, ASAF Alliance Growth Fund, and ASAF Alliance Growth and
Income Fund commenced operations on January 2, 1998. The ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund, ASAF
Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund, and ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund commenced operations on August 19,
1998. The ASAF AIM International Equity Fund, ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund, and ASAF MFS Growth
with Income Fund commenced operations on November 1, 1999. The ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund commences
operations on March The ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund, Alger All-Cap Growth Fund, ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value
Fund, ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund, ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund, commenced operations on September 11, 2000. The
ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund, ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund, ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth +
Value Fund and the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund had not commenced operations prior to March 1, 2001;
therefore, no fees were paid during the periods presented in the above table. As discussed in this SAI under
"Fund Expenses" and in the Company's Prospectus under "Expense Information," the Investment Manager has
voluntarily agreed to reimburse the other expenses of each Fund so that each Fund's total expenses do not exceed
specified levels. During the fiscal period, the amounts of these reimbursements exceeded the investment
management fees included in the above table.
Each Management Agreement will continue in effect from year to year, provided it is approved at least
annually by a vote of the majority of the Directors or Trustees, where applicable, who are not parties to the
agreement or interested persons of any such party, cast in person at a meeting specifically called for the
purpose of voting on such approval. Each Management Agreement may be terminated without penalty on 60 days'
written notice by vote of a majority of the Directors or Trustees, where applicable, or by the Investment
Manager, or by holders of a majority of the applicable Fund or Portfolio's outstanding shares, and will
automatically terminate in the event of its "assignment" (as that term is defined in the 1940 Act).
THE SUB-ADVISORS:
ASISI currently engages the following Sub-advisors to conduct the investment programs of each Non-Feeder
Fund and Portfolio pursuant to separate sub-advisory agreements with the Investment Manager (the "Sub-Advisory
Agreements"): (a) Founders Asset Management LLC for the ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund;
(b) A I M Capital Management, Inc. for the ASAF AIM International Equity Fund; (c) Janus Capital Corporation for
the ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund, the ASMT Janus Capital Growth Portfolio, the ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth
Fund and the ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund; (d) American Century Investment Management, Inc. (formerly known as,
"Investors Research Corporation") for the ASAF American Century International Growth Fund and the ASAF American
Century Strategic Balanced Fund; (d) Zurich Scudder Investments, Inc. (formerly known as, "Scudder Kemper
Investments, Inc." for the ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund; (e) GAMCO Investors, Inc. for the ASAF Gabelli
Small-Cap Value Fund and the ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund; (f) Neuberger Berman Management Inc. for the ASAF
Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund and the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund; (g) Fred Alger Management,
Inc. for the ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund; (h) INVESCO Funds Group, Inc. for the ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund,
ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund and the ASMT INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio; (i) Rydex Global Advisors for the
ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund; (j) Alliance Capital Management L.P. for the ASAF Alliance Growth Fund and the ASAF
Alliance Growth and Income Fund; (k) Marsico Capital Management, LLC for the ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund; T.
Rowe Price Associates, Inc. for the ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund; (l) Alliance Capital Management L.P. and
Sanford C. Bernstein & Co., LLC for the ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth+Value Fund; (m) Sanford C. Bernstein
& Co., LLC for the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund and the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund;
(n) Massachusetts Financial Services Company for the ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund; (o) Federated Investment
Counseling for the ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund; (p) Pacific Investment Management Company LLC for the
ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond Portfolio; (q) J.P. Morgan Investment Management Inc. for the ASMT JPM Money Market
Portfolio.
The Sub-Advisory Agreements provide that the Sub-advisors will formulate and implement a continuous
investment program for each Non-Feeder Fund or Portfolio in accordance with the Fund or Portfolio's investment
objective, policies and limitations and any investment guidelines established by the Investment Manager. Each
Sub-advisor will, subject to the supervision and control of the Investment Manager, determine in its discretion
which issuers and securities will be purchased, held, sold or exchanged by the Fund or Portfolio, and will place
orders with and give instructions to brokers and dealers to cause the execution of such transactions. The
Sub-advisors are required to furnish the Investment Manager with periodic reports concerning the transactions and
performance of the Fund or Portfolio. Each Sub-advisor is required to furnish at its own expense all investment
facilities necessary to perform its obligations under the Sub-Advisory Agreement. Nothing in the Sub-advisory
Agreements prevents the Investment Manager from engaging other sub-advisors to provide investment advice and
other services to a Fund or Portfolio, or from providing such services itself.
Corporate Structure. Several of the Sub-advisors are controlled by other parties as noted below:
Founders Asset Management LLC ("Founders") is a 90%-owned subsidiary of Mellon Bank, N.A., with the
remaining 10% held by certain Founders executives and portfolio managers. Mellon Bank, N.A. is a wholly owned
subsidiary of Mellon Financial Corporation, a publicly owned multibank holding company which provides a
comprehensive range of financial products and services in domestic and selected international markets.
A I M Capital Management, Inc. is a wholly-owned subsidiary of A I M Advisors, Inc. also a registered
investment adviser. A I M Advisors, Inc. is wholly-owned by A I M Management Group Inc., a holding company
engaged in the financial services business and an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of AMVESCAP PLC. AMVESCAP PLC
and its subsidiaries are an independent investment management group engaged in institutional investment
management and retail mutual fund businesses in the United States, Europe and the Pacific Region.
Stilwell Financial ("Stilwell") owns approximately 81.5% of the outstanding voting stock of Janus
Capital Corporation. Stilwell is a publicly traded holding company with principal operations in financial asset
management businesses. Thomas H. Bailey, President and Chairman of the Board of Janus Capital, owns
approximately 12% of its voting stock and, by agreement with Stilwell, selects a majority of Janus Capital's
Board subject to the approval of Stilwell, which approval can not be unreasonably withheld.
American Century Companies, Inc. is the parent of American Century Investment Management, Inc.
Zurich Insurance Company, a leading provider of insurance and financial services, owns approximately 70%
of Scudder Kemper, with the balance owned by Scudder Kemper's officers and employees.
All of the voting stock of Neuberger Berman Management Inc. is owned by Neuberger Berman Inc., a
publicly traded company listed on the NYSE.
GAMCO Investors, Inc. ("GAMCO") is a New York corporation organized in 1999 as successor to the
investment advisory business of a New York corporation of the same name that was organized in 1978. GAMCO is a
wholly-owned subsidiary of Gabelli Asset Management Inc. ("GAMI"), a publicly held company listed on the New York
Stock Exchange. Mr. Mario J. Gabelli may be deemed a "controlling person" of GAMCO on the basis of his
controlling interest in GAMI. GAMCO has several affiliates that also provide investment advisory services.
INVESCO is an indirect wholly owned subsidiary of AMVESCAP PLC, a publicly traded holding company.
As of October 2, 2000, Alliance Capital Management Holding L.P. ("Alliance Holding") owns approximately
30% of the outstanding units of limited partnership interest in Alliance Capital Management L.P. ("Alliance
Capital"). Equity interests in Alliance Holding are traded on the New York Stock Exchange ("NYSE") in the form
of units ("Alliance Holding Units"). Alliance Capital Management Corporation ("ACMC"), an indirect wholly-owned
subsidiary of AXA Financial, Inc. ("AXA Financial"), is the general partner of both Alliance Capital and Alliance
Holding. As of October 2, 2000, AXA Financial, together with ACMC and certain of its other wholly-owned
subsidiaries, beneficially owned approximately 2% of the outstanding Alliance Holding Units and 53% of the
outstanding units of limited partnership interest in Alliance Capital. AXA Financial is a Delaware corporation
whose shares are traded on the NYSE. As of September 30, 2000, AXA, a French insurance holding company, directly
and indirectly owned approximately 60.1% of the issued and outstanding shares of the common stock of AXA
Financial.
Bank of America N.A., a national bank subsidiary of Bank of America Corporation, indirectly owns 50% of
the voting control of Marsico Capital Management, LLC ("Marsico Capital"). Thomas F. Marsico and a company
controlled by Mr. Marsico own the remainder of Marsico Capital's voting interests. Bank of America N.A. has
agreed to purchase the remaining 50% of Marsico Capital that it does not currently own. The purchase is expected
to occur in January 2001.
Sanford C. Bernstein & Co., LLC is an indirect wholly owned subsidiary of Alliance.
Massachusetts Financial Services Company is a subsidiary of Sun Life of Canada (US) Financial Services
Holdings, Inc. whose ultimate parent is Sun Life Assurance Co. of Canada.
Federated Investment Counseling is a wholly owned subsidiary of Federated Investors.
Pacific Investment Management Company LLC ("PIMCO") is a subsidiary general partnership of PIMCO
Advisors L.P. ("PIMCO Advisors"). Allianz AG ("Allianz") is the majority owner of PIMCO Advisors and its
subsidiaries, including PIMCO. Allianz is a European-based, multinational insurance and financial services
holding company. Pacific Life Insurance Company holds an approximately 30% interest in PIMCO Advisors.
J.P. Morgan Investment Management Inc. is a wholly owned subsidiary of J.P. Morgan & Co. Incorporated, a
bank holding company organized under the laws of Delaware.
Sub-Advisory Fees. ASISI pays each Sub-advisor on a monthly basis for the performance of sub-advisory
services. The fee payable to the Sub-advisors with respect to each Non-Feeder Fund and Portfolio may differ,
reflecting, among other things, the investment objective, policies and limitations of each Fund or Portfolio and
the nature of each Sub-advisory Agreement. Each Sub-advisor's fee is accrued daily for purposes of determining
the amount payable by the Investment Manager to the Sub-advisor. The fees payable to the Sub-advisors, based on
a stated percentage of the Non-Feeder Fund or Portfolio's average daily net assets, are as follows:
Founders Asset Management LLC for the ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund: An annual
rate of .60% of the portion of the average daily net assets of the Fund not in excess of $100 million; plus .50%
of the portion over $100 million.
A I M Capital Management, Inc. for the ASAF AIM International Equity Fund: An annual rate equal to the
following percentages of the combined average daily net assets of the Fund and the series of American Skandia
Trust that is managed by A I M Capital Management Inc. and identified by the Sub-advisor and ASISI as being
similar to the Fund: .55% of the portion of the combined average daily net assets not in excess of $75 million;
plus .45% of the portion in excess of $75 million.
Janus Capital Corporation for the ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund: An annual rate of .60% of the
portion of the average daily net assets of the Fund not in excess of $100 million; when the average daily net
assets of the Fund equal or exceed $100 million, the annual rate will be .50% of the entire average daily net
assets of the Fund.
American Century Investment Management, Inc. for the ASMT American Century International Growth
Portfolio: Because of the large amount of assets being sub-advised for the Investment Manager by American Century
Investment Management, Inc., the Investment Manager was able to negotiate a reduction to the Sub-advisor's
standard fee schedule. This reduced fee schedule is an annual rate equal to .45% of the combined average daily
net assets of the Fund and certain series of American Skandia Trust that are managed by the Sub-advisor and
identified by the Sub-advisor and ASISI as being similar to the Fund. Prior to May 1, 2000, the Investment
Manager had engaged Rowe Price-Fleming International, Inc. as Sub-advisor for the Portfolio (formerly the ASMT T.
Rowe Price International Equity Portfolio), for a total Sub-advisory fee of .75% of the portion of the average
daily net assets of the Portfolio not in excess of $20 million; plus .60% of the portion of the net assets over
$20 million but not in excess of $50 million; plus .50% of the portion of the net assets over $50 million.
Janus Capital Corporation for the ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund: An annual rate of .50% of the
portion of the average daily net assets of the Fund not in excess of $100 million; plus .45% of the portion over
$100 million but not in excess of $500 million; plus .40% of the portion over $500 million but not in excess of
$1 billion; plus .35% of the portion in excess of $1 billion.
Zurich Scudder Investments, Inc. for the ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund: An annual rate of .50% of
the portion of the average daily net assets of the Fund not in excess of $100 million; plus .45% of the portion
over $100 million but not in excess of $400 million; plus .40% of the portion over $400 million but not in excess
of $900 million; plus .35% of the portion in excess of $900 million.
GAMCO Investors, Inc. for the ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund: An annual rate equal to the following
percentages of the combined average daily net assets of the Fund and the series of American Skandia Trust that is
managed by the Sub-Advisor and identified by the Sub-advisor and the Investment Manager as being similar to the
Fund: .40% of the portion of the combined average daily net assets not in excess of $1 billion; plus .30% of the
portion in excess of $1 billion.
Janus Capital Corporation for the ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund: An annual rate equal to the following
percentages of the combined average daily net assets of the Fund and the series of American Skandia Trust that is
managed by the Sub-Advisor and identified by the Sub-advisor and the Investment Manager as being similar to the
Fund: .55% of the portion of the average daily net assets of the Fund not in excess of $100 million; plus .50% of
the portion of the net assets over $100 million but not in excess of $500 million; plus .45% of the portion of
the net assets over $500 million but not in excess of $2 billion; plus .40% of the portion of the net assets over
$2 billion but not in excess of $5 billion; plus .375% of the portion of the net assets over $5 billion but not
in excess of $10 billion; plus .35% of the portion of the net assets over $10 billion.
Neuberger Berman Management Inc. for the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund: An annual rate of
.40% of the average daily net assets of the Fund.
Neuberger Berman Management Inc. for the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund: An annual rate of
.40% of the average daily net assets of the Fund.
Fred Alger Management, Inc. for the ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund: An annual rate equal to the
following percentages of the combined average daily net assets of the Fund and all series of American Skandia
Trust that are managed by the Sub-Advisor: .40% of the portion of the combined average daily net assets not in
excess of $500 million; plus .35% of the portion over $500 million but not in excess of $1 billion; plus .30% of
the portion over $1 billion but not in excess of $1.5 billion; plus .25% of the portion in excess of $1.5
billion.
GAMCO Investors, Inc. for the ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund: An annual rate equal to the following
percentages of the combined average daily net assets of the Fund and the series of American Skandia Trust that is
managed by the Sub-Advisor and identified by the Sub-advisor and the Investment Manager as being similar to the
Fund: .50% of the combined average daily net assets not in excess of $500 million; plus .40% of the portion over
$500 million.
INVESCO Funds Group, Inc. for the ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund: An annual rate equal to the following
percentages of the combined average daily net assets of the Fund and the ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund .55%
of the of the portion of the average daily net assets not in excess of $100 million; plus .45% of the portion of
the average daily net assets over $100 million but not in excess of $200 million; plus .425% of the portion of
the average daily net assets over $200 million but not in excess of $400 million; plus .40% of the portion of the
average daily net assets over $400 million but not in excess of $900 million; plus .35% of the average daily net
assets in excess of $900 million.
INVESCO Funds Group, Inc. for the ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund: An annual rate equal to the
following percentages of the combined average daily net assets of the Fund and the ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund
.55% of the of the portion of the average daily net assets not in excess of $100 million; plus .45% of the
portion of the average daily net assets over $100 million but not in excess of $200 million; plus .425% of the
portion of the average daily net assets over $200 million but not in excess of $400 million; plus .40% of the
portion of the average daily net assets over $400 million but not in excess of $900 million; plus .35% of the
average daily net assets in excess of $900 million.
Rydex Global Services for the ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund: An annual rate of .35% of the portion of the
average daily net assets of the Fund not in excess of $400 million; plus .25% of the portion over $400 million.
Alliance Capital Management L.P. for the ASAF Alliance Growth Portfolio: An annual rate equal to .40% of
the combined average daily net assets of the Fund and the series of American Skandia Trust that is managed by the
Sub-Adviser and identified by the Sub-advisor and the Investment Manager as being similar to the Fund. Between
December 31, 1998 and April 30, 2000, the Investment Manager had engaged OppenheimerFunds, Inc. as Sub-advisor
for the Fund at a total Sub-advisory fee of .35% of the portion of the average daily net assets of the Fund not
in excess of $500 million; plus .30% of the portion over $500 million but not in excess of $1 billion; plus .25%
of the portion in excess of $1 billion. Prior to January 1, 1999, the Investment Manager had engaged Robertson,
Stephens & Company Investment Management, L.P. as Sub-advisor for the Fund, at a total Sub-advisory fee of .60%
of the portion of the average daily net assets of the Fund not in excess of $200 million; plus .50% of the
portion of the net assets over $200 million.
Marsico Capital Management, LLC for the ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund: An annual rate of .45% of the
average daily net assets of the Fund.
T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc. for the ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund: An annual rate equal to
.45% of the of the portion of the Fund's average daily net assets not in excess of $100 million. Once the
average daily net assets of the Fund exceed $100 million, the amount equals .40% on average daily net assets not
in excess of $250 million; plus .35% of the portion of the Fund's average daily net assets in excess of $250
million.
Alliance Capital Management L.P. and Sanford C. Bernstein & Co., LLC for the ASAF Alliance/Bernstein
50/50 Growth + Value Fund: An annual rate of .40% of the average daily net assets of the Fund.
Sanford C. Bernstein & Co., LLC for the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund: An annual rate of .25%
of the of the portion of the Fund's average daily net assets not in excess of $500 million; plus .20% of the
portion over $500 million.
Sanford C. Bernstein & Co., LLC for the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund: An annual rate
equal to the following percentages of the combined average daily net assets of the Fund and the series of
American Skandia Trust that is managed by the Sub-Advisor and identified by the Sub-advisor and the Investment
Manager as being similar to the Fund: .1533% of the portion of the combined average daily net assets not in
excess of $300 million; plus .10% of the portion of the net assets over $300 million. Notwithstanding the
foregoing, the following annual rate will apply for each day that the combined average daily net assets are not
in excess of $300 million: .40% of the first $10 million of combined average daily net assets; plus .30% on the
next $40 million of combined average daily net assets; plus .20% on the next $50 million of combined average
daily net assets; plus .10% on the next $200 million of combined average daily net assets. Prior to May 1, 2000,
the Investment Manager had engaged Bankers Trust Company as Sub-advisor for the Fund at a total Sub-advisory fee
equal to the following percentages of the combined average daily net assets of the Fund and the series of
American Skandia Trust that was managed by Bankers Trust Company and identified by the Sub-Advisor and ASISI as
being similar to the Fund: .17% of the portion of the combined average daily net assets not in excess of $300
million; plus .13% of the portion over $300 million but not in excess of $1 billion; plus .08% of the portion in
excess of $1 billion.
Janus Capital Corporation for the ASMT Janus Capital Growth Portfolio: An annual rate of .45% of the
average daily net assets of the Portfolio.
Alliance Capital Management L.P. for the ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Portfolio: An annual rate
equal to the following percentages of the combined average daily net assets of the Fund and the series of
American Skandia Trust that is managed by the Sub-Adviser and identified by the Sub-advisor and the Investment
Manager as being similar to the Portfolio: .30% of the portion of the combined average daily net assets not in
excess of $1 billion; plus .25% of the portion over $1 billion but not in excess of $1.5 billion; plus .20% of
the portion in excess of $1.5 billion. Prior to May 1, 2000, the Investment Manager had engaged Lord, Abbett &
Co. as Sub-advisor for the Fund at a total Sub-advisory fee of .50% of the portion of the average daily net
assets of the Fund not in excess of $200 million; plus .40% of the portion over $200 million but not in excess of
$500 million; plus .375% of the portion over $500 million but not in excess of $700 million; plus .35% of the
portion over $700 million but not in excess of $900 million; when the average daily net assets of the Fund equal
or exceed $900 million, the annual rate will be .30% of the entire average daily net assets of the Fund.
Massachusetts Financial Services Company for the ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund: An annual rate equal
to the following percentages of the combined average daily net assets of the Fund and the domestic equity series
of American Skandia Trust that are managed by Massachusetts Financial Services Company: .40% of the portion of
the combined average daily net assets not in excess of $300 million; plus .375% of the portion over $300 million
but not in excess of $600 million; plus .35% of the portion over $600 million but not in excess of $900 million;
plus .325% of the portion over $900 million but not over $1.5 billion; plus .25% of the portion in excess of $1.5
billion.
INVESCO Funds Group, Inc. for the ASMT INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio: An annual rate of .35% of the
average daily net assets of the Portfolio.
American Century Investment Management, Inc. for the ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund:
Because of the large amount of assets being sub-advised for the Investment Manager by American Century Investment
Management, Inc., the Investment Manager was able to negotiate a reduction to the Sub-advisor's standard fee
schedule. This reduced fee schedule is an annual rate equal to the following percentages of the combined average
daily net assets of the Fund and the series of American Skandia Trust that is managed by the Sub-advisor and
identified by the Sub-advisor and Investment Manager as being similar to the Fund: .45% of the portion of the
average daily net assets of the Fund not in excess of $50 million; plus .40% of the portion over $50 million but
not in excess of $100 million; plus .35% of the portion over $100 million but not in excess of $500 million; plus
.30% of the portion over $500 million.
Federated Investment Counseling for the ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund: An annual rate of .25% of
the portion of the average daily net assets of the Fund not in excess of $200 million; plus .20% of the portion
over $200 million.
Pacific Investment Management Company LLC for the ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond Portfolio: An annual
rate of .25% of the average daily net assets of the Portfolio.
J.P. Morgan Investment Management Inc. for the ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio: An annual rate equal to
the following percentages of the combined average daily net assets of the Portfolio and the series of American
Skandia Trust that is managed by J.P. Morgan Investment Management, Inc. and identified by it and ASISI as being
similar to the Portfolio: .09% of the portion of the combined average daily net assets not in excess of $500
million; plus .06% of the portion over $500 million but not in excess of $1.5 billion; plus .04% of the portion
over $1.5 billion.
Sub-Advisory Fee Waivers. Certain Sub-advisors have voluntarily agreed to waive a portion of their sub-advisory
fees set forth above, as follows:
Commencing January 1, 1998, Janus Capital Corporation, the Sub-advisor for the ASAF Janus Overseas
Growth Fund, has voluntarily agreed to waive a portion of its sub-advisory fee equal to .10% of the portion of
the average daily net assets of the Fund not in excess of $100 million. When the average daily net assets of the
Fund equal or exceed $100 million, such voluntary fee waiver is no longer applicable, and the sub-advisory annual
fee rate of .50% of the entire average daily net assets of the Fund will be applied.
Commencing March 1, 1999, Janus Capital Corporation, the Sub-advisor for the ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth
Fund, has voluntarily agreed to waive a portion of its sub-advisory fee equal to .05% of the portion of the
average daily net assets over $400 million but not in excess of $500 million and .05% on assets over $900 million
but not in excess of $1 billion.
Commencing August 28, 2000, GAMCO Investors, Inc., the Sub-advisor for the ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value
Fund, has voluntarily agreed to waive a portion of its sub-advisory fee equal to the following percentages of the
combined average daily net assets of the Fund and the corresponding series of American Skandia Trust as
referenced above under "Sub-advisory Fees": .10% of the portion of the combined average daily net assets not in
excess of $500 million; .05% on combined assets over $500 million but not in excess of $1 billion; and .10% on
combined assets over $1 billion.
Commencing March 1, 2000, Janus Capital Corporation, the Sub-advisor for the ASMT Janus Capital Growth
Portfolio, has voluntarily agreed to the following revised fee schedule based on the combined average daily net
assets of the Portfolio and the AST JanCap Growth Portfolio of American Skandia Trust: .55% of the portion of the
combined average daily net assets not in excess of $100 million; plus .50% of the portion over $100 million but
not in excess of $500 million; plus .45% of the portion over $500 million but not in excess of $2 billion; plus
.40% of the portion over $2 billion but not in excess of $5 billion; plus .375% of the portion over $5 billion
but not in excess of $10 billion; plus .35% of the portion in excess of $10 billion.
Commencing May 1, 2000, INVESCO Funds Group, Inc., the Sub-advisor for the ASMT INVESCO Equity Income
Portfolio, has voluntarily agreed to waive a portion of its fee so that the following fee schedule based on the
combined average daily net assets of the Portfolio and the AST INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio is in effect: .35%
of the portion of the combined average daily net assets not in excess of $1 billion; plus .30% of the portion
over $1 billion.
The sub-advisory fees paid by the Investment Manager for each Fund and Portfolio for the fiscal years
ended October 31, 1998, October 31, 1999 and October 31, 2000, were as follows:
Name of Fund Year Ended Year Ended Period Ended
------------ ---------- ---------- ------------
October 31, 1998 October 31, 1999 October 31,2000
---------------- ---------------- ---------------
ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund $18,941 $56,357 $insert
ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund $66,472 $653,259 $insert
ASMT American Century International Growth Portfolio(1) $47,029 $108,959 $insert
ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund(2) $25,777 $307,453 $insert
ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund(3) $126,019 $332,996 $insert
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund $853 $101,131 $insert
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund $1,231 $83,233 $insert
ASAF Alliance Growth Fund(4) $40,530 $149,346 $insert
ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund $19,698 $1,268,283 $insert
ASMT Janus Capital Growth Portfolio $260,237 $3,071,198 $insert
ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund(5) $34,297 $242,657 $insert
ASMT INVESCO Equity Income Portfolio $114,014 $462,222 $insert
ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund $45,233 $343,430 $insert
ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund $53,150 $224,060 $insert
ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond Portfolio $58,336 $293,262 $insert
ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio $15,061 $89,274 $insert
(1) For fiscal years 1998 and 1999, the entire fee noted above was paid to Rowe Price-Fleming International,
Inc., the prior Sub-advisor for the Fund.
(2) For fiscal year 1998, the entire fee noted was paid to Founders Asset Management LLC, the prior Sub-advisor
for the Fund. For fiscal year 1999, $10,776 was paid to Founders and $296,677 was paid to Janus Capital
Corporation.
(3) For fiscal years 1998 and 1999, the entire fee noted above was paid to T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc., the
prior Sub-advisor for the Fund.
(4) For fiscal years 1997 and 1998, the entire fee noted was paid to Robertson, Stephens & Company Investment
Management, L.P. For fiscal year 1999, $19,192 was paid to Robertson Stephens and $130,154 was paid to
OppenheimerFunds, Inc.
(5) For fiscal year 1999, the entire fee noted above was paid to Lord, Abbett & Co., Inc., the prior Sub-advisor
for the Fund.
Fees for the Portfolios are based upon the total assets of each Portfolio, which include assets other
than those of the Feeder Funds. The Portfolios commenced operations in June 1997, while the ASAF Founders
International Small Capitalization Fund, ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund, ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund,
ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund, and ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund commenced operations on
July 28, 1997. The ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund, Alliance Growth Fund, and ASAF Alliance Growth and Income
Fund commenced operations on January 2, 1998. The ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund, ASAF Neuberger
Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund, and ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund commenced operations on August 19, 1998. The
ASAF AIM International Equity Fund, ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund, and ASAF MFS Growth Fund
commenced operations on November 1, 1999. The ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund commenced operations on March
1, 2000. The ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund, ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund, ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund,
ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund and ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund commenced operations on September 11, 2000. The
ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund, ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund, ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth +
Value Fund and the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund had not commenced operations prior to the date of this
SAI.
Each Sub-Advisory Agreement will continue in effect from year to year, provided it is approved at least
annually by a vote of the majority of the Directors or Trustees, where applicable, who are not parties to the
agreement or interested persons of any such party, cast in person at a meeting specifically called for the
purpose of voting on such approval. Each Sub-Advisory Agreement may be terminated without penalty at any time by
the Investment Manager or the Sub-advisor upon 60 days' written notice, and will automatically terminate in the
event of its "assignment" (as that term is defined in the 1940 Act) or upon termination of the Management
Agreement with respect to that particular Fund or Portfolio (provided that the Sub-advisor has received notice of
such termination).
THE ADMINISTRATOR:
PFPC Inc. (the "Administrator"), 103 Bellevue Parkway, Wilmington, Delaware 19809, a Delaware
corporation which is an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of PNC Financial Corp., serves as the administrator for
both the Company and the Trust. Pursuant to administration agreements between the Administrator and the Company
and the Trust, respectively (the "Administration Agreements"), the Administrator has agreed to provide certain
fund accounting and administrative services to the Company and the Trust, including, among other services,
accounting relating to the Company and the Trust and the investment transactions of the foregoing; computing
daily NAVs; monitoring the investments and income of the Company and the Trust for compliance with applicable tax
laws; preparing for execution and filing federal and state tax returns, and annual and semi-annual shareholder
reports; preparing monthly financial statements including a schedule of investments; assisting in the preparation
of registration statements and other filings related to the registration of shares; coordinating contractual
relationships and communications between the Investment Manager and the Company's and the Trust's custodians;
preparing and maintaining the Company's and the Trust's books of account, records of securities transactions, and
all other books and records in accordance with applicable laws, rules and regulations (including, but not limited
to, those records required to be kept pursuant to the 1940 Act); and performing such other duties related to the
administration of the Company and the Trust as may be agreed upon in writing by the parties to the respective
Administration Agreements. The administrator does not have any responsibility or authority for the management of
the assets of the Funds or Portfolios, the determination of their investment policies, or for any matter
pertaining to the distribution of securities issued by the Company.
Under the terms of the Administration Agreements, the Administrator shall be obligated to exercise care
and diligence in the performance of its duties, to act in good faith and to use its best efforts, within
reasonable limits, in performing services to be provided for under the agreements. The Administrator shall be
liable for any damages arising out of its failure to perform its duties under the Administration Agreements to
the extent such damages arise out of its willful misfeasance, bad faith, gross negligence or reckless disregard
of such duties. Any person, even though also an officer, director, partner, employee or agent of the
Administrator, who may be or become an officer, director, trustee, employee or agent of the Company or the Trust,
shall be deemed when rendering services to the Company or the Trust or acting on any business of the Company or
the Trust (other than services or business in connection with the Administrator's duties under the Administration
Agreements) to be rendering such services to or acting solely for the Company or the Trust and not as an officer,
director, partner, employee or agent or one under the control or direction of the Administrator even though paid
by them. The Administration Agreements shall continue until terminated by either party on 60 days' prior written
notice to the other party.
As compensation for the services and facilities provided by the Administrator to the Company, the
Company has agreed to pay the Administrator its "out-of-pocket" expenses, plus a monthly multi-class fee of
$3,000 per Fund, plus a monthly feeder fee of $2,000 per Feeder Fund, plus (except for the ASAF Sanford Bernstein
Managed Index 500 Fund) the greater of the following monthly fee based on the average daily net assets of the
Non-Feeder Funds -- 0.10% (first $200 million), 0.06% (next $200 million), 0.0275% (next $200 million), 0.02%
(next $400 million) and 0.01% (over $1 billion) -- or a minimum monthly fee of $6,250 per Non-Feeder Fund. The
fee for the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund is the greater of the following monthly fee based on
the average daily net assets of the Fund -- 0.05% (first $200 million), 0.03% (next $200 million), 0.0275% (next
$200 million), 0.02% (next $400 million) and 0.01% (over $1 billion) - or a minimum monthly fee of $6,250. The
Administrator has agreed to waive the above monthly multi-class fee, the monthly feeder fee and the minimum
monthly fee for the first two months of each Fund's operations, and thereafter will decrease such waiver by 10%
increments for each of the remaining ten months of the initial contract year.
In addition, as compensation for the services and facilities provided by the Administrator to the Trust,
the Trust has agreed to pay the Administrator its "out-of-pocket" expenses, plus the greater of the following
monthly fee based on the average daily net assets of the Portfolios -- 0.10% (first $200 million), 0.06% (next
$200 million), 0.0275% (next $200 million), 0.02% (next $400 million) and 0.01% ($1+ billion) -- or a minimum
monthly fee of $6,250 per Portfolio. The Administrator has agreed to waive the above minimum monthly fee for the
first two months of each Portfolio's operations, and thereafter will decrease such waiver by 10% increments for
each of the remaining ten months of the initial contract year.
For all of the Funds and Portfolios that commenced operations prior to November 1, 1999, monthly fees
payable to the Administrator have been frozen at the amounts paid for the month of December 1999. The fees
payable to the Administrator for those Funds that commenced operations on or after November 1, 1999 (the ASAF AIM
International Equity Fund, the ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF
Alger All-Cap Growth Fund, the ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund, the ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund, the ASAF Rydex
Managed OTC Fund, the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund, and the ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund)
are not subject to any freeze and will pay the Administrator under the fee schedule set forth above, giving
effect to the phased-in minimum fees as applicable. These fee arrangements will remain in effect until such time
as the aggregate fee resulting from the application of revised fee schedules based on the combined average daily
net assets of each Fund or Portfolio and its corresponding portfolio of American Skandia Trust would result in a
lower fee, at which point the revised fee schedules will take effect.
Reimbursable "out-of-pocket" expenses include, but are not limited to, postage and mailing, telephone,
telex, Federal Express, outside independent pricing service charges and record retention/storage. For the fiscal
year ended October 31, 1998, the Company paid the Administrator $507,368 and the Trust paid the Administrator
$291,316. For the fiscal year ended October 31, 1999, the Company paid the Administrator $1,395,979 and the
Trust paid the Administrator $724,469. For the fiscal year ended October 31, 2000, the Company paid the
Administrator $insert and the Trust paid the Administrator $insert. These amounts do not include out-of-pocket
expenses for which the Administrator was reimbursed.
QUALIFIED PLANS ADMINISTRATOR:
American Skandia Fund Services, Inc. ("ASFS"), an affiliate of ASISI, receives a fee from each Fund
under an Administration Agreement between ASFS and the Company with respect to services provided in connection
with investments in the Company by certain qualified retirement plans. Pursuant to this agreement, ASFS selects
and contracts with third parties providing administrative services for such plans ("third-party administrators")
or agents for such third-party administrators. Among other matters, third party administrators maintain records
of the holdings in the Funds of individual plan participants. As a result of the third-party administrators'
services, the Company may realize savings on costs that it would otherwise incur in maintaining shareholder
accounts.
ASFS uses its fee from each Fund to pay the third-party administrators and their agents, which fee may
be used to reduce fees that would otherwise be payable by the qualified plan to the third-party administrator.
The fee payable to ASFS corresponds to the aggregate fees payable by ASFS to third-party administrators and
agents under the terms of the agreements between ASFS and such third-party administrators and agents. Such fees,
depending on the particular agreement, are payable by ASFS either (a) at an annual rate of 0.20% of plan assets
invested in the Company through such third-party administrator or agent, or (b) at a fixed dollar amount up to
$15 annually per participant account that is maintained by a third-party administrator reflecting the holdings of
a plan participant in a Fund. ASFS does not receive any compensation as qualified plans administrator in
addition to amounts it pays to third-party administrators and their agents and for other out-of -pocket expenses.
FUND EXPENSES
Each Non-Feeder Fund and Portfolio pays its own expenses including, without limitation: (i) expenses of
maintaining the Fund or Portfolio and continuing its existence; (ii) registration of the Fund or Portfolio under
the 1940 Act; (iii) auditing, accounting and legal expenses; (iv) taxes and interest; (v) governmental fees; (vi)
expenses of issue, sale, repurchase and redemption of Fund shares; (vii) expenses of registering and qualifying
the Fund or Portfolio and its shares under federal and state securities laws and of preparing and printing
prospectuses for such purposes and for distributing the same to shareholders and investors; (viii) fees and
expenses of registering and maintaining registrations of the Fund or Portfolio and of the Fund's principal
underwriter as a broker-dealer or agent under state securities laws; (ix) expenses of reports and notices to
shareholders and of meetings of shareholders and proxy solicitations therefor; (x) expenses of reports to
governmental officers and commissions; (xi) insurance expenses; (xii) association membership dues; (xiii) fees,
expenses and disbursements of custodians for all services to the Fund or Portfolio; (xiv) fees, expenses and
disbursements of transfer agents, dividend disbursing agents, shareholder servicing agents and registrars for all
services to the Fund or Portfolio; (xv) expenses for servicing shareholder accounts; (xvi) any direct charges to
shareholders approved by the Directors of the Company or the Trustees of the Trust, where applicable; (xvii)
compensation and expenses of Directors of the Company or the Trustees of the Trust, where applicable, who are not
"interested persons" of the Fund or Portfolio, respectively; and (xviii) such nonrecurring items as may arise,
including expenses incurred in connection with litigation, proceedings and claims and the obligation of the
Company and the Trust to indemnify its directors, trustees and officers with respect thereto. Expenses incurred
by the Company or the Trust not directly attributable to any specific Non-Feeder Fund or Portfolio are allocated
on the basis of the net assets of the respective Non-Feeder Funds and Portfolios.
The Investment Manager has voluntarily agreed until May 1, 2001 to reimburse each Fund for its
respective operating expenses (and, in the case of the Feeder Funds, the Feeder Fund's pro rata share of
operating expenses of the Fund's corresponding Portfolio), exclusive of taxes, interest, brokerage commissions,
distribution fees and extraordinary expenses, but inclusive of the management fee, which in the aggregate exceed
specified percentages of the Fund's average net assets as follows:
ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund: 1.70%
ASAF AIM International Equity Fund: 1.60%
ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund: 1.60%
ASAF American Century International Growth Fund: 1.60%
ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund: 1.30%
ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund: 1.30%
ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund: 1.40%
ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund: 1.40%
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund: 1.35%
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund: 1.35%
ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund: 1.35%
ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund: 1.35%
ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund: 1.40%
ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund: 1.25%
ASAF Alliance Growth Fund: 1.30%
ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund: 1.30%
ASAF Janus Capital Growth Fund: 1.30%
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund: 1.00%
ASAF Alliance Growth & Income Fund: 1.15%
ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund: 1.30%
ASAF INVESCO Equity Income Fund: 1.20%
ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced Fund: 1.20%
ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund: 1.00%
ASAF PIMCO Total Return Bond Fund: 1.00%
ASAF JPM Money Market Fund: 1.00%
The Investment Manager may terminate the above voluntary agreements at any time after May 1, 2001.
Voluntary payments of Fund expenses by the Investment Manager may be made subject to reimbursement by the Fund,
at the Investment Manager's discretion, within the two year period following such payment to the extent
permissible under applicable law and provided that the Fund is able to effect such reimbursement and remain in
compliance with applicable expense limitations.
DISTRIBUTION ARRANGEMENTS
THE DISTRIBUTOR:
American Skandia Marketing, Incorporated ("ASM" or the "Distributor"), located at One Corporate Drive,
Shelton, Connecticut 06484, serves as the principal underwriter and distributor for each Fund pursuant to an
underwriting agreement initially approved by the Directors of the Company (the "Underwriting Agreement"). The
Distributor is a registered broker-dealer and member of the National Association of Securities Dealers, Inc.
("NASD"). The Distributor is an "affiliated person" (within the meaning of the 1940 Act) of the Company, the
Trust and the Investment Manager, being a wholly-owned subsidiary of American Skandia, Incorporated.
Shares of each Fund will be continuously offered and will be sold by selected broker-dealers who have
executed selling agreements with the Distributor. The Distributor bears all the expenses of providing services
pursuant to the Underwriting Agreement. Each Fund bears the expenses of registering its shares with the SEC and
with applicable state regulatory authorities. The Underwriting Agreement continues in effect for two years from
initial approval and for successive one-year periods thereafter, provided that each such continuance is
specifically approved (i) by the vote of a majority of the Directors of the Company, including a majority of the
Directors who are not parties to the Underwriting Agreement or "interested persons" of any such party (as defined
in the 1940 Act); or (ii) by the vote of a "majority of the outstanding voting securities" of a Fund (as defined
in the 1940 Act). In the event that the Underwriting Agreement terminates, all obligations of the Distributor
thereunder shall cease, including the Distributor's undertaking to purchase Class X Bonus Shares. For
information regarding Class X Bonus Shares and the Distributor's undertaking, see the Company's Prospectus under
"How to Buy Shares: Purchase of Class X Shares." The Distributor is not obligated to sell any specific amount of
shares of any Fund.
The following table shows, for the fiscal year ended October 31, 2000, information about the
compensation received by the Distributor:
Net Underwriting Commissions
(portion of initial sales charge retained by Distributor): $0
Compensation on Redemptions: $insert
Brokerage Commissions (compensation from Supplemental
Distribution Plans as described below under "The Distribution
Plans"): $insert
Other Compensation (compensation from other Distribution Plans): $insert
For the fiscal year ended October 31, 2000, aggregate underwriting commissions were $insert, of which $0
was retained by the Distributor.. For the fiscal year ended October 31, 1999, aggregate underwriting commissions
were $13,231,476 of which, as noted above $0, was retained by the Distributor. For the fiscal year ended October
31, 1998, aggregate underwriting commissions were $2,691,543, of which, $0 was retained by the Distributor.
THE DISTRIBUTION PLANS:
The Company has adopted separate Distribution and Service plans (commonly referred to as "12b-1 Plans")
for Class A, B, C and X shares of each Fund (the "Class A Plan," "Class B Plan," "Class C Plan" and "Class X
Plan," individually, and collectively, the "Class Plans") pursuant to appropriate resolutions of the Directors of
the Company and in accordance with the requirements of Rule 12b-1 under the 1940 Act and the requirements of the
applicable rules of the NASD regarding asset based sales charges. The Class Plans permit the payment of certain
fees from Fund assets to the Distributor, an affiliate of the Investment Manager, for its services and costs in
distributing Fund shares and providing for services to shareholder accounts. In addition, the Company has
adopted a Supplemental Distribution Plan and the Trust has adopted a Distribution Plan (the "Supplemental Plans,"
and together with the Class Plans, the "Plans") under Rule 12b-1 under the 1940 Act to permit the Distributor to
receive brokerage commissions in connection with purchases and sales of securities held by the Funds and the
Portfolios, and to use these commissions to promote the sale of shares of the Funds.
Under the Plans, the Distributor may use the amounts received to pay various distribution-related
expenses, such as advertising, printing of sales materials, training sales personnel, and compensating
broker-dealers who sell shares of the Company and provide services to shareholder accounts. Such broker-dealer
compensation may include initial sales concessions, ongoing sales and service fees, and additional marketing fees
requested by selling broker-dealers, all as described below under "Dealer Compensation Information." The
Distributor may receive compensation under the Plans regardless of whether it actually uses such compensation to
pay distribution expenses. The Distributor has assigned its right to receive any distribution and service fees
under the Class B Plan and the Class X Plan, as well as any contingent deferred sales charge for Class B and
Class X shares, to an unaffiliated third party that finances the sale of Class B and Class X shares.
The following table shows, for the twelve months ended September 30, 2000, the nature and amount of the
expenditures made under the Plans:
Advertising and sales literature: $insert
Printing of prospectuses and reports
for other than current
shareholders $ insert
Compensation to sales personnel
(including direct expenses
of sales personnel) $ insert
Compensation to dealers
(Class A shares) $ insert
Compensation to dealers
(Class B shares) $ insert
Compensation to dealers
(Class C shares) $ insert
Compensation to dealers
(Class X shares) $ insert
Purchase of Class X bonus
shares $ insert
Other dealer compensation $ insert
Conferences and seminars for
dealer personnel $ insert
The distribution expenses paid under the Plans will be intended to result in the sale of shares of the
Company's various Funds. As a result, amounts incurred by a Fund or Portfolio under the Plans (including
brokerage commissions paid by a Fund or Portfolio under the Supplemental Plans) may be used in a manner that
promotes the sale of shares of other Funds or Portfolios. Certain Funds of the Company may not be available for
additional investments or for purchase by new investors. Distribution expenses that are not attributable to a
particular Fund or Portfolio will be allocated among the Funds and Portfolios on different bases (e.g., relative
asset size and relative new sales of the Funds or Portfolios) depending on the nature of the expense and the
manner in which the amount of such expense is determined. Distribution expenses that are attributable to a
particular class of a Fund (e.g., sales concessions) will be allocated to that class.
The Plans were adopted by a majority vote of the Directors of the Company and Trustees of the Trust,
including at least a majority of Directors or Trustees, as applicable, who are not "interested persons" of the
Funds or the Portfolios (as defined in the 1940 Act) and who do not have any direct or indirect financial
interest in the operation of the Plans, cast in person at meetings called for the purpose of voting on the
Plans. In approving the Plans, the Directors of the Company and the Trustees of the Trust identified and
considered a number of potential benefits which the Plans may provide, including, but not limited to, improving
the Distributor's ability to attract investments by enabling it to compensate broker-dealers selling shares of
the Funds adequately and in the most effective manner, and that the resulting increases in assets should enable
the Funds and Portfolios to achieve greater economies of scale and lower their per-share operating expenses. The
Directors also considered the benefit of promoting shareholder access to the services of broker-dealer
representatives who have knowledge of the shareholders' particular circumstances and goals. With respect to the
Class X Plan, the Directors considered the possible increase in investor interest and consequent increase in
portfolio assets resulting from the use of the fees payable under such plan, in part, to facilitate the
Distributor's purchase of additional shares for Class X investors as a bonus. The Directors of the Company and
the Trustees of the Trust believe that there is a reasonable likelihood that the Plans will benefit each Fund and
Portfolio and its current and future shareholders in the manner contemplated.
Each Plan, pursuant to its terms, remains in effect from year to year provided such continuance is
approved annually by vote of the Directors or Trustees, as applicable, in the manner described above. All
material amendments to the Plans must be approved by the Directors or Trustees, as applicable, in the manner
described above. The Class Plans may not be amended to increase materially the amount to be spent for
distribution without approval of the shareholders of each class of a Fund or Portfolio affected thereby entitled
to vote thereon under the 1940 Act. The Supplemental Plans may not be amended to materially change the source of
monies from which distribution expenses are paid without approval of the shareholders of each Fund or Portfolio
affected thereby entitled to vote thereon under the 1940 Act. The Plans may be terminated at any time, without
payment of a penalty, by vote of the majority of the Directors or Trustees, as applicable, who are not interested
persons of the Fund or the Portfolio and have no direct or indirect financial interest in the operations of the
Plans, or by a vote of a "majority of the outstanding voting securities" (as defined in the 1940 Act) of the
class, Fund or Portfolio affected thereby entitled to vote thereon under the 1940 Act. A Plan will automatically
terminate in the event of its "assignment" (as defined in the 1940 Act).
DEALER COMPENSATION INFORMATION
In addition to the dealer compensation information described in the Company's Prospectus, the following
may be applicable to the purchase of Fund shares.
Class A Dealer Compensation. The concessions paid to dealers and brokers from the initial sales charge
on the sale of Class A shares are as follows:
High Yield Bond & Total Return Bond Funds: All Other Funds (other than Money Market
Fund):
Concession Concession
(as % of (as % of
Amount of Purchase: offering offering
------------------ -------------- --------
price) price)
------ ------
Less than $50,000 3.50% 5.00%
$50,000 up to $100,000 3.00% 4.25%
$100,000 up to $250,000 2.50% 3.25%
$250,000 up to $500,000 1.75% 2.50%
$500,000 up to $1 million 1.25% 2.00%
In addition, the Distributor may allocate the entire amount of the initial sales charge for the sale of
Class A shares to dealers for all sales occurring during a particular period.
The Distributor uses distribution and service fees received under the Class A Plan to compensate
qualified dealers for services provided in connection with the sale of shares and the maintenance of shareholder
accounts. Such compensation generally is paid by the Distributor quarterly at an annual rate not to exceed 0.50%
of the Fund's average daily net assets attributable to Class A shares held in accounts of the dealer or its
customers. However, in the case of shares purchased at NAV with a CDSC, the Distributor will pay the dealer of
record a sales commission in an amount equal to 0.50% of the amount invested, and the ongoing compensation will
not begin until one year after purchase. NAV shares are not subject to the one-year exclusion in cases where the
shareholder has made arrangements with the Company and the dealer of record waives the sales commission.
Class B Dealer Compensation. The Distributor uses distribution and service fees received under the Class
B Plan to compensate qualified dealers for services provided in connection with the sale of shares and the
maintenance of shareholder accounts. Such compensation is paid by the Distributor quarterly at an annual rate
not to exceed 0.50% of the Fund's average daily net assets attributable to Class B shares (and any shares
purchased by the reinvestment of dividends or capital gains) held for over seven years.
The Distributor normally pays a sales concession of 5.50% (and may pay up to 6.00%) of the purchase
price of Class B shares to the dealer from its own resources at the time of the sale.
Class X Dealer Compensation. The Distributor uses distribution and service fees received under the Class
X Plan as reimbursement for its purchases of Bonus Shares, as well as to compensate qualified dealers, brokers,
banks and other financial institutions for services provided in connection with the sale of Class X shares and
the maintenance of shareholder accounts. Such latter compensation is paid by the Distributor quarterly at an
annual rate not to exceed 0.50% of the Fund's average daily net assets attributable to Class X shares (and any
shares purchased by the reinvestment of dividends or capital gains as such shares) held for over seven years.
The Distributor normally pays a sales concession of 3.00% (and may pay up to 3.50%) of the purchase
price of Class X shares to the dealer from its own resources at the time of the sale.
Class C Dealer Compensation. The Distributor uses distribution and service fees received under the Class
C Plan to compensate qualified dealers for services provided in connection with the sale of shares and the
maintenance of shareholder accounts. The Distributor currently pays a 1.00% fee to dealers in advance upon sale
of Class C shares and retains the fee paid by the Fund in the first year. After the shares have been held for a
year, the Distributor pays the fee to dealers on a quarterly basis. The Class C CDSC is waived, and the one-year
exclusion on ongoing compensation does not apply, in cases where the shareholder has made arrangements with the
Company and the dealer of record waives the 1.00% fee upon sale. Similarly, the initial fee is not paid and the
payment of ongoing quarterly compensation begins immediately after purchase with respect to shares purchased
under an asset allocation program sponsored by ASISI or its affiliates.
Additional Dealer Compensation. In addition to the amounts paid to dealers as concessions that are
discussed above with respect to each class of the Company's shares, the Distributor may enter into special
compensation arrangements with dealers that have sold or are expected to sell large amounts of shares. As of
January 13, 2000, the Distributor had entered into nineteen such arrangements, one of which called for
compensation based on a specified percentage of the value of shares held by the Dealer's customers, thirteen of
which called for compensation based on a specified percentage of the value of shares sold by the Dealer, and five
of which called for compensation based on a combination of assets and sales. None of these payments will change
the price an investor pays for shares.
DETERMINATION OF NET ASSET VALUE
The net asset value ("NAV") per share of each Fund is determined in the manner described in the
Company's Prospectus. Each Fund will determine the NAV of its shares on each day that the New York Stock
Exchange (the "NYSE") is open for business. The Directors of the Company and the Trustees of the Trust have each
established procedures for valuing the assets of the Funds and Portfolios, respectively. In general, these
valuations are based on market quotations. However, in certain circumstances where market quotations are not
readily available, assets are valued by methods specified in the procedures that are believed to accurately
reflect the assets' fair value.
Securities held by each Non-Feeder Fund and Portfolio, other than the ASMT JPM Money Market Portfolio
(the "Money Market Portfolio"), that are valued based on market quotations will be valued as follows: portfolio
securities, including open short positions and options written, are valued at the last sale price on the
securities exchange or securities market (including the NASDAQ National Market System) on which such securities
primarily are traded. Securities not listed on an exchange or securities market, or securities in which there
were not transactions on that day, are valued at the average of the most recent bid and asked price, except in
the case of open short positions where the asked price is available. Portfolio securities which are traded both
"over-the-counter" and on an exchange are valued according to their primary market, and it is expected that for
debt securities this ordinarily will be the over-the-counter market.
Generally, trading in foreign securities, as well as U.S. Government securities, money market
instruments and repurchase agreements, is substantially completed each day at various times prior to the close of
the NYSE. The values of such securities used in computing the net asset value of the shares of a Fund or
Portfolio generally are determined as of such earlier times. Foreign currency exchange rates are also generally
determined prior to the close of the NYSE. Occasionally, events affecting the value of such securities and such
exchange rates may occur between the times at which such values usually are determined and the close of the
NYSE. If such extraordinary events occur, their effects may not be reflected in the net asset value of a Fund or
Portfolio calculated as of the close of the NYSE on that day.
The NAV per share of the Money Market Portfolio is determined by using the amortized cost method of
valuing portfolio instruments. Under the amortized cost method of valuation, an instrument is valued at cost and
the interest payable at maturity upon the instrument is accrued as income, on a daily basis, over the remaining
life of the instrument. Neither the amount of daily income nor the NAV is affected by unrealized appreciation or
depreciation of the Portfolio's investments assuming the instrument's obligation is paid in full on maturity. In
periods of declining interest rates, the indicated daily yield on shares of the Portfolio computed using
amortized cost may tend to be higher than a similar computation made using a method of valuation based upon
market prices and estimates. In periods of rising interest rates, the indicated daily yield on shares of the
Portfolio computed using amortized cost may tend to be lower than a similar computation made using a method of
valuation based upon market prices and estimates. In addition, short-term obligations with remaining maturities
of less than 60 days that are held by any Fund or Portfolio are valued at amortized cost.
The amortized method of valuation is intended to permit the Money Market Portfolio to maintain a
constant NAV per share of $1.00. No assurances can be given that this can be attained. The Directors of the
Company and the Trustees of the Trust, where applicable, periodically review the extent of any deviation from the
$1.00 per share value that would occur if a method of valuation based on market prices and estimates were used.
In the event such a deviation would exceed one-half of one percent, the Directors of the Company and the Trustees
of the Trust, where applicable, will promptly consider any action that reasonably should be initiated to
eliminate or reduce material dilution or other unfair results to shareholders. Such action may include selling
portfolio securities prior to maturity, not declaring earned income dividends, valuing portfolio securities on
the basis of current market prices, if available, or, if not available, at fair value, and (considered highly
unlikely by management of the Company and the Trust) redemption of shares in kind (i.e., with portfolio
securities).
A Fund's maximum offering price per Class A share, other than for the ASAF JPM Money Market Fund, is
determined by adding the maximum sales charge to the NAV per share. Class A shares of the ASAF JPM Money Market
fund, Class B, C and X shares are offered at NAV without the imposition of an initial sales charge.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ON THE
PURCHASE AND REDEMPTION OF SHARES
REDUCTION OR WAIVER OF SALES CHARGES AND CDSC ON CLASS A SHARES:
The Company's Prospectus under "How to Buy Shares" describes certain reductions and/or waivers of sales
charges and CDSC that apply to the purchase of Class A Shares. The following provides more specific information
on such reductions or waivers as well as certain additional waivers.
Waiver of All Class A Sales Charges. No sales charge is imposed on sales of Class A shares for the
following investors: (1) the Investment Manager, its parent company, any affiliate or subsidiary of the parent
company; (2) present or former officers, directors, trustees and employees (and their parents, spouses, siblings
and dependent children) of the Company, the Investment Manager (including its parent company or any affiliate or
subsidiary of the parent company) or the Sub-advisors, and any retirement plans established by such entities for
their employees; (3) accounts with respect to which any person described in (2) above acts as a custodian on
behalf of a minor (including Uniform Gift to Minors Act and Uniform Transfer to Minors Act accounts); (4) present
partners and employees (and their parents, spouses and dependent children) of the Transfer Agent and the
Company's or the Trust's legal counsel and administrator; (5) dealers that have a sales agreement with the
Distributor, if they purchase shares for their own accounts or for retirement plans for their employees; (6)
employees and registered representatives (and their parents, spouses and dependent children) of dealers or
financial institutions that have entered into sales arrangements with such dealers (and are identified to the
Distributor) or with the Distributor; the purchaser must certify to the Distributor at the time of purchase that
the purchase is for the purchaser's own account (or for the benefit of such employee's parents, spouse, parents
of spouse, or minor children); (7) employees (and their parents, spouses and dependent children) of firms
providing the Company, the Trust or their affiliates with regular legal, actuarial, auditing, underwriting,
claims, administrative, computer-support, marketing, office or other services; (8) any Sub-advisor of the Company
or the Trust; and (9) shares issued in plans of reorganization, such as mergers, asset acquisitions and exchange
offers, to which a Fund is a party.
Waiver of Class A CDSC. The Class A CDSC is waived in the following cases if shares are redeemed and
the Transfer Agent is notified: (1) redemptions under a Systematic Withdrawal Plan as described in this
Prospectus under "Special Investment Programs and Privileges"; (2) redemptions to pay premiums for optional
insurance coverage described in this Prospectus under "Special Investment Programs and Privileges"; (3)
redemptions following death or post-purchase disability (as defined by Section 72(m)(7) of the Code); (4)
distributions or loans to participants of qualified retirement plans and other employee benefit plans; (5) the
portion of a mandated minimum distribution from an IRA, SIMPLE IRA or 403(b)(7) plan equal to the percentage of
your plan assets held in Class A shares of the Company; (6) the portion of any substantially equal periodic
payments (as described in Section 72(t) of the Code) equal to the percentage of your plan assets held in class A
shares of the Company; (7) the return of excess contributions made to your IRA, SIMPLE IRA, 403(b)(7) plan or
401(k) plan; and (8) where the shareholder has made arrangements with the Company and the dealer of record waives
its initial sales commission.
Combined Purchases. Initial sales charge reductions are available by combining into a single
transaction the purchase of Class A shares with the purchase of any other class of shares. Qualifying purchases
include: (1) individual purchases by a trustee (or other fiduciary) if the investment is for a single trust
estate or single fiduciary account, including an employee benefit plan other than those described above; and (2)
purchases by qualified employee benefit plans, other than those described above, of a single employer, or of
affiliated employers as defined in the 1940 Act. Purchases made for nominee or street name accounts (securities
held in the name of an investment dealer or another nominee such as a bank trust department instead of the
customer) may not be aggregated with purchases made for other accounts and may not be aggregated with other
nominee or street name accounts unless otherwise qualified as described above.
Rights of Accumulation: Each Fund offers to all qualifying investors certain "rights of accumulation"
under which investors are permitted to purchase Class A shares of any Fund at the price applicable to the total
of (a) the then current purchase amount plus (b) an amount equal to the then current NAV of the purchaser's
holdings of all shares of any Fund of the Company. Acceptance of the purchase order is subject to confirmation
of qualification. A qualifying investor's rights of accumulation may be amended or terminated at any time as to
subsequent purchases.
Letter of Intent: Any person may qualify for a reduced sales charge on purchases of Class A shares made
within a thirteen-month period pursuant to a Letter of Intent ("LOI"). In computing the total amount purchased
for purposes of determining the applicable sales commission, the offering price of shares currently held in the
Funds which were purchased within 90 days from the date of acceptance of the LOI may be used as a credit toward
Fund shares to be purchased under the LOI. Class A, B, C and X shares acquired through the reinvestment of
distributions do not constitute purchases for purposes of the LOI. During the term of an LOI, Boston Financial
Data Services, Inc., the Company's transfer agent (the "Transfer Agent"), will hold shares in escrow to secure
payment of the higher sales charge applicable for shares actually purchased if the amount indicated on the LOI is
not purchased. Dividends and capital gains will be paid on all escrowed shares and these shares will be released
when the amount indicated on the LOI has been purchased. An LOI does not obligate the investor to buy or the
Fund to sell the indicated amount of the LOI. If the specified amount of the LOI is not purchased, the
shareholder shall remit to the Transfer Agent an amount equal to the difference between the sales charge paid and
the sales charge that would have been paid had the aggregate purchases been made at a single time. If the Class
A shareholder does not (within twenty days after a written request by the Transfer Agent) pay such difference in
sales charge, the Transfer Agent will redeem an appropriate number of escrowed shares in order to realize such
difference. Additional information about the terms of the LOI are available from your registered representative.
SPECIAL REDEMPTIONS:
Although it would not normally do so, each Fund has the right to pay the redemption price of shares of
the Fund in whole or in part in portfolio securities as prescribed by the Directors of the Company. When the
shareholder sells portfolio securities received in this fashion, he would incur a brokerage charge. Any such
securities would be valued for the purposes of making such payment at the same value as used in determining NAV.
The Funds have elected to be governed by Rule 18f-1 under the 1940 Act, pursuant to which each Fund is obligated
to redeem shares solely in cash from any one account during any 90-day period up to the lesser of $250,000 or 1%
of the NAV of the applicable Fund or Portfolio at the beginning of such period.
SUSPENSION OF REDEMPTIONS:
A Fund may not suspend a shareholder's right of redemption or postpone payment for a redemption for more
than seven days, unless the New York Stock Exchange ("NYSE") is closed for other than customary weekends or
holidays, or trading on the NYSE is restricted, or for any period during which an emergency exists as a result of
which (1) disposal by a Fund or Portfolio of securities owned by it is not reasonably practicable, or (2) it is
not reasonably practicable for a Fund to fairly determine the value of its assets, or for such other periods as
the SEC may permit for the protection of investors.
For further information regarding the purchase and redemption of Fund shares, see "How to Buy Shares"
and "How to Redeem Shares," respectively, in the Company's Prospectus.
PORTFOLIO TRANSACTIONS
BROKERAGE ALLOCATION:
Subject to the supervision of the Directors of the Company and the Trustees of the Trust, where
applicable, decisions to buy and sell securities for the Company and the Trust are made for each Non-Feeder Fund
and Portfolio by its respective Sub-advisor. Each Sub-advisor is authorized to allocate the orders placed by it
on behalf of the applicable Fund or Portfolio to brokers who also provide research or statistical material or
other services to the Sub-advisor or the Fund or Portfolio for the use of the applicable Fund or Portfolio and
other accounts as to which the Sub-advisor exercises investment discretion. Such allocation shall be in such
amounts and proportions as the Sub-advisor shall determine. The Sub-advisor will report on allocations of
brokerage either to the Investment Manager, which will report on such allocations to the Directors of the Company
or the Trustees of the Trust, where applicable, or, if requested, directly to the Directors or Trustees. These
reports will indicate the brokers to whom such allocations have been made and the basis therefor. The
Sub-advisor may consider sale of shares of the Funds, or may consider or follow recommendations of the Investment
Manager that take such sales into account, as factors in the selection of brokers to effect portfolio
transactions for a Fund or Portfolio, subject to the requirements of best net price available and most favorable
execution. In this regard, the Investment Manager may direct certain of the Sub-advisors to try to effect a
portion of their Fund or Portfolio's investment transactions through broker-dealers that sell shares of the Fund
(or corresponding Fund, in the case of the Portfolios), to the extent consistent with best net price available
and most favorable execution.
Subject to the rules promulgated by the SEC, as well as other regulatory requirements, a Sub-advisor
also may allocate orders to brokers or dealers affiliated with the Sub-advisor or the Investment Manager. Such
allocation shall be in amounts and proportions as the Sub-advisor shall determine. The Sub-advisor will report
on these allocations of brokerage either to the Investment Manager, which will report on such allocations to the
Directors of the Company or the Trustees of the Trust, where applicable, or, if requested, directly to the
Directors or Trustees.
In selecting a broker to effect each particular transaction, each Sub-advisor will take the following
into consideration: the best net price available; the reliability, integrity and financial condition of the
broker; the size and difficulty in executing the order; and the value of the expected contribution of the broker
to the investment performance of the Fund on a continuing basis. Subject to such policies and procedures as the
Directors of the Company and the Trustees of the Trust may determine, a Sub-advisor shall not be deemed to have
acted unlawfully or to have breached any duty solely by reason of its having caused a Fund or Portfolio to pay a
broker that provides research services to the Sub-advisor an amount of commission for effecting an investment
transaction in excess of the amount of commission another broker would have charged for effecting that
transaction, if the Sub-advisor determines in good faith that such amount of commission was reasonable in
relation to the value of the research service provided by such broker viewed in terms of either that particular
transaction or the Sub-advisor's ongoing responsibilities with respect to the Fund or Portfolio and other
accounts as to which the Sub-advisor exercises investment discretion. Accordingly, the amount of the brokerage
commission in any transaction may be greater than that available from other brokers if the difference is
reasonably justified by other aspects of the services offered. For the fiscal year ended October 31, 1998,
aggregate brokerage commissions of $320,297 and $177,016 were paid in relation to brokerage transactions of the
Company and the Trust, respectively. For the fiscal year ended October 31, 1999, aggregate brokerage commissions
of $2,169,322 and $853,911 were paid in relation to brokerage transaction of the Company and the Trust,
respectively. For the fiscal year ended October 31, 2000, aggregate brokerage commissions of $insert and $insert
were paid in relation to brokerage transactions of the Company and the Trust, respectively. The increase in
commissions paid is primarily the result of the increase in the Company's and Trust's net assets.
During the fiscal years ended October 31, 1998, October 31, 1999 and October 31, 2000, brokerage
commissions were paid by the ASMT American Century International Growth Portfolio to certain affiliates of Rowe
Price-Fleming International, Inc., the former Sub-advisor of the Portfolio, in the amount of $821, $1,924, and
$insert respectively. For the year ended October 31, 2000, insert% of the total brokerage commissions paid by
this Portfolio were paid to the affiliated brokers, with respect to transactions representing insert% of the
Portfolio's total dollar amount of transactions involving the payment of commissions. During the fiscal year
ended October 31, 1998, brokerage commissions were paid to NationsBanc Montgomery Securities LLC, an affiliate of
the former Sub-advisor to the ASAF Alliance Growth Fund, by this Fund in the amount of $3,542. During the fiscal
years ended October 31, 1998, October 31, 1999, and October 31, 2000 brokerage commissions were paid to J.P.
Morgan Securities, Inc., an affiliate of American Century Investment Management, Inc., by the ASAF American
Century Strategic Balanced Fund in the amount of $735, $150 and $insert, respectively. For the year ended
October 31, 2000, insert% of the total brokerage commissions paid by this Fund were paid to the affiliated
broker, with respect to transactions representing insert% of the Fund's total dollar amount of transactions
involving the payment of commissions. During the fiscal years ended October 31, 1998, October 31, 1999 and
October 31, 2000, brokerage commissions were paid to Neuberger Berman, LLC, an affiliate of Neuberger Berman
Management Inc., by the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund in the amount of $1,812, $10,650 and $insert,
respectively. For the year ended October 31, 2000, insert% of the total brokerage commissions paid by this Fund
were paid to the affiliated broker, with respect to transactions representing insert% of the Fund's total dollar
amount of transactions involving the payment of commissions. During the fiscal years ended October 31, 1998,
October 31, 1999 and October 31, 2000, brokerage commissions were paid to Neuberger Berman, LLC by the ASAF
Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund in the amount of $688, $28,311 and $insert, respectively. For the year ended
October 31, 2000, insert% of the total brokerage commissions paid by this Fund were paid to the affiliated
broker, with respect to transactions representing insert% of the Fund's total dollar amount of transactions
involving the payment of commissions. For the fiscal years ended October 31, 1999 and October 31, 2000,
brokerage commissions were paid to NationsBanc Montgomery Services, LLC, an affiliate of Marsico Capital
Management, LLC, by the ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund in the amount of $28,029 and $insert, respectively. For
that period, insert% of the total brokerage commissions paid by this Fund were paid to the affiliated broker,
with respect to transactions representing insert% of the Fund's total dollar amount of transactions involving the
payment of commissions.
In addition, as described above under "The Distribution Plans," certain Funds and Portfolios directed
brokerage transactions to a broker-dealer acting as the clearing firm for the Company's Distributor, which acted
as introducing broker in connection with the transactions. The table below reflects the commission amounts
directed to such clearing firm for each such Fund or Portfolio, the percentage of the Fund or Portfolio's total
commissions this represents, and the percentage of the Fund or Portfolio's total transaction value involving the
payment of commissions that was directed in this manner.
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
Fund Name Commissions % of Total Fund % of Dollar Amount of
Commissions Fund Transactions
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund $insert Insert% Insert%
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
ASMT American Century International Growth Portfolio $insert insert% insert%
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund $insert Insert% Insert%
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund $insert insert% insert%
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund $insert Insert% Insert%
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund $insert Insert% Insert%
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
ASMT Janus Capital Growth Portfolio $insert Insert% Insert%
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund $insert Insert% Insert%
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
ASAF INVESCO Equity Income Fund $insert insert% insert%
------------------------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------------ -------------------------
ALLOCATION OF INVESTMENTS:
The Sub-advisors of the Non-Feeder Funds and Portfolios have other advisory clients, some of which have
similar investment objectives to one or more of the Funds or Portfolios for which advisory services are being
provided. In addition, a Sub-advisor may be engaged to provide advisory services for more than one Fund or
Portfolio. There will be times when a Sub-advisor may recommend purchases and/or sales of the same securities
for a Fund or Portfolio and the Sub-advisor's other clients. In such circumstances, it will be the policy of
each Sub-advisor to allocate purchases and sales among a Fund or Portfolio and its other clients, including other
Funds or Portfolios for which the Sub-advisor provides advisory services, in a manner which the Sub-advisor deems
equitable, taking into consideration such factors as size of account, concentration of holdings, investment
objectives, tax status, cash availability, purchase costs, holding period and other pertinent factors relative to
each account.
PORTFOLIO TURNOVER:
Each Non-Feeder Fund and Portfolio may sell its portfolio securities, regardless of the length of time
that they have been held, if the Sub-advisor and/or the Investment Manager determines that such a disposition is
in the Fund's or Portfolio's best interest. Portfolio turnover rates may increase as a result of the need for a
Fund or Portfolio to effect significant amounts of purchases or redemptions of portfolio securities due to
economic, market, or other factors that are not within the Sub-advisor's or Investment Manager's control. A high
rate of portfolio turnover (generally in excess of 100%) involves correspondingly higher brokerage commission
expenses and other transaction costs, which must be ultimately borne by a Fund's shareholders. Trading in fixed
income securities does not generally involve the payment of brokerage commissions, but does involve indirect
transaction costs. High portfolio turnover rates may also generate larger taxable income and taxable capital
gains than would result from lower portfolio turnover rates and may create higher tax liability for a Fund's
shareholders.
The turnover rates for the ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund for the year ended
October 31, 1999 and the year ended October 31, 2000 were 268% and insert%, respectively. The increase in
portfolio turnover resulted primarily from a change in the portfolio manager responsible for the management of
the Fund, who is expected to engage in more frequent trading for the Fund than the prior portfolio manager. The
turnover rates for the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund for the period ended October 31, 1999 and the
year ended October 31, 2000 were 126% and insert%, respectively. The turnover rates for the ASAF Alliance Growth
Fund for the period ended October 31, 1999 and the year ended October 31, 2000 were 320% and insert%,
respectively. OppenheimerFunds, Inc. became the Fund's Sub-advisor on December 31, 1998 and there was a change
in the portfolio manager responsible for the management of the Fund during 1999. Trading precipitated by these
changes resulted in the unusually high portfolio turnover for the year ended October 31, 1999. The turnover
rates for the ASMT PIMCO Total Return Bond Fund for the year ended October 31, 1999 and the year ended October
31, 2000 were 145% and insert%, respectively. The substantial reduction in the portfolio turnover rate was
caused in large part by the Fund's decreased use of certain derivative instruments.
A 100% portfolio turnover rate would occur if all of the securities in a portfolio of investments were
replaced during a given period. For additional information regarding portfolio turnover, see the Company's
Prospectus under "Portfolio Turnover" and "Financial Highlights."
ADDITIONAL TAX CONSIDERATIONS
Federal Income Tax Consequences. Each Fund is treated as a separate entity for federal income tax
purposes. Each Fund has qualified and elected or intends to qualify and elect to be treated as a "regulated
investment company" under Subchapter M of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the "Code"), and intends
to continue to so qualify in the future. As a regulated investment company, a Fund must, among other things, (a)
derive at least 90% of its gross income from dividends, interest, payments with respect to loans of stock and
securities, gains from the sale or other disposition of stock, securities or foreign currency and other income
(including but not limited to gains from options, futures, and forward contracts) derived with respect to its
business of investing in such stock, securities or foreign currency; and (b) diversify its holdings so that, at
the end of each quarter of its taxable year, (i) at least 50% of the value of the Fund's total assets is
represented by cash, cash items, U.S. Government securities, securities of other regulated investment companies,
and other securities limited, in respect of any one issuer, to an amount not greater than 5% of the Fund's total
assets, and 10% of the outstanding voting securities of such issuer, and (ii) not more than 25% of the value of
its total assets is invested in the securities of any one issuer (other than U.S. Government securities or
securities of other regulated investment companies). As a regulated investment company, a Fund (as opposed to
its shareholders) will not be subject to federal income taxes on the net investment income and capital gain that
it distributes to its shareholders, provided that at least 90% of its net investment income and realized net
short-term capital gain in excess of net long-term capital loss for the taxable year is distributed in accordance
with the Code's timing requirements (the "Distribution Requirement"). For additional information regarding the
Funds' treatment as regulated investment companies under the Code, and certain consequences if such treatment is
not accorded any Fund, see the Company's Prospectus under "Dividends, Capital Gains and Taxes."
Each Fund will be subject to a 4% non-deductible federal excise tax on a portion of its undistributed
taxable income and capital gains if it fails to meet certain distribution requirements by the end of the calendar
year. Each Fund intends to avoid liability for such tax by satisfying such distribution requirements.
Each of the Feeder Funds will invest all of its investable assets in a corresponding Portfolio of the
Trust. Each such Fund will be deemed to own a proportionate share of its corresponding Portfolio's assets and
income for the purpose of determining whether the Fund qualifies as a regulated investment company. Accordingly,
each Portfolio intends to conduct its operations so that its corresponding Fund will be able to satisfy
applicable tax requirements.
If a Fund or Portfolio acquires stock in certain non-U.S. corporations ("passive foreign investment
companies" or "PFICs") that receive at least 75% of their annual gross income from passive sources (such as
interest, dividends, rents, royalties or capital gains) or at least 50% of whose average assets produce or are
held for the production of such passive income, that Fund (or, in the case of a Portfolio, its corresponding Fund
indirectly through its interest in the Portfolio) could be subject to federal income tax and additional interest
charges on "excess distributions" received from such companies or gain from the sale of stock in such companies,
even if the Fund distributes its share of the PFIC income as a taxable dividend to its shareholders. A certain
election (treating the PFIC as a "qualified electing fund") filed with the Fund's federal income tax return may,
if available, ameliorate these adverse tax consequences, but any such election would require the applicable Fund
to recognize ordinary taxable income and net capital gain of the PFIC without the corresponding receipt of cash
which may need to be distributed by the Fund to satisfy the Distribution Requirement.
Pursuant to proposed regulations, open-end regulated investment companies such as the Funds would be
entitled to avoid the tax consequences described in the previous paragraph by electing to mark-to-market their
stock in certain PFICs. Marking to market in this context means recognizing as gain for each taxable year the
excess, as of the end of that year, of the fair market value of each PFIC's stock over the owner's adjusted basis
in that stock (including mark to market gains of a prior year for which an election was in effect).
Gains and losses realized by a Fund (directly, or through its interest in a Portfolio) in connection
with certain transactions involving foreign currency-denominated debt securities, certain foreign currency
futures and options, foreign currency forward contracts, foreign currencies themselves, or payables or
receivables denominated in a foreign currency are generally treated as ordinary income and loss.
Some Funds, or, in certain cases, the Portfolio in which a Fund may invest its assets, may be subject to
withholding and other taxes imposed by foreign countries with respect to their investments in foreign
securities. Tax conventions between certain countries and the U.S. may reduce or eliminate such taxes. A Fund,
more than 50% of the value of whose total assets at the close of a taxable year (held directly or indirectly
through a corresponding Portfolio) consists of stock or securities in foreign corporations, may elect to
"pass-through" these foreign taxes to its shareholders, in which case each shareholder will be required to
include its pro rata portion thereof in its gross income but, if it itemizes deductions, will be able to deduct
or (subject to various limitations) will be able to claim a credit for its portion of such taxes, in computing
its federal income tax liability.
Each Fund or Portfolio that invests in zero coupon securities or in other securities with original issue
discount (or securities with market discount, if the Fund or Portfolio elects to include market discount in
income currently) must accrue such discount income currently even if no corresponding payment is received.
However, because income subject to a Fund's Distribution Requirement includes such accrued discount, to satisfy
that requirement, a Fund may have to dispose of its (or, as the case may be, its corresponding Portfolio's)
securities under disadvantageous circumstances, or borrow, to generate the needed cash.
Forward currency contracts, options and futures contracts entered into by a Fund or Portfolio may create
"straddles" for federal income tax purposes with other such contracts or with securities positions, and this may
affect the character and timing of gains or losses realized by the Fund (or, in the case of a Portfolio, by its
corresponding Fund) on such contracts, options or securities. Certain straddles treated as short sales for tax
purposes may also result in the loss of the holding period of securities included in the straddles for purposes
of the 30% of gross income test described above, and therefore, a Fund's or Portfolio's ability to enter into
forward currency contracts, options and futures contracts may be limited.
Certain options, futures and foreign currency contracts held by a Fund or Portfolio at the end of each
taxable year will be required to be "marked-to-market" for federal income tax purposes -- i.e., treated as having
been sold at market value. For options and futures contracts, 60% of any gain or loss recognized on these deemed
sales and on actual dispositions will be treated as long-term capital gain or loss, and the remainder will be
treated as short-term capital gain or loss regardless of how long the Fund or Portfolio has held such options or
futures. However, gain or loss recognized on certain foreign currency contracts will be treated as ordinary
income or loss.
If a Fund or Portfolio satisfies certain requirements, any increase in value of a position that is part
of a "designated hedge" will be offset by any decrease in value (whether realized or not) of the offsetting
hedging position during the period of the hedge for purposes of determining whether the Fund (or, in the case of
a Portfolio, its corresponding Fund) satisfies the 30% gross income test above. Thus, only the net gain (if any)
from the designated hedge will be included in gross income for purposes of that limitation. Each Fund or
Portfolio will consider whether it should seek to satisfy those requirements to enable the Fund (or, in the case
of a Portfolio, its corresponding Fund) to qualify for this treatment for hedging transactions.
To maintain a constant $1.00 per share NAV, the Directors of the ASAF JPM Money Market Fund (the "Money
Market Fund") may direct that the number of outstanding shares be reduced pro rata. If this adjustment is made,
it will reflect the lower market value of portfolio securities and not realized losses. The adjustment may
result in a shareholder having more dividend income than net income in his account for a period. When the number
of outstanding shares of the Money Market Fund is reduced, the shareholder's basis in the shares of the Fund may
be adjusted to reflect the difference between taxable income and net dividends actually distributed. This
difference may be realized as a capital loss when the shares are liquidated.
Distributions from a Fund's current or accumulated earnings and profits ("E&P"), as computed for federal
income tax purposes, will be taxable as described in the Company's Prospectus whether taken in shares or in
cash. These distributions will be treated as dividends, but will qualify for the 70% dividends-received
deduction for the Fund's corporate shareholders only to the extent designated in a notice to the Fund's
shareholders as being attributable to dividends received by the Fund. Distributions, if any, in excess of E&P
will constitute a return of capital, which will first reduce an investor's tax basis in a Fund's shares and
thereafter (after such basis is reduced to zero) will generally give rise to capital gains. Shareholders
electing to receive distributions in the form of additional shares will have a cost basis for federal income tax
purposes in each share so received equal to the amount of cash they would have received had they elected to
receive the distributions in cash, divided by the number of shares received.
At the time of an investor's purchase of shares of a Fund (other than the Money Market Fund), a portion
of the purchase price is often attributable to realized or unrealized appreciation in the Fund's portfolio or
undistributed taxable income of the Fund. Consequently, subsequent distributions from such appreciation or
income may be taxable to such investor even if the NAV of the investor's shares is, as a result of the
distributions, reduced below the investor's cost for such shares, and the distributions in reality represent a
return of a portion of the purchase price.
Upon a redemption of shares of a Fund, other than the Money Market Fund (including an exchange for other
Fund shares), a shareholder may realize a taxable gain or loss. Such gain or loss will be capital if the shares
are capital assets in the shareholder's hands and will be long-term or short-term capital gain or loss, depending
upon the shareholder's holding period for the shares. A sales charge paid in purchasing shares of a Fund ("load
charge") cannot be taken into account for purposes of determining gain or loss on the redemption or exchange of
such shares within 90 days after their purchase to the extent shares of the same or another Fund are subsequently
acquired without payment of a load charge pursuant to a reinvestment or exchange privilege. Such disregarded
load charge will result in an increase in the shareholder's tax basis in the Fund shares subsequently acquired.
Also, any loss realized on a redemption or exchange of shares of a Fund will be disallowed to the extent the
shares disposed of are replaced with shares of the same Fund within a period of 61 days beginning 30 days before
and ending 30 days after such disposition. In such a case, the basis of the shares acquired will be adjusted to
reflect the disallowed loss. If Fund shares are redeemed or exchanged at a loss after being held for six months
or less, the loss will be treated as long-term, instead of short-term, capital loss to the extent of any capital
gains distributions received on those shares.
Each shareholder will be required to furnish its social security or taxpayer identification number and
certify that such number is correct and that the shareholder is not subject to back-up withholding for failure to
report income to the IRS. Failure to comply with applicable IRS regulations, including the certification
procedures described above, may result in the Fund being required to collect back-up withholding at a 31% rate on
taxable distributions and redemptions to the shareholder.
Different tax treatment, including penalties on certain excess contributions and deferrals, certain
pre-retirement and post-retirement distributions and certain prohibited transactions, is accorded to shareholder
accounts maintained as qualified retirement plans. Shareholders should consult their tax advisers for more
information.
The foregoing discussion relates solely to federal income tax law as applicable to U.S. persons (i.e.,
U.S. citizens or residents and U.S. domestic corporations, partnerships, trusts or estates) generally. The
discussion does not address special tax rules applicable to certain classes of investors, such as tax-exempt
entities, insurance companies, and financial institutions.
A foreign shareholder (i.e., a nonresident alien individual, foreign trust or estate, foreign
corporation or foreign partnership) not engaged in a U.S. trade or business with which its investment in a Fund
is effectively connected will be subject to federal income tax treatment that is different from that described
above. These investors may be subject to U.S. withholding tax at the rate of 30% (or a lower rate under an
applicable tax treaty) on amounts treated as ordinary dividends from a Fund and, unless an effective IRS Form W-8
or authorized substitute is on file, to backup withholding at the rate of 31% on certain other payments from the
Fund. Distributions treated as long term capital gains to foreign shareholders will not be subject to federal
income tax unless the distributions are effectively connected with the shareholder's U.S. trade or business or,
in the case of a non-resident alien individual, the shareholder is present in the U.S. for more than 182 days
during the taxable year and certain other conditions are met. Non-U.S. investors should consult their tax
advisers regarding such treatment and the application of foreign taxes to an investment in any Fund.
State and Local Tax Consequences. Each Fund may be subject to state or local taxes in jurisdictions in
which such Fund may be deemed to be doing business. In addition, in those states or localities which have income
tax laws, the treatment of such Fund and its shareholders under such laws may differ from their treatment under
federal income tax laws, and investment in such Fund may have different tax consequences for shareholders than
would direct investment in such Fund's (or, in the case of a Feeder Fund, its corresponding Portfolio's)
portfolio securities. Shareholders should consult their own tax advisers with respect to any state or local
taxes.
CAPITAL STOCK OF THE COMPANY &
PRINCIPAL HOLDERS OF SECURITIES
Capital Stock. The authorized capital stock of the Company consists of the following shares (par value
$.001 per share): ASAF Founders International Small Capitalization Fund (190 million); ASAF American Century
International Growth Fund (190 million); ASAF AIM International Equity Fund (190 million); ASAF Janus Overseas
Growth Fund (100 million); ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund (100 million); ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund
(190 million); ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund (190 million); ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund (190 million);
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund (190 million); ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund (190 million);
ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund (190 million); ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund (190 million); ASAF INVESCO
Technology Fund (190 million); ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund (190 million); ASAF Alliance Growth Fund (190
million); ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund (190 million); ASAF Janus Capital Growth Fund (300 million); ASAF
Sanford Bernstein Managed Index 500 Fund (190 million); ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund (190 million); ASAF
MFS Growth with Income Fund (190 million); ASAF INVESCO Equity Income Fund (190 million); ASAF American Century
Strategic Balanced Fund (190 million); ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund (190 million); ASAF PIMCO Total Return
Bond Fund (190 million); and ASAF JPM Money Market Fund (1.01 billion).
Description of Shares. The Company currently has twenty-five separate series of shares, each of which
is divided into Class A, B, C and X shares. The Directors of the Company are authorized to establish, from time
to time and without shareholder approval, additional series or classes of shares. The assets of each series of
shares belong only to that series, and the liabilities of each series are borne solely by that series and no
other. Shares of each Fund represent equal proportionate interests in the assets of that Fund only and have
identical voting, dividend, redemption, liquidation, and other rights. Each class of shares, however, bears
different sales charges, distribution fees and related expenses, and has exclusive voting rights with respect to
its respective 12b-1 Distribution and Service Plan. All shares issued are fully paid, non-assessable and freely
transferable, and have no preference, preemptive or similar rights.
Shareholder Voting and Meetings. The shares of the Funds are entitled to vote separately to approve
investment advisory agreements or changes in investment restrictions, but shareholders of all series vote
together in the election and selection of directors. Each shareholder is entitled to one vote for each share
(and to the appropriate fractional vote for each fractional share) of the Funds held upon all matters submitted
to the shareholders generally. Shareholders of all Funds and classes will vote together as a single class,
except when otherwise required by applicable law or as determined by the Directors of the Company; and provided
that shareholders of a particular Fund or class shall not be entitled to vote on any matter which does not affect
any interest of that Fund or class, except as otherwise required by applicable law. The Directors of the Company
do not intend to hold annual meetings of shareholders of the Funds, and will call special meetings of
shareholders of a Fund only if required under the 1940 Act and other applicable law, in their discretion or upon
written request of holders of 10% or more of the outstanding shares of that Fund entitled to vote. Although
Directors are not elected annually by the shareholders, shareholders have under certain circumstances the right
to remove one or more Directors. If required by applicable law, a meeting will be held to vote on the removal of
a Director or Directors of the Company if requested in writing by the holders of not less than 10% of the
Company's outstanding shares.
The following table lists persons owning more than 5% of any class of the Fund's outstanding shares as
of December 11, 2000.
American Skandia Advisor Funds, Inc., - Report of 5% or Greater Owners
----------------------------------------------------------------------
As of December 11, 2000
-----------------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
Fund and Share Class Owner Name Address Percent
Ownership
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF Founders International Small N/A N/A N/A
Capitalization Fund Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF AIM International Equity Fund N/A N/A N/A
Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund N/A N/A N/A
Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF American Century International N/A N/A N/A
Growth Fund Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund N/A N/A N/A
Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF Scudder Small-Cap Growth Fund N/A N/A N/A
Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund N/A N/A N/A
Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth N/A N/A N/A
Fund Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value N/A N/A N/A
Fund Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF Alliance Growth Fund N/A N/A N/A
Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund N/A N/A N/A
Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF Janus Capital Growth Fund N/A N/A N/A
Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index N/A N/A N/A
500 Fund
Class A, B and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF Sanford Bernstein Managed Index Attn: Murray L. Hammock HC 75 Box 4280 20.34%
500 Fund Raymond James & Assoc Inc. FBO Mayer, AZ 86333
Class C Cordes Junction Investors LP
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund N/A N/A N/A
Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund Class N/A N/A N/A
A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF INVESCO Equity Income Fund N/A N/A N/A
Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF American Century Strategic N/A N/A N/A
Balanced Fund Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund N/A N/A N/A
Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF PIMCO Total Return Bond Fund N/A N/A N/A
Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
ASAF JPM Money Market Fund N/A N/A N/A
Class A, B, C and X
----------------------------------------- -------------------------------- ----------------------------------- --------------
OTHER INFORMATION
REPORTS TO SHAREHOLDERS:
Shareholders of each Fund are provided unaudited semi-annual financial statements, as well as year-end
financial statements audited by the Company's independent public accountants. Each Fund's financial statements
show the investments owned by the Fund or its corresponding Portfolio, where applicable, and the market values
thereof. Additionally, each Fund's financial statements provide other information about the Fund and its
operations, including in the case of the Feeder Funds, the Fund's beneficial interest in its corresponding
Portfolio.
DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN CUSTODIANS:
pFPC Trust Company, located at Airport Business Center, International Court 2, 200 Stevens Drive,
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19113, serves as custodian for all domestic cash and securities holdings of the Funds
and Portfolios investing primarily in domestic securities. The Chase Manhattan Bank, located at One Pierrepont
Plaza, Brooklyn, New York 11201, serves as custodian for all cash and securities holdings of the ASAF Founders
International Small Capitalization Fund, the ASAF American Century International Growth Fund (and corresponding
Portfolio), the ASAF AIM International Equity Fund, and the ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund, and co-custodian for
all foreign securities holdings of the Funds and Portfolios which invest primarily in domestic securities.
TRANSFER AGENT:
Boston Financial Data Services, Inc. (the "Transfer Agent," as previously defined), located at Two
Heritage Drive, Quincy, Massachusetts 02171, serves as the transfer agent and dividend paying agent for the
Company. In addition, American Skandia Fund Services, Inc., an affiliate of ASISI and the Company, provides
certain shareholder-related services to the Company. ASAF pays ASFS per-service fees for such services at rates
identical to those that are payable by ASAF to the Transfer Agent for performing equivalent services.
INDEPENDENT ACCOUNTANTS:
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, located at Two Commerce Square, Suite 1700, 2001 Market Street,
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19103, has been selected as the independent certified public accountants of the
Company, providing audit services and assistance and consultation with respect to the preparation of filings with
the SEC.
Legal Counsel:
Stradley Ronon Stevens & Young, LLP, located at 2600 One Commerce Square, Philadelphia, PA 19103-7098,
serves as counsel to the Company.
REGISTRATION STATEMENT:
This SAI and the Company's Prospectus do not contain all the information included in the Company's
Registration Statement filed with the SEC under the Securities Act of 1933 with respect to the securities offered
by the Prospectus. The Registration Statement, including the exhibits filed therewith, may be examined at the
SEC's offices in Washington, D.C. The SEC maintains a Website (http://www.sec.gov) that contains this SAI,
material incorporated by reference, and other information regarding the Funds and Portfolios.
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The financial statements appearing in the Annual Report to Shareholders for each Fund for the period
ended October 31, 2000 have been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, independent accountants. Such financial
statements are incorporated herein by reference.
APPENDIX
--------
The rating information which follows describes how the rating services mentioned presently rate the
described securities. No reliance is made upon the rating firms as "experts" as that term is defined for
securities purposes. Rather, reliance on this information is on the basis that such ratings have become
generally accepted in the investment business.
Description of Certain Debt Securities Ratings
----------------------------------------------
Moody's Investors Service, Inc. ("Moody's"):
Aaa -- Bonds which are rated Aaa are judged to be of the best quality. They carry the smallest degree
of investment risk and are generally referred to as "gilt edge." Interest payments are protected by a large, or
exceptionally stable, margin, and principal is secure. While the various protective elements are likely to
change, such changes as can be visualized are most unlikely to impair the fundamentally strong position of such
issues.
Aa -- Bonds which are rated Aa are judged to be of high quality by all standards. Together with the Aaa
group they comprise what are generally known as high grade bonds. They are rated lower than the best bonds
because margins of protection may not be as large as in Aaa securities or fluctuation of protective elements may
be of greater amplitude or there may be other elements present which make the long-term risk appear somewhat
larger than the Aaa securities.
A -- Bonds which are rated A possess many favorable investment attributes and are to be considered as
upper-medium-grade obligations. Factors giving security to principal and interest are considered adequate, but
elements may be present which suggest a susceptibility to impairment some time in the future.
Baa -- Bonds which are rated Baa are considered as medium grade obligations (i.e., they are neither
highly protected nor poorly secured). Interest payments and principal security appear adequate for the present
but certain protective elements may be lacking or may be characteristically unreliable over any great length of
time. Such bonds lack outstanding investment characteristics and in fact have speculative characteristics as
well.
Ba -- Bonds which are rated Ba are judged to have speculative elements; their future cannot be
considered as well assured. Often the protection of interest and principal payments may be very moderate and
thereby not well safeguarded during both good and bad times over the future. Uncertainty of position
characterizes bonds in this class.
B -- Bonds which are rated B generally lack characteristics of a desirable investment. Assurance of
interest and principal payments or of maintenance of other terms of the contract over any long period of time may
be small.
Caa -- Bonds which are rated Caa are of poor standing. Such issues may be in default or there may be
present elements of danger with respect to principal or interest.
Ca -- Bonds which are rated Ca represent obligations which are speculative in a high degree. Such
issues are often in default or have other marked shortcomings.
C -- Bonds which are rated C are the lowest rated class of bonds and issues so rated can be regarded as
having extremely poor prospects of ever attaining any real investment standing.
Standard & Poor's Corporation ("Standard & Poor's"):
AAA -- Debt rated AAA has the highest rating assigned by Standard & Poor's. Capacity to pay interest
and repay principal is extremely strong.
AA -- Debt rated AA has a strong capacity to pay interest and repay principal, and differs from the
highest rated issues only in a small degree.
A -- Debt rated A has a strong capacity to pay interest and repay principal, although it is somewhat
more susceptible to the adverse effects of changes in circumstances and economic conditions than debt in higher
rated categories.
BBB - Debt rated BBB is regarded as having an adequate capacity to pay interest and repay principal.
Whereas they normally exhibit adequate protection parameters, adverse economic conditions or changing
circumstances are more likely to lead to a weakened capacity to pay interest and repay principal for debt in this
category than in higher rated categories.
BB, B, CCC, CC, C -- Debt rated BB, B, CCC, CC and C is regarded as having predominantly speculative
characteristics with respect to capacity to pay interest and repay principal. BB indicates the least degree of
speculation and C the highest. While such debt will likely have some quality and protective characteristics,
these are outweighed by large uncertainties of major risk exposures to adverse conditions.
BB -- Debt rated BB has less near-term vulnerability to default than other speculative issues. However,
it faces major ongoing uncertainties or exposure to adverse business, financial, or economic conditions which
could lead to inadequate capacity to meet timely interest and principal payments. The BB rating is also used for
debt subordinated to senior debt that is assigned an actual or implied BBB rating.
B -- Debt rated B has a greater vulnerability to default but currently has the capacity to meet interest
payments and principal repayments. Adverse business, financial, or economic conditions will likely impair
capacity or willingness to pay interest and repay principal. The B rating category is also used for debt
subordinated to senior debt that is assigned an actual or implied BB or BB-rating.
CCC -- Debt rated CCC has a currently identifiable vulnerability to default, and is dependent upon
favorable business, financial, and economic conditions to meet timely payment of interest and repayment of
principal. In the event of adverse business, economic or financial conditions, it is not likely to have the
capacity to pay interest and repay principal. The CCC rating category is also used for debt subordinated to
senior debt that is assigned an actual or implied B or B- rating.
CC -- The rating CC typically is applied to debt subordinated to senior debt that is assigned an actual
or implied CCC rating.
C -- The C rating may be used to cover a situation where a bankruptcy petition has been filed, but debt
service payments are continued.
CI -- The rating CI is reserved for income bonds on which no interest is being paid.
D -- Debt rated D is in payment default. The D rating category is used when interest payments or
principal payments are not made on the date due, even if the applicable grace period has not expired, unless
Standard & Poor's believes that such payments will be made during such grace period. The D rating also will be
used upon the filing of bankruptcy petition if debt service payments are jeopardized.
Plus (+) or minus (-) -- Ratings from AA to CCC may be modified by the addition of a plus of minus sign
to show relative standing within the major rating categories.
Description of Certain Commercial Paper Ratings
-----------------------------------------------
Moody's:
Prime-1 -- Issuers rated Prime-1 (or supporting institutions) have a superior ability for repayment of
senior short-term debt obligations. Prime-1 repayment ability will often be evidenced by many of the following
characteristics: leading market positions in well-established industries; high rates of return on funds
employed; conservative capitalization structures with moderate reliance on debt and ample asset protection; broad
margins in earnings coverage of fixed financial charges and high internal cash generation; and well-established
access to a range of financial markets and assured sources of alternate liquidity.
Prime-2 -- Issuers rated Prime-2 (or related supporting institutions) have a strong ability for
repayment of senior short-term debt obligations. This will normally be evidenced by many of the characteristics
cited above, but to a lesser degree. Earnings trends and coverage ratios, while sound, may be more subject to
variation. Capitalization characteristics, while still appropriate, may be more affected by external
conditions. Ample alternate liquidity is maintained.
Prime-3 -- Issuers rated Prime-3 (or related supporting institutions) have an acceptable ability for
repayment of senior short-term debt obligations. The effect of industry characteristics and market compositions
may be more pronounced. Variability in earnings and profitability may result in changes in the level of debt
protection measurements and may require relatively high financial leverage. Adequate alternate liquidity is
maintained.
Not Prime - Issuers rated Not Prime do not fall within any of the Prime rating categories.
Standard & Poor's:
A-1 -- This highest category indicates that the degree of safety regarding time payment is strong.
Those issues determined to possess extremely strong safety characteristics are denoted with a plus sign
designation.
A-2 -- Capacity for timely payment on issues with this designation is satisfactory. However, the
relative degree of safety is not as high as for issues designated "A-1".
A-3 -- Issues carrying this designation have adequate capacity for timely payment. They are, however,
more vulnerable to the adverse effects of the changes in circumstances than obligations carrying the higher
designations.
B -- Issues rated B are regarded as having only speculative capacity for timely payment.
C -- This rating is assigned to short-term debt obligations with a doubtful capacity for payment.
D - Debt rated D is in payment default. The D rating category is used when interest payments or
principal payments are not made on the date due, even if the applicable grace period has not expired, unless
Standard & Poor's believes that such payments will be made during such grace period.
PART C: OTHER INFORMATION
--------------------------
ITEM 23. Exhibits
--------
(i) (a). (1) Articles of Incorporation of Registrant.
(iii) (2) Amendment to Articles of Incorporation of Registrant dated July 3, 1997.
(iv) (3) Amendment to Articles of Incorporation of Registrant dated July 17, 1997.
(vi) (4) Articles Supplementary of Registrant dated December 29, 1997.
(viii) (5) Articles Supplementary of Registrant dated August 14, 1998.
(viii) (6) Articles Supplementary of Registrant dated December 16, 1998.
(xi) (7) Articles Supplementary of Registrant dated September 24, 1999.
(xiii) (8) Articles Supplementary of Registrant dated February 16, 2000.
(xv) (9) Articles Supplementary of Registrant dated May 1, 2000.
(10) Articles Supplementary of Registrant dated September 8, 2000
(i) (b). By-laws of Registrant.
(c). None.
(ii) (d). (1) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Founders International Small
Capitalization Fund.
(xi) (2) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF AIM International Equity Fund.
(v) (3) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund.
(viii) (4) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund.
(xii) (5) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Kemper Small-Cap Growth Fund.
(6) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund.
(xv) (7) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund.
(vii) (8) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Growth Fund.
(vii) (9) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Neuberger Berman Mid-Cap Value Fund.
(xv) (10) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund.
(xv) (11) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund.
(xv) (12) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund.
* (13) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund.
(xv) (14) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund.
(xiii) (15) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Alliance Growth Fund.
(vii) (16) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Marsico Capital Growth Fund.
* (17) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund.
* (18) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth + Value
Fund.
* (19) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund.
(xiii) (20) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Managed Index 500 Fund.
(xiii) (21) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Alliance Growth and Income Fund.
(xi) (22) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF MFS Growth with Income Fund.
(ii) (23) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF American Century Strategic Balanced
Fund.
(ii) (24) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia
Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF Federated High Yield Bond Fund.
(vii) (25) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Founders Asset Management LLC for the ASAF Founders International
Small Capitalization Fund.
(v) (26) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Janus Capital Corporation for the ASAF Janus Overseas Growth Fund.
(xi) (27) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and A I M Capital Management, Inc. for the ASAF AIM International Equity
Fund.
(ix) (28) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Janus Capital Corporation for the ASAF Janus Small-Cap Growth Fund.
(xii) (29) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Scudder Kemper Investments, Inc. for the ASAF Kemper Small-Cap Growth
Fund.
(30) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and GAMCO Investors, Inc. for the ASAF Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund.
(xv) (31) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Janus Capital Corporation for the ASAF Janus Mid-Cap Growth Fund.
(vii) (32) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Neuberger&Berman Management Inc. for the ASAF Neuberger Berman
Mid-Cap Growth Fund.
(vii) (33) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Neuberger&Berman Management Inc. for the ASAF Neuberger Berman
Mid-Cap Value Fund.
(xv) (34) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Fred Alger Management, Inc. for the ASAF Alger All-Cap Growth Fund.
(xv) (35) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and GAMCO Investors, Inc. for the ASAF Gabelli All-Cap Value Fund.
(xv) (36) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and INVESCO Funds Group, Inc. for the ASAF INVESCO Technology Fund.
(xv) (37) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and INVESCO Funds Group, Inc. for the ASAF INVESCO Health Sciences Fund.
(xv) (38) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Rydex Global Advisors for the ASAF Rydex Managed OTC Fund.
(xiii) (39) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Alliance Capital Management L.P. for the ASAF Alliance Growth Fund.
* (40) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc. for the ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed
Fund.
* (41) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Alliance Capital Management L.P. for the ASAF Alliance/Bernstein
50/50 Growth + Value Fund.
* (42) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Sanford C. Bernstein & Co., LLC for the ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50
Growth + Value Fund.
* (43) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Sanford C. Bernstein & Co., LLC for the ASAF Sanford Bernstein Deep
Value Fund.
(xiii) (44) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Sanford C. Bernstein & Co. for the ASAF Managed Index 500 Fund.
(xiii) (45) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Alliance Capital Management L.P. for the ASAF Alliance Growth and
Income Fund.
(xi) (46) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Massachusetts Financial Services Company for the ASAF MFS Growth with
Income Fund.
(xiv) (47) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and American Century Investment Management, Inc. for the ASAF American
Century Strategic Balanced Fund.
(iii) (48) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment Services,
Incorporated and Federated Investment Counseling for the ASAF Federated High Yield
Bond Fund.
(xiv) (e). (1) Form of Amended and Restated Underwriting and Distribution Agreement between
Registrant and American Skandia Marketing, Incorporated.
(iii) (2) Form of Sales Agreement with American Skandia Marketing, Incorporated.
(xiii) (f). Form of Deferred Compensation Plan.
(ii) (g). (1) Form of Custody Agreement between Registrant and PNC Bank.
(ii) (2) Form of Custody Agreement between Registrant and Morgan Stanley Trust Company.
(vi) (3) Form of Amendment to Custody Agreement between Registrant and PNC Bank.
(viii) (4) Form of Foreign Custody Manager Delegation Amendment.
(xiii) (5) Form of Amendment to Custody Agreement between Registrant and PFPC Trust Company.
(ii) (h). (1) Form of Administration Agreement between Registrant and PFPC Inc.
(ii) (2) Form of Transfer Agency and Service Agreement between Registrant and State Street Bank
and Trust Company.
(xv) (3) Form of Administration Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia Investment
Services, Incorporated.
(vii) (4) Form of Amendment to Transfer Agency and Service Agreement between Registrant and
State Street Bank and Trust Company.
(xv) (5) Form of Shareholder Services Agreement between Registrant and American Skandia Fund
Services, Inc.
(xii) (i). Opinion and Consent of Counsel to Registrant.
* (j). (1) Consent of Independent Public Accountants of Registrant and American Skandia Master
Trust
(iii) (2) Consent of Caplin & Drysdale.
(v) (3) Opinion of Caplin & Drysdale
(iii) (4) Consent of Rogers & Wells.
(v) (5) Opinion of Rogers & Wells.
(k). None.
(ii) (l). Form of Share Purchase Agreement.
(ii) (m). (1) Form of Distribution and Service Plan for Class A Shares.
(ii) (2) Form of Distribution and Service Plan for Class B Shares.
(ii) (3) Form of Distribution and Service Plan for Class C Shares.
(ii) (4) Form of Distribution and Service Plan for Class X Shares.
(vi) (5) Form of Distribution and Service Plan for New Class X Shares.
(xiii) (6) Form of Supplemental Distribution Plan.
(xi) (n). Form of Rule 18f-3 Plan.
(o) (1) Form of Code of Ethics of Registrant pursuant to Rule 17j-1.
(2) Form of Code of Ethics of American Skandia Investment Services, Incorporated.
(3) Form of Code of Ethics of American Skandia Marketing, Incorporated.
--------------------------------------
* To be filed by future amendment.
(i) Incorporated by reference to Registrant's Initial Registration Statement on Form N-1A as filed with the
Securities and Exchange Commission (the "Commission") on March 10, 1997.
(ii) Incorporated by reference to Pre-Effective Amendment No. 2 to Registrant's Registration Statement on Form N-1A as
filed with the Commission on June 4, 1997.
(iii) Incorporated by reference to Pre-Effective Amendment No. 3 to Registrant's Registration Statement on Form N-1A as
filed with the Commission on July 9, 1997.
(iv) Incorporated by reference to Post-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Registrant's Registration Statement on Form N-1A
as filed with the Commission on October 17, 1997.
(v) Incorporated by reference to Post-Effective Amendment No. 2 to Registrant's Registration Statement on Form N-1A
as filed with the Commission on December 31, 1997.
(vi) Incorporated by reference to Post-Effective Amendment No. 3 to Registrant's Registration Statement on Form N-1A
as filed with the Commission on June 5, 1998.
(vii) Incorporated by reference to Post-Effective Amendment No. 4 to Registrant's Registration Statement on Form N-1A
as filed with the Commission on August 18, 1998.
(viii) Incorporated by reference to Post-Effective Amendment No. 5 to Registrant's Registration Statement on Form N-1A
as filed with the Commission on December 31, 1998.
(ix) Incorporated by reference to Post-Effective Amendment No. 6 to Registrant's Registration Statement on Form N-1A
as filed with the Commission on February 26, 1999.
(x) Incorporated by reference to Post-Effective Amendment No. 7 to Registrant's Registration Statement on Form N-1A
as filed with the Commission on July 23, 1999.
(xi) Incorporated by reference to Post-Effective Amendment No. 8 to Registrant's Registration Statement on Form N-1A
as filed with the Commission on October 15, 1999.
(xii) Incorporated by reference to Post-Effective Amendment No. 9 to Registrant's Registration Statement on Form N-1A
as filed with the Commission on January 14, 2000.
(xiii) Incorporated by reference to Post-Effective Amendment No. 10 to Registrant's Registration Statement on Form N-1A
as filed with the Commission on March 2, 2000.
(xiv) Incorporated by reference to Post-Effective Amendment No. 11 to Registrant's Registration Statement on Form N-1A
as filed with the Commission on June 9, 2000.
(xv) Incorporated by reference to Post-Effective Amendment No. 12 to Registrant's Registration Statement on Form N-1A
as filed with the Commission on August 22, 2000.
ITEM 24. Persons Controlled By or Under Common Control with Registrant
-------------------------------------------------------------
Five series of the Registrant currently are organized under a "master/feeder" fund structure and may be
considered to control the corresponding master portfolios of American Skandia Master Trust in which they invest.
Registrant is not under common control with any person except to the extent Registrant is deemed to be under the control
of its Investment Manager.
ITEM 25. Indemnification
---------------
Section 2-418 of the General Corporation Law of the State of Maryland provides for indemnification of officers,
directors, employees and agents of a Maryland corporation. With respect to indemnification of the officers and directors
of the Registrant, and of other employees and agents to such extent as shall be authorized by the Board of Directors or
the By-laws of the Registrant and be permitted by law, reference is made to Article VIII, Paragraph (a)(5) of the
Registrant's Articles of Incorporation and Article V of the Registrant's By-laws, both filed herewith.
With respect to liability of the Investment Manager to Registrant or to shareholders of Registrant's Funds under
the Investment Management Agreements, reference is made to Section 13 of each form of Investment Management Agreement
filed herewith.
With respect to the Sub-Advisors' indemnification under the Sub-Advisory Agreements of the Investment Manager,
any affiliated person within the meaning of Section 2(a)(3) of the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the
"ICA"), of the Investment Manager and each person, if any, who controls the Investment Manager within the meaning of
Section 15 of the 1933 Act, as amended (the "1933 Act"), reference is made to Section 14 of each form of Sub-Advisory
Agreement filed herewith.
With respect to Registrant's indemnification of American Skandia Marketing, Incorporated (the "Distributor"), its
officers and directors and any person who controls the Distributor within the meaning of Section 15 of the 1933 Act, and
the Distributor's indemnification of Registrant, its officers and directors and any person who controls Registrant, if
any, within the meaning of the 1933 Act, reference is made to Section 10 of the form of Underwriting and Distribution
Agreement filed herewith.
Insofar as indemnification for liability arising under the 1933 Act may be permitted to directors, officers and
controlling persons of the Registrant pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, the Registrant has been advised
that in the opinion of the Commission such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the 1933 Act and is,
therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment
by the Registrant or expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the Registrant in the
successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in
connection with the securities being registered, the Registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has
been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such
indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the 1933 Act and will be governed by the final
adjudication of such issue.
ITEM 26. Business and Other Connections of Investment Adviser
----------------------------------------------------
American Skandia Investment Services, Incorporated ("ASISI"), One Corporate Drive, Shelton, Connecticut 06484,
serves as the investment manager to the Registrant. Information as to the officers and directors of ASISI is included in
ASISI's Form ADV (File No. 801-40532), including the amendment to such Form ADV filed with the Commission on April 4,
2000 and is incorporated herein by reference.
ASISI currently engages the following sub-advisors (the "Sub-advisors") to conduct the investment programs of the
funds of the Registrant or the master portfolios in which certain of Registrant's funds invest: (a) Founders Asset
Management LLC, Founders Financial Center, 2930 East Third Avenue, Denver, Colorado 80206; (b) A I M Capital Management,
Inc., 11 Greenway Plaza, Suite 100, Houston, TX 77046 (c) Janus Capital Corporation, 100 Fillmore Street, Denver,
Colorado 80206-4923; (d) American Century Investment Management, Inc., Twentieth Century Tower, 4500 Main Street, Kansas
City, Missouri 64111; (e) Zurich Scudder Investments, Inc. , 345 Park Avenue, New York, NY 10154; (f) GAMCO Investors,
Inc. One Corporate Center, Rye, New York 10580; (g) Neuberger Berman Management Inc. 605 Third Avenue, New York, NY
10158; (h) Fred Alger Management, Inc., One World Trade Center, Suite 9333, New York, NY 10048; (i) INVESCO Funds Group,
Inc., 7800 East Union Avenue, Denver, Colorado 80217-3706; (j) Rydex Global Advisors, 6116 Executive Boulevard, Suite
400, Rockville, MD 20852; (k) Alliance Capital Management L.P., 1345 Avenue of the Americas, New York, NY 10105; (l)
Marsico Capital Management, LLC, 1200 17th Street, Denver, CO 80202; (m) T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc., 100 East Pratt
Street, Baltimore, Maryland 21209 (n) Sanford C. Bernstein & Co., Inc., LLC, 767 Fifth Avenue, New York, NY 10153; (o)
Massachusetts Financial Services Company, 500 Boylston Street, Boston, Massachusetts 02116 (p) Federated Investment
Counseling, Federated Investors Tower, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15222-3779; (q) Pacific Investment Management Company
LLC, 840 Newport Center Drive, Suite 360, Newport Beach, California 92660; and (r) J.P. Morgan Investment Management,
Inc., 522 Fifth Avenue, New York, New York, 10036. Information as to the officers and directors of each of the
Sub-advisors is included in each Sub-advisor's current Form ADV, as amended and filed with the Commission, and is
incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 27. Principal Underwriter
---------------------
American Skandia Marketing, Incorporated (the "Distributor," as previously defined), One Corporate Drive,
Shelton, Connecticut 06484, serves as the principal underwriter and distributor for the Registrant. The Distributor is a
registered broker-dealer and member of the National Association of Securities Dealers, Inc. The Distributor is an
"affiliated person" (as defined under the ICA) of the Registrant and ASISI, being a wholly-owned subsidiary of American
Skandia Incorporated.
The following table sets forth information on the current officers and directors of the Distributor, all of whom
have as their principal business address, One Corporate Drive, Shelton, Connecticut 06484:
Name: Position Held with the Distributor: Position Held with the Registrant:
---- ---------------------------------- ---------------------------------
Patricia J. Abram Senior Vice Present None
Lori Allen Vice President None
Kimberly Anderson Vice President None
Gordon C. Boronow Deputy Chief Executive Officer & Vice President
Director
Robert Brinkman Senior Vice President None
Carl Cavaliere Vice President None
Kathleen A. Chapman Assistant Corporate Secretary None
Y.K. Chan Senior Vice President, Chief None
Information Officer and Director
Lucinda C. Ciccarello Vice President, Mutual Funds None
Lincoln R. Collins Director None
Timothy S. Cronin Vice President None
Wade A. Dokken President, Chairman, Chief Executive None
Officer & Director
Jacob Herschler Vice President None
Ian Kennedy Senior Vice President & Director None
Thomas M. Mazzaferro Executive Vice President, Director
Chief Financial Officer & Director
David R. Monroe Senior Vice President, Treasurer and None
Corporate Controller
Michael A. Murray Senior Vice President None
Brian O'Connor Vice President None
Carl E. Oberholtzer Vice President None
William O'Loughlin Vice President None
M. Priscilla Pannell Corporate Secretary None
Kathleen A. Pritchard Vice President None
Polly Rae Vice President None
Hayward L. Sawyer Senior Vice President & Director None
Leslie S. Sutherland Vice President None
Amanda C. Sutyak Vice President None
Christian A. Thwaites Senior Vice President & Director None
Mary Toumpas Vice President & Compliance Director None
Bayard F. Tracy Senior Vice President & Director None
Deborah G. Ullman Senior Vice President & Director None
Brett M. Winson Director None
ITEM 28. Location of Accounts and Records
--------------------------------
Records regarding the Registrant's securities holdings are maintained at Registrant's Custodians, PFPC Trust
Company, Airport Business Center, International Court 2, 200 Stevens Drive, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19113, and The
Chase Manhattan Bank, One Pierrepont Plaza, Brooklyn, New York 11201. Certain records with respect to the Registrant's
securities transactions are maintained at the offices of the various sub-advisors to the Registrant. The Registrant's
corporate records are maintained at its offices at One Corporate Drive, Shelton, Connecticut 06484. The Registrant's
financial ledgers and similar financial records are maintained at the offices of its Administrator, PFPC Inc., 103
Bellevue Parkway, Wilmington, DE 19809. Certain records regarding the shareholders of the Registrant are maintained at
the offices of the Registrant's transfer agent, Boston Financial Data Services, Inc., Two Heritage Drive, Quincy,
Massachusetts 02171.
All accounts, books and other documents required to be maintained by Section 31(a) of the ICA, and the Rules
promulgated thereunder with respect to American Skandia Master Trust (the "Master Trust") are maintained at the Master
Trust's offices at One Corporate Drive, Shelton, Connecticut 06484, at the offices of the various sub-advisors, and at
the offices of the above-mentioned Custodians and Administrator.
ITEM 29. Management Services
-------------------
None.
ITEM 30. Undertakings
------------
None.
SIGNATURES
----------
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933 and the Investment Company Act of 1940, the
Registrant, American Skandia Advisor Funds, Inc., has duly caused this Registration Statement to be signed on its behalf
by the undersigned, duly authorized, in the City of Shelton, and State of Connecticut, on the 15th day of December, 2000.
AMERICAN SKANDIA ADVISOR FUNDS, INC.
By: /s/Edward P. Macdonald
----------------------
Edward P. Macdonald
Secretary
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, this Registration Statement has been signed below by
the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature Title Date
--------- ----- ----
/s/ Jan R. Carendi* President, Principal Executive 12/15/00
------------------- --------
Jan R. Carendi Officer & Director
/s/ David E.A. Carson* Director 12/15/00
---------------------- --------
David E.A. Carson
/s/ Richard G. Davy, Jr. Treasurer (Chief Financial and 12/15/00
------------------------ --------
Richard G. Davy, Jr. Accounting Officer)
/s/ Julian A. Lerner* Director 12/15/00
--------------------- --------
Julian A. Lerner
/s/ Thomas M. Mazzaferro* Director 12/15/00
------------------------- --------
Thomas M. Mazzaferro
/s/ Thomas M. O'Brien* Director 12/15/00
---------------------- --------
Thomas M. O'Brien
/s/ F. Don Schwartz* Director 12/15/00
-------------------- --------
F. Don Schwartz
*By: /s/ Susann A. Palumbo
---------------------
Susann A. Palumbo
Assistant Secretary
*Pursuant to Powers of Attorney previously filed.
SIGNATURES
----------
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933 and the Investment Company Act of 1940, the
Registrant, American Skandia Master Trust has duly caused this Registration Statement to be signed on its behalf by the
undersigned, duly authorized, in the City of Shelton, and State of Connecticut, on the 15th day of December, 2000.
AMERICAN SKANDIA MASTER TRUST
By: /s/ Edward P. Macdonald
-----------------------
Edward P. Macdonald
Secretary
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, this Registration Statement has been signed below by
the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature Title Date
--------- ----- ----
/s/ Jan R. Carendi* President (Chief Executive Officer) & 12/15/00
------------------- --------
Jan R. Carendi Trustee
/s/ David E.A. Carson* Trustee 12/15/00
---------------------- --------
David E.A. Carson
/s/ Richard G. Davy, Jr. Vice President (Controller) 12/15/00
------------------------ --------
Richard G. Davy, Jr.
/s/ Julian A. Lerner* Trustee 12/15/00
--------------------- --------
Julian A. Lerner
/s/ Thomas M. Mazzaferro* Trustee 12/15/00
------------------------- --------
Thomas M. Mazzaferro
/s/Thomas M. O'Brien* Trustee 12/15/00
--------------------- --------
Thomas M. O'Brien
/s/ F. Don Schwartz* Trustee 12/15/00
-------------------- --------
F. Don Schwartz
/s/ C. Ake Svensson* Treasurer 12/15/00
-------------------- --------
C. Ake Svensson
*By: /s/ Susann A. Palumbo
---------------------
Susann A. Palumbo
Assistant Secretary
*Pursuant to Powers of Attorney previously filed.
AMERICAN SKANDIA ADVISOR FUNDS, INC.
Registration Statement Under
The Securities Act of 1933 and
The Investment Company Act of 1940
INDEX TO EXHIBITS
-----------------
Exhibit Number Description
-------------- -----------
(a)(10) Articles Supplementary of Registrant dated September 8, 2000
(d)(6) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and
American Skandia Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF
Gabelli Small-Cap Value Fund.
(d)(13) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and
American Skandia Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF
INVESCO Health Sciences Fund.
(d)(17) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and
American Skandia Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF T.
Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund.
(d)(18) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and
American Skandia Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF
Sanford Bernstein Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Growth + Value Fund.
(d)(19) Form of Investment Management Agreement between Registrant and
American Skandia Investment Services, Incorporated for the ASAF
Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund.
(d)(30) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment
Services, Incorporated and GAMCO Investors, Inc. for the ASAF Gabelli
Small-Cap Value Fund.
(d)(37) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment
Services, Incorporated and INVESCO Funds Group, Inc. for the ASAF
INVESCO Health Sciences Fund.
(d)(40) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment
Services, Incorporated and T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc. for the
ASAF T. Rowe Price Tax Managed Fund.
(d)(41) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment
Services, Incorporated and Alliance Capital Management L.P. for the
ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Value + Growth Fund.
(d)(42) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment
Services, Incorporated and Sanford C. Bernstein & Co., LLC for the
ASAF Alliance/Bernstein 50/50 Value + Growth Fund.
(d)(43) Form of Sub-advisory Agreement between American Skandia Investment
Services, Incorporated and Sanford C. Bernstein & Co., LLC for the
Sanford Bernstein Deep Value Fund.
(j)(1) Consent of Independent Public Accountants of Registrant and
American Skandia Master Trust.
(o)(1) Form of Code of Ethics of Registrant
(o)(2) Form of Code of Ethics of American Skandia Investment
Services, Incorporated.
(o)(3) Form of Code of Ethics of American Skandia Marketing,
Incorporated.


















